Junfeng Ge
LEMUR: Large scale End-to-end MUltimodal Recommendation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Traditional ID-based recommender systems often struggle with cold-start and generalization challenges. Multimodal recommendation systems, which leverage textual and visual data, offer a promising solution to mitigate these issues. However, existing industrial approaches typically adopt a two-stage training paradigm: first pretraining a multimodal model, then applying its frozen representations to train the recommendation model. This decoupled framework suffers from misalignment between multimodal learning and recommendation objectives, as well as an inability to adapt dynamically to new data. To address these limitations, we propose LEMUR, the first large-scale multimodal recommender system trained end-to-end from raw data. By jointly optimizing both the multimodal and recommendation components, LEMUR ensures tighter alignment with downstream objectives while enabling real-time parameter updates. Constructing multimodal sequential representations from user history often entails prohibitively high computational costs. To alleviate this bottleneck, we propose a novel memory bank mechanism that incrementally accumulates historical multimodal representations throughout the training process. After one month of deployment in Douyin Search, LEMUR has led to a 0.843% reduction in query change rate decay and a 0.81% improvement in QAUC. Additionally, LEMUR has shown significant gains across key offline metrics for Douyin Advertisement. Our results validate the superiority of end-to-end multimodal recommendation in real-world industrial scenarios.
Multi-factor Sequential Re-ranking with Perception-Aware Diversification
May 21, 2023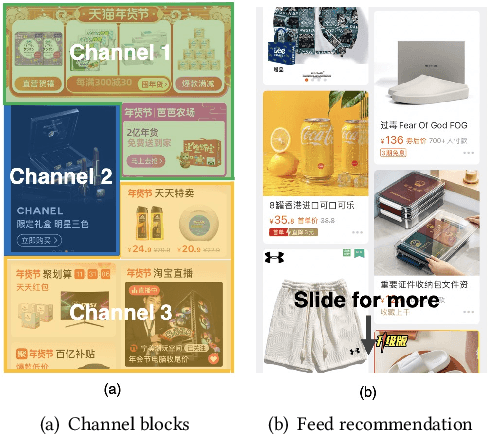
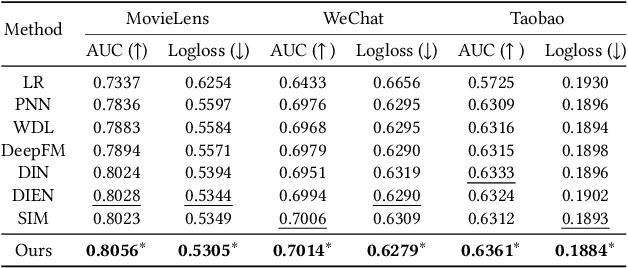
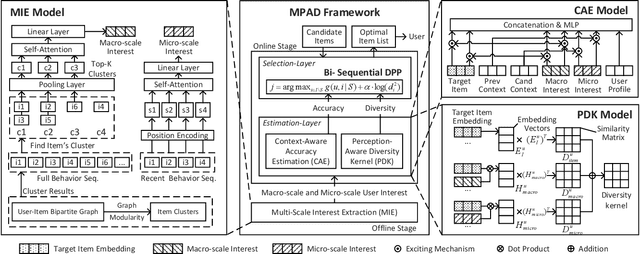
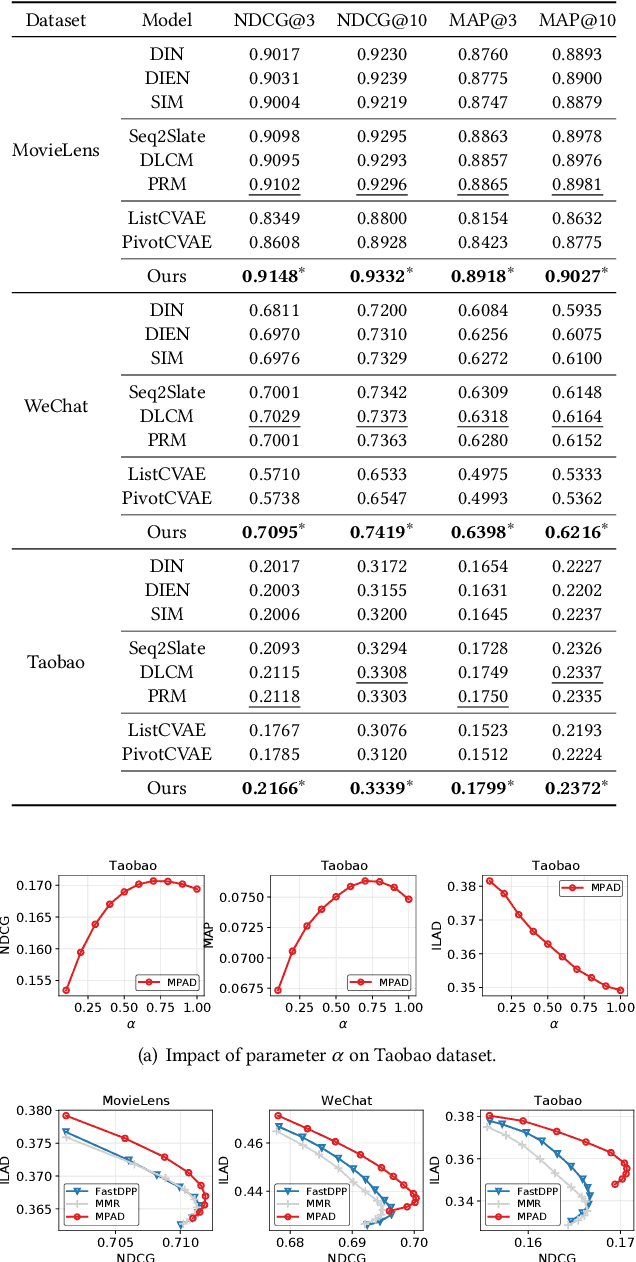
Abstract:Feed recommendation systems, which recommend a sequence of items for users to browse and interact with, have gained significant popularity in practical applications. In feed products, users tend to browse a large number of items in succession, so the previously viewed items have a significant impact on users' behavior towards the following items. Therefore, traditional methods that mainly focus on improving the accuracy of recommended items are suboptimal for feed recommendations because they may recommend highly similar items. For feed recommendation, it is crucial to consider both the accuracy and diversity of the recommended item sequences in order to satisfy users' evolving interest when consecutively viewing items. To this end, this work proposes a general re-ranking framework named Multi-factor Sequential Re-ranking with Perception-Aware Diversification (MPAD) to jointly optimize accuracy and diversity for feed recommendation in a sequential manner. Specifically, MPAD first extracts users' different scales of interests from their behavior sequences through graph clustering-based aggregations. Then, MPAD proposes two sub-models to respectively evaluate the accuracy and diversity of a given item by capturing users' evolving interest due to the ever-changing context and users' personal perception of diversity from an item sequence perspective. This is consistent with the browsing nature of the feed scenario. Finally, MPAD generates the return list by sequentially selecting optimal items from the candidate set to maximize the joint benefits of accuracy and diversity of the entire list. MPAD has been implemented in Taobao's homepage feed to serve the main traffic and provide services to recommend billions of items to hundreds of millions of users every day.
Multi-channel Integrated Recommendation with Exposure Constraints
May 21, 2023
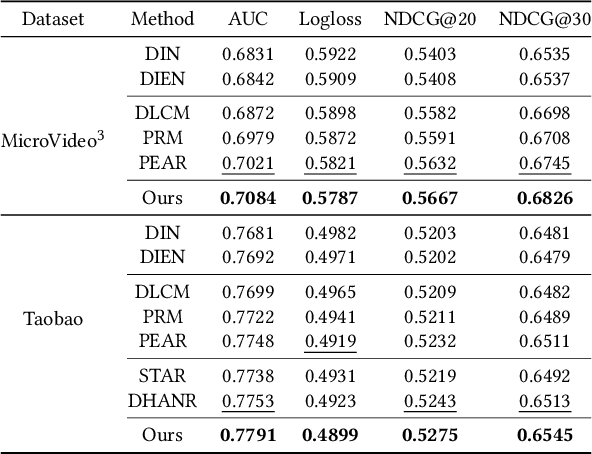
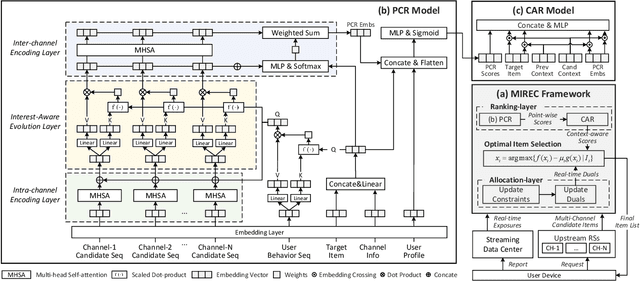
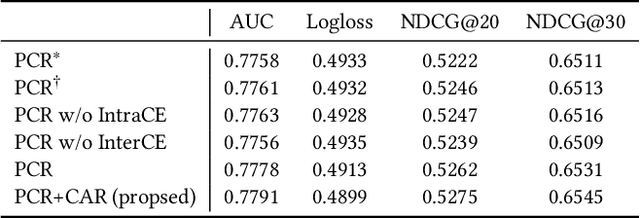
Abstract:Integrated recommendation, which aims at jointly recommending heterogeneous items from different channels in a main feed, has been widely applied to various online platforms. Though attractive, integrated recommendation requires the ranking methods to migrate from conventional user-item models to the new user-channel-item paradigm in order to better capture users' preferences on both item and channel levels. Moreover, practical feed recommendation systems usually impose exposure constraints on different channels to ensure user experience. This leads to greater difficulty in the joint ranking of heterogeneous items. In this paper, we investigate the integrated recommendation task with exposure constraints in practical recommender systems. Our contribution is forth-fold. First, we formulate this task as a binary online linear programming problem and propose a two-layer framework named Multi-channel Integrated Recommendation with Exposure Constraints (MIREC) to obtain the optimal solution. Second, we propose an efficient online allocation algorithm to determine the optimal exposure assignment of different channels from a global view of all user requests over the entire time horizon. We prove that this algorithm reaches the optimal point under a regret bound of $ \mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T}) $ with linear complexity. Third, we propose a series of collaborative models to determine the optimal layout of heterogeneous items at each user request. The joint modeling of user interests, cross-channel correlation, and page context in our models aligns more with the browsing nature of feed products than existing models. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on both offline datasets and online A/B tests to verify the effectiveness of MIREC. The proposed framework has now been implemented on the homepage of Taobao to serve the main traffic.
Entire Space Learning Framework: Unbias Conversion Rate Prediction in Full Stages of Recommender System
Mar 01, 2023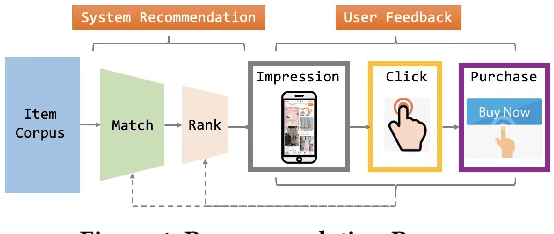

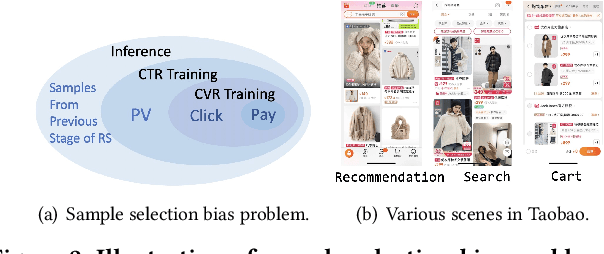

Abstract:Recommender system is an essential part of online services, especially for e-commerce platform. Conversion Rate (CVR) prediction in RS plays a significant role in optimizing Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV) goal of e-commerce. However, CVR suffers from well-known Sample Selection Bias (SSB) and Data Sparsity (DS) problems. Although existing methods ESMM and ESM2 train with all impression samples over the entire space by modeling user behavior paths, SSB and DS problems still exist. In real practice, the online inference space are samples from previous stage of RS process, rather than the impression space modeled by existing methods. Moreover, existing methods solve the DS problem mainly by building behavior paths of their own specific scene, ignoring the behaviors in various scenes of e-commerce platform. In this paper, we propose Entire Space Learning Framework: Unbias Conversion Rate Prediction in Full Stages of Recommender System, solving SSB and DS problems by reformulating GMV goal in a novel manner. Specifically, we rebuild the CVR on the entire data space with samples from previous stage of RS process, unifying training and online inference space. Moreover, we explicitly introduce purchase samples from other scenes of e-commerce platform in model learning process. Online A/B test and offline experiments show the superiority of our framework. Our framework has been deployed in rank stage of Taobao recommendation, providing recommendation service for hundreds of millions of consumers everyday.
Hierarchical Multi-Interest Co-Network For Coarse-Grained Ranking
Oct 19, 2022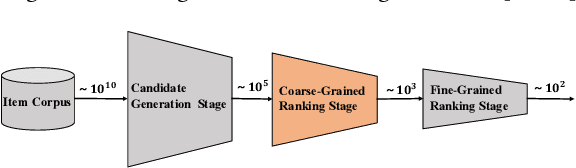
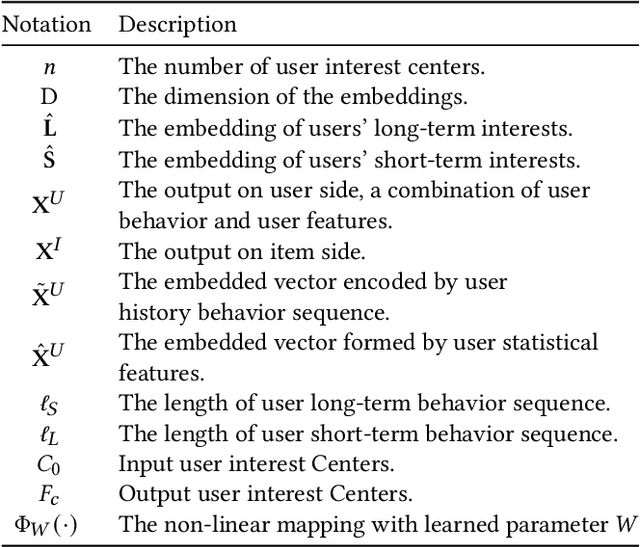
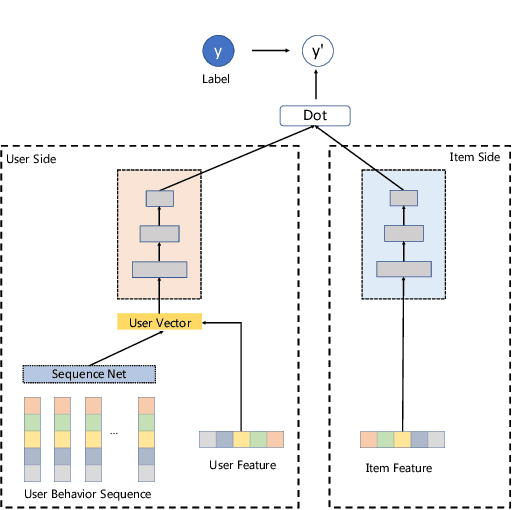
Abstract:In this era of information explosion, a personalized recommendation system is convenient for users to get information they are interested in. To deal with billions of users and items, large-scale online recommendation services usually consist of three stages: candidate generation, coarse-grained ranking, and fine-grained ranking. The success of each stage depends on whether the model accurately captures the interests of users, which are usually hidden in users' behavior data. Previous research shows that users' interests are diverse, and one vector is not sufficient to capture users' different preferences. Therefore, many methods use multiple vectors to encode users' interests. However, there are two unsolved problems: (1) The similarity of different vectors in existing methods is too high, with too much redundant information. Consequently, the interests of users are not fully represented. (2) Existing methods model the long-term and short-term behaviors together, ignoring the differences between them. This paper proposes a Hierarchical Multi-Interest Co-Network (HCN) to capture users' diverse interests in the coarse-grained ranking stage. Specifically, we design a hierarchical multi-interest extraction layer to update users' diverse interest centers iteratively. The multiple embedded vectors obtained in this way contain more information and represent the interests of users better in various aspects. Furthermore, we develop a Co-Interest Network to integrate users' long-term and short-term interests. Experiments on several real-world datasets and one large-scale industrial dataset show that HCN effectively outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. We deploy HCN into a large-scale real world E-commerce system and achieve extra 2.5\% improvements on GMV (Gross Merchandise Value).
Efficient Long Sequential User Data Modeling for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Sep 25, 2022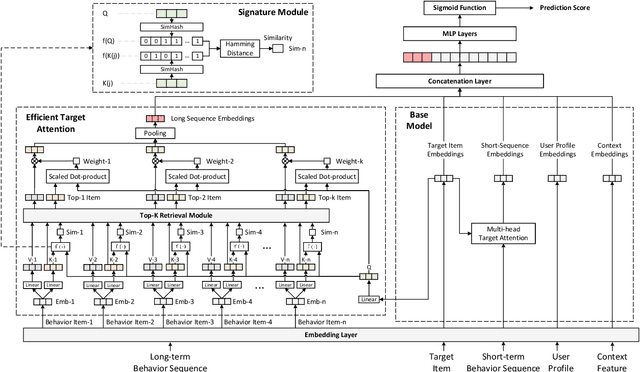

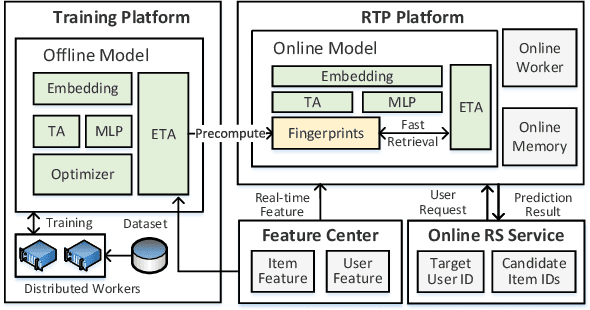
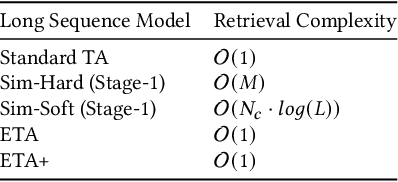
Abstract:Recent studies on Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction has reached new levels by modeling longer user behavior sequences. Among others, the two-stage methods stand out as the state-of-the-art (SOTA) solution for industrial applications. The two-stage methods first train a retrieval model to truncate the long behavior sequence beforehand and then use the truncated sequences to train a CTR model. However, the retrieval model and the CTR model are trained separately. So the retrieved subsequences in the CTR model is inaccurate, which degrades the final performance. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end paradigm to model long behavior sequences, which is able to achieve superior performance along with remarkable cost-efficiency compared to existing models. Our contribution is three-fold: First, we propose a hashing-based efficient target attention (TA) network named ETA-Net to enable end-to-end user behavior retrieval based on low-cost bit-wise operations. The proposed ETA-Net can reduce the complexity of standard TA by orders of magnitude for sequential data modeling. Second, we propose a general system architecture as one viable solution to deploy ETA-Net on industrial systems. Particularly, ETA-Net has been deployed on the recommender system of Taobao, and brought 1.8% lift on CTR and 3.1% lift on Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) compared to the SOTA two-stage methods. Third, we conduct extensive experiments on both offline datasets and online A/B test. The results verify that the proposed model outperforms existing CTR models considerably, in terms of both CTR prediction performance and online cost-efficiency. ETA-Net now serves the main traffic of Taobao, delivering services to hundreds of millions of users towards billions of items every day.
End-to-End User Behavior Retrieval in Click-Through RatePrediction Model
Aug 10, 2021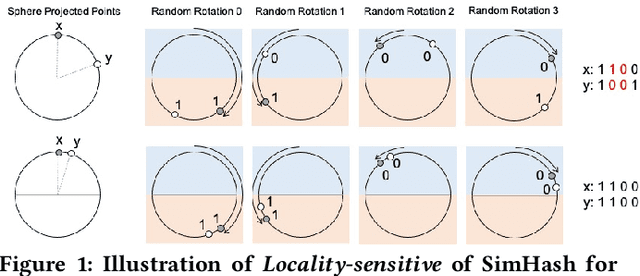

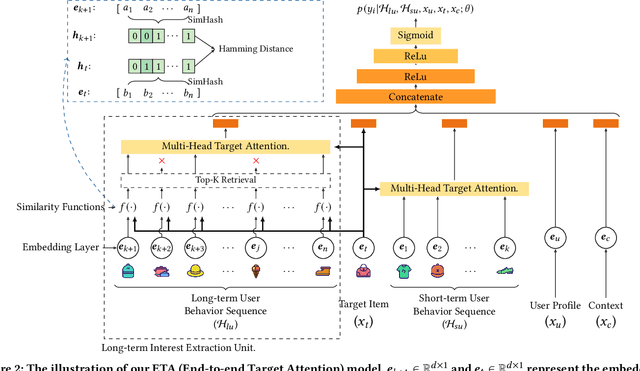

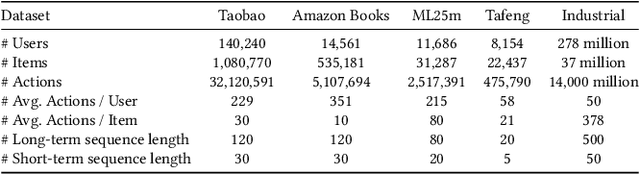
Abstract:Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction is one of the core tasks in recommender systems (RS). It predicts a personalized click probability for each user-item pair. Recently, researchers have found that the performance of CTR model can be improved greatly by taking user behavior sequence into consideration, especially long-term user behavior sequence. The report on an e-commerce website shows that 23\% of users have more than 1000 clicks during the past 5 months. Though there are numerous works focus on modeling sequential user behaviors, few works can handle long-term user behavior sequence due to the strict inference time constraint in real world system. Two-stage methods are proposed to push the limit for better performance. At the first stage, an auxiliary task is designed to retrieve the top-$k$ similar items from long-term user behavior sequence. At the second stage, the classical attention mechanism is conducted between the candidate item and $k$ items selected in the first stage. However, information gap happens between retrieval stage and the main CTR task. This goal divergence can greatly diminishing the performance gain of long-term user sequence. In this paper, inspired by Reformer, we propose a locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) method called ETA (End-to-end Target Attention) which can greatly reduce the training and inference cost and make the end-to-end training with long-term user behavior sequence possible. Both offline and online experiments confirm the effectiveness of our model. We deploy ETA into a large-scale real world E-commerce system and achieve extra 3.1\% improvements on GMV (Gross Merchandise Value) compared to a two-stage long user sequence CTR model.
Towards Long-term Fairness in Recommendation
Jan 10, 2021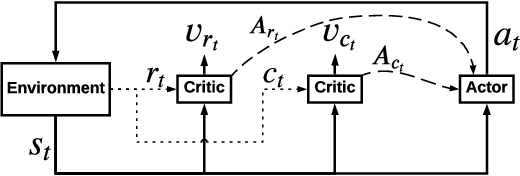
Abstract:As Recommender Systems (RS) influence more and more people in their daily life, the issue of fairness in recommendation is becoming more and more important. Most of the prior approaches to fairness-aware recommendation have been situated in a static or one-shot setting, where the protected groups of items are fixed, and the model provides a one-time fairness solution based on fairness-constrained optimization. This fails to consider the dynamic nature of the recommender systems, where attributes such as item popularity may change over time due to the recommendation policy and user engagement. For example, products that were once popular may become no longer popular, and vice versa. As a result, the system that aims to maintain long-term fairness on the item exposure in different popularity groups must accommodate this change in a timely fashion. Novel to this work, we explore the problem of long-term fairness in recommendation and accomplish the problem through dynamic fairness learning. We focus on the fairness of exposure of items in different groups, while the division of the groups is based on item popularity, which dynamically changes over time in the recommendation process. We tackle this problem by proposing a fairness-constrained reinforcement learning algorithm for recommendation, which models the recommendation problem as a Constrained Markov Decision Process (CMDP), so that the model can dynamically adjust its recommendation policy to make sure the fairness requirement is always satisfied when the environment changes. Experiments on several real-world datasets verify our framework's superiority in terms of recommendation performance, short-term fairness, and long-term fairness.
Semi-supervised Collaborative Filtering by Text-enhanced Domain Adaptation
Jun 28, 2020
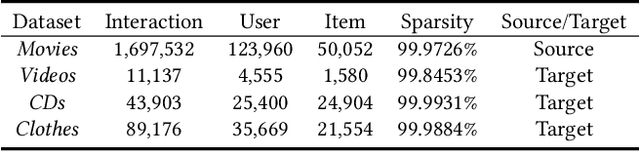
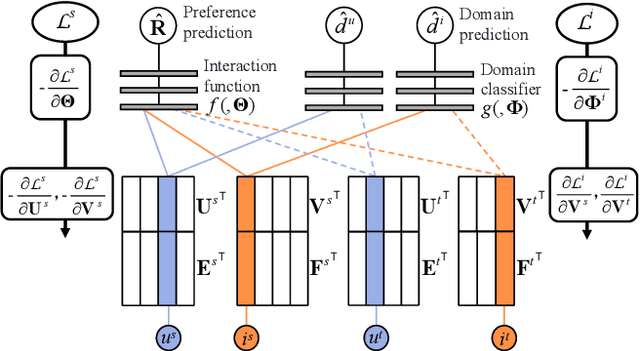
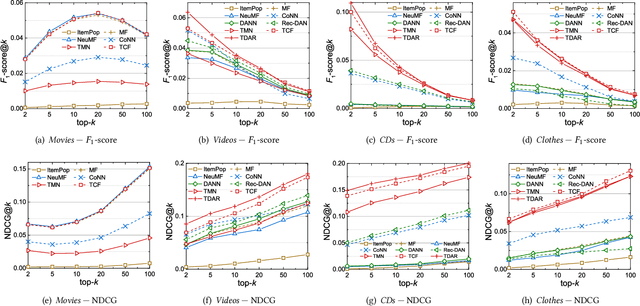
Abstract:Data sparsity is an inherent challenge in the recommender systems, where most of the data is collected from the implicit feedbacks of users. This causes two difficulties in designing effective algorithms: first, the majority of users only have a few interactions with the system and there is no enough data for learning; second, there are no negative samples in the implicit feedbacks and it is a common practice to perform negative sampling to generate negative samples. However, this leads to a consequence that many potential positive samples are mislabeled as negative ones and data sparsity would exacerbate the mislabeling problem. To solve these difficulties, we regard the problem of recommendation on sparse implicit feedbacks as a semi-supervised learning task, and explore domain adaption to solve it. We transfer the knowledge learned from dense data to sparse data and we focus on the most challenging case -- there is no user or item overlap. In this extreme case, aligning embeddings of two datasets directly is rather sub-optimal since the two latent spaces encode very different information. As such, we adopt domain-invariant textual features as the anchor points to align the latent spaces. To align the embeddings, we extract the textual features for each user and item and feed them into a domain classifier with the embeddings of users and items. The embeddings are trained to puzzle the classifier and textual features are fixed as anchor points. By domain adaptation, the distribution pattern in the source domain is transferred to the target domain. As the target part can be supervised by domain adaptation, we abandon negative sampling in target dataset to avoid label noise. We adopt three pairs of real-world datasets to validate the effectiveness of our transfer strategy. Results show that our models outperform existing models significantly.
Privileged Features Distillation for E-Commerce Recommendations
Jul 11, 2019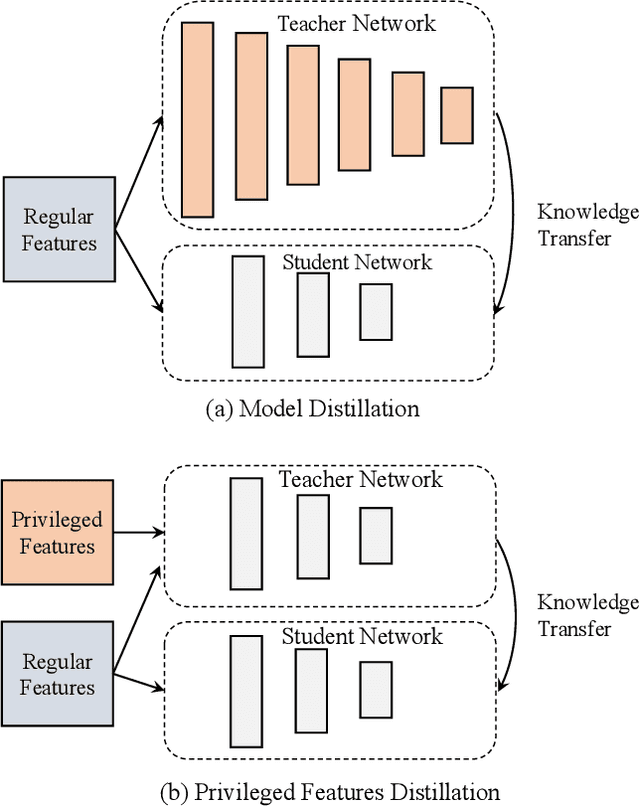
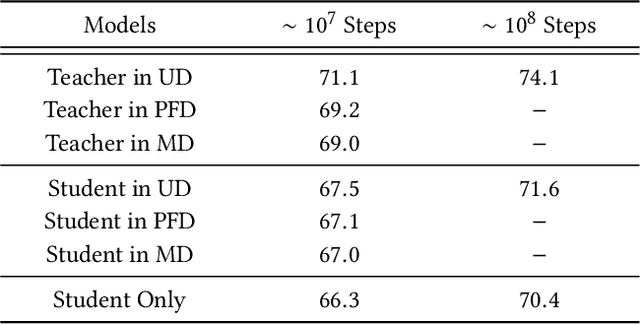
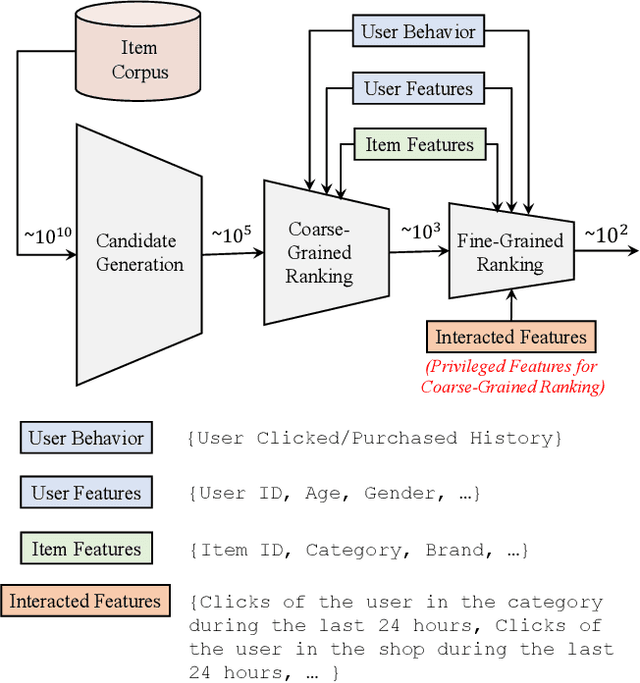
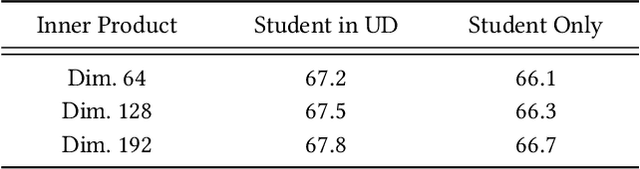
Abstract:Features play an important role in most prediction tasks of e-commerce recommendations. To guarantee the consistence of off-line training and on-line serving, we usually utilize the same features that are both available. However, the consistence in turn neglects some discriminative features. For example, when estimating the conversion rate (CVR), i.e., the probability that a user would purchase the item after she has clicked it, features like dwell time on the item detailed page can be very informative. However, CVR prediction should be conducted for on-line ranking before the click happens. Thus we cannot get such post-event features during serving. Here we define the features that are discriminative but only available during training as the privileged features. Inspired by the distillation techniques which bridge the gap between training and inference, in this work, we propose privileged features distillation (PFD). We train two models, i.e., a student model that is the same as the original one and a teacher model that additionally utilizes the privileged features. Knowledge distilled from the more accurate teacher is transferred to the student, which helps to improve its prediction accuracy. During serving, only the student part is extracted. To our knowledge, this is the first work to fully exploit the potential of such features. To validate the effectiveness of PFD, we conduct experiments on two fundamental prediction tasks in Taobao recommendations, i.e., click-through rate (CTR) at coarse-grained ranking and CVR at fine-grained ranking. By distilling the interacted features that are prohibited during serving for CTR and the post-event features for CVR, we achieve significant improvements over both of the strong baselines. Besides, by addressing several issues of training PFD, we obtain comparable training speed as the baselines without any distillation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge