Keping Yang
Deep Disentangled Representation Network for Treatment Effect Estimation
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Estimating individual-level treatment effect from observational data is a fundamental problem in causal inference and has attracted increasing attention in the fields of education, healthcare, and public policy.In this work, we concentrate on the study of disentangled representation methods that have shown promising outcomes by decomposing observed covariates into instrumental, confounding, and adjustment factors. However, most of the previous work has primarily revolved around generative models or hard decomposition methods for covariates, which often struggle to guarantee the attainment of precisely disentangled factors. In order to effectively model different causal relationships, we propose a novel treatment effect estimation algorithm that incorporates a mixture of experts with multi-head attention and a linear orthogonal regularizer to softly decompose the pre-treatment variables, and simultaneously eliminates selection bias via importance sampling re-weighting techniques. We conduct extensive experiments on both public semi-synthetic and real-world production datasets. The experimental results clearly demonstrate that our algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art methods focused on individual treatment effects.
Modeling User Behavior with Graph Convolution for Personalized Product Search
Feb 12, 2022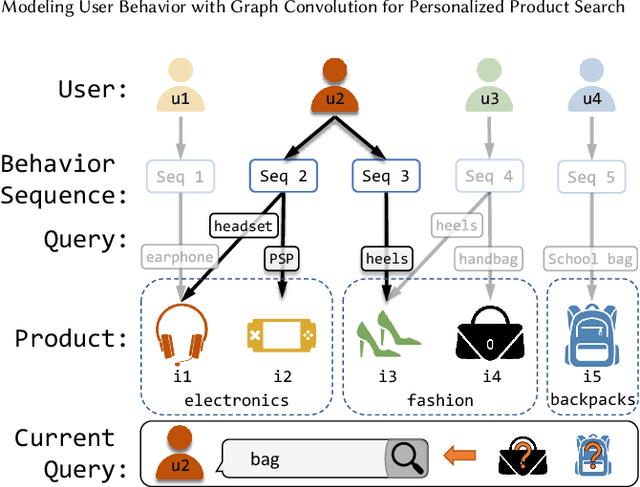
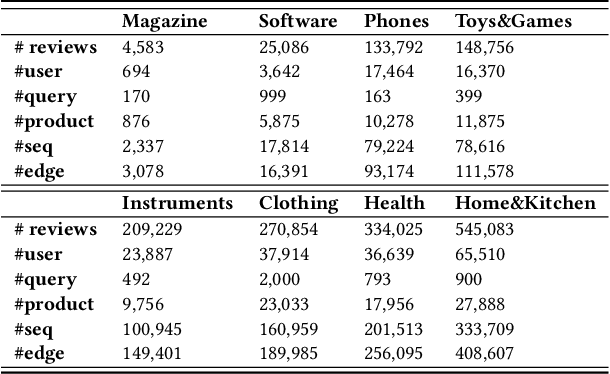
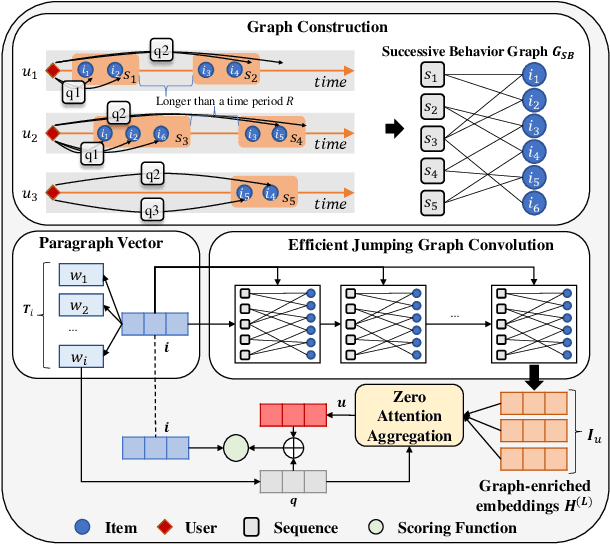
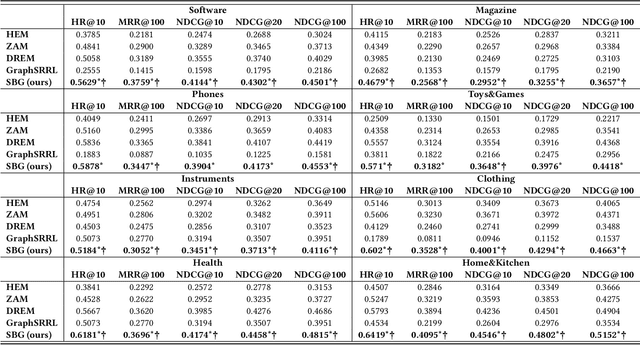
Abstract:User preference modeling is a vital yet challenging problem in personalized product search. In recent years, latent space based methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance by jointly learning semantic representations of products, users, and text tokens. However, existing methods are limited in their ability to model user preferences. They typically represent users by the products they visited in a short span of time using attentive models and lack the ability to exploit relational information such as user-product interactions or item co-occurrence relations. In this work, we propose to address the limitations of prior arts by exploring local and global user behavior patterns on a user successive behavior graph, which is constructed by utilizing short-term actions of all users. To capture implicit user preference signals and collaborative patterns, we use an efficient jumping graph convolution to explore high-order relations to enrich product representations for user preference modeling. Our approach can be seamlessly integrated with existing latent space based methods and be potentially applied in any product retrieval method that uses purchase history to model user preferences. Extensive experiments on eight Amazon benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of our approach. The source code is available at \url{https://github.com/floatSDSDS/SBG}.
Embedding-based Product Retrieval in Taobao Search
Jun 17, 2021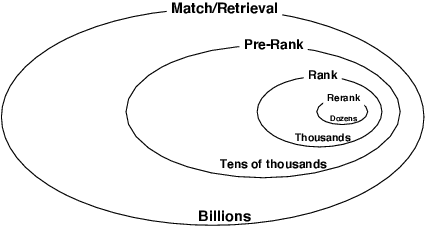
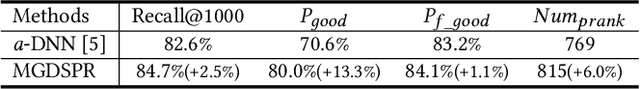
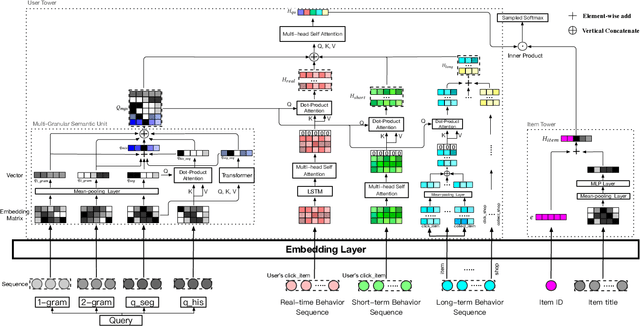
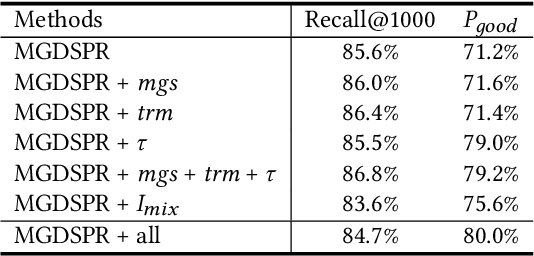
Abstract:Nowadays, the product search service of e-commerce platforms has become a vital shopping channel in people's life. The retrieval phase of products determines the search system's quality and gradually attracts researchers' attention. Retrieving the most relevant products from a large-scale corpus while preserving personalized user characteristics remains an open question. Recent approaches in this domain have mainly focused on embedding-based retrieval (EBR) systems. However, after a long period of practice on Taobao, we find that the performance of the EBR system is dramatically degraded due to its: (1) low relevance with a given query and (2) discrepancy between the training and inference phases. Therefore, we propose a novel and practical embedding-based product retrieval model, named Multi-Grained Deep Semantic Product Retrieval (MGDSPR). Specifically, we first identify the inconsistency between the training and inference stages, and then use the softmax cross-entropy loss as the training objective, which achieves better performance and faster convergence. Two efficient methods are further proposed to improve retrieval relevance, including smoothing noisy training data and generating relevance-improving hard negative samples without requiring extra knowledge and training procedures. We evaluate MGDSPR on Taobao Product Search with significant metrics gains observed in offline experiments and online A/B tests. MGDSPR has been successfully deployed to the existing multi-channel retrieval system in Taobao Search. We also introduce the online deployment scheme and share practical lessons of our retrieval system to contribute to the community.
AutoDebias: Learning to Debias for Recommendation
May 10, 2021
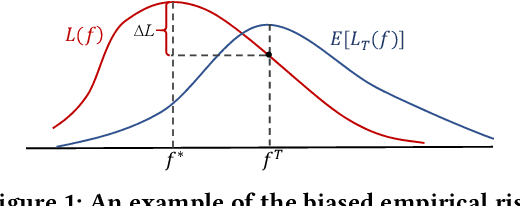
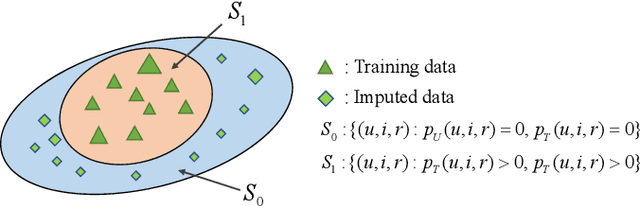
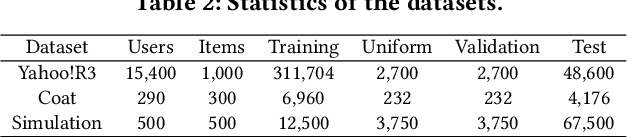
Abstract:Recommender systems rely on user behavior data like ratings and clicks to build personalization model. However, the collected data is observational rather than experimental, causing various biases in the data which significantly affect the learned model. Most existing work for recommendation debiasing, such as the inverse propensity scoring and imputation approaches, focuses on one or two specific biases, lacking the universal capacity that can account for mixed or even unknown biases in the data. Towards this research gap, we first analyze the origin of biases from the perspective of \textit{risk discrepancy} that represents the difference between the expectation empirical risk and the true risk. Remarkably, we derive a general learning framework that well summarizes most existing debiasing strategies by specifying some parameters of the general framework. This provides a valuable opportunity to develop a universal solution for debiasing, e.g., by learning the debiasing parameters from data. However, the training data lacks important signal of how the data is biased and what the unbiased data looks like. To move this idea forward, we propose \textit{AotoDebias} that leverages another (small) set of uniform data to optimize the debiasing parameters by solving the bi-level optimization problem with meta-learning. Through theoretical analyses, we derive the generalization bound for AutoDebias and prove its ability to acquire the appropriate debiasing strategy. Extensive experiments on two real datasets and a simulated dataset demonstrated effectiveness of AutoDebias. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/DongHande/AutoDebias}.
Learning a Product Relevance Model from Click-Through Data in E-Commerce
Feb 14, 2021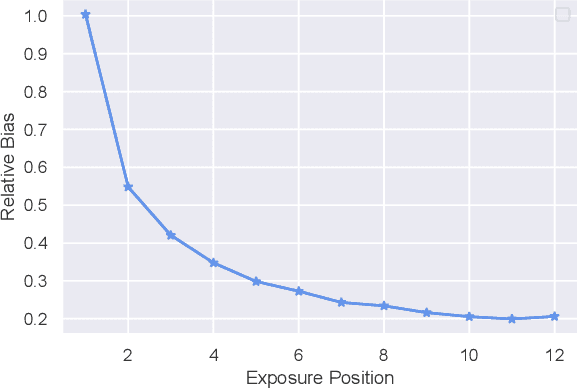
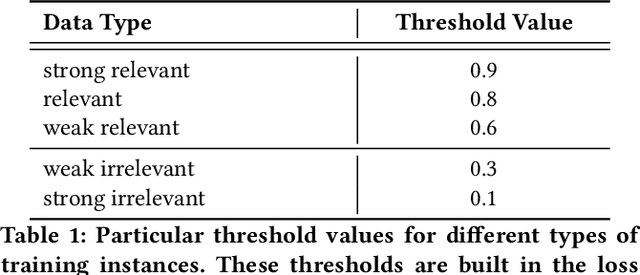
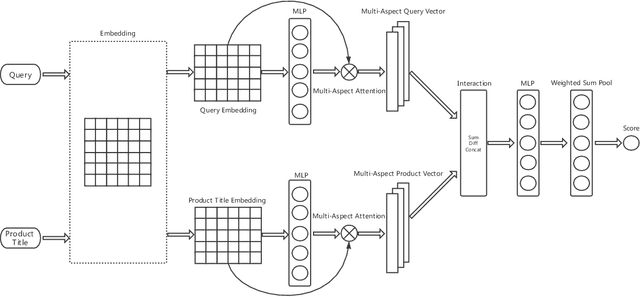
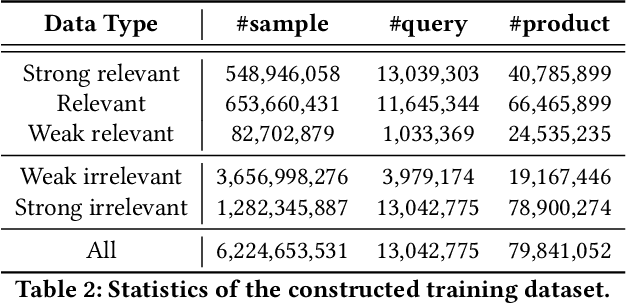
Abstract:The search engine plays a fundamental role in online e-commerce systems, to help users find the products they want from the massive product collections. Relevance is an essential requirement for e-commerce search, since showing products that do not match search query intent will degrade user experience. With the existence of vocabulary gap between user language of queries and seller language of products, measuring semantic relevance is necessary and neural networks are engaged to address this task. However, semantic relevance is different from click-through rate prediction in that no direct training signal is available. Most previous attempts learn relevance models from user click-through data that are cheap and abundant. Unfortunately, click behavior is noisy and misleading, which is affected by not only relevance but also factors including price, image and attractive titles. Therefore, it is challenging but valuable to learn relevance models from click-through data. In this paper, we propose a new relevance learning framework that concentrates on how to train a relevance model from the weak supervision of click-through data. Different from previous efforts that treat samples as either relevant or irrelevant, we construct more fine-grained samples for training. We propose a novel way to consider samples of different relevance confidence, and come up with a new training objective to learn a robust relevance model with desirable score distribution. The proposed model is evaluated on offline annotated data and online A/B testing, and it achieves both promising performance and high computational efficiency. The model has already been deployed online, serving the search traffic of Taobao for over a year.
M2GRL: A Multi-task Multi-view Graph Representation Learning Framework for Web-scale Recommender Systems
Jun 01, 2020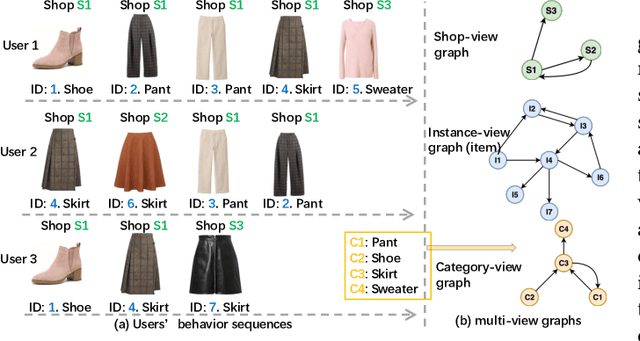


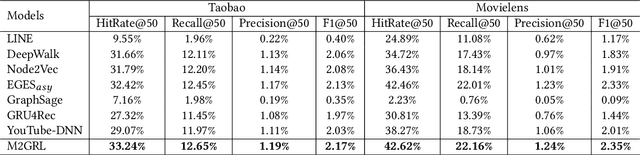
Abstract:Combining graph representation learning with multi-view data (side information) for recommendation is a trend in industry. Most existing methods can be categorized as \emph{multi-view representation fusion}; they first build one graph and then integrate multi-view data into a single compact representation for each node in the graph. However, these methods are raising concerns in both engineering and algorithm aspects: 1) multi-view data are abundant and informative in industry and may exceed the capacity of one single vector, and 2) inductive bias may be introduced as multi-view data are often from different distributions. In this paper, we use a \emph{multi-view representation alignment} approach to address this issue. Particularly, we propose a multi-task multi-view graph representation learning framework (M2GRL) to learn node representations from multi-view graphs for web-scale recommender systems. M2GRL constructs one graph for each single-view data, learns multiple separate representations from multiple graphs, and performs alignment to model cross-view relations. M2GRL chooses a multi-task learning paradigm to learn intra-view representations and cross-view relations jointly. Besides, M2GRL applies homoscedastic uncertainty to adaptively tune the loss weights of tasks during training. We deploy M2GRL at Taobao and train it on 57 billion examples. According to offline metrics and online A/B tests, M2GRL significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art algorithms. Further exploration on diversity recommendation in Taobao shows the effectiveness of utilizing multiple representations produced by \method{}, which we argue is a promising direction for various industrial recommendation tasks of different focus.
AliCoCo: Alibaba E-commerce Cognitive Concept Net
Mar 30, 2020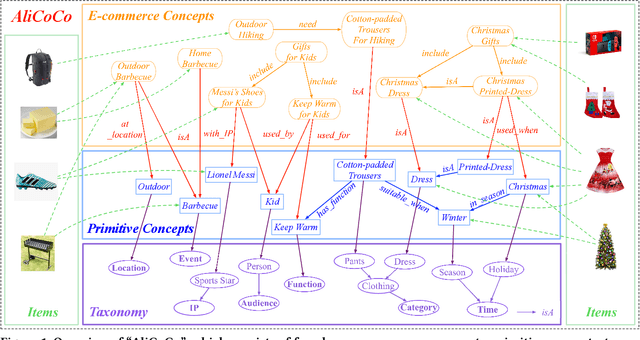
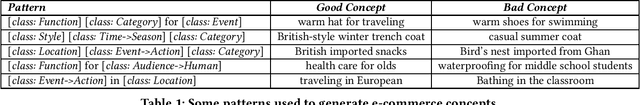
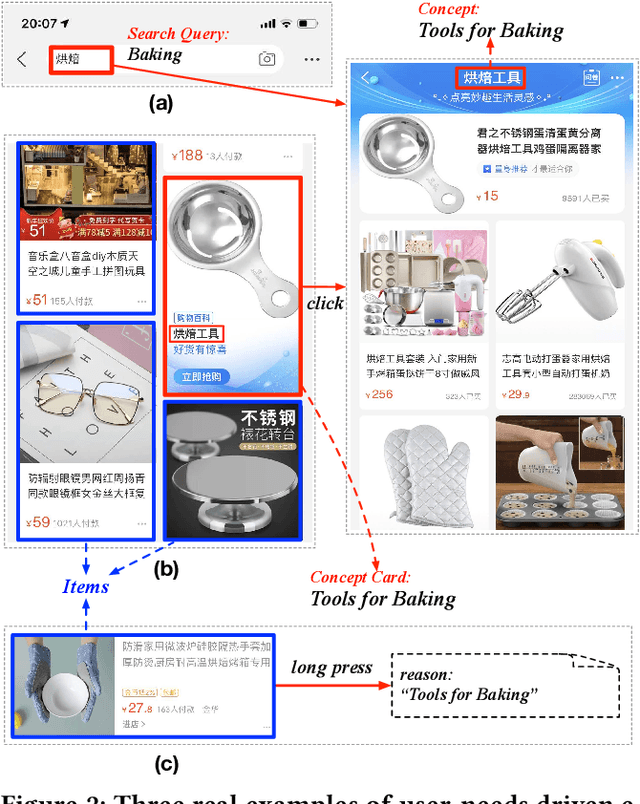
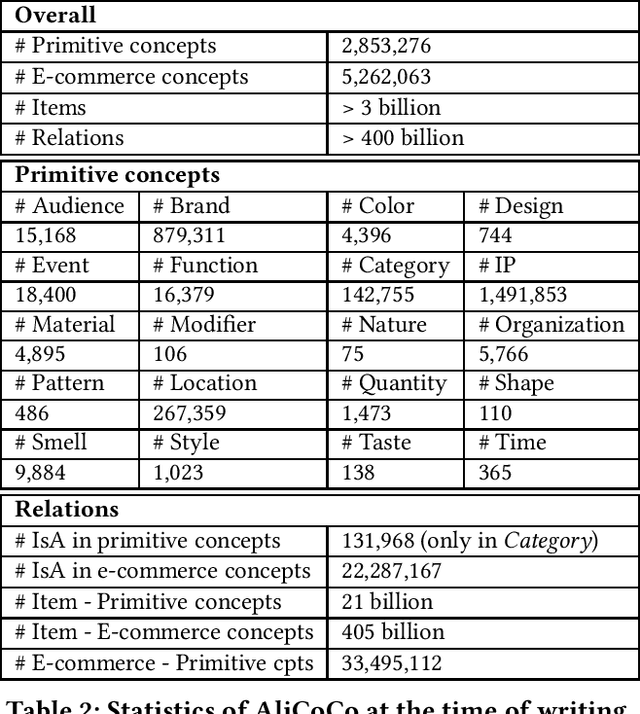
Abstract:One of the ultimate goals of e-commerce platforms is to satisfy various shopping needs for their customers. Much efforts are devoted to creating taxonomies or ontologies in e-commerce towards this goal. However, user needs in e-commerce are still not well defined, and none of the existing ontologies has the enough depth and breadth for universal user needs understanding. The semantic gap in-between prevents shopping experience from being more intelligent. In this paper, we propose to construct a large-scale e-commerce cognitive concept net named "AliCoCo", which is practiced in Alibaba, the largest Chinese e-commerce platform in the world. We formally define user needs in e-commerce, then conceptualize them as nodes in the net. We present details on how AliCoCo is constructed semi-automatically and its successful, ongoing and potential applications in e-commerce.
Tracing the Propagation Path: A Flow Perspective of Representation Learning on Graphs
Dec 12, 2019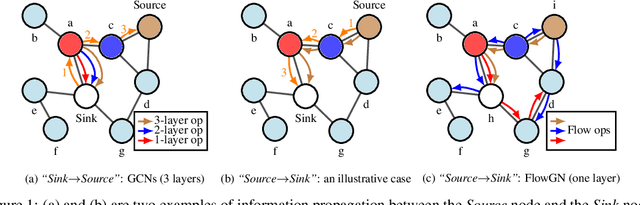
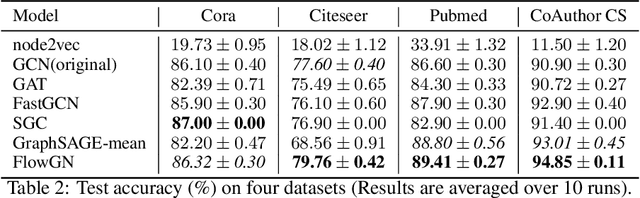
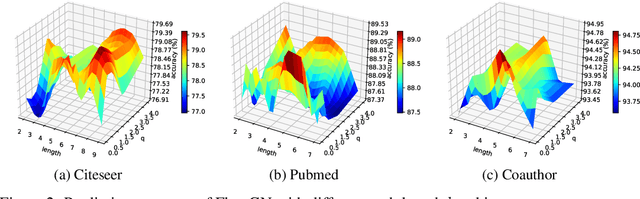
Abstract:Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have gained significant developments in representation learning on graphs. However, current GCNs suffer from two common challenges: 1) GCNs are only effective with shallow structures; stacking multiple GCN layers will lead to over-smoothing. 2) GCNs do not scale well with large, dense graphs due to the recursive neighborhood expansion. We generalize the propagation strategies of current GCNs as a \emph{"Sink$\to$Source"} mode, which seems to be an underlying cause of the two challenges. To address these issues intrinsically, in this paper, we study the information propagation mechanism in a \emph{"Source$\to$Sink"} mode. We introduce a new concept "information flow path" that explicitly defines where information originates and how it diffuses. Then a novel framework, namely Flow Graph Network (FlowGN), is proposed to learn node representations. FlowGN is computationally efficient and flexible in propagation strategies. Moreover, FlowGN decouples the layer structure from the information propagation process, removing the interior constraint of applying deep structures in traditional GCNs. Further experiments on public datasets demonstrate the superiority of FlowGN against state-of-the-art GCNs.
A Causal Perspective to Unbiased Conversion Rate Estimation on Data Missing Not at Random
Oct 16, 2019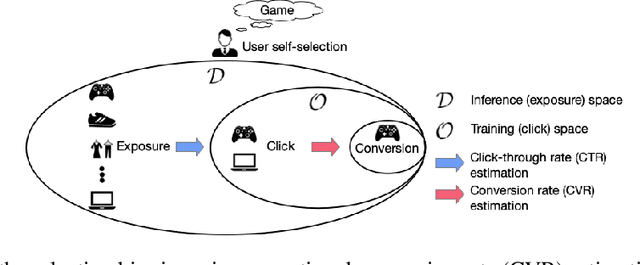
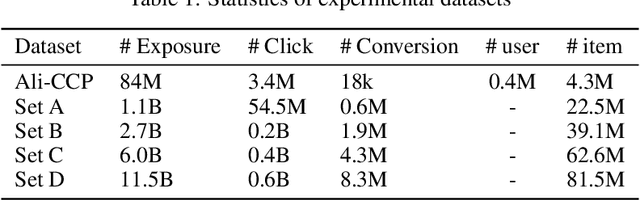
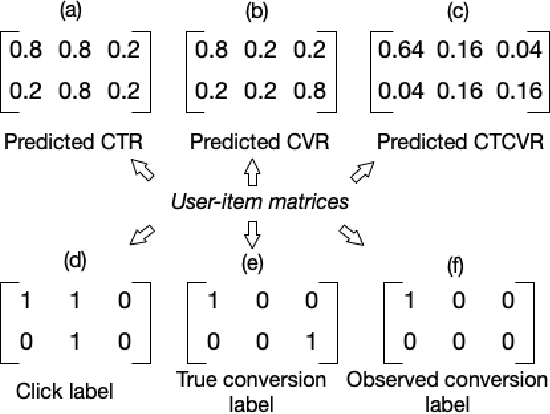
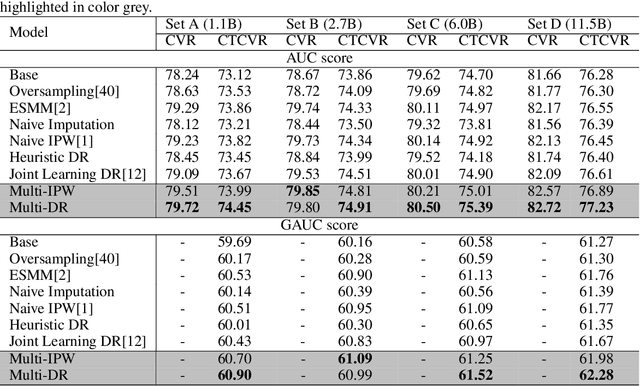
Abstract:In modern e-commerce and advertising recommender systems, ongoing research works attempt to optimize conversion rate (CVR) estimation, and increase the gross merchandise volume. Even though the state-of-the-art CVR estimators adopt deep learning methods, their model performances are still subject to sample selection bias and data sparsity issues. Conversion labels of exposed items in training dataset are typically missing not at random due to selection bias. Empirically, data sparsity issue causes the performance degradation of model with large parameter space. In this paper, we proposed two causal estimators combined with multi-task learning, and aim to solve sample selection bias (SSB) and data sparsity (DS) issues in conversion rate estimation. The proposed estimators adjust for the MNAR mechanism as if they are trained on a "do dataset" where users are forced to click on all exposed items. We evaluate the causal estimators with billion data samples. Experiment results demonstrate that the proposed CVR estimators outperform other state-of-the-art CVR estimators. In addition, empirical study shows that our methods are cost-effective with large scale dataset.
Conversion Rate Prediction via Post-Click Behaviour Modeling
Oct 15, 2019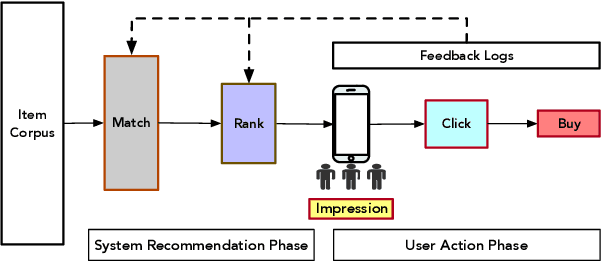
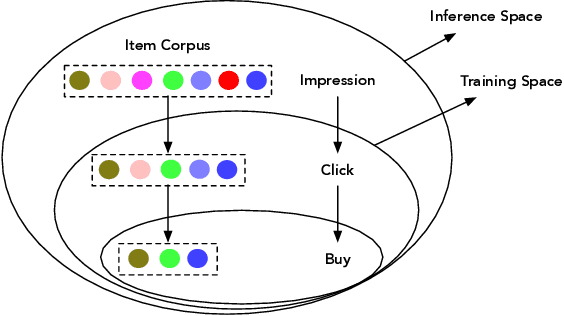
Abstract:Effective and efficient recommendation is crucial for modern e-commerce platforms. It consists of two indispensable components named Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction and Conversion Rate (CVR) prediction, where the latter is an essential factor contributing to the final purchasing volume. Existing methods specifically predict CVR using the clicked and purchased samples, which has limited performance affected by the well-known sample selection bias and data sparsity issues. To address these issues, we propose a novel deep CVR prediction method by considering the post-click behaviors. After grouping deterministic actions together, we construct a novel sequential path, which elaborately depicts the post-click behaviors of users. Based on the path, we define the CVR and several related probabilities including CTR, etc., and devise a deep neural network with multiple targets involved accordingly. It takes advantage of the abundant samples with deterministic labels derived from the post-click actions, leading to a significant improvement of CVR prediction. Extensive experiments on both offline and online settings demonstrate its superiority over representative state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge