Zuohui Fu
VIP5: Towards Multimodal Foundation Models for Recommendation
May 23, 2023Abstract:Computer Vision (CV), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Recommender Systems (RecSys) are three prominent AI applications that have traditionally developed independently, resulting in disparate modeling and engineering methodologies. This has impeded the ability for these fields to directly benefit from each other's advancements. With the increasing availability of multimodal data on the web, there is a growing need to consider various modalities when making recommendations for users. With the recent emergence of foundation models, large language models have emerged as a potential general-purpose interface for unifying different modalities and problem formulations. In light of this, we propose the development of a multimodal foundation model by considering both visual and textual modalities under the P5 recommendation paradigm (VIP5) to unify various modalities and recommendation tasks. This will enable the processing of vision, language, and personalization information in a shared architecture for improved recommendations. To achieve this, we introduce multimodal personalized prompts to accommodate multiple modalities under a shared format. Additionally, we propose a parameter-efficient training method for foundation models, which involves freezing the backbone and fine-tuning lightweight adapters, resulting in improved recommendation performance and increased efficiency in terms of training time and memory usage.
Dynamic Causal Collaborative Filtering
Aug 23, 2022



Abstract:Causal graph, as an effective and powerful tool for causal modeling, is usually assumed as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). However, recommender systems usually involve feedback loops, defined as the cyclic process of recommending items, incorporating user feedback in model updates, and repeating the procedure. As a result, it is important to incorporate loops into the causal graphs to accurately model the dynamic and iterative data generation process for recommender systems. However, feedback loops are not always beneficial since over time they may encourage more and more narrowed content exposure, which if left unattended, may results in echo chambers. As a result, it is important to understand when the recommendations will lead to echo chambers and how to mitigate echo chambers without hurting the recommendation performance. In this paper, we design a causal graph with loops to describe the dynamic process of recommendation. We then take Markov process to analyze the mathematical properties of echo chamber such as the conditions that lead to echo chambers. Inspired by the theoretical analysis, we propose a Dynamic Causal Collaborative Filtering ($\partial$CCF) model, which estimates users' post-intervention preference on items based on back-door adjustment and mitigates echo chamber with counterfactual reasoning. Multiple experiments are conducted on real-world datasets and results show that our framework can mitigate echo chambers better than other state-of-the-art frameworks while achieving comparable recommendation performance with the base recommendation models.
A Survey on Trustworthy Recommender Systems
Jul 25, 2022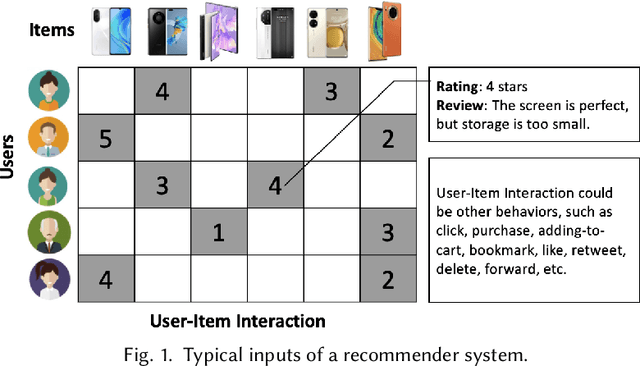
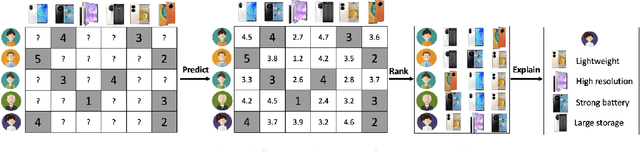

Abstract:Recommender systems (RS), serving at the forefront of Human-centered AI, are widely deployed in almost every corner of the web and facilitate the human decision-making process. However, despite their enormous capabilities and potential, RS may also lead to undesired counter-effects on users, items, producers, platforms, or even the society at large, such as compromised user trust due to non-transparency, unfair treatment of different consumers, or producers, privacy concerns due to extensive use of user's private data for personalization, just to name a few. All of these create an urgent need for Trustworthy Recommender Systems (TRS) so as to mitigate or avoid such adverse impacts and risks. In this survey, we will introduce techniques related to trustworthy and responsible recommendation, including but not limited to explainable recommendation, fairness in recommendation, privacy-aware recommendation, robustness in recommendation, user controllable recommendation, as well as the relationship between these different perspectives in terms of trustworthy and responsible recommendation. Through this survey, we hope to deliver readers with a comprehensive view of the research area and raise attention to the community about the importance, existing research achievements, and future research directions on trustworthy recommendation.
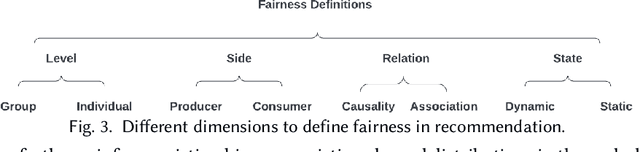
Explainable Fairness in Recommendation
Apr 24, 2022



Abstract:Existing research on fairness-aware recommendation has mainly focused on the quantification of fairness and the development of fair recommendation models, neither of which studies a more substantial problem--identifying the underlying reason of model disparity in recommendation. This information is critical for recommender system designers to understand the intrinsic recommendation mechanism and provides insights on how to improve model fairness to decision makers. Fortunately, with the rapid development of Explainable AI, we can use model explainability to gain insights into model (un)fairness. In this paper, we study the problem of explainable fairness, which helps to gain insights about why a system is fair or unfair, and guides the design of fair recommender systems with a more informed and unified methodology. Particularly, we focus on a common setting with feature-aware recommendation and exposure unfairness, but the proposed explainable fairness framework is general and can be applied to other recommendation settings and fairness definitions. We propose a Counterfactual Explainable Fairness framework, called CEF, which generates explanations about model fairness that can improve the fairness without significantly hurting the performance.The CEF framework formulates an optimization problem to learn the "minimal" change of the input features that changes the recommendation results to a certain level of fairness. Based on the counterfactual recommendation result of each feature, we calculate an explainability score in terms of the fairness-utility trade-off to rank all the feature-based explanations, and select the top ones as fairness explanations.
Recommendation as Language Processing (RLP): A Unified Pretrain, Personalized Prompt & Predict Paradigm (P5)
Apr 06, 2022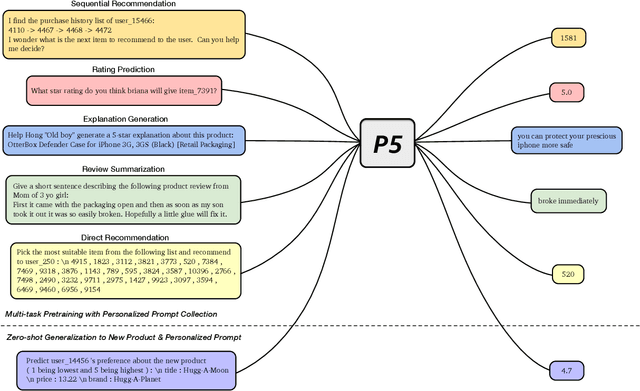
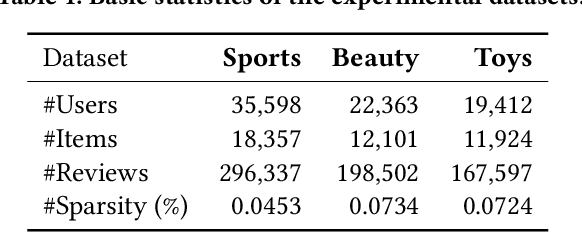
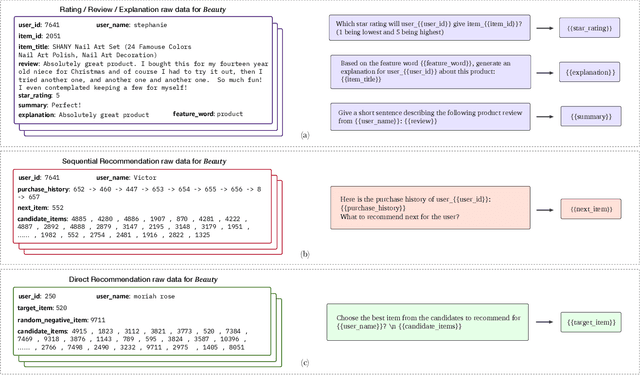
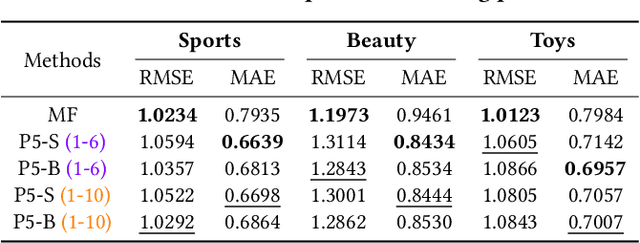
Abstract:For a long period, different recommendation tasks typically require designing task-specific architectures and training objectives. As a result, it is hard to transfer the learned knowledge and representations from one task to another, thus restricting the generalization ability of existing recommendation approaches, e.g., a sequential recommendation model can hardly be applied or transferred to a review generation method. To deal with such issues, considering that language grounding is a powerful medium to describe and represent various problems or tasks, we present a flexible and unified text-to-text paradigm called "Pretrain, Personalized Prompt, and Predict Paradigm" (P5) for recommendation, which unifies various recommendation tasks in a shared framework. In P5, all data such as user-item interactions, item metadata, and user reviews are converted to a common format -- natural language sequences. The rich information from natural language assist P5 to capture deeper semantics for recommendation. P5 learns different tasks with the same language modeling objective during pretraining. Thus, it possesses the potential to serve as the foundation model for downstream recommendation tasks, allows easy integration with other modalities, and enables instruction-based recommendation, which will revolutionize the technical form of recommender system towards universal recommendation engine. With adaptive personalized prompt for different users, P5 is able to make predictions in a zero-shot or few-shot manner and largely reduces the necessity for extensive fine-tuning. On several recommendation benchmarks, we conduct experiments to show the effectiveness of our generative approach. We will release our prompts and pretrained P5 language model to help advance future research on Recommendation as Language Processing (RLP) and Personalized Foundation Models.
Learning and Evaluating Graph Neural Network Explanations based on Counterfactual and Factual Reasoning
Feb 17, 2022



Abstract:Structural data well exists in Web applications, such as social networks in social media, citation networks in academic websites, and threads data in online forums. Due to the complex topology, it is difficult to process and make use of the rich information within such data. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown great advantages on learning representations for structural data. However, the non-transparency of the deep learning models makes it non-trivial to explain and interpret the predictions made by GNNs. Meanwhile, it is also a big challenge to evaluate the GNN explanations, since in many cases, the ground-truth explanations are unavailable. In this paper, we take insights of Counterfactual and Factual (CF^2) reasoning from causal inference theory, to solve both the learning and evaluation problems in explainable GNNs. For generating explanations, we propose a model-agnostic framework by formulating an optimization problem based on both of the two casual perspectives. This distinguishes CF^2 from previous explainable GNNs that only consider one of them. Another contribution of the work is the evaluation of GNN explanations. For quantitatively evaluating the generated explanations without the requirement of ground-truth, we design metrics based on Counterfactual and Factual reasoning to evaluate the necessity and sufficiency of the explanations. Experiments show that no matter ground-truth explanations are available or not, CF^2 generates better explanations than previous state-of-the-art methods on real-world datasets. Moreover, the statistic analysis justifies the correlation between the performance on ground-truth evaluation and our proposed metrics.
Dense Contrastive Visual-Linguistic Pretraining
Sep 24, 2021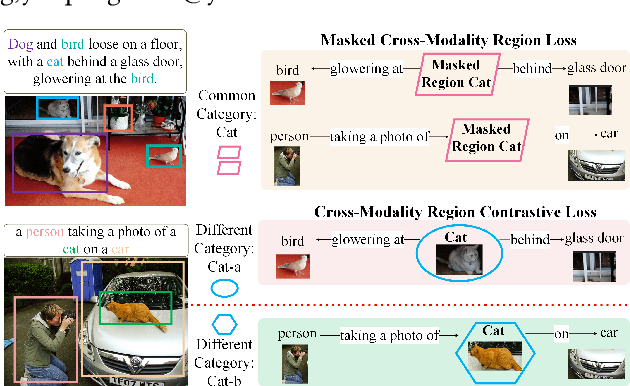
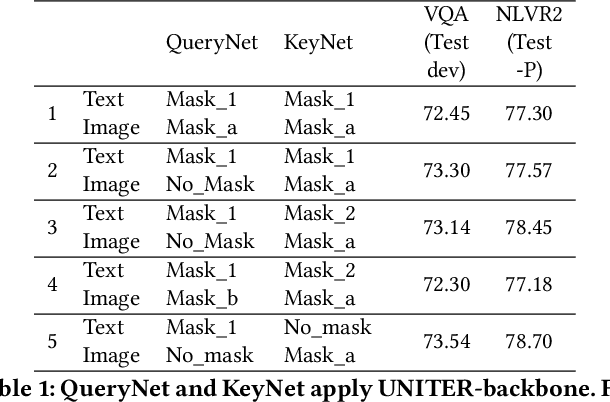
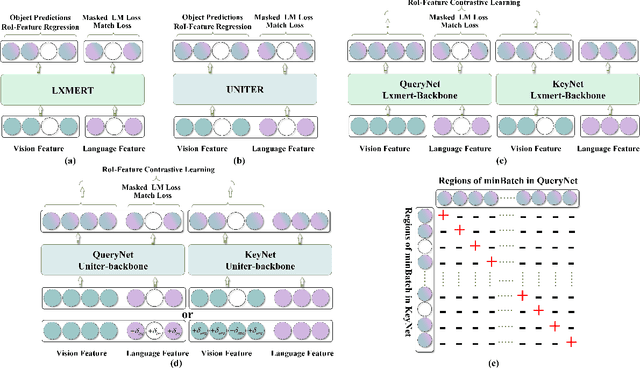
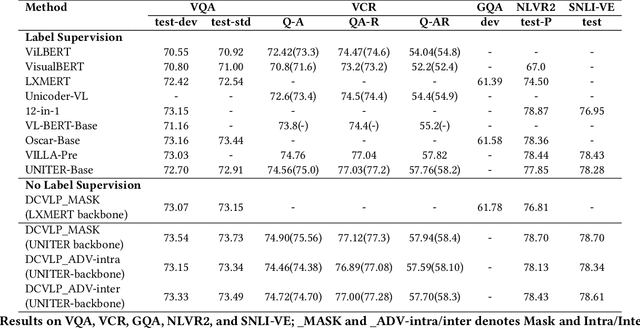
Abstract:Inspired by the success of BERT, several multimodal representation learning approaches have been proposed that jointly represent image and text. These approaches achieve superior performance by capturing high-level semantic information from large-scale multimodal pretraining. In particular, LXMERT and UNITER adopt visual region feature regression and label classification as pretext tasks. However, they tend to suffer from the problems of noisy labels and sparse semantic annotations, based on the visual features having been pretrained on a crowdsourced dataset with limited and inconsistent semantic labeling. To overcome these issues, we propose unbiased Dense Contrastive Visual-Linguistic Pretraining (DCVLP), which replaces the region regression and classification with cross-modality region contrastive learning that requires no annotations. Two data augmentation strategies (Mask Perturbation and Intra-/Inter-Adversarial Perturbation) are developed to improve the quality of negative samples used in contrastive learning. Overall, DCVLP allows cross-modality dense region contrastive learning in a self-supervised setting independent of any object annotations. We compare our method against prior visual-linguistic pretraining frameworks to validate the superiority of dense contrastive learning on multimodal representation learning.
Efficient Non-Sampling Knowledge Graph Embedding
Apr 30, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge Graph (KG) is a flexible structure that is able to describe the complex relationship between data entities. Currently, most KG embedding models are trained based on negative sampling, i.e., the model aims to maximize some similarity of the connected entities in the KG, while minimizing the similarity of the sampled disconnected entities. Negative sampling helps to reduce the time complexity of model learning by only considering a subset of negative instances, which may fail to deliver stable model performance due to the uncertainty in the sampling procedure. To avoid such deficiency, we propose a new framework for KG embedding -- Efficient Non-Sampling Knowledge Graph Embedding (NS-KGE). The basic idea is to consider all of the negative instances in the KG for model learning, and thus to avoid negative sampling. The framework can be applied to square-loss based knowledge graph embedding models or models whose loss can be converted to a square loss. A natural side-effect of this non-sampling strategy is the increased computational complexity of model learning. To solve the problem, we leverage mathematical derivations to reduce the complexity of non-sampling loss function, which eventually provides us both better efficiency and better accuracy in KG embedding compared with existing models. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our NS-KGE framework can achieve a better performance on efficiency and accuracy over traditional negative sampling based models, and that the framework is applicable to a large class of knowledge graph embedding models.
User-oriented Fairness in Recommendation
Apr 21, 2021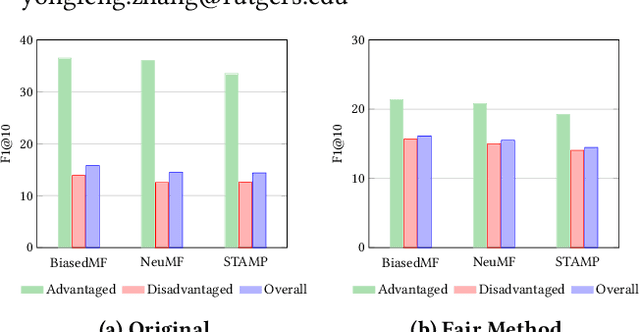
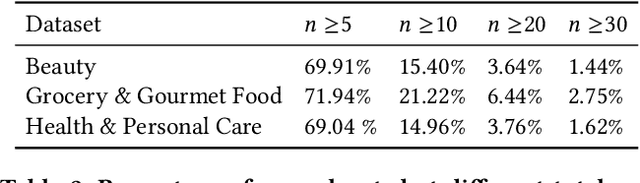
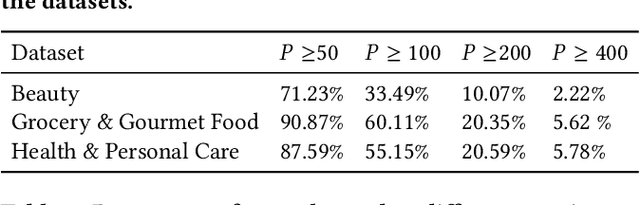
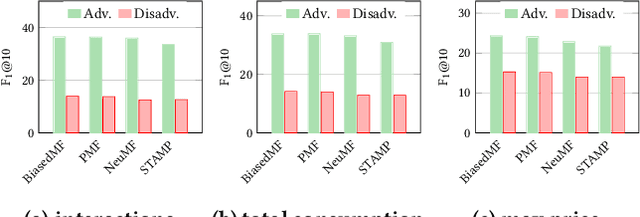
Abstract:As a highly data-driven application, recommender systems could be affected by data bias, resulting in unfair results for different data groups, which could be a reason that affects the system performance. Therefore, it is important to identify and solve the unfairness issues in recommendation scenarios. In this paper, we address the unfairness problem in recommender systems from the user perspective. We group users into advantaged and disadvantaged groups according to their level of activity, and conduct experiments to show that current recommender systems will behave unfairly between two groups of users. Specifically, the advantaged users (active) who only account for a small proportion in data enjoy much higher recommendation quality than those disadvantaged users (inactive). Such bias can also affect the overall performance since the disadvantaged users are the majority. To solve this problem, we provide a re-ranking approach to mitigate this unfairness problem by adding constraints over evaluation metrics. The experiments we conducted on several real-world datasets with various recommendation algorithms show that our approach can not only improve group fairness of users in recommender systems, but also achieve better overall recommendation performance.
Context-Aware Interaction Network for Question Matching
Apr 17, 2021



Abstract:Impressive milestones have been achieved in text matching by adopting a cross-attention mechanism to capture pertinent semantic connections between two sentences. However, these cross-attention mechanisms focus on word-level links between the two inputs, neglecting the importance of contextual information. We propose a context-aware interaction network (COIN) to properly align two sequences and infer their semantic relationship. Specifically, each interaction block includes (1) a context-aware cross-attention mechanism to effectively integrate contextual information, and (2) a gate fusion layer to flexibly interpolate aligned representations. We apply multiple stacked interaction blocks to produce alignments at different levels and gradually refine the attention results. Experiments on two question matching datasets and detailed analyses confirm the effectiveness of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge