Fairness-Aware Explainable Recommendation over Knowledge Graphs
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2020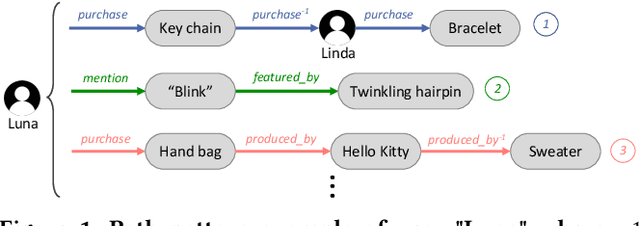
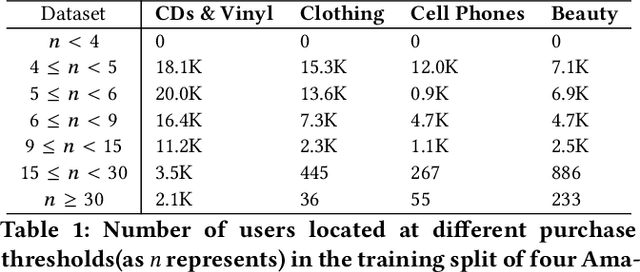
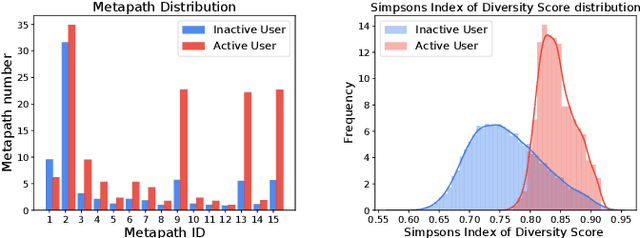
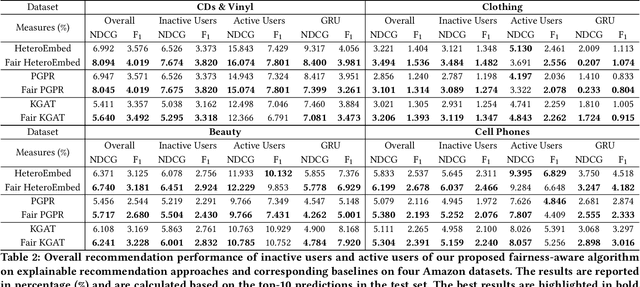
There has been growing attention on fairness considerations recently, especially in the context of intelligent decision making systems. Explainable recommendation systems, in particular, may suffer from both explanation bias and performance disparity. In this paper, we analyze different groups of users according to their level of activity, and find that bias exists in recommendation performance between different groups. We show that inactive users may be more susceptible to receiving unsatisfactory recommendations, due to insufficient training data for the inactive users, and that their recommendations may be biased by the training records of more active users, due to the nature of collaborative filtering, which leads to an unfair treatment by the system. We propose a fairness constrained approach via heuristic re-ranking to mitigate this unfairness problem in the context of explainable recommendation over knowledge graphs. We experiment on several real-world datasets with state-of-the-art knowledge graph-based explainable recommendation algorithms. The promising results show that our algorithm is not only able to provide high-quality explainable recommendations, but also reduces the recommendation unfairness in several respects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge