Qijie Shen
ChoirRec: Semantic User Grouping via LLMs for Conversion Rate Prediction of Low-Activity Users
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Accurately predicting conversion rates (CVR) for low-activity users remains a fundamental challenge in large-scale e-commerce recommender systems.Existing approaches face three critical limitations: (i) reliance on noisy and unreliable behavioral signals; (ii) insufficient user-level information due to the lack of diverse interaction data; and (iii) a systemic training bias toward high-activity users that overshadows the needs of low-activity users.To address these challenges, we propose ChoirRec, a novel framework that leverages the semantic capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to construct semantic user groups and enhance CVR prediction for low-activity users.With a dual-channel architecture designed for robust cross-user knowledge transfer, ChoirRec comprises three components: (i) a Semantic Group Generation module that utilizes LLMs to form reliable, cross-activity user clusters, thereby filtering out noisy signals; (ii) a Group-aware Hierarchical Representation module that enriches sparse user embeddings with informative group-level priors to mitigate data insufficiency; and (iii) a Group-aware Multi-granularity Modual that employs a dual-channel architecture and adaptive fusion mechanism to ensure effective learning and utilization of group knowledge. We conduct extensive offline and online experiments on Taobao, a leading industrial-scale e-commerce platform.ChoirRec improves GAUC by 1.16\% in offline evaluations, while online A/B testing reveals a 7.24\% increase in order volume, highlighting its substantial practical value in real-world applications.
Macro Graph of Experts for Billion-Scale Multi-Task Recommendation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Graph-based multi-task learning at billion-scale presents a significant challenge, as different tasks correspond to distinct billion-scale graphs. Traditional multi-task learning methods often neglect these graph structures, relying solely on individual user and item embeddings. However, disregarding graph structures overlooks substantial potential for improving performance. In this paper, we introduce the Macro Graph of Expert (MGOE) framework, the first approach capable of leveraging macro graph embeddings to capture task-specific macro features while modeling the correlations between task-specific experts. Specifically, we propose the concept of a Macro Graph Bottom, which, for the first time, enables multi-task learning models to incorporate graph information effectively. We design the Macro Prediction Tower to dynamically integrate macro knowledge across tasks. MGOE has been deployed at scale, powering multi-task learning for the homepage of a leading billion-scale recommender system. Extensive offline experiments conducted on three public benchmark datasets demonstrate its superiority over state-of-the-art multi-task learning methods, establishing MGOE as a breakthrough in multi-task graph-based recommendation. Furthermore, online A/B tests confirm the superiority of MGOE in billion-scale recommender systems.
FilterLLM: Text-To-Distribution LLM for Billion-Scale Cold-Start Recommendation
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based cold-start recommendation systems continue to face significant computational challenges in billion-scale scenarios, as they follow a "Text-to-Judgment" paradigm. This approach processes user-item content pairs as input and evaluates each pair iteratively. To maintain efficiency, existing methods rely on pre-filtering a small candidate pool of user-item pairs. However, this severely limits the inferential capabilities of LLMs by reducing their scope to only a few hundred pre-filtered candidates. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel "Text-to-Distribution" paradigm, which predicts an item's interaction probability distribution for the entire user set in a single inference. Specifically, we present FilterLLM, a framework that extends the next-word prediction capabilities of LLMs to billion-scale filtering tasks. FilterLLM first introduces a tailored distribution prediction and cold-start framework. Next, FilterLLM incorporates an efficient user-vocabulary structure to train and store the embeddings of billion-scale users. Finally, we detail the training objectives for both distribution prediction and user-vocabulary construction. The proposed framework has been deployed on the Alibaba platform, where it has been serving cold-start recommendations for two months, processing over one billion cold items. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FilterLLM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cold-start recommendation tasks, achieving over 30 times higher efficiency. Furthermore, an online A/B test validates its effectiveness in billion-scale recommendation systems.
Feedback Reciprocal Graph Collaborative Filtering
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Collaborative filtering on user-item interaction graphs has achieved success in the industrial recommendation. However, recommending users' truly fascinated items poses a seesaw dilemma for collaborative filtering models learned from the interaction graph. On the one hand, not all items that users interact with are equally appealing. Some items are genuinely fascinating to users, while others are unfascinated. Training graph collaborative filtering models in the absence of distinction between them can lead to the recommendation of unfascinating items to users. On the other hand, disregarding the interacted but unfascinating items during graph collaborative filtering will result in an incomplete representation of users' interaction intent, leading to a decline in the model's recommendation capabilities. To address this seesaw problem, we propose Feedback Reciprocal Graph Collaborative Filtering (FRGCF), which emphasizes the recommendation of fascinating items while attenuating the recommendation of unfascinating items. Specifically, FRGCF first partitions the entire interaction graph into the Interacted & Fascinated (I&F) graph and the Interacted & Unfascinated (I&U) graph based on the user feedback. Then, FRGCF introduces separate collaborative filtering on the I&F graph and the I&U graph with feedback-reciprocal contrastive learning and macro-level feedback modeling. This enables the I&F graph recommender to learn multi-grained interaction characteristics from the I&U graph without being misdirected by it. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets and a billion-scale industrial dataset demonstrate that FRGCF improves the performance by recommending more fascinating items and fewer unfascinating items. Besides, online A/B tests on Taobao's recommender system verify the superiority of FRGCF.
Multi-Behavior Collaborative Filtering with Partial Order Graph Convolutional Networks
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:Representing the information of multiple behaviors in the single graph collaborative filtering (CF) vector has been a long-standing challenge. This is because different behaviors naturally form separate behavior graphs and learn separate CF embeddings. Existing models merge the separate embeddings by appointing the CF embeddings for some behaviors as the primary embedding and utilizing other auxiliaries to enhance the primary embedding. However, this approach often results in the joint embedding performing well on the main tasks but poorly on the auxiliary ones. To address the problem arising from the separate behavior graphs, we propose the concept of Partial Order Graphs (POG). POG defines the partial order relation of multiple behaviors and models behavior combinations as weighted edges to merge separate behavior graphs into a joint POG. Theoretical proof verifies that POG can be generalized to any given set of multiple behaviors. Based on POG, we propose the tailored Partial Order Graph Convolutional Networks (POGCN) that convolute neighbors' information while considering the behavior relations between users and items. POGCN also introduces a partial-order BPR sampling strategy for efficient and effective multiple-behavior CF training. POGCN has been successfully deployed on the homepage of Alibaba for two months, providing recommendation services for over one billion users. Extensive offline experiments conducted on three public benchmark datasets demonstrate that POGCN outperforms state-of-the-art multi-behavior baselines across all types of behaviors. Furthermore, online A/B tests confirm the superiority of POGCN in billion-scale recommender systems.
Macro Graph Neural Networks for Online Billion-Scale Recommender Systems
Jan 26, 2024



Abstract:Predicting Click-Through Rate (CTR) in billion-scale recommender systems poses a long-standing challenge for Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) due to the overwhelming computational complexity involved in aggregating billions of neighbors. To tackle this, GNN-based CTR models usually sample hundreds of neighbors out of the billions to facilitate efficient online recommendations. However, sampling only a small portion of neighbors results in a severe sampling bias and the failure to encompass the full spectrum of user or item behavioral patterns. To address this challenge, we name the conventional user-item recommendation graph as "micro recommendation graph" and introduce a more suitable MAcro Recommendation Graph (MAG) for billion-scale recommendations. MAG resolves the computational complexity problems in the infrastructure by reducing the node count from billions to hundreds. Specifically, MAG groups micro nodes (users and items) with similar behavior patterns to form macro nodes. Subsequently, we introduce tailored Macro Graph Neural Networks (MacGNN) to aggregate information on a macro level and revise the embeddings of macro nodes. MacGNN has already served Taobao's homepage feed for two months, providing recommendations for over one billion users. Extensive offline experiments on three public benchmark datasets and an industrial dataset present that MacGNN significantly outperforms twelve CTR baselines while remaining computationally efficient. Besides, online A/B tests confirm MacGNN's superiority in billion-scale recommender systems.
Multi-factor Sequential Re-ranking with Perception-Aware Diversification
May 21, 2023
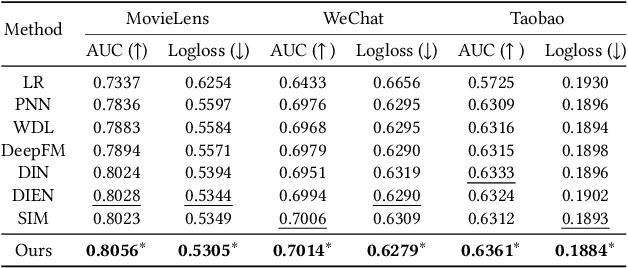
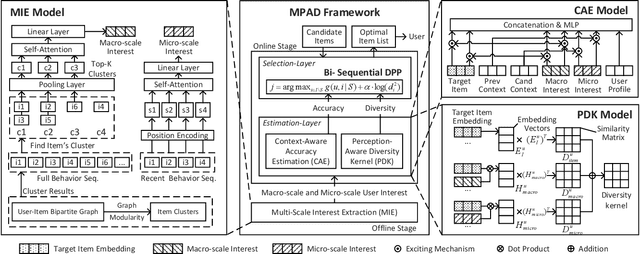
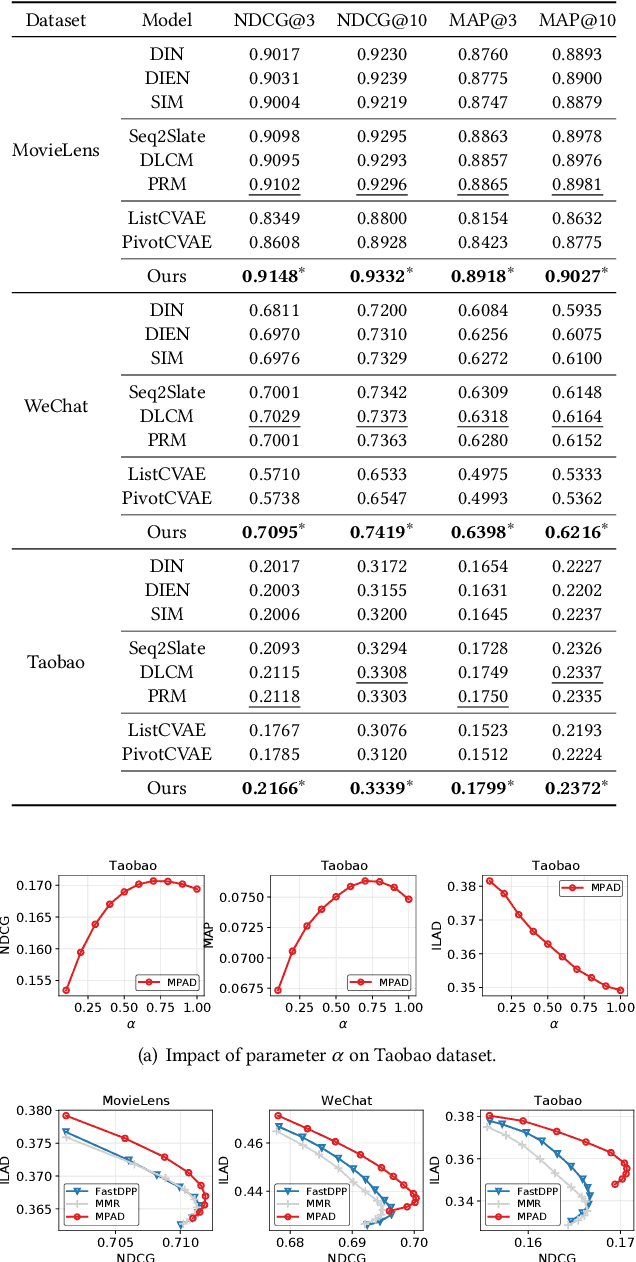
Abstract:Feed recommendation systems, which recommend a sequence of items for users to browse and interact with, have gained significant popularity in practical applications. In feed products, users tend to browse a large number of items in succession, so the previously viewed items have a significant impact on users' behavior towards the following items. Therefore, traditional methods that mainly focus on improving the accuracy of recommended items are suboptimal for feed recommendations because they may recommend highly similar items. For feed recommendation, it is crucial to consider both the accuracy and diversity of the recommended item sequences in order to satisfy users' evolving interest when consecutively viewing items. To this end, this work proposes a general re-ranking framework named Multi-factor Sequential Re-ranking with Perception-Aware Diversification (MPAD) to jointly optimize accuracy and diversity for feed recommendation in a sequential manner. Specifically, MPAD first extracts users' different scales of interests from their behavior sequences through graph clustering-based aggregations. Then, MPAD proposes two sub-models to respectively evaluate the accuracy and diversity of a given item by capturing users' evolving interest due to the ever-changing context and users' personal perception of diversity from an item sequence perspective. This is consistent with the browsing nature of the feed scenario. Finally, MPAD generates the return list by sequentially selecting optimal items from the candidate set to maximize the joint benefits of accuracy and diversity of the entire list. MPAD has been implemented in Taobao's homepage feed to serve the main traffic and provide services to recommend billions of items to hundreds of millions of users every day.
Multi-channel Integrated Recommendation with Exposure Constraints
May 21, 2023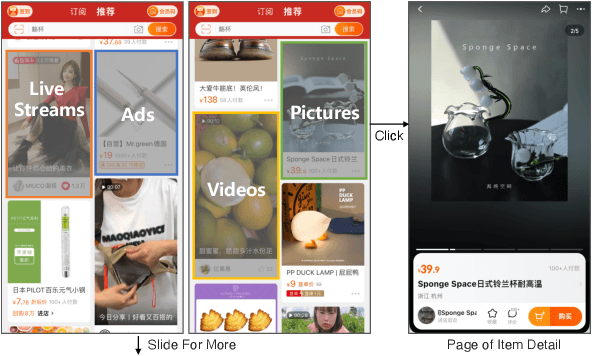
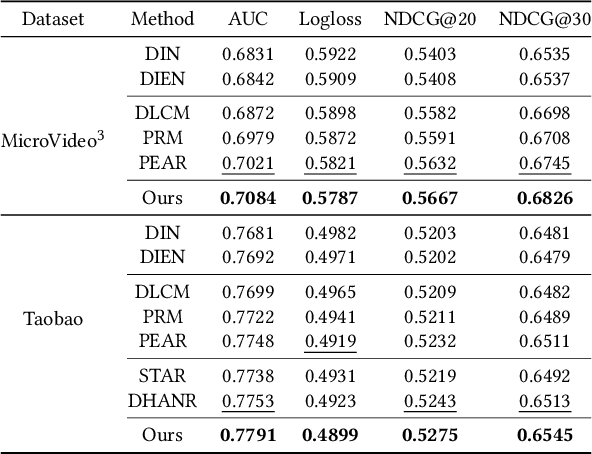
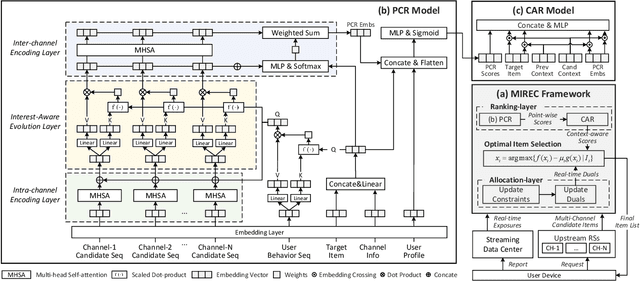
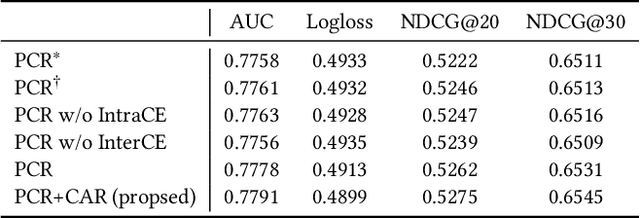
Abstract:Integrated recommendation, which aims at jointly recommending heterogeneous items from different channels in a main feed, has been widely applied to various online platforms. Though attractive, integrated recommendation requires the ranking methods to migrate from conventional user-item models to the new user-channel-item paradigm in order to better capture users' preferences on both item and channel levels. Moreover, practical feed recommendation systems usually impose exposure constraints on different channels to ensure user experience. This leads to greater difficulty in the joint ranking of heterogeneous items. In this paper, we investigate the integrated recommendation task with exposure constraints in practical recommender systems. Our contribution is forth-fold. First, we formulate this task as a binary online linear programming problem and propose a two-layer framework named Multi-channel Integrated Recommendation with Exposure Constraints (MIREC) to obtain the optimal solution. Second, we propose an efficient online allocation algorithm to determine the optimal exposure assignment of different channels from a global view of all user requests over the entire time horizon. We prove that this algorithm reaches the optimal point under a regret bound of $ \mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T}) $ with linear complexity. Third, we propose a series of collaborative models to determine the optimal layout of heterogeneous items at each user request. The joint modeling of user interests, cross-channel correlation, and page context in our models aligns more with the browsing nature of feed products than existing models. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on both offline datasets and online A/B tests to verify the effectiveness of MIREC. The proposed framework has now been implemented on the homepage of Taobao to serve the main traffic.
Cold-Start based Multi-Scenario Ranking Model for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Apr 16, 2023Abstract:Online travel platforms (OTPs), e.g., Ctrip.com or Fliggy.com, can effectively provide travel-related products or services to users. In this paper, we focus on the multi-scenario click-through rate (CTR) prediction, i.e., training a unified model to serve all scenarios. Existing multi-scenario based CTR methods struggle in the context of OTP setting due to the ignorance of the cold-start users who have very limited data. To fill this gap, we propose a novel method named Cold-Start based Multi-scenario Network (CSMN). Specifically, it consists of two basic components including: 1) User Interest Projection Network (UIPN), which firstly purifies users' behaviors by eliminating the scenario-irrelevant information in behaviors with respect to the visiting scenario, followed by obtaining users' scenario-specific interests by summarizing the purified behaviors with respect to the target item via an attention mechanism; and 2) User Representation Memory Network (URMN), which benefits cold-start users from users with rich behaviors through a memory read and write mechanism. CSMN seamlessly integrates both components in an end-to-end learning framework. Extensive experiments on real-world offline dataset and online A/B test demonstrate the superiority of CSMN over state-of-the-art methods.
Hierarchically Fusing Long and Short-Term User Interests for Click-Through Rate Prediction in Product Search
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Estimating Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a vital yet challenging task in personalized product search. However, existing CTR methods still struggle in the product search settings due to the following three challenges including how to more effectively extract users' short-term interests with respect to multiple aspects, how to extract and fuse users' long-term interest with short-term interests, how to address the entangling characteristic of long and short-term interests. To resolve these challenges, in this paper, we propose a new approach named Hierarchical Interests Fusing Network (HIFN), which consists of four basic modules namely Short-term Interests Extractor (SIE), Long-term Interests Extractor (LIE), Interests Fusion Module (IFM) and Interests Disentanglement Module (IDM). Specifically, SIE is proposed to extract user's short-term interests by integrating three fundamental interests encoders within it namely query-dependent, target-dependent and causal-dependent interest encoder, respectively, followed by delivering the resultant representation to the module LIE, where it can effectively capture user long-term interests by devising an attention mechanism with respect to the short-term interests from SIE module. In IFM, the achieved long and short-term interests are further fused in an adaptive manner, followed by concatenating it with original raw context features for the final prediction result. Last but not least, considering the entangling characteristic of long and short-term interests, IDM further devises a self-supervised framework to disentangle long and short-term interests. Extensive offline and online evaluations on a real-world e-commerce platform demonstrate the superiority of HIFN over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge