Pipei Huang
Behavior Sequence Transformer for E-commerce Recommendation in Alibaba
May 15, 2019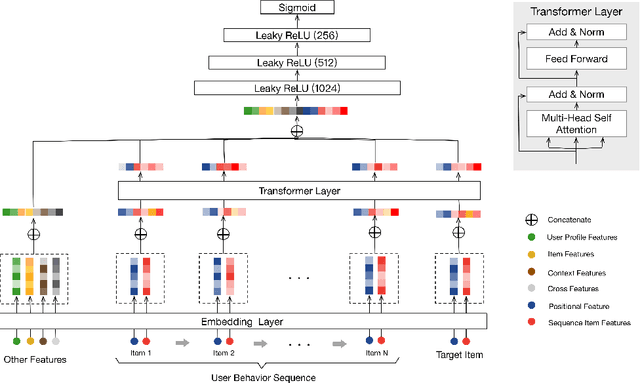



Abstract:Deep learning based methods have been widely used in industrial recommendation systems (RSs). Previous works adopt an Embedding&MLP paradigm: raw features are embedded into low-dimensional vectors, which are then fed on to MLP for final recommendations. However, most of these works just concatenate different features, ignoring the sequential nature of users' behaviors. In this paper, we propose to use the powerful Transformer model to capture the sequential signals underlying users' behavior sequences for recommendation in Alibaba. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model, which is then deployed online at Taobao and obtain significant improvements in online Click-Through-Rate (CTR) comparing to two baselines.
Multi-Interest Network with Dynamic Routing for Recommendation at Tmall
Apr 17, 2019

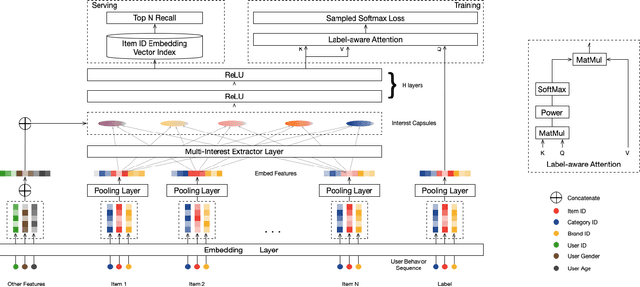

Abstract:Industrial recommender systems usually consist of the matching stage and the ranking stage, in order to handle the billion-scale of users and items. The matching stage retrieves candidate items relevant to user interests, while the ranking stage sorts candidate items by user interests. Thus, the most critical ability is to model and represent user interests for either stage. Most of the existing deep learning-based models represent one user as a single vector which is insufficient to capture the varying nature of user's interests. In this paper, we approach this problem from a different view, to represent one user with multiple vectors encoding the different aspects of the user's interests. We propose the Multi-Interest Network with Dynamic routing (MIND) for dealing with user's diverse interests in the matching stage. Specifically, we design a multi-interest extractor layer based on capsule routing mechanism, which is applicable for clustering historical behaviors and extracting diverse interests. Furthermore, we develop a technique named label-aware attention to help learn a user representation with multiple vectors. Through extensive experiments on several public benchmarks and one large-scale industrial dataset from Tmall, we demonstrate that MIND can achieve superior performance than state-of-the-art methods for recommendation. Currently, MIND has been deployed for handling major online traffic at the homepage on Mobile Tmall App.
Multi-Level Deep Cascade Trees for Conversion Rate Prediction
Aug 29, 2018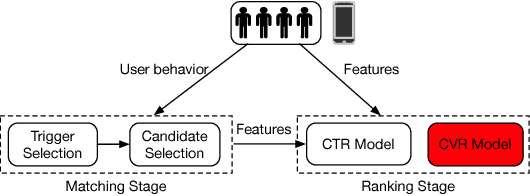
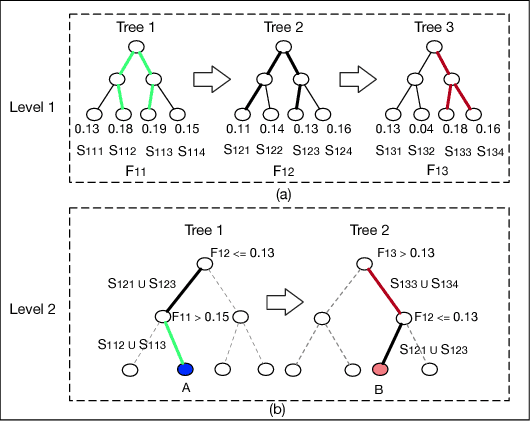
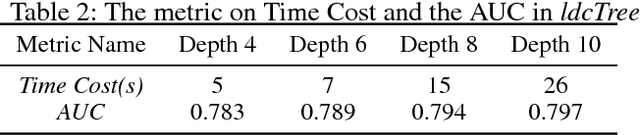
Abstract:Developing effective and efficient recommendation methods is very challenging for modern e-commerce platforms (e.g., Taobao). In this paper, we tackle this problem by proposing multi-Level Deep Cascade Trees (ldcTree), which is a novel decision tree ensemble approach. It leverages deep cascade structures by stacking Gradient Boosting Decision Trees (GBDT) to effectively learn feature representation. In addition, we propose to utilize the cross-entropy in each tree of the preceding GBDT as the input feature representation for next level GBDT, which has a clear explanation, i.e., a traversal from root to leaf nodes in the next level GBDT corresponds to the combination of certain traversals in the preceding GBDT. The deep cascade structure and the combination rule enable the proposed ldcTree to have a stronger distributed feature representation ability. Moreover, we propose an ensemble ldcTree to take full use of weak and strong correlation features. Experimental results on off-line dataset and online deployment demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Billion-scale Commodity Embedding for E-commerce Recommendation in Alibaba
May 24, 2018



Abstract:Recommender systems (RSs) have been the most important technology for increasing the business in Taobao, the largest online consumer-to-consumer (C2C) platform in China. The billion-scale data in Taobao creates three major challenges to Taobao's RS: scalability, sparsity and cold start. In this paper, we present our technical solutions to address these three challenges. The methods are based on the graph embedding framework. We first construct an item graph from users' behavior history. Each item is then represented as a vector using graph embedding. The item embeddings are employed to compute pairwise similarities between all items, which are then used in the recommendation process. To alleviate the sparsity and cold start problems, side information is incorporated into the embedding framework. We propose two aggregation methods to integrate the embeddings of items and the corresponding side information. Experimental results from offline experiments show that methods incorporating side information are superior to those that do not. Further, we describe the platform upon which the embedding methods are deployed and the workflow to process the billion-scale data in Taobao. Using online A/B test, we show that the online Click-Through-Rate (CTRs) are improved comparing to the previous recommendation methods widely used in Taobao, further demonstrating the effectiveness and feasibility of our proposed methods in Taobao's live production environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge