Re-weighting Negative Samples for Model-Agnostic Matching
Paper and Code
Jul 06, 2022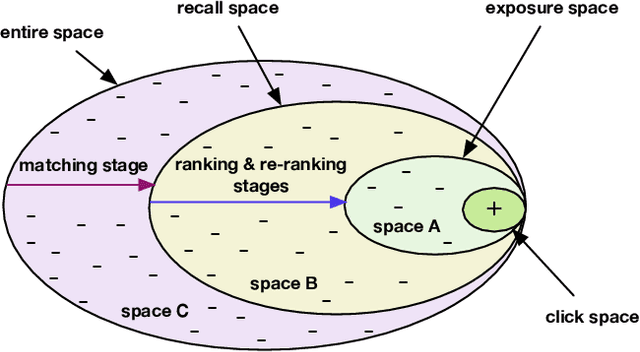
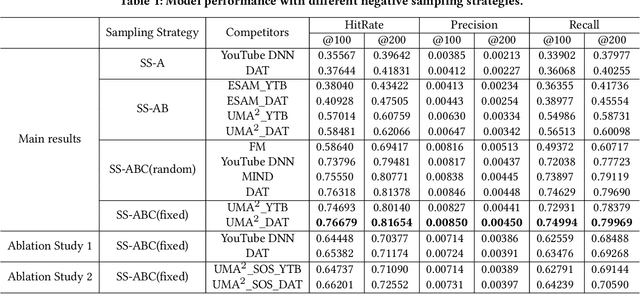
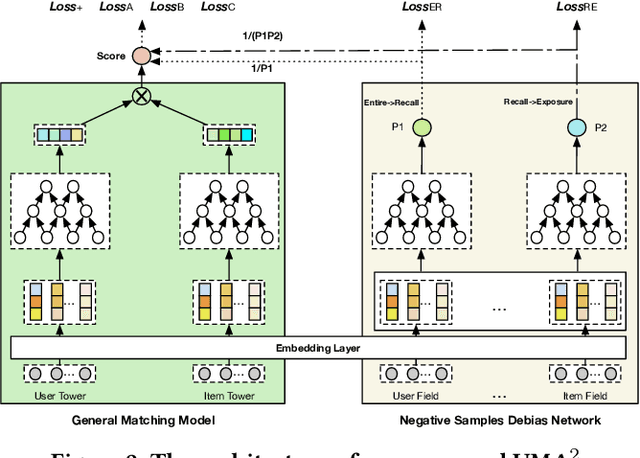
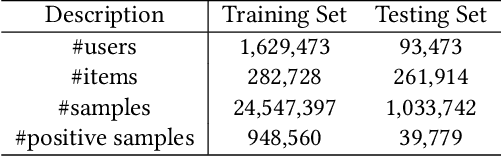
Recommender Systems (RS), as an efficient tool to discover users' interested items from a very large corpus, has attracted more and more attention from academia and industry. As the initial stage of RS, large-scale matching is fundamental yet challenging. A typical recipe is to learn user and item representations with a two-tower architecture and then calculate the similarity score between both representation vectors, which however still struggles in how to properly deal with negative samples. In this paper, we find that the common practice that randomly sampling negative samples from the entire space and treating them equally is not an optimal choice, since the negative samples from different sub-spaces at different stages have different importance to a matching model. To address this issue, we propose a novel method named Unbiased Model-Agnostic Matching Approach (UMA$^2$). It consists of two basic modules including 1) General Matching Model (GMM), which is model-agnostic and can be implemented as any embedding-based two-tower models; and 2) Negative Samples Debias Network (NSDN), which discriminates negative samples by borrowing the idea of Inverse Propensity Weighting (IPW) and re-weighs the loss in GMM. UMA$^2$ seamlessly integrates these two modules in an end-to-end multi-task learning framework. Extensive experiments on both real-world offline dataset and online A/B test demonstrate its superiority over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge