Fuyu Lv
TaoSearchEmb: A Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning Framework for Dense Retrieval in Taobao Search
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Dense retrieval, as the core component of e-commerce search engines, maps user queries and items into a unified semantic space through pre-trained embedding models to enable large-scale real-time semantic retrieval. Despite the rapid advancement of LLMs gradually replacing traditional BERT architectures for embedding, their training paradigms still adhere to BERT-like supervised fine-tuning and hard negative mining strategies. This approach relies on complex offline hard negative sample construction pipelines, which constrain model iteration efficiency and hinder the evolutionary potential of semantic representation capabilities. Besides, existing multi-task learning frameworks face the seesaw effect when simultaneously optimizing semantic relevance and non-relevance objectives. In this paper, we propose Retrieval-GRPO, a multi-objective reinforcement learning-based dense retrieval framework designed to address these challenges. The method eliminates offline hard negative sample construction by dynamically retrieving Top-K candidate products for each query during training, while introducing a relevance LLM as a reward model to generate real-time feedback. Specifically, the retrieval model dynamically optimizes embedding representations through reinforcement learning, with reward signals combining LLM-generated relevance scores, product quality scores, and multi-way exclusivity metrics to achieve multi-objective user preference alignment and real-time error correction. This mechanism not only removes dependency on hard negatives but also mitigates the seesaw effect through collaborative multi-objective optimization, significantly enhancing the model's semantic generalization capability for complex long-tail queries. Extensive offline and online experiments validate the effectiveness of Retrieval-GRPO, which has been deployed on China's largest e-commerce platform.
C2T-ID: Converting Semantic Codebooks to Textual Document Identifiers for Generative Search
Oct 22, 2025



Abstract:Designing document identifiers (docids) that carry rich semantic information while maintaining tractable search spaces is a important challenge in generative retrieval (GR). Popular codebook methods address this by building a hierarchical semantic tree and constraining generation to its child nodes, yet their numeric identifiers cannot leverage the large language model's pretrained natural language understanding. Conversely, using text as docid provides more semantic expressivity but inflates the decoding space, making the system brittle to early-step errors. To resolve this trade-off, we propose C2T-ID: (i) first construct semantic numerical docid via hierarchical clustering; (ii) then extract high-frequency metadata keywords and iteratively replace each numeric label with its cluster's top-K keywords; and (iii) an optional two-level semantic smoothing step further enhances the fluency of C2T-ID. Experiments on Natural Questions and Taobao's product search demonstrate that C2T-ID significantly outperforms atomic, semantic codebook, and pure-text docid baselines, demonstrating its effectiveness in balancing semantic expressiveness with search space constraints.
Large Reasoning Embedding Models: Towards Next-Generation Dense Retrieval Paradigm
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:In modern e-commerce search systems, dense retrieval has become an indispensable component. By computing similarities between query and item (product) embeddings, it efficiently selects candidate products from large-scale repositories. With the breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs), mainstream embedding models have gradually shifted from BERT to LLMs for more accurate text modeling. However, these models still adopt direct-embedding methods, and the semantic accuracy of embeddings remains inadequate. Therefore, contrastive learning is heavily employed to achieve tight semantic alignment between positive pairs. Consequently, such models tend to capture statistical co-occurrence patterns in the training data, biasing them toward shallow lexical and semantic matches. For difficult queries exhibiting notable lexical disparity from target items, the performance degrades significantly. In this work, we propose the Large Reasoning Embedding Model (LREM), which novelly integrates reasoning processes into representation learning. For difficult queries, LREM first conducts reasoning to achieve a deep understanding of the original query, and then produces a reasoning-augmented query embedding for retrieval. This reasoning process effectively bridges the semantic gap between original queries and target items, significantly improving retrieval accuracy. Specifically, we adopt a two-stage training process: the first stage optimizes the LLM on carefully curated Query-CoT-Item triplets with SFT and InfoNCE losses to establish preliminary reasoning and embedding capabilities, and the second stage further refines the reasoning trajectories via reinforcement learning (RL). Extensive offline and online experiments validate the effectiveness of LREM, leading to its deployment on China's largest e-commerce platform since August 2025.
Delving into E-Commerce Product Retrieval with Vision-Language Pre-training
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:E-commerce search engines comprise a retrieval phase and a ranking phase, where the first one returns a candidate product set given user queries. Recently, vision-language pre-training, combining textual information with visual clues, has been popular in the application of retrieval tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel V+L pre-training method to solve the retrieval problem in Taobao Search. We design a visual pre-training task based on contrastive learning, outperforming common regression-based visual pre-training tasks. In addition, we adopt two negative sampling schemes, tailored for the large-scale retrieval task. Besides, we introduce the details of the online deployment of our proposed method in real-world situations. Extensive offline/online experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our method on the retrieval task. Our proposed method is employed as one retrieval channel of Taobao Search and serves hundreds of millions of users in real time.
Cold-Start based Multi-Scenario Ranking Model for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Apr 16, 2023Abstract:Online travel platforms (OTPs), e.g., Ctrip.com or Fliggy.com, can effectively provide travel-related products or services to users. In this paper, we focus on the multi-scenario click-through rate (CTR) prediction, i.e., training a unified model to serve all scenarios. Existing multi-scenario based CTR methods struggle in the context of OTP setting due to the ignorance of the cold-start users who have very limited data. To fill this gap, we propose a novel method named Cold-Start based Multi-scenario Network (CSMN). Specifically, it consists of two basic components including: 1) User Interest Projection Network (UIPN), which firstly purifies users' behaviors by eliminating the scenario-irrelevant information in behaviors with respect to the visiting scenario, followed by obtaining users' scenario-specific interests by summarizing the purified behaviors with respect to the target item via an attention mechanism; and 2) User Representation Memory Network (URMN), which benefits cold-start users from users with rich behaviors through a memory read and write mechanism. CSMN seamlessly integrates both components in an end-to-end learning framework. Extensive experiments on real-world offline dataset and online A/B test demonstrate the superiority of CSMN over state-of-the-art methods.
Re-weighting Negative Samples for Model-Agnostic Matching
Jul 06, 2022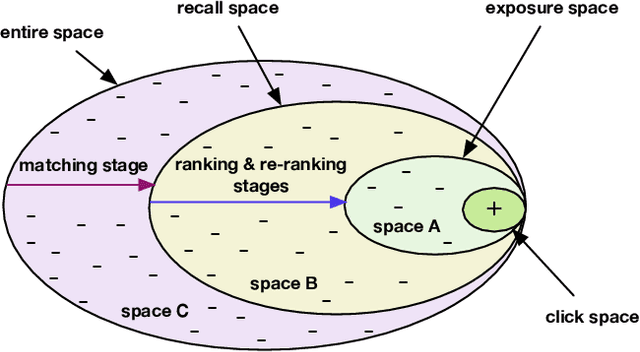
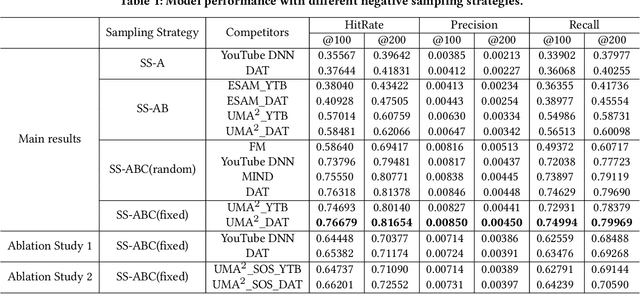
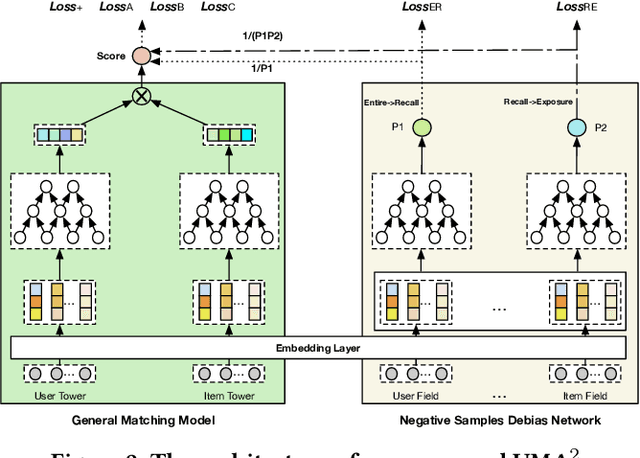
Abstract:Recommender Systems (RS), as an efficient tool to discover users' interested items from a very large corpus, has attracted more and more attention from academia and industry. As the initial stage of RS, large-scale matching is fundamental yet challenging. A typical recipe is to learn user and item representations with a two-tower architecture and then calculate the similarity score between both representation vectors, which however still struggles in how to properly deal with negative samples. In this paper, we find that the common practice that randomly sampling negative samples from the entire space and treating them equally is not an optimal choice, since the negative samples from different sub-spaces at different stages have different importance to a matching model. To address this issue, we propose a novel method named Unbiased Model-Agnostic Matching Approach (UMA$^2$). It consists of two basic modules including 1) General Matching Model (GMM), which is model-agnostic and can be implemented as any embedding-based two-tower models; and 2) Negative Samples Debias Network (NSDN), which discriminates negative samples by borrowing the idea of Inverse Propensity Weighting (IPW) and re-weighs the loss in GMM. UMA$^2$ seamlessly integrates these two modules in an end-to-end multi-task learning framework. Extensive experiments on both real-world offline dataset and online A/B test demonstrate its superiority over state-of-the-art methods.
Intelligent Request Strategy Design in Recommender System
Jun 23, 2022



Abstract:Waterfall Recommender System (RS), a popular form of RS in mobile applications, is a stream of recommended items consisting of successive pages that can be browsed by scrolling. In waterfall RS, when a user finishes browsing a page, the edge (e.g., mobile phones) would send a request to the cloud server to get a new page of recommendations, known as the paging request mechanism. RSs typically put a large number of items into one page to reduce excessive resource consumption from numerous paging requests, which, however, would diminish the RSs' ability to timely renew the recommendations according to users' real-time interest and lead to a poor user experience. Intuitively, inserting additional requests inside pages to update the recommendations with a higher frequency can alleviate the problem. However, previous attempts, including only non-adaptive strategies (e.g., insert requests uniformly), would eventually lead to resource overconsumption. To this end, we envision a new learning task of edge intelligence named Intelligent Request Strategy Design (IRSD). It aims to improve the effectiveness of waterfall RSs by determining the appropriate occasions of request insertion based on users' real-time intention. Moreover, we propose a new paradigm of adaptive request insertion strategy named Uplift-based On-edge Smart Request Framework (AdaRequest). AdaRequest 1) captures the dynamic change of users' intentions by matching their real-time behaviors with their historical interests based on attention-based neural networks. 2) estimates the counterfactual uplift of user purchase brought by an inserted request based on causal inference. 3) determines the final request insertion strategy by maximizing the utility function under online resource constraints. We conduct extensive experiments on both offline dataset and online A/B test to verify the effectiveness of AdaRequest.
Modeling User Behavior with Graph Convolution for Personalized Product Search
Feb 12, 2022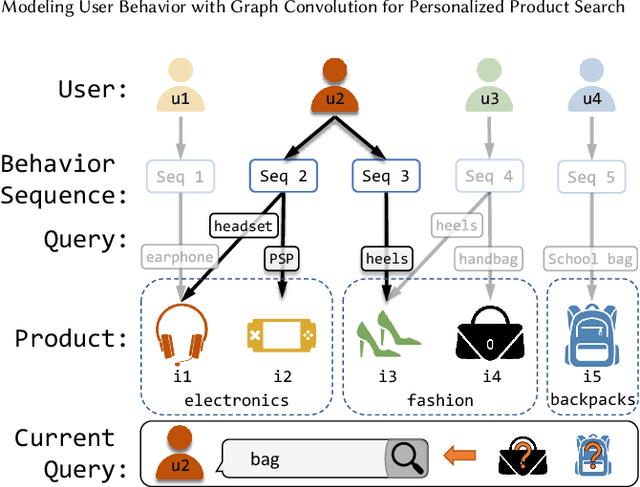
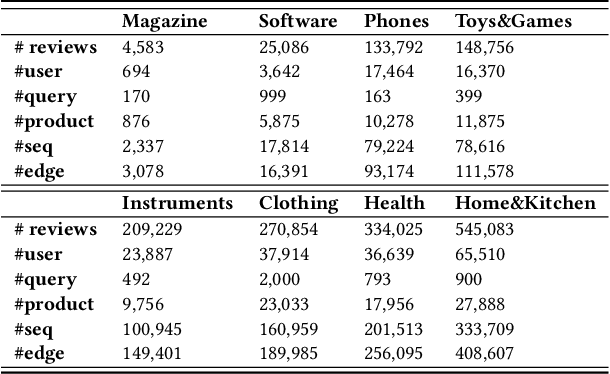
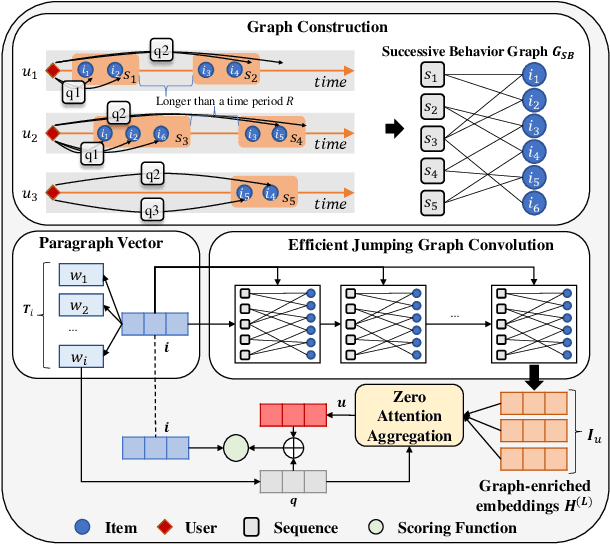
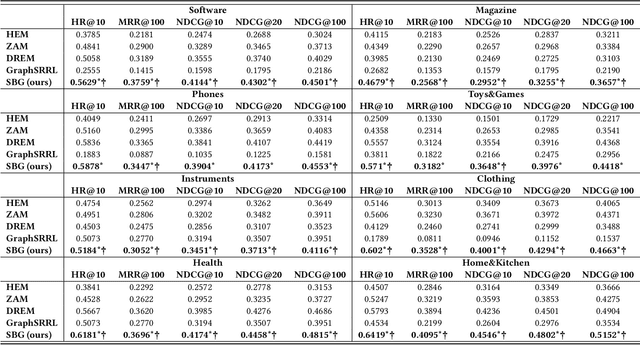
Abstract:User preference modeling is a vital yet challenging problem in personalized product search. In recent years, latent space based methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance by jointly learning semantic representations of products, users, and text tokens. However, existing methods are limited in their ability to model user preferences. They typically represent users by the products they visited in a short span of time using attentive models and lack the ability to exploit relational information such as user-product interactions or item co-occurrence relations. In this work, we propose to address the limitations of prior arts by exploring local and global user behavior patterns on a user successive behavior graph, which is constructed by utilizing short-term actions of all users. To capture implicit user preference signals and collaborative patterns, we use an efficient jumping graph convolution to explore high-order relations to enrich product representations for user preference modeling. Our approach can be seamlessly integrated with existing latent space based methods and be potentially applied in any product retrieval method that uses purchase history to model user preferences. Extensive experiments on eight Amazon benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of our approach. The source code is available at \url{https://github.com/floatSDSDS/SBG}.
IHGNN: Interactive Hypergraph Neural Network for Personalized Product Search
Feb 10, 2022


Abstract:A good personalized product search (PPS) system should not only focus on retrieving relevant products, but also consider user personalized preference. Recent work on PPS mainly adopts the representation learning paradigm, e.g., learning representations for each entity (including user, product and query) from historical user behaviors (aka. user-product-query interactions). However, we argue that existing methods do not sufficiently exploit the crucial collaborative signal, which is latent in historical interactions to reveal the affinity between the entities. Collaborative signal is quite helpful for generating high-quality representation, exploiting which would benefit the representation learning of one node from its connected nodes. To tackle this limitation, in this work, we propose a new model IHGNN for personalized product search. IHGNN resorts to a hypergraph constructed from the historical user-product-query interactions, which could completely preserve ternary relations and express collaborative signal based on the topological structure. On this basis, we develop a specific interactive hypergraph neural network to explicitly encode the structure information (i.e., collaborative signal) into the embedding process. It collects the information from the hypergraph neighbors and explicitly models neighbor feature interaction to enhance the representation of the target entity. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets validate the superiority of our proposal over the state-of-the-arts.
Embedding-based Product Retrieval in Taobao Search
Jun 17, 2021
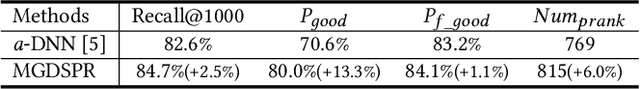
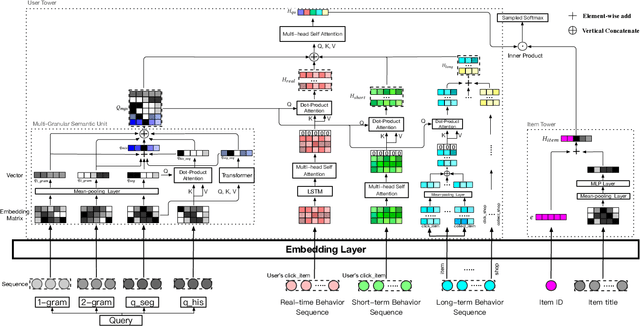
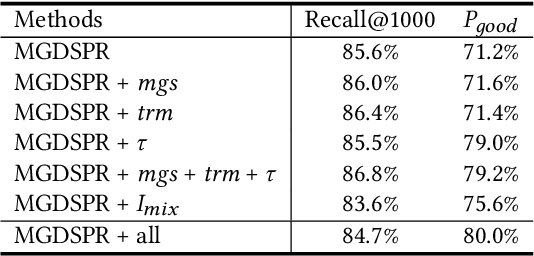
Abstract:Nowadays, the product search service of e-commerce platforms has become a vital shopping channel in people's life. The retrieval phase of products determines the search system's quality and gradually attracts researchers' attention. Retrieving the most relevant products from a large-scale corpus while preserving personalized user characteristics remains an open question. Recent approaches in this domain have mainly focused on embedding-based retrieval (EBR) systems. However, after a long period of practice on Taobao, we find that the performance of the EBR system is dramatically degraded due to its: (1) low relevance with a given query and (2) discrepancy between the training and inference phases. Therefore, we propose a novel and practical embedding-based product retrieval model, named Multi-Grained Deep Semantic Product Retrieval (MGDSPR). Specifically, we first identify the inconsistency between the training and inference stages, and then use the softmax cross-entropy loss as the training objective, which achieves better performance and faster convergence. Two efficient methods are further proposed to improve retrieval relevance, including smoothing noisy training data and generating relevance-improving hard negative samples without requiring extra knowledge and training procedures. We evaluate MGDSPR on Taobao Product Search with significant metrics gains observed in offline experiments and online A/B tests. MGDSPR has been successfully deployed to the existing multi-channel retrieval system in Taobao Search. We also introduce the online deployment scheme and share practical lessons of our retrieval system to contribute to the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge