Siyuan Xu
Parallel Training in Spiking Neural Networks
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:The bio-inspired integrate-fire-reset mechanism of spiking neurons constitutes the foundation for efficient processing in Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). Recent progress in large models demands that spiking neurons support highly parallel computation to scale efficiently on modern GPUs. This work proposes a novel functional perspective that provides general guidance for designing parallel spiking neurons. We argue that the reset mechanism, which induces complex temporal dependencies and hinders parallel training, should be removed. However, any such modification should satisfy two principles: 1) preserving the functions of reset as a core biological mechanism; and 2) enabling parallel training without sacrificing the serial inference ability of spiking neurons, which underpins their efficiency at test time. To this end, we identify the functions of the reset and analyze how to reconcile parallel training with serial inference, upon which we propose a dynamic decay spiking neuron. We conduct comprehensive testing of our method in terms of: 1) Training efficiency and extrapolation capability. On 16k-length sequences, we achieve a 25.6x training speedup over the pioneering parallel spiking neuron, and our models trained on 2k-length can stably perform inference on sequences as long as 30k. 2) Generality. We demonstrate the consistent effectiveness of the proposed method across five task categories (image classification, neuromorphic event processing, time-series forecasting, language modeling, and reinforcement learning), three network architectures (spiking CNN/Transformer/SSMs), and two spike activation modes (spike/integer activation). 3) Energy consumption. The spiking firing of our neuron is lower than that of vanilla and existing parallel spiking neurons.
BrainFuse: a unified infrastructure integrating realistic biological modeling and core AI methodology
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Neuroscience and artificial intelligence represent distinct yet complementary pathways to general intelligence. However, amid the ongoing boom in AI research and applications, the translational synergy between these two fields has grown increasingly elusive-hampered by a widening infrastructural incompatibility: modern AI frameworks lack native support for biophysical realism, while neural simulation tools are poorly suited for gradient-based optimization and neuromorphic hardware deployment. To bridge this gap, we introduce BrainFuse, a unified infrastructure that provides comprehensive support for biophysical neural simulation and gradient-based learning. By addressing algorithmic, computational, and deployment challenges, BrainFuse exhibits three core capabilities: (1) algorithmic integration of detailed neuronal dynamics into a differentiable learning framework; (2) system-level optimization that accelerates customizable ion-channel dynamics by up to 3,000x on GPUs; and (3) scalable computation with highly compatible pipelines for neuromorphic hardware deployment. We demonstrate this full-stack design through both AI and neuroscience tasks, from foundational neuron simulation and functional cylinder modeling to real-world deployment and application scenarios. For neuroscience, BrainFuse supports multiscale biological modeling, enabling the deployment of approximately 38,000 Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with 100 million synapses on a single neuromorphic chip while consuming as low as 1.98 W. For AI, BrainFuse facilitates the synergistic application of realistic biological neuron models, demonstrating enhanced robustness to input noise and improved temporal processing endowed by complex HH dynamics. BrainFuse therefore serves as a foundational engine to facilitate cross-disciplinary research and accelerate the development of next-generation bio-inspired intelligent systems.
MaP-AVR: A Meta-Action Planner for Agents Leveraging Vision Language Models and Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Embodied robotic AI systems designed to manage complex daily tasks rely on a task planner to understand and decompose high-level tasks. While most research focuses on enhancing the task-understanding abilities of LLMs/VLMs through fine-tuning or chain-of-thought prompting, this paper argues that defining the planned skill set is equally crucial. To handle the complexity of daily environments, the skill set should possess a high degree of generalization ability. Empirically, more abstract expressions tend to be more generalizable. Therefore, we propose to abstract the planned result as a set of meta-actions. Each meta-action comprises three components: {move/rotate, end-effector status change, relationship with the environment}. This abstraction replaces human-centric concepts, such as grasping or pushing, with the robot's intrinsic functionalities. As a result, the planned outcomes align seamlessly with the complete range of actions that the robot is capable of performing. Furthermore, to ensure that the LLM/VLM accurately produces the desired meta-action format, we employ the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technique, which leverages a database of human-annotated planning demonstrations to facilitate in-context learning. As the system successfully completes more tasks, the database will self-augment to continue supporting diversity. The meta-action set and its integration with RAG are two novel contributions of our planner, denoted as MaP-AVR, the meta-action planner for agents composed of VLM and RAG. To validate its efficacy, we design experiments using GPT-4o as the pre-trained LLM/VLM model and OmniGibson as our robotic platform. Our approach demonstrates promising performance compared to the current state-of-the-art method. Project page: https://map-avr.github.io/.
Explainable reinforcement learning from human feedback to improve alignment
Dec 15, 2025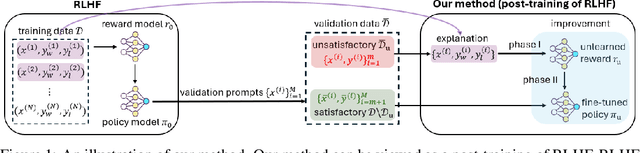
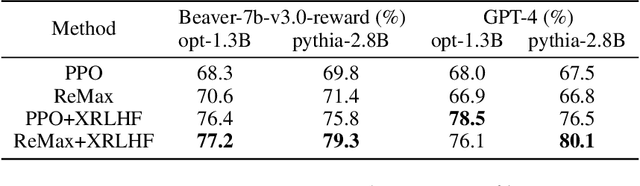
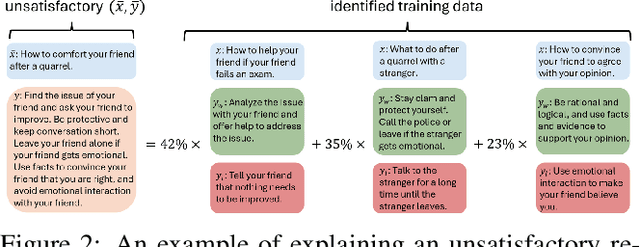
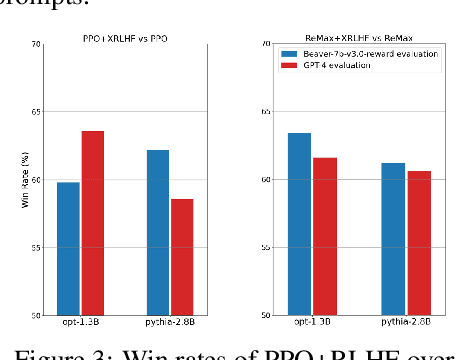
Abstract:A common and effective strategy for humans to improve an unsatisfactory outcome in daily life is to find a cause of this outcome and correct the cause. In this paper, we investigate whether this human improvement strategy can be applied to improving reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) for alignment of language models (LMs). In particular, it is observed in the literature that LMs tuned by RLHF can still output unsatisfactory responses. This paper proposes a method to improve the unsatisfactory responses by correcting their causes. Our method has two parts. The first part proposes a post-hoc explanation method to explain why an unsatisfactory response is generated to a prompt by identifying the training data that lead to this response. We formulate this problem as a constrained combinatorial optimization problem where the objective is to find a set of training data closest to this prompt-response pair in a feature representation space, and the constraint is that the prompt-response pair can be decomposed as a convex combination of this set of training data in the feature space. We propose an efficient iterative data selection algorithm to solve this problem. The second part proposes an unlearning method that improves unsatisfactory responses to some prompts by unlearning the training data that lead to these unsatisfactory responses and, meanwhile, does not significantly degrade satisfactory responses to other prompts. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm can improve RLHF.
Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP: Macro Placement by Recursively Prototyping and Packing Tree-based Relocating
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:This work introduces the Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP method, which generates expert-quality macro placements through recursively prototyping and packing tree-based relocating. We first perform multi-level macro grouping and PPA-aware cell clustering to produce a unified connection matrix that captures both wirelength and dataflow among macros and clusters. Next, we use DREAMPlace to build a mixed-size placement prototype and obtain reference positions for each macro and cluster. Based on this prototype, we introduce ABPlace, an angle-based analytical method that optimizes macro positions on an ellipse to distribute macros uniformly near chip periphery, while optimizing wirelength and dataflow. A packing tree-based relocating procedure is then designed to jointly adjust the locations of macro groups and the macros within each group, by optimizing an expertise-inspired cost function that captures various design constraints through evolutionary search. Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP repeats the above process: Only a subset of macro groups are positioned in each iteration, and the remaining macros are deferred to the next iteration to improve the prototype's accuracy. Using a well-established backend flow with sufficient timing optimizations, Re$^{\text{2}}$MaP achieves up to 22.22% (average 10.26%) improvement in worst negative slack (WNS) and up to 97.91% (average 33.97%) improvement in total negative slack (TNS) compared to the state-of-the-art academic placer Hier-RTLMP. It also ranks higher on WNS, TNS, power, design rule check (DRC) violations, and runtime than the conference version ReMaP, across seven tested cases. Our code is available at https://github.com/lamda-bbo/Re2MaP.
Simple Denoising Diffusion Language Models
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have recently been extended to language generation through Masked Diffusion Language Models (MDLMs), which achieve performance competitive with strong autoregressive models. However, MDLMs tend to degrade in the few-step regime and cannot directly adopt existing few-step distillation methods designed for continuous diffusion models, as they lack the intrinsic property of mapping from noise to data. Recent Uniform-state Diffusion Models (USDMs), initialized from a uniform prior, alleviate some limitations but still suffer from complex loss formulations that hinder scalability. In this work, we propose a simplified denoising-based loss for USDMs that optimizes only noise-replaced tokens, stabilizing training and matching ELBO-level performance. Furthermore, by framing denoising as self-supervised learning, we introduce a simple modification to our denoising loss with contrastive-inspired negative gradients, which is practical and yield additional improvements in generation quality.
Open3DBench: Open-Source Benchmark for 3D-IC Backend Implementation and PPA Evaluation
Mar 17, 2025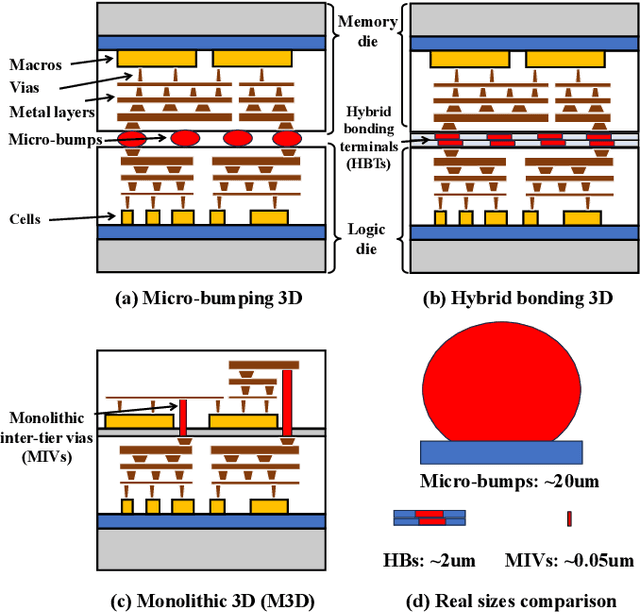
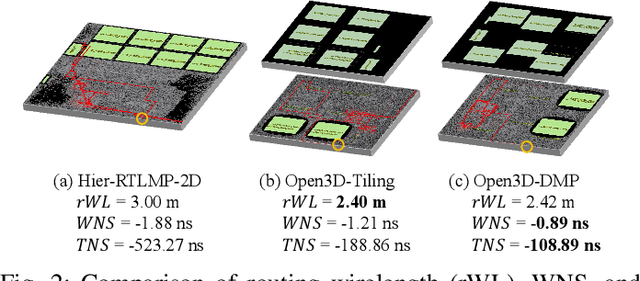
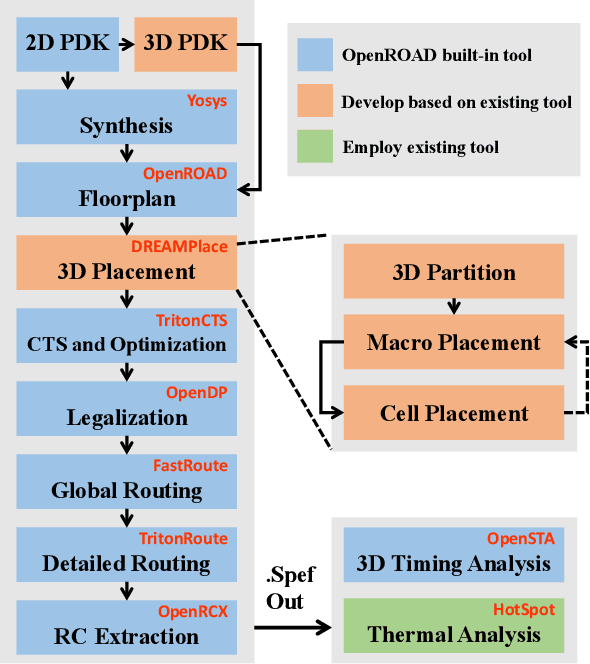

Abstract:This work introduces Open3DBench, an open-source 3D-IC backend implementation benchmark built upon the OpenROAD-flow-scripts framework, enabling comprehensive evaluation of power, performance, area, and thermal metrics. Our proposed flow supports modular integration of 3D partitioning, placement, 3D routing, RC extraction, and thermal simulation, aligning with advanced 3D flows that rely on commercial tools and in-house scripts. We present two foundational 3D placement algorithms: Open3D-Tiling, which emphasizes regular macro placement, and Open3D-DMP, which enhances wirelength optimization through cross-die co-placement with analytical placer DREAMPlace. Experimental results show significant improvements in area (51.19%), wirelength (24.06%), timing (30.84%), and power (5.72%) compared to 2D flows. The results also highlight that better wirelength does not necessarily lead to PPA gain, emphasizing the need of developing PPA-driven methods. Open3DBench offers a standardized, reproducible platform for evaluating 3D EDA methods, effectively bridging the gap between open-source tools and commercial solutions in 3D-IC design.
TransPlace: Transferable Circuit Global Placement via Graph Neural Network
Jan 10, 2025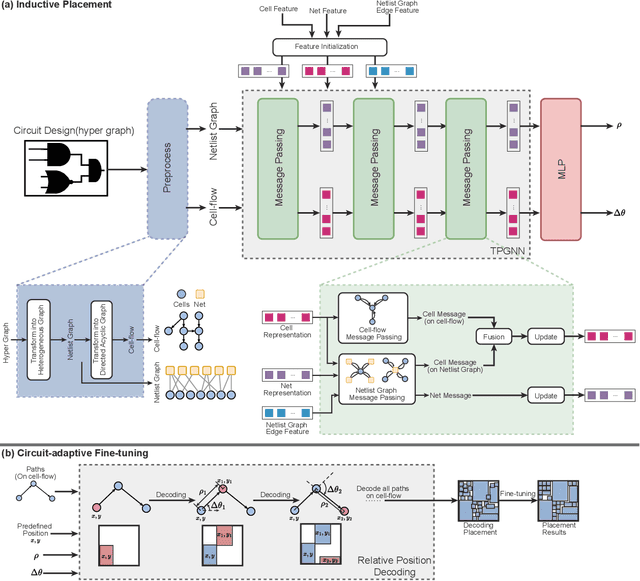
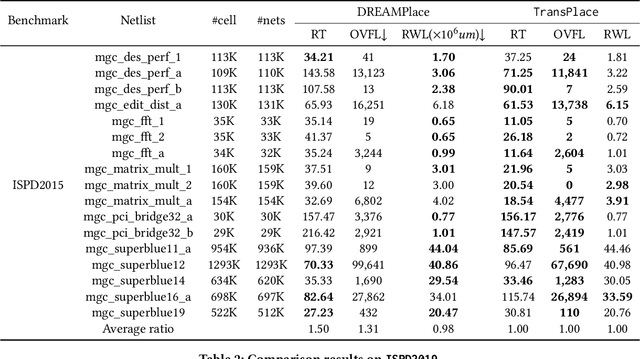
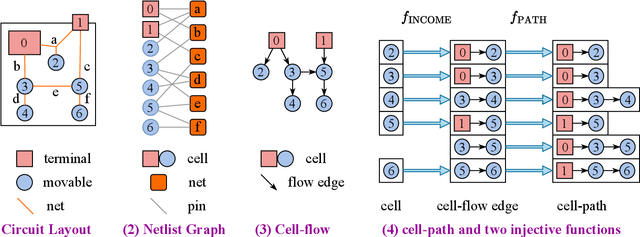
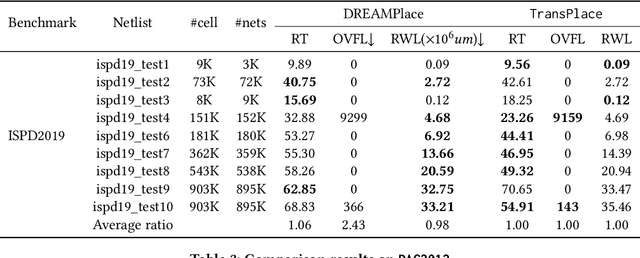
Abstract:Global placement, a critical step in designing the physical layout of computer chips, is essential to optimize chip performance. Prior global placement methods optimize each circuit design individually from scratch. Their neglect of transferable knowledge limits solution efficiency and chip performance as circuit complexity drastically increases. This study presents TransPlace, a global placement framework that learns to place millions of mixed-size cells in continuous space. TransPlace introduces i) Netlist Graph to efficiently model netlist topology, ii) Cell-flow and relative position encoding to learn SE(2)-invariant representation, iii) a tailored graph neural network architecture for informed parameterization of placement knowledge, and iv) a two-stage strategy for coarse-to-fine placement. Compared to state-of-the-art placement methods, TransPlace-trained on a few high-quality placements-can place unseen circuits with 1.2x speedup while reducing congestion by 30%, timing by 9%, and wirelength by 5%.
Reinforcement Learning Policy as Macro Regulator Rather than Macro Placer
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:In modern chip design, placement aims at placing millions of circuit modules, which is an essential step that significantly influences power, performance, and area (PPA) metrics. Recently, reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising technique for improving placement quality, especially macro placement. However, current RL-based placement methods suffer from long training times, low generalization ability, and inability to guarantee PPA results. A key issue lies in the problem formulation, i.e., using RL to place from scratch, which results in limits useful information and inaccurate rewards during the training process. In this work, we propose an approach that utilizes RL for the refinement stage, which allows the RL policy to learn how to adjust existing placement layouts, thereby receiving sufficient information for the policy to act and obtain relatively dense and precise rewards. Additionally, we introduce the concept of regularity during training, which is considered an important metric in the chip design industry but is often overlooked in current RL placement methods. We evaluate our approach on the ISPD 2005 and ICCAD 2015 benchmark, comparing the global half-perimeter wirelength and regularity of our proposed method against several competitive approaches. Besides, we test the PPA performance using commercial software, showing that RL as a regulator can achieve significant PPA improvements. Our RL regulator can fine-tune placements from any method and enhance their quality. Our work opens up new possibilities for the application of RL in placement, providing a more effective and efficient approach to optimizing chip design. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/lamda-bbo/macro-regulator}.
Meta-Reinforcement Learning with Universal Policy Adaptation: Provable Near-Optimality under All-task Optimum Comparator
Oct 13, 2024Abstract:Meta-reinforcement learning (Meta-RL) has attracted attention due to its capability to enhance reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms, in terms of data efficiency and generalizability. In this paper, we develop a bilevel optimization framework for meta-RL (BO-MRL) to learn the meta-prior for task-specific policy adaptation, which implements multiple-step policy optimization on one-time data collection. Beyond existing meta-RL analyses, we provide upper bounds of the expected optimality gap over the task distribution. This metric measures the distance of the policy adaptation from the learned meta-prior to the task-specific optimum, and quantifies the model's generalizability to the task distribution. We empirically validate the correctness of the derived upper bounds and demonstrate the superior effectiveness of the proposed algorithm over benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge