Xiaofeng Pan
TuningIQA: Fine-Grained Blind Image Quality Assessment for Livestreaming Camera Tuning
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:Livestreaming has become increasingly prevalent in modern visual communication, where automatic camera quality tuning is essential for delivering superior user Quality of Experience (QoE). Such tuning requires accurate blind image quality assessment (BIQA) to guide parameter optimization decisions. Unfortunately, the existing BIQA models typically only predict an overall coarse-grained quality score, which cannot provide fine-grained perceptual guidance for precise camera parameter tuning. To bridge this gap, we first establish FGLive-10K, a comprehensive fine-grained BIQA database containing 10,185 high-resolution images captured under varying camera parameter configurations across diverse livestreaming scenarios. The dataset features 50,925 multi-attribute quality annotations and 19,234 fine-grained pairwise preference annotations. Based on FGLive-10K, we further develop TuningIQA, a fine-grained BIQA metric for livestreaming camera tuning, which integrates human-aware feature extraction and graph-based camera parameter fusion. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate that TuningIQA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art BIQA methods in both score regression and fine-grained quality ranking, achieving superior performance when deployed for livestreaming camera tuning.
Fine-grained Image Quality Assessment for Perceptual Image Restoration
Aug 20, 2025



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed remarkable achievements in perceptual image restoration (IR), creating an urgent demand for accurate image quality assessment (IQA), which is essential for both performance comparison and algorithm optimization. Unfortunately, the existing IQA metrics exhibit inherent weakness for IR task, particularly when distinguishing fine-grained quality differences among restored images. To address this dilemma, we contribute the first-of-its-kind fine-grained image quality assessment dataset for image restoration, termed FGRestore, comprising 18,408 restored images across six common IR tasks. Beyond conventional scalar quality scores, FGRestore was also annotated with 30,886 fine-grained pairwise preferences. Based on FGRestore, a comprehensive benchmark was conducted on the existing IQA metrics, which reveal significant inconsistencies between score-based IQA evaluations and the fine-grained restoration quality. Motivated by these findings, we further propose FGResQ, a new IQA model specifically designed for image restoration, which features both coarse-grained score regression and fine-grained quality ranking. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate that FGResQ significantly outperforms state-of-the-art IQA metrics. Codes and model weights have been released in https://pxf0429.github.io/FGResQ/
Bridging the Gap Between Semantic and User Preference Spaces for Multi-modal Music Representation Learning
May 29, 2025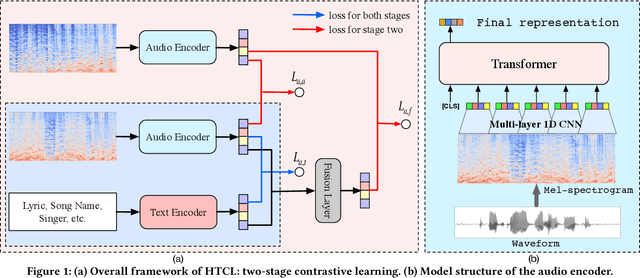
Abstract:Recent works of music representation learning mainly focus on learning acoustic music representations with unlabeled audios or further attempt to acquire multi-modal music representations with scarce annotated audio-text pairs. They either ignore the language semantics or rely on labeled audio datasets that are difficult and expensive to create. Moreover, merely modeling semantic space usually fails to achieve satisfactory performance on music recommendation tasks since the user preference space is ignored. In this paper, we propose a novel Hierarchical Two-stage Contrastive Learning (HTCL) method that models similarity from the semantic perspective to the user perspective hierarchically to learn a comprehensive music representation bridging the gap between semantic and user preference spaces. We devise a scalable audio encoder and leverage a pre-trained BERT model as the text encoder to learn audio-text semantics via large-scale contrastive pre-training. Further, we explore a simple yet effective way to exploit interaction data from our online music platform to adapt the semantic space to user preference space via contrastive fine-tuning, which differs from previous works that follow the idea of collaborative filtering. As a result, we obtain a powerful audio encoder that not only distills language semantics from the text encoder but also models similarity in user preference space with the integrity of semantic space preserved. Experimental results on both music semantic and recommendation tasks confirm the effectiveness of our method.
DPAN: Dynamic Preference-based and Attribute-aware Network for Relevant Recommendations
Aug 21, 2023Abstract:In e-commerce platforms, the relevant recommendation is a unique scenario providing related items for a trigger item that users are interested in. However, users' preferences for the similarity and diversity of recommendation results are dynamic and vary under different conditions. Moreover, individual item-level diversity is too coarse-grained since all recommended items are related to the trigger item. Thus, the two main challenges are to learn fine-grained representations of similarity and diversity and capture users' dynamic preferences for them under different conditions. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method called the Dynamic Preference-based and Attribute-aware Network (DPAN) for predicting Click-Through Rate (CTR) in relevant recommendations. Specifically, based on Attribute-aware Activation Values Generation (AAVG), Bi-dimensional Compression-based Re-expression (BCR) is designed to obtain similarity and diversity representations of user interests and item information. Then Shallow and Deep Union-based Fusion (SDUF) is proposed to capture users' dynamic preferences for the diverse degree of recommendation results according to various conditions. DPAN has demonstrated its effectiveness through extensive offline experiments and online A/B testing, resulting in a significant 7.62% improvement in CTR. Currently, DPAN has been successfully deployed on our e-commerce platform serving the primary traffic for relevant recommendations. The code of DPAN has been made publicly available.
FAN: Fatigue-Aware Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction in E-commerce Recommendation
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:Since clicks usually contain heavy noise, increasing research efforts have been devoted to modeling implicit negative user behaviors (i.e., non-clicks). However, they either rely on explicit negative user behaviors (e.g., dislikes) or simply treat non-clicks as negative feedback, failing to learn negative user interests comprehensively. In such situations, users may experience fatigue because of seeing too many similar recommendations. In this paper, we propose Fatigue-Aware Network (FAN), a novel CTR model that directly perceives user fatigue from non-clicks. Specifically, we first apply Fourier Transformation to the time series generated from non-clicks, obtaining its frequency spectrum which contains comprehensive information about user fatigue. Then the frequency spectrum is modulated by category information of the target item to model the bias that both the upper bound of fatigue and users' patience is different for different categories. Moreover, a gating network is adopted to model the confidence of user fatigue and an auxiliary task is designed to guide the learning of user fatigue, so we can obtain a well-learned fatigue representation and combine it with user interests for the final CTR prediction. Experimental results on real-world datasets validate the superiority of FAN and online A/B tests also show FAN outperforms representative CTR models significantly.
AIM 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution of Compressed Image and Video: Dataset, Methods and Results
Aug 25, 2022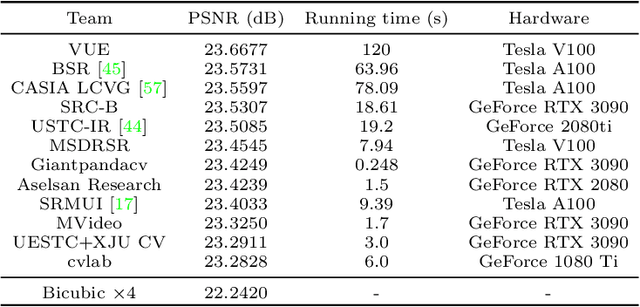
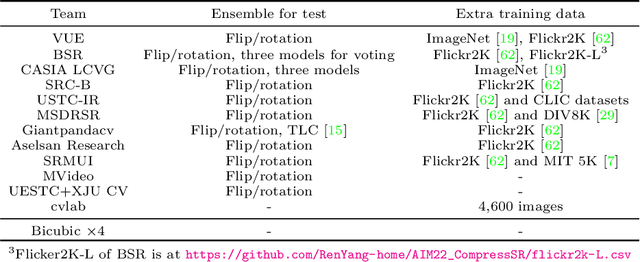
Abstract:This paper reviews the Challenge on Super-Resolution of Compressed Image and Video at AIM 2022. This challenge includes two tracks. Track 1 aims at the super-resolution of compressed image, and Track~2 targets the super-resolution of compressed video. In Track 1, we use the popular dataset DIV2K as the training, validation and test sets. In Track 2, we propose the LDV 3.0 dataset, which contains 365 videos, including the LDV 2.0 dataset (335 videos) and 30 additional videos. In this challenge, there are 12 teams and 2 teams that submitted the final results to Track 1 and Track 2, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of super-resolution on compressed image and video. The proposed LDV 3.0 dataset is available at https://github.com/RenYang-home/LDV_dataset. The homepage of this challenge is at https://github.com/RenYang-home/AIM22_CompressSR.
Conversion Rate Prediction via Meta Learning in Small-Scale Recommendation Scenarios
Dec 27, 2021



Abstract:Different from large-scale platforms such as Taobao and Amazon, developing CVR models in small-scale recommendation scenarios is more challenging due to the severe Data Distribution Fluctuation (DDF) issue. DDF prevents existing CVR models from being effective since 1) several months of data are needed to train CVR models sufficiently in small scenarios, leading to considerable distribution discrepancy between training and online serving; and 2) e-commerce promotions have much more significant impacts on small scenarios, leading to distribution uncertainty of the upcoming time period. In this work, we propose a novel CVR method named MetaCVR from a perspective of meta learning to address the DDF issue. Firstly, a base CVR model which consists of a Feature Representation Network (FRN) and output layers is elaborately designed and trained sufficiently with samples across months. Then we treat time periods with different data distributions as different occasions and obtain positive and negative prototypes for each occasion using the corresponding samples and the pre-trained FRN. Subsequently, a Distance Metric Network (DMN) is devised to calculate the distance metrics between each sample and all prototypes to facilitate mitigating the distribution uncertainty. At last, we develop an Ensemble Prediction Network (EPN) which incorporates the output of FRN and DMN to make the final CVR prediction. In this stage, we freeze the FRN and train the DMN and EPN with samples from recent time period, therefore effectively easing the distribution discrepancy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of CVR prediction targeting the DDF issue in small-scale recommendation scenarios. Experimental results on real-world datasets validate the superiority of our MetaCVR and online A/B test also shows our model achieves impressive gains of 11.92% on PCVR and 8.64% on GMV.
SAME: Scenario Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts for Promotion-Aware Click-Through Rate Prediction
Dec 27, 2021



Abstract:Promotions are becoming more important and prevalent in e-commerce platforms to attract customers and boost sales. However, Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction methods in recommender systems are not able to handle such circumstances well since: 1) they can't generalize well to serving because the online data distribution is uncertain due to the potentially upcoming promotions; 2) without paying enough attention to scenario signals, they are incapable of learning different feature representation patterns which coexist in each scenario. In this work, we propose Scenario Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts (SAME), a simple yet effective model that serves both promotion and normal scenarios. Technically, it follows the idea of Mixture-of-Experts by adopting multiple experts to learn feature representations, which are modulated by a Feature Gated Network (FGN) via an attention mechanism. To obtain high-quality representations, we design a Stacked Parallel Attention Unit (SPAU) to help each expert better handle user behavior sequence. To tackle the distribution uncertainty, a set of scenario signals are elaborately devised from a perspective of time series prediction and fed into the FGN, whose output is concatenated with feature representation from each expert to learn the attention. Accordingly, a mixture of the feature representations is obtained scenario-adaptively and used for the final CTR prediction. In this way, each expert can learn a discriminative representation pattern. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study for promotion-aware CTR prediction. Experimental results on real-world datasets validate the superiority of SAME. Online A/B test also shows SAME achieves significant gains of 3.58% on CTR and 5.94% on IPV during promotion periods as well as 3.93% and 6.57% in normal days, respectively.
ANL: Anti-Noise Learning for Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification
Dec 27, 2020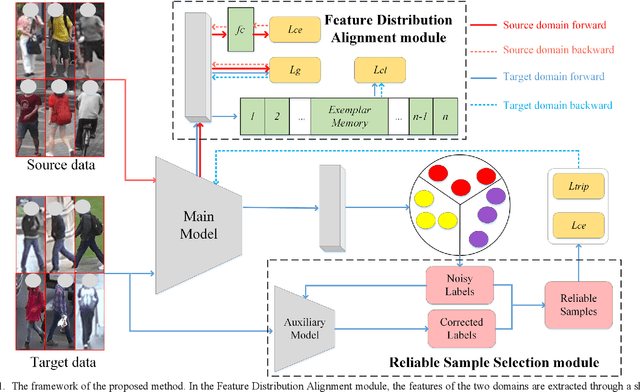
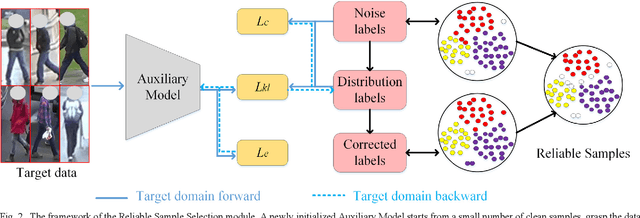
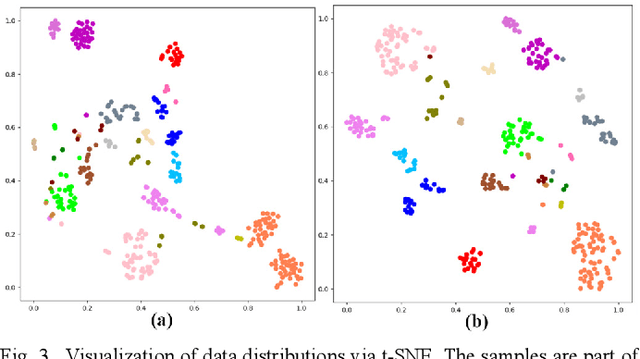
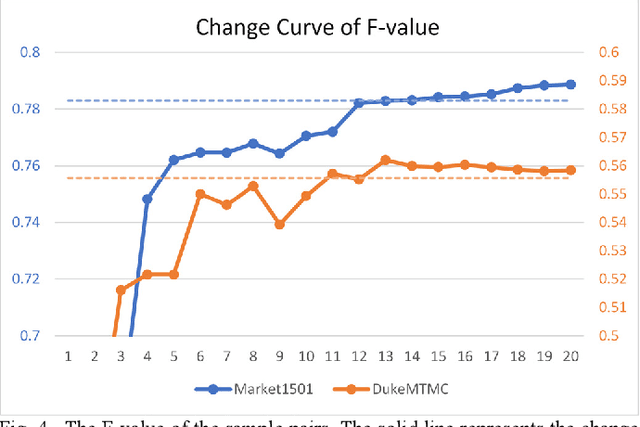
Abstract:Due to the lack of labels and the domain diversities, it is a challenge to study person re-identification in the cross-domain setting. An admirable method is to optimize the target model by assigning pseudo-labels for unlabeled samples through clustering. Usually, attributed to the domain gaps, the pre-trained source domain model cannot extract appropriate target domain features, which will dramatically affect the clustering performance and the accuracy of pseudo-labels. Extensive label noise will lead to sub-optimal solutions doubtlessly. To solve these problems, we propose an Anti-Noise Learning (ANL) approach, which contains two modules. The Feature Distribution Alignment (FDA) module is designed to gather the id-related samples and disperse id-unrelated samples, through the camera-wise contrastive learning and adversarial adaptation. Creating a friendly cross-feature foundation for clustering that is to reduce clustering noise. Besides, the Reliable Sample Selection (RSS) module utilizes an Auxiliary Model to correct noisy labels and select reliable samples for the Main Model. In order to effectively utilize the outlier information generated by the clustering algorithm and RSS module, we train these samples at the instance-level. The experiments demonstrate that our proposed ANL framework can effectively reduce the domain conflicts and alleviate the influence of noisy samples, as well as superior performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
MAT: Motion-Aware Multi-Object Tracking
Sep 18, 2020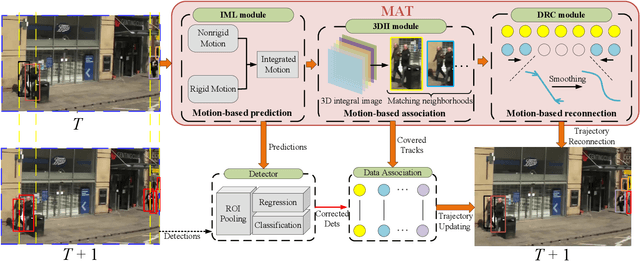
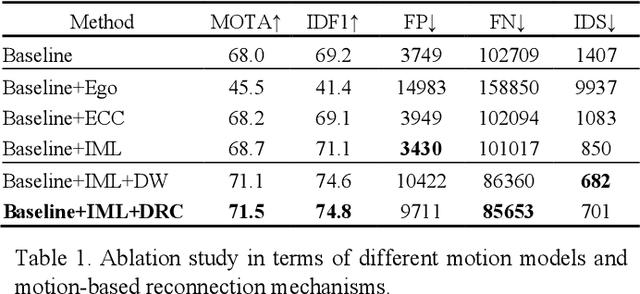
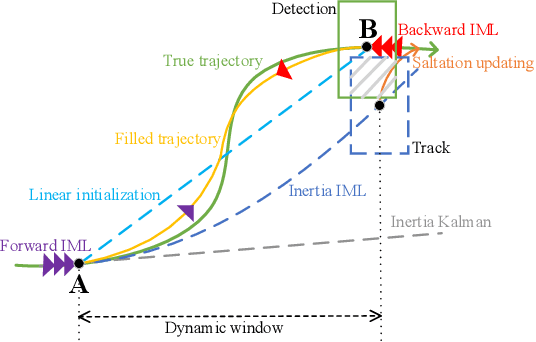
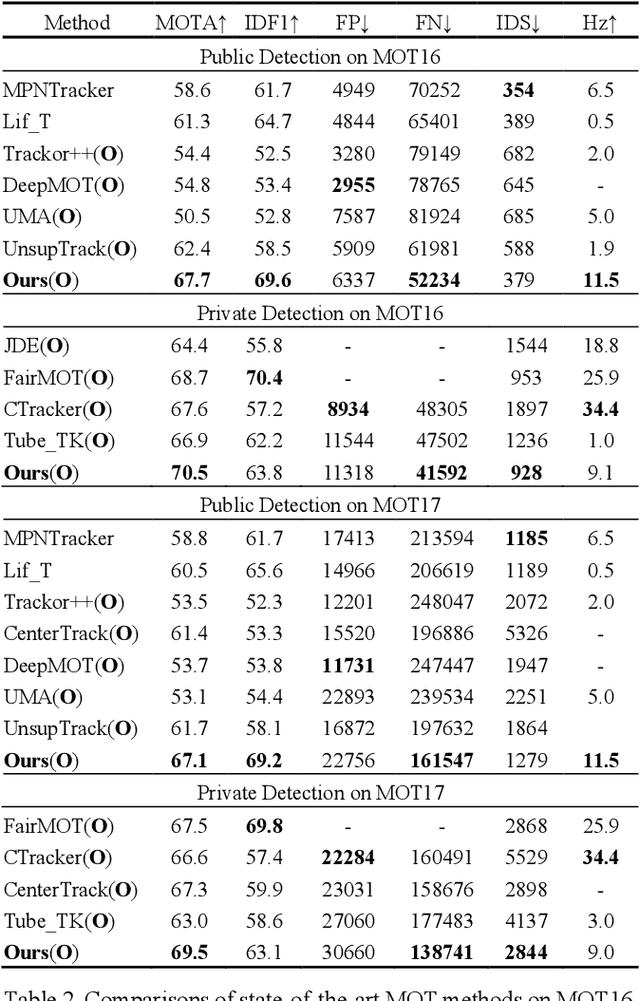
Abstract:Modern multi-object tracking (MOT) systems usually model the trajectories by associating per-frame detections. However, when camera motion, fast motion, and occlusion challenges occur, it is difficult to ensure long-range tracking or even the tracklet purity, especially for small objects. Although re-identification is often employed, due to noisy partial-detections, similar appearance, and lack of temporal-spatial constraints, it is not only unreliable and time-consuming, but still cannot address the false negatives for occluded and blurred objects. In this paper, we propose an enhanced MOT paradigm, namely Motion-Aware Tracker (MAT), focusing more on various motion patterns of different objects. The rigid camera motion and nonrigid pedestrian motion are blended compatibly to form the integrated motion localization module. Meanwhile, we introduce the dynamic reconnection context module, which aims to balance the robustness of long-range motion-based reconnection, and includes the cyclic pseudo-observation updating strategy to smoothly fill in the tracking fragments caused by occlusion or blur. Additionally, the 3D integral image module is presented to efficiently cut useless track-detection association connections with temporal-spatial constraints. Extensive experiments on MOT16 and MOT17 challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our MAT approach can achieve the superior performance by a large margin with high efficiency, in contrast to other state-of-the-art trackers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge