Yikun Xian
A Survey on Trustworthy Recommender Systems
Jul 25, 2022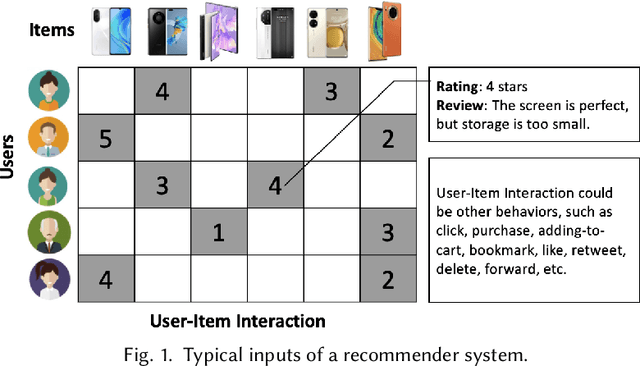
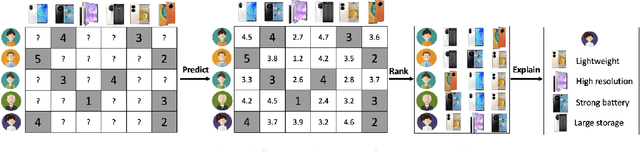
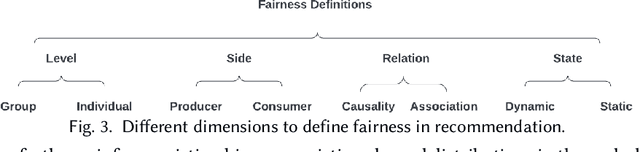

Abstract:Recommender systems (RS), serving at the forefront of Human-centered AI, are widely deployed in almost every corner of the web and facilitate the human decision-making process. However, despite their enormous capabilities and potential, RS may also lead to undesired counter-effects on users, items, producers, platforms, or even the society at large, such as compromised user trust due to non-transparency, unfair treatment of different consumers, or producers, privacy concerns due to extensive use of user's private data for personalization, just to name a few. All of these create an urgent need for Trustworthy Recommender Systems (TRS) so as to mitigate or avoid such adverse impacts and risks. In this survey, we will introduce techniques related to trustworthy and responsible recommendation, including but not limited to explainable recommendation, fairness in recommendation, privacy-aware recommendation, robustness in recommendation, user controllable recommendation, as well as the relationship between these different perspectives in terms of trustworthy and responsible recommendation. Through this survey, we hope to deliver readers with a comprehensive view of the research area and raise attention to the community about the importance, existing research achievements, and future research directions on trustworthy recommendation.
Faithfully Explainable Recommendation via Neural Logic Reasoning
Apr 16, 2021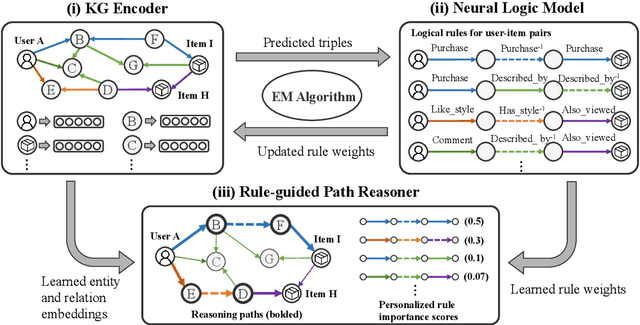
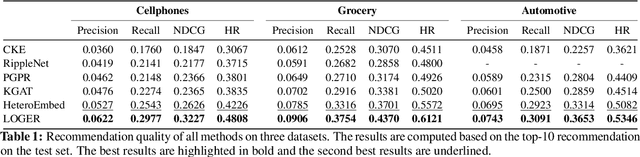
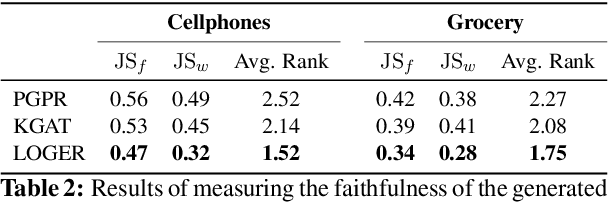
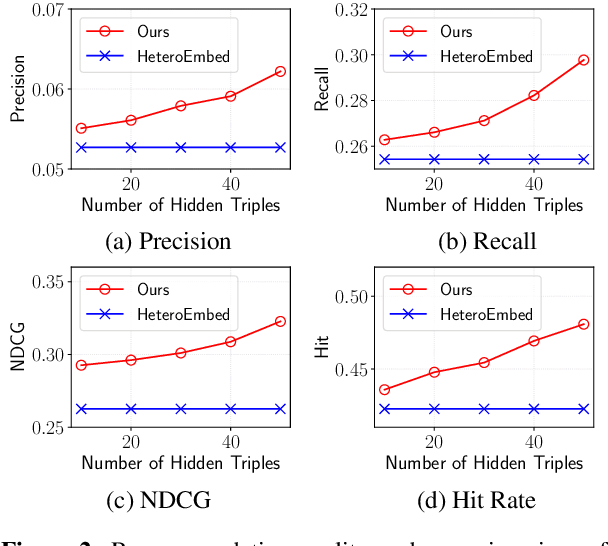
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KG) have become increasingly important to endow modern recommender systems with the ability to generate traceable reasoning paths to explain the recommendation process. However, prior research rarely considers the faithfulness of the derived explanations to justify the decision making process. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that models and evaluates faithfully explainable recommendation under the framework of KG reasoning. Specifically, we propose neural logic reasoning for explainable recommendation (LOGER) by drawing on interpretable logical rules to guide the path reasoning process for explanation generation. We experiment on three large-scale datasets in the e-commerce domain, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method in delivering high-quality recommendations as well as ascertaining the faithfulness of the derived explanation.
Towards Long-term Fairness in Recommendation
Jan 10, 2021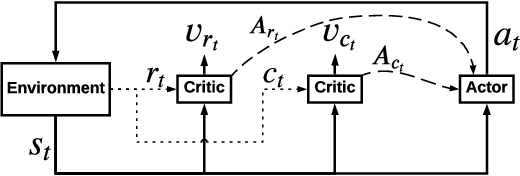
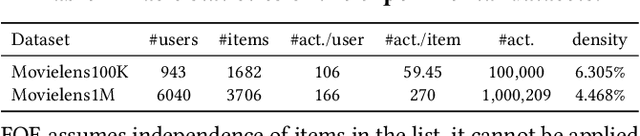
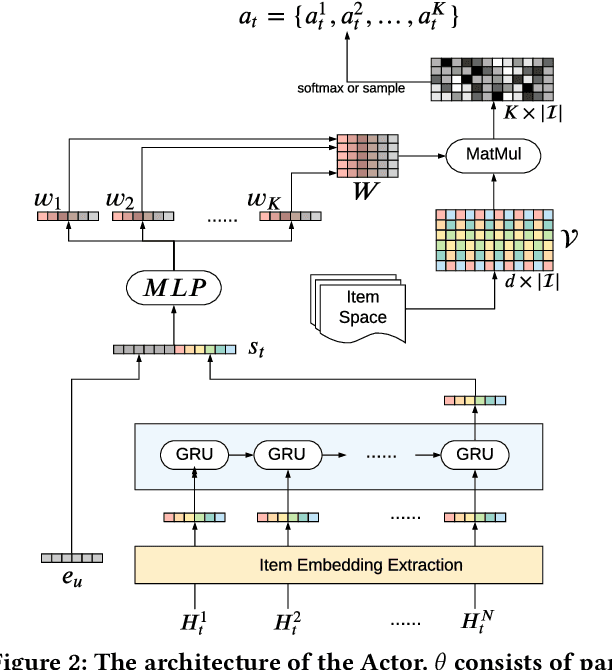
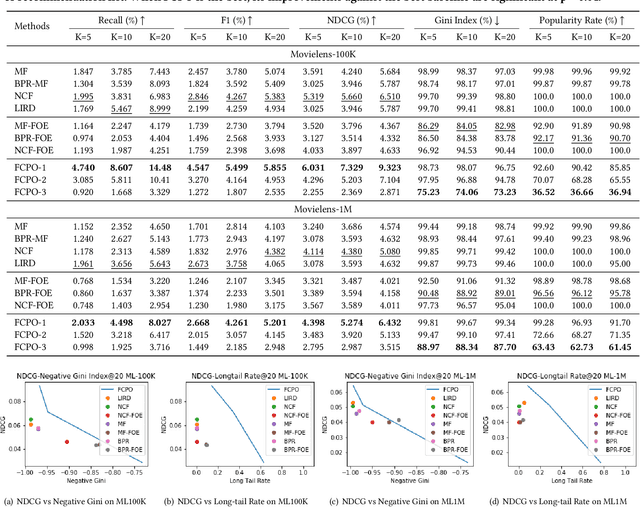
Abstract:As Recommender Systems (RS) influence more and more people in their daily life, the issue of fairness in recommendation is becoming more and more important. Most of the prior approaches to fairness-aware recommendation have been situated in a static or one-shot setting, where the protected groups of items are fixed, and the model provides a one-time fairness solution based on fairness-constrained optimization. This fails to consider the dynamic nature of the recommender systems, where attributes such as item popularity may change over time due to the recommendation policy and user engagement. For example, products that were once popular may become no longer popular, and vice versa. As a result, the system that aims to maintain long-term fairness on the item exposure in different popularity groups must accommodate this change in a timely fashion. Novel to this work, we explore the problem of long-term fairness in recommendation and accomplish the problem through dynamic fairness learning. We focus on the fairness of exposure of items in different groups, while the division of the groups is based on item popularity, which dynamically changes over time in the recommendation process. We tackle this problem by proposing a fairness-constrained reinforcement learning algorithm for recommendation, which models the recommendation problem as a Constrained Markov Decision Process (CMDP), so that the model can dynamically adjust its recommendation policy to make sure the fairness requirement is always satisfied when the environment changes. Experiments on several real-world datasets verify our framework's superiority in terms of recommendation performance, short-term fairness, and long-term fairness.
COOKIE: A Dataset for Conversational Recommendation over Knowledge Graphs in E-commerce
Aug 21, 2020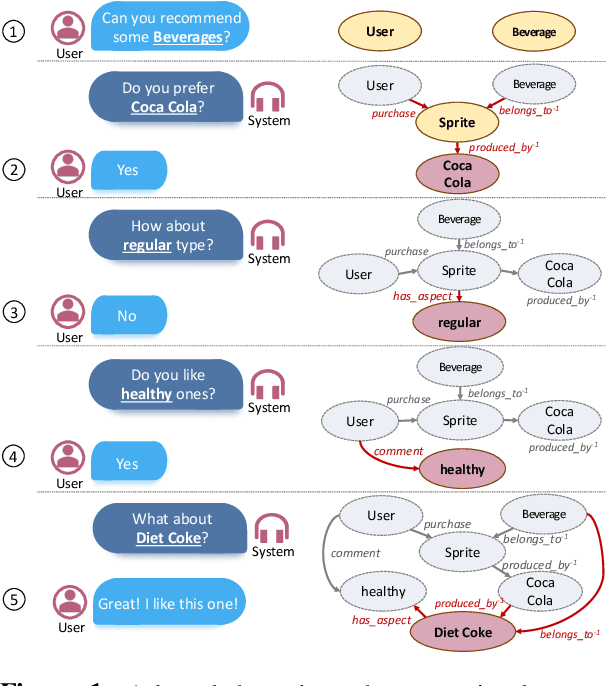
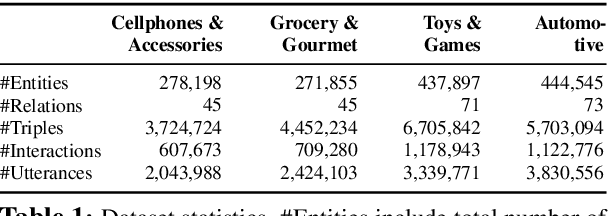
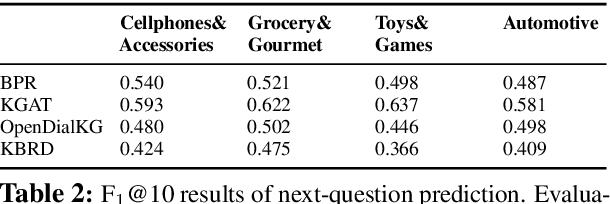
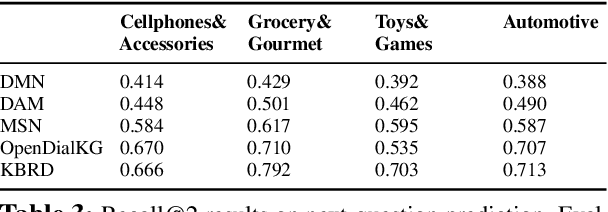
Abstract:In this work, we present a new dataset for conversational recommendation over knowledge graphs in e-commerce platforms called COOKIE. The dataset is constructed from an Amazon review corpus by integrating both user-agent dialogue and custom knowledge graphs for recommendation. Specifically, we first construct a unified knowledge graph and extract key entities between user--product pairs, which serve as the skeleton of a conversation. Then we simulate conversations mirroring the human coarse-to-fine process of choosing preferred items. The proposed baselines and experiments demonstrate that our dataset is able to provide innovative opportunities for conversational recommendation.
Enhanced MRI Reconstruction Network using Neural Architecture Search
Aug 19, 2020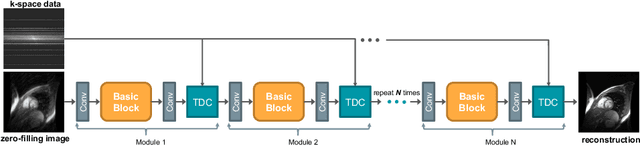
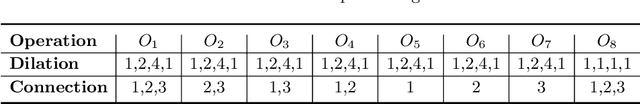
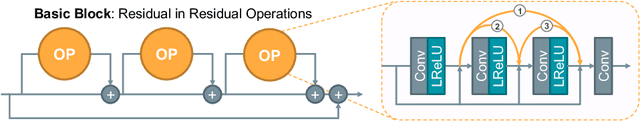
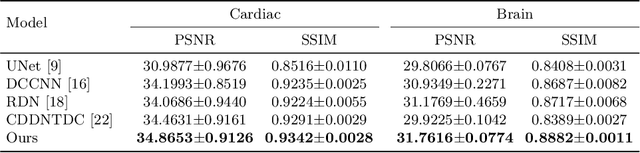
Abstract:The accurate reconstruction of under-sampled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data using modern deep learning technology, requires significant effort to design the necessary complex neural network architectures. The cascaded network architecture for MRI reconstruction has been widely used, while it suffers from the "vanishing gradient" problem when the network becomes deep. In addition, homogeneous architecture degrades the representation capacity of the network. In this work, we present an enhanced MRI reconstruction network using a residual in residual basic block. For each cell in the basic block, we use the differentiable neural architecture search (NAS) technique to automatically choose the optimal operation among eight variants of the dense block. This new heterogeneous network is evaluated on two publicly available datasets and outperforms all current state-of-the-art methods, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Fairness-Aware Explainable Recommendation over Knowledge Graphs
Jun 28, 2020
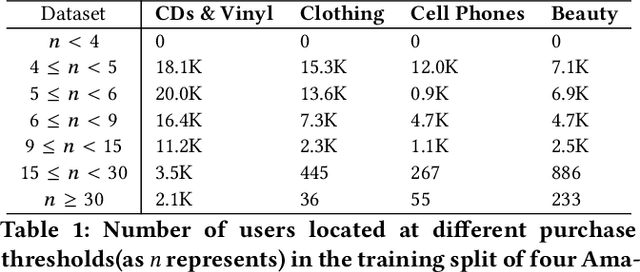
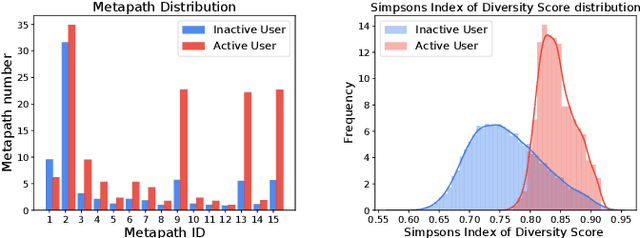
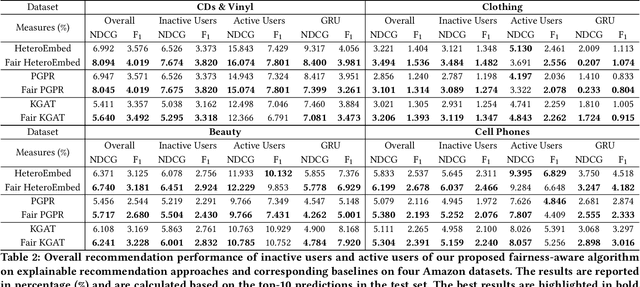
Abstract:There has been growing attention on fairness considerations recently, especially in the context of intelligent decision making systems. Explainable recommendation systems, in particular, may suffer from both explanation bias and performance disparity. In this paper, we analyze different groups of users according to their level of activity, and find that bias exists in recommendation performance between different groups. We show that inactive users may be more susceptible to receiving unsatisfactory recommendations, due to insufficient training data for the inactive users, and that their recommendations may be biased by the training records of more active users, due to the nature of collaborative filtering, which leads to an unfair treatment by the system. We propose a fairness constrained approach via heuristic re-ranking to mitigate this unfairness problem in the context of explainable recommendation over knowledge graphs. We experiment on several real-world datasets with state-of-the-art knowledge graph-based explainable recommendation algorithms. The promising results show that our algorithm is not only able to provide high-quality explainable recommendations, but also reduces the recommendation unfairness in several respects.
ABSent: Cross-Lingual Sentence Representation Mapping with Bidirectional GANs
Jan 29, 2020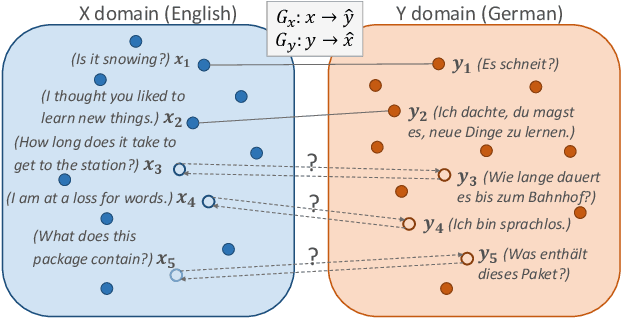
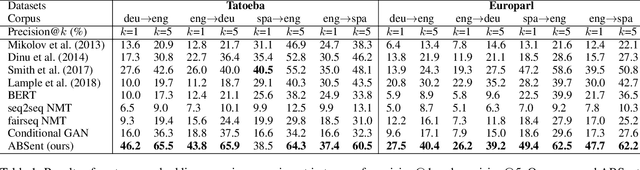
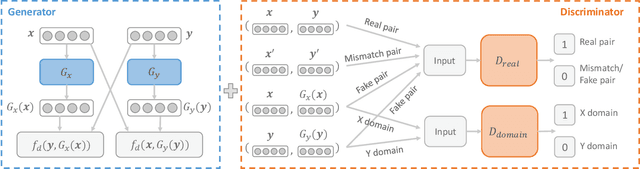
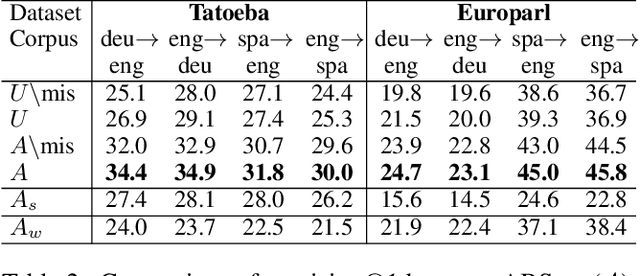
Abstract:A number of cross-lingual transfer learning approaches based on neural networks have been proposed for the case when large amounts of parallel text are at our disposal. However, in many real-world settings, the size of parallel annotated training data is restricted. Additionally, prior cross-lingual mapping research has mainly focused on the word level. This raises the question of whether such techniques can also be applied to effortlessly obtain cross-lingually aligned sentence representations. To this end, we propose an Adversarial Bi-directional Sentence Embedding Mapping (ABSent) framework, which learns mappings of cross-lingual sentence representations from limited quantities of parallel data.
Reinforcement Knowledge Graph Reasoning for Explainable Recommendation
Jun 12, 2019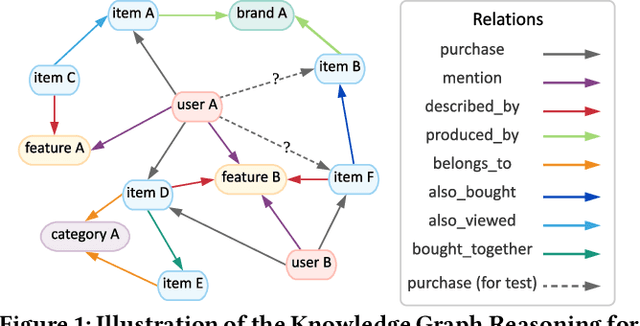
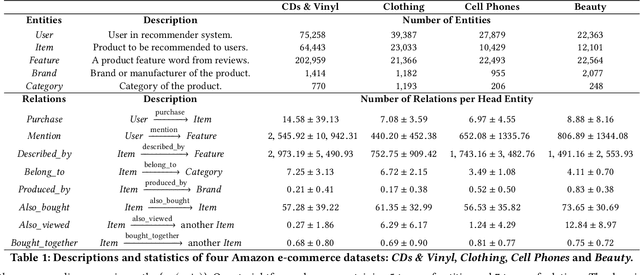
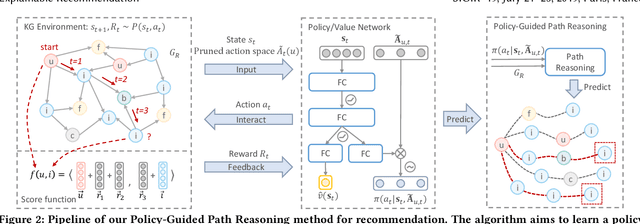
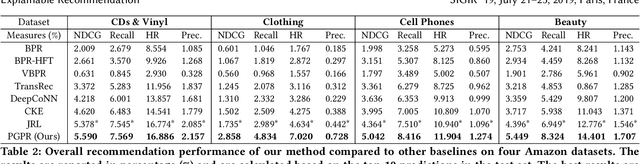
Abstract:Recent advances in personalized recommendation have sparked great interest in the exploitation of rich structured information provided by knowledge graphs. Unlike most existing approaches that only focus on leveraging knowledge graphs for more accurate recommendation, we perform explicit reasoning with knowledge for decision making so that the recommendations are generated and supported by an interpretable causal inference procedure. To this end, we propose a method called Policy-Guided Path Reasoning (PGPR), which couples recommendation and interpretability by providing actual paths in a knowledge graph. Our contributions include four aspects. We first highlight the significance of incorporating knowledge graphs into recommendation to formally define and interpret the reasoning process. Second, we propose a reinforcement learning (RL) approach featuring an innovative soft reward strategy, user-conditional action pruning and a multi-hop scoring function. Third, we design a policy-guided graph search algorithm to efficiently and effectively sample reasoning paths for recommendation. Finally, we extensively evaluate our method on several large-scale real-world benchmark datasets, obtaining favorable results compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Waterfall Bandits: Learning to Sell Ads Online
Apr 20, 2019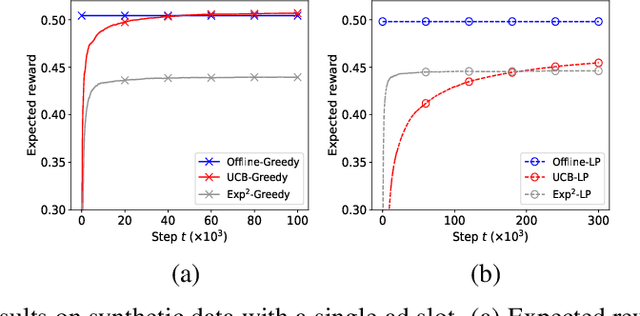
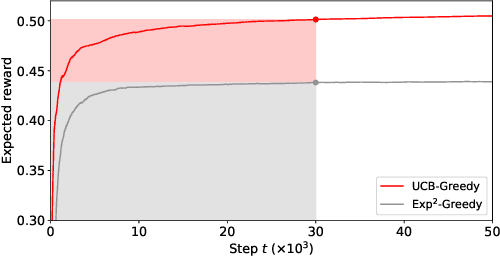
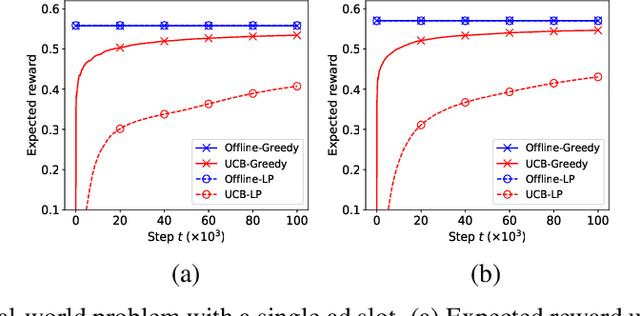
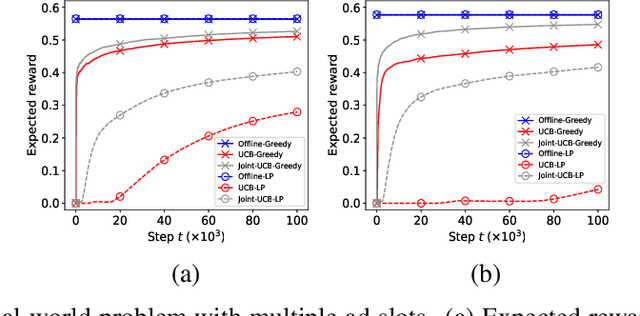
Abstract:A popular approach to selling online advertising is by a waterfall, where a publisher makes sequential price offers to ad networks for an inventory, and chooses the winner in that order. The publisher picks the order and prices to maximize her revenue. A traditional solution is to learn the demand model and then subsequently solve the optimization problem for the given demand model. This will incur a linear regret. We design an online learning algorithm for solving this problem, which interleaves learning and optimization, and prove that this algorithm has sublinear regret. We evaluate the algorithm on both synthetic and real-world data, and show that it quickly learns high quality pricing strategies. This is the first principled study of learning a waterfall design online by sequential experimentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge