Yujie Wu
BrainFuse: a unified infrastructure integrating realistic biological modeling and core AI methodology
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Neuroscience and artificial intelligence represent distinct yet complementary pathways to general intelligence. However, amid the ongoing boom in AI research and applications, the translational synergy between these two fields has grown increasingly elusive-hampered by a widening infrastructural incompatibility: modern AI frameworks lack native support for biophysical realism, while neural simulation tools are poorly suited for gradient-based optimization and neuromorphic hardware deployment. To bridge this gap, we introduce BrainFuse, a unified infrastructure that provides comprehensive support for biophysical neural simulation and gradient-based learning. By addressing algorithmic, computational, and deployment challenges, BrainFuse exhibits three core capabilities: (1) algorithmic integration of detailed neuronal dynamics into a differentiable learning framework; (2) system-level optimization that accelerates customizable ion-channel dynamics by up to 3,000x on GPUs; and (3) scalable computation with highly compatible pipelines for neuromorphic hardware deployment. We demonstrate this full-stack design through both AI and neuroscience tasks, from foundational neuron simulation and functional cylinder modeling to real-world deployment and application scenarios. For neuroscience, BrainFuse supports multiscale biological modeling, enabling the deployment of approximately 38,000 Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with 100 million synapses on a single neuromorphic chip while consuming as low as 1.98 W. For AI, BrainFuse facilitates the synergistic application of realistic biological neuron models, demonstrating enhanced robustness to input noise and improved temporal processing endowed by complex HH dynamics. BrainFuse therefore serves as a foundational engine to facilitate cross-disciplinary research and accelerate the development of next-generation bio-inspired intelligent systems.
BMAM: Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory Framework
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Language-model-based agents operating over extended interaction horizons face persistent challenges in preserving temporally grounded information and maintaining behavioral consistency across sessions, a failure mode we term soul erosion. We present BMAM (Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory), a general-purpose memory architecture that models agent memory as a set of functionally specialized subsystems rather than a single unstructured store. Inspired by cognitive memory systems, BMAM decomposes memory into episodic, semantic, salience-aware, and control-oriented components that operate at complementary time scales. To support long-horizon reasoning, BMAM organizes episodic memories along explicit timelines and retrieves evidence by fusing multiple complementary signals. Experiments on the LoCoMo benchmark show that BMAM achieves 78.45 percent accuracy under the standard long-horizon evaluation setting, and ablation analyses confirm that the hippocampus-inspired episodic memory subsystem plays a critical role in temporal reasoning.
CogniSNN: Enabling Neuron-Expandability, Pathway-Reusability, and Dynamic-Configurability with Random Graph Architectures in Spiking Neural Networks
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs), regarded as the third generation of artificial neural networks, are expected to bridge the gap between artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience. However, most mainstream SNN research directly adopts the rigid, chain-like hierarchical architecture of traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs), ignoring key structural characteristics of the brain. Biological neurons are stochastically interconnected, forming complex neural pathways that exhibit Neuron-Expandability, Pathway-Reusability, and Dynamic-Configurability. In this paper, we introduce a new SNN paradigm, named Cognition-aware SNN (CogniSNN), by incorporating Random Graph Architecture (RGA). Furthermore, we address the issues of network degradation and dimensional mismatch in deep pathways by introducing an improved pure spiking residual mechanism alongside an adaptive pooling strategy. Then, we design a Key Pathway-based Learning without Forgetting (KP-LwF) approach, which selectively reuses critical neural pathways while retaining historical knowledge, enabling efficient multi-task transfer. Finally, we propose a Dynamic Growth Learning (DGL) algorithm that allows neurons and synapses to grow dynamically along the internal temporal dimension. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CogniSNN achieves performance comparable to, or even surpassing, current state-of-the-art SNNs on neuromorphic datasets and Tiny-ImageNet. The Pathway-Reusability enhances the network's continuous learning capability across different scenarios, while the dynamic growth algorithm improves robustness against interference and mitigates the fixed-timestep constraints during neuromorphic chip deployment. This work demonstrates the potential of SNNs with random graph structures in advancing brain-inspired intelligence and lays the foundation for their practical application on neuromorphic hardware.
Neuromorphic Sequential Arena: A Benchmark for Neuromorphic Temporal Processing
May 28, 2025Abstract:Temporal processing is vital for extracting meaningful information from time-varying signals. Recent advancements in Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have shown immense promise in efficiently processing these signals. However, progress in this field has been impeded by the lack of effective and standardized benchmarks, which complicates the consistent measurement of technological advancements and limits the practical applicability of SNNs. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Neuromorphic Sequential Arena (NSA), a comprehensive benchmark that offers an effective, versatile, and application-oriented evaluation framework for neuromorphic temporal processing. The NSA includes seven real-world temporal processing tasks from a diverse range of application scenarios, each capturing rich temporal dynamics across multiple timescales. Utilizing NSA, we conduct extensive comparisons of recently introduced spiking neuron models and neural architectures, presenting comprehensive baselines in terms of task performance, training speed, memory usage, and energy efficiency. Our findings emphasize an urgent need for efficient SNN designs that can consistently deliver high performance across tasks with varying temporal complexities while maintaining low computational costs. NSA enables systematic tracking of advancements in neuromorphic algorithm research and paves the way for developing effective and efficient neuromorphic temporal processing systems.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images: Methods and Results
Apr 19, 2025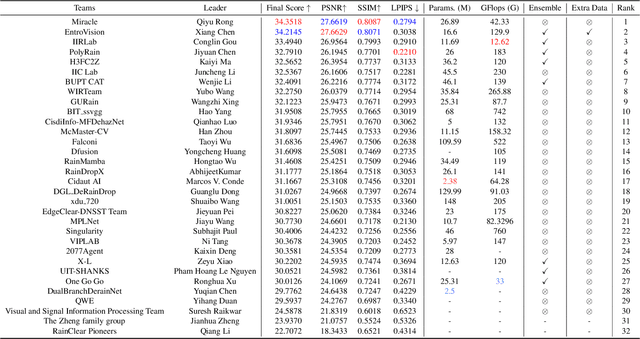
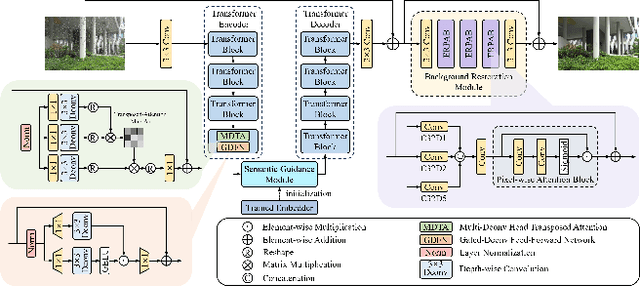
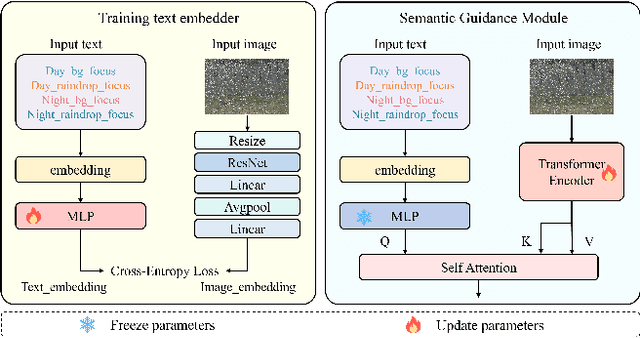
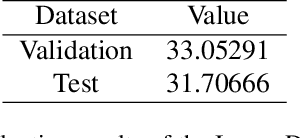
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images. This challenge received a wide range of impressive solutions, which are developed and evaluated using our collected real-world Raindrop Clarity dataset. Unlike existing deraining datasets, our Raindrop Clarity dataset is more diverse and challenging in degradation types and contents, which includes day raindrop-focused, day background-focused, night raindrop-focused, and night background-focused degradations. This dataset is divided into three subsets for competition: 14,139 images for training, 240 images for validation, and 731 images for testing. The primary objective of this challenge is to establish a new and powerful benchmark for the task of removing raindrops under varying lighting and focus conditions. There are a total of 361 participants in the competition, and 32 teams submitting valid solutions and fact sheets for the final testing phase. These submissions achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the Raindrop Clarity dataset. The project can be found at https://lixinustc.github.io/CVPR-NTIRE2025-RainDrop-Competition.github.io/.
Spiking Neural Networks for Temporal Processing: Status Quo and Future Prospects
Feb 13, 2025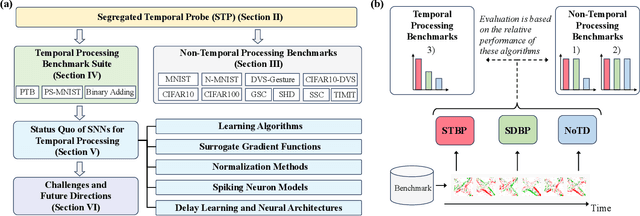

Abstract:Temporal processing is fundamental for both biological and artificial intelligence systems, as it enables the comprehension of dynamic environments and facilitates timely responses. Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) excel in handling such data with high efficiency, owing to their rich neuronal dynamics and sparse activity patterns. Given the recent surge in the development of SNNs, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive evaluation of their temporal processing capabilities. In this paper, we first conduct an in-depth assessment of commonly used neuromorphic benchmarks, revealing critical limitations in their ability to evaluate the temporal processing capabilities of SNNs. To bridge this gap, we further introduce a benchmark suite consisting of three temporal processing tasks characterized by rich temporal dynamics across multiple timescales. Utilizing this benchmark suite, we perform a thorough evaluation of recently introduced SNN approaches to elucidate the current status of SNNs in temporal processing. Our findings indicate significant advancements in recently developed spiking neuron models and neural architectures regarding their temporal processing capabilities, while also highlighting a performance gap in handling long-range dependencies when compared to state-of-the-art non-spiking models. Finally, we discuss the key challenges and outline potential avenues for future research.
NeuroVE: Brain-inspired Linear-Angular Velocity Estimation with Spiking Neural Networks
Aug 28, 2024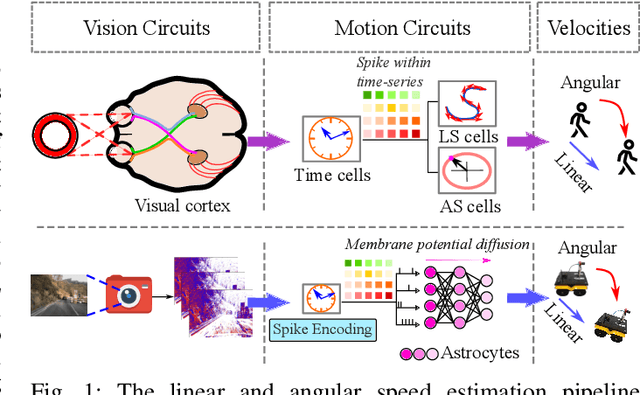
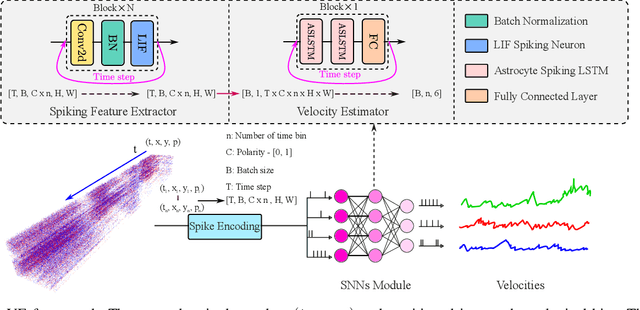
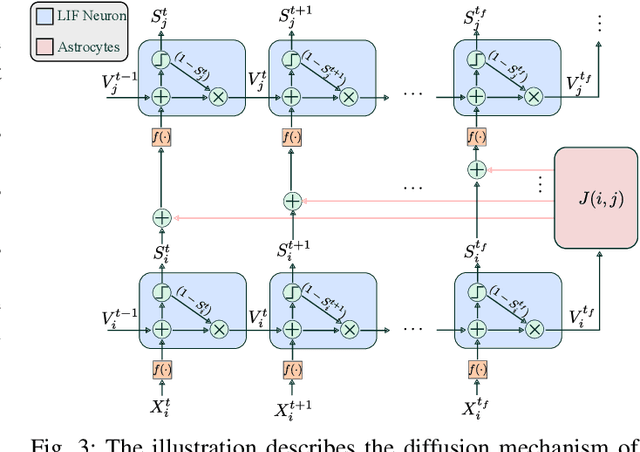
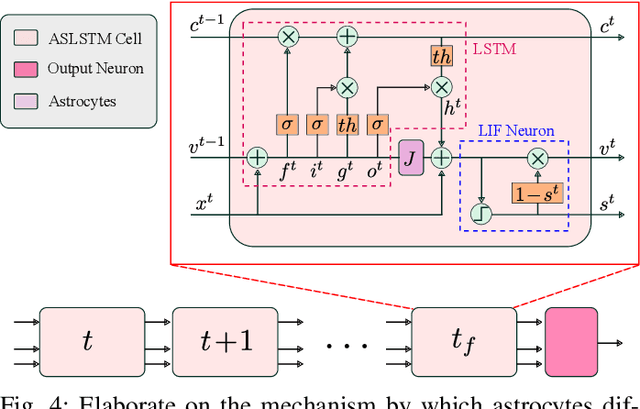
Abstract:Vision-based ego-velocity estimation is a fundamental problem in robot state estimation. However, the constraints of frame-based cameras, including motion blur and insufficient frame rates in dynamic settings, readily lead to the failure of conventional velocity estimation techniques. Mammals exhibit a remarkable ability to accurately estimate their ego-velocity during aggressive movement. Hence, integrating this capability into robots shows great promise for addressing these challenges. In this paper, we propose a brain-inspired framework for linear-angular velocity estimation, dubbed NeuroVE. The NeuroVE framework employs an event camera to capture the motion information and implements spiking neural networks (SNNs) to simulate the brain's spatial cells' function for velocity estimation. We formulate the velocity estimation as a time-series forecasting problem. To this end, we design an Astrocyte Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (ALIF) neuron model to encode continuous values. Additionally, we have developed an Astrocyte Spiking Long Short-term Memory (ASLSTM) structure, which significantly improves the time-series forecasting capabilities, enabling an accurate estimate of ego-velocity. Results from both simulation and real-world experiments indicate that NeuroVE has achieved an approximate 60% increase in accuracy compared to other SNN-based approaches.
Distance-Forward Learning: Enhancing the Forward-Forward Algorithm Towards High-Performance On-Chip Learning
Aug 27, 2024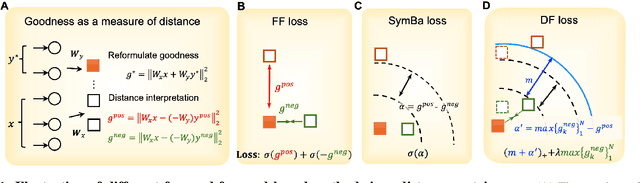

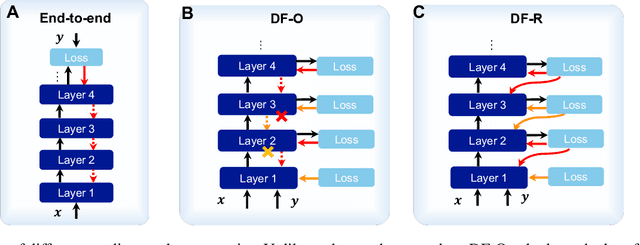

Abstract:The Forward-Forward (FF) algorithm was recently proposed as a local learning method to address the limitations of backpropagation (BP), offering biological plausibility along with memory-efficient and highly parallelized computational benefits. However, it suffers from suboptimal performance and poor generalization, largely due to inadequate theoretical support and a lack of effective learning strategies. In this work, we reformulate FF using distance metric learning and propose a distance-forward algorithm (DF) to improve FF performance in supervised vision tasks while preserving its local computational properties, making it competitive for efficient on-chip learning. To achieve this, we reinterpret FF through the lens of centroid-based metric learning and develop a goodness-based N-pair margin loss to facilitate the learning of discriminative features. Furthermore, we integrate layer-collaboration local update strategies to reduce information loss caused by greedy local parameter updates. Our method surpasses existing FF models and other advanced local learning approaches, with accuracies of 99.7\% on MNIST, 88.2\% on CIFAR-10, 59\% on CIFAR-100, 95.9\% on SVHN, and 82.5\% on ImageNette, respectively. Moreover, it achieves comparable performance with less than 40\% memory cost compared to BP training, while exhibiting stronger robustness to multiple types of hardware-related noise, demonstrating its potential for online learning and energy-efficient computation on neuromorphic chips.
PMSN: A Parallel Multi-compartment Spiking Neuron for Multi-scale Temporal Processing
Aug 27, 2024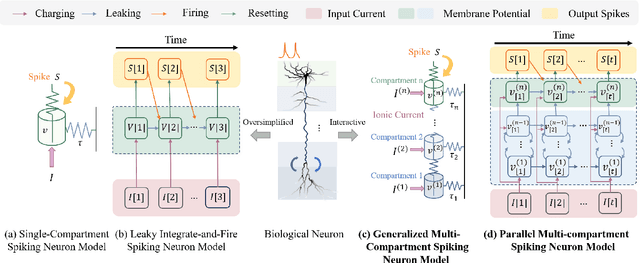
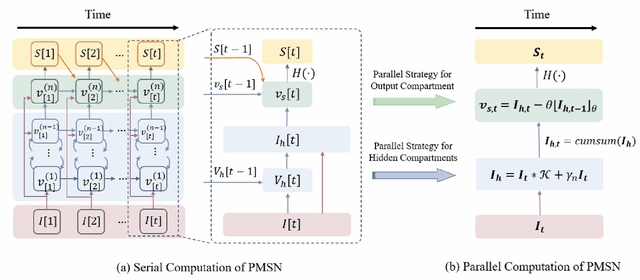


Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) hold great potential to realize brain-inspired, energy-efficient computational systems. However, current SNNs still fall short in terms of multi-scale temporal processing compared to their biological counterparts. This limitation has resulted in poor performance in many pattern recognition tasks with information that varies across different timescales. To address this issue, we put forward a novel spiking neuron model called Parallel Multi-compartment Spiking Neuron (PMSN). The PMSN emulates biological neurons by incorporating multiple interacting substructures and allows for flexible adjustment of the substructure counts to effectively represent temporal information across diverse timescales. Additionally, to address the computational burden associated with the increased complexity of the proposed model, we introduce two parallelization techniques that decouple the temporal dependencies of neuronal updates, enabling parallelized training across different time steps. Our experimental results on a wide range of pattern recognition tasks demonstrate the superiority of PMSN. It outperforms other state-of-the-art spiking neuron models in terms of its temporal processing capacity, training speed, and computation cost. Specifically, compared with the commonly used Leaky Integrate-and-Fire neuron, PMSN offers a simulation acceleration of over 10 $\times$ and a 30 % improvement in accuracy on Sequential CIFAR10 dataset, while maintaining comparable computational cost.
Unveiling the Potential of Spiking Dynamics in Graph Representation Learning through Spatial-Temporal Normalization and Coding Strategies
Jul 30, 2024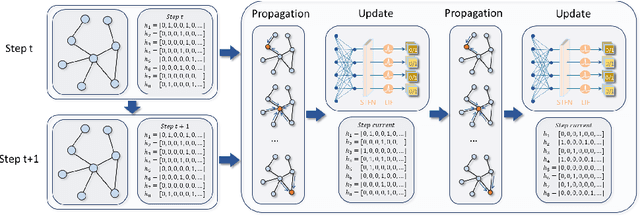
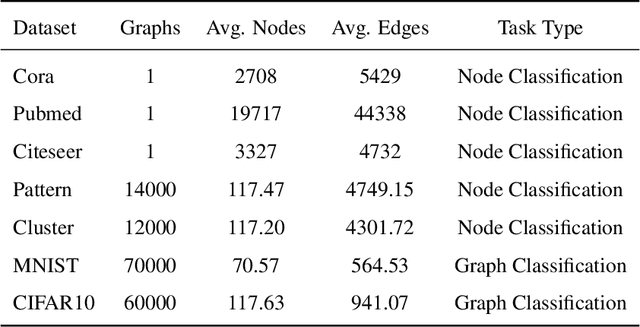
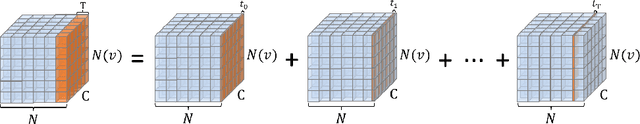
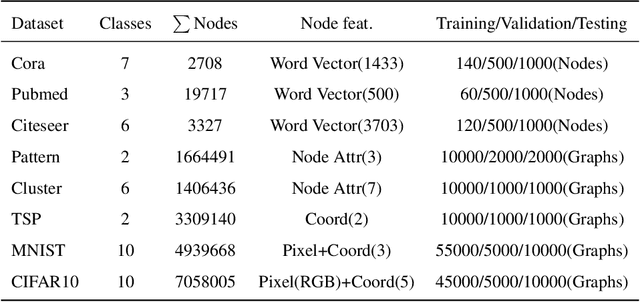
Abstract:In recent years, spiking neural networks (SNNs) have attracted substantial interest due to their potential to replicate the energy-efficient and event-driven processing of biological neurons. Despite this, the application of SNNs in graph representation learning, particularly for non-Euclidean data, remains underexplored, and the influence of spiking dynamics on graph learning is not yet fully understood. This work seeks to address these gaps by examining the unique properties and benefits of spiking dynamics in enhancing graph representation learning. We propose a spike-based graph neural network model that incorporates spiking dynamics, enhanced by a novel spatial-temporal feature normalization (STFN) technique, to improve training efficiency and model stability. Our detailed analysis explores the impact of rate coding and temporal coding on SNN performance, offering new insights into their advantages for deep graph networks and addressing challenges such as the oversmoothing problem. Experimental results demonstrate that our SNN models can achieve competitive performance with state-of-the-art graph neural networks (GNNs) while considerably reducing computational costs, highlighting the potential of SNNs for efficient neuromorphic computing applications in complex graph-based scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge