Hanxiao Sun
HarmonRank: Ranking-aligned Multi-objective Ensemble for Live-streaming E-commerce Recommendation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Recommendation for live-streaming e-commerce is gaining increasing attention due to the explosive growth of the live streaming economy. Different from traditional e-commerce, live-streaming e-commerce shifts the focus from products to streamers, which requires ranking mechanism to balance both purchases and user-streamer interactions for long-term ecology. To trade off multiple objectives, a popular solution is to build an ensemble model to integrate multi-objective scores into a unified score. The ensemble model is usually supervised by multiple independent binary classification losses of all objectives. However, this paradigm suffers from two inherent limitations. First, the optimization direction of the binary classification task is misaligned with the ranking task (evaluated by AUC). Second, this paradigm overlooks the alignment between objectives, e.g., comment and buy behaviors are partially dependent which can be revealed in labels correlations. The model can achieve better trade-offs if it learns the aligned parts of ranking abilities among different objectives. To mitigate these limitations, we propose a novel multi-objective ensemble framework HarmonRank to fulfill both alignment to the ranking task and alignment among objectives. For alignment to ranking, we formulate ranking metric AUC as a rank-sum problem and utilize differentiable ranking techniques for ranking-oriented optimization. For inter-objective alignment, we change the original one-step ensemble paradigm to a two-step relation-aware ensemble scheme. Extensive offline experiments results on two industrial datasets and online experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method has been fully deployed in Kuaishou's live-streaming e-commerce recommendation platform with 400 million DAUs, contributing over 2% purchase gain.
SVG-IR: Spatially-Varying Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering
Apr 09, 2025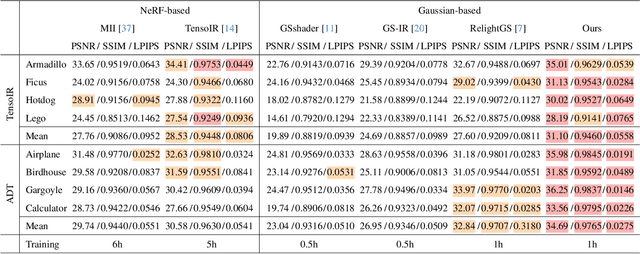
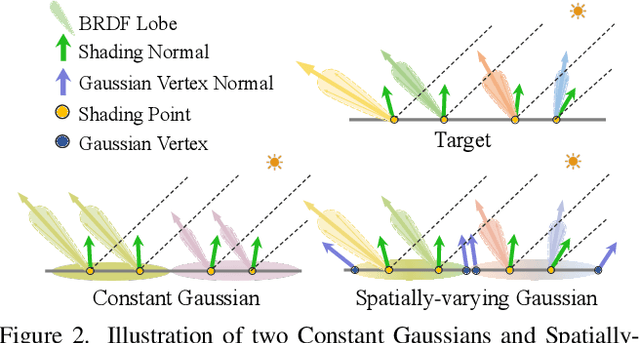
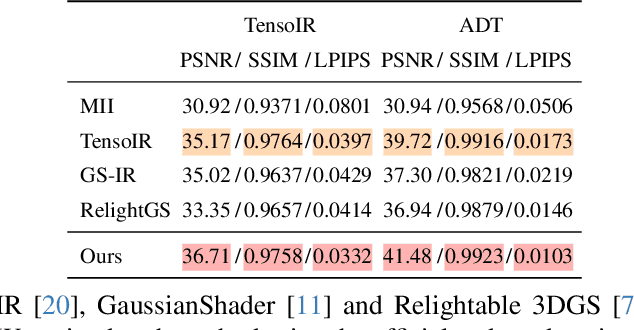
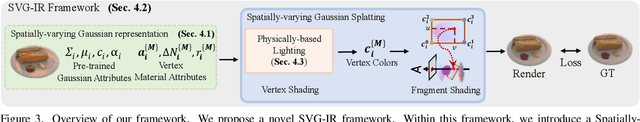
Abstract:Reconstructing 3D assets from images, known as inverse rendering (IR), remains a challenging task due to its ill-posed nature. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive capabilities for novel view synthesis (NVS) tasks. Methods apply it to relighting by separating radiance into BRDF parameters and lighting, yet produce inferior relighting quality with artifacts and unnatural indirect illumination due to the limited capability of each Gaussian, which has constant material parameters and normal, alongside the absence of physical constraints for indirect lighting. In this paper, we present a novel framework called Spatially-vayring Gaussian Inverse Rendering (SVG-IR), aimed at enhancing both NVS and relighting quality. To this end, we propose a new representation-Spatially-varying Gaussian (SVG)-that allows per-Gaussian spatially varying parameters. This enhanced representation is complemented by a SVG splatting scheme akin to vertex/fragment shading in traditional graphics pipelines. Furthermore, we integrate a physically-based indirect lighting model, enabling more realistic relighting. The proposed SVG-IR framework significantly improves rendering quality, outperforming state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods by 2.5 dB in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and surpassing existing Gaussian-based techniques by 3.5 dB in relighting tasks, all while maintaining a real-time rendering speed.
Privileged Features Distillation for E-Commerce Recommendations
Jul 11, 2019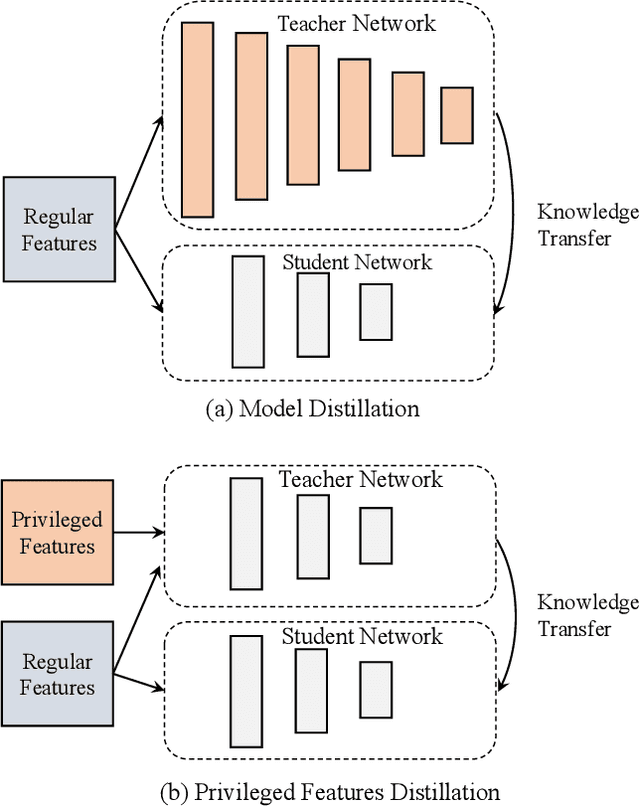
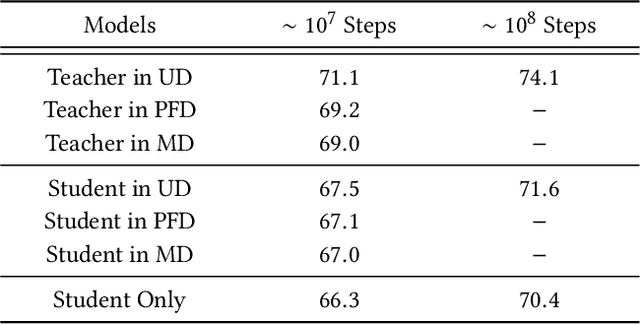
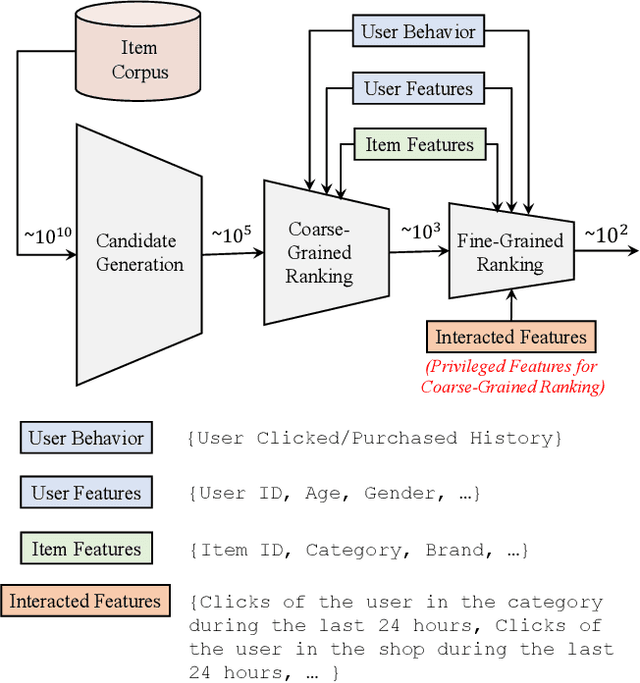
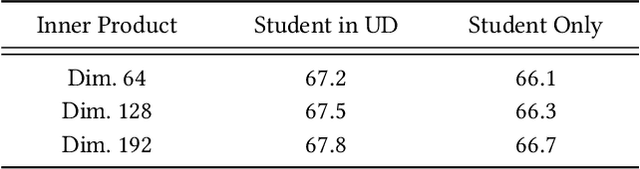
Abstract:Features play an important role in most prediction tasks of e-commerce recommendations. To guarantee the consistence of off-line training and on-line serving, we usually utilize the same features that are both available. However, the consistence in turn neglects some discriminative features. For example, when estimating the conversion rate (CVR), i.e., the probability that a user would purchase the item after she has clicked it, features like dwell time on the item detailed page can be very informative. However, CVR prediction should be conducted for on-line ranking before the click happens. Thus we cannot get such post-event features during serving. Here we define the features that are discriminative but only available during training as the privileged features. Inspired by the distillation techniques which bridge the gap between training and inference, in this work, we propose privileged features distillation (PFD). We train two models, i.e., a student model that is the same as the original one and a teacher model that additionally utilizes the privileged features. Knowledge distilled from the more accurate teacher is transferred to the student, which helps to improve its prediction accuracy. During serving, only the student part is extracted. To our knowledge, this is the first work to fully exploit the potential of such features. To validate the effectiveness of PFD, we conduct experiments on two fundamental prediction tasks in Taobao recommendations, i.e., click-through rate (CTR) at coarse-grained ranking and CVR at fine-grained ranking. By distilling the interacted features that are prohibited during serving for CTR and the post-event features for CVR, we achieve significant improvements over both of the strong baselines. Besides, by addressing several issues of training PFD, we obtain comparable training speed as the baselines without any distillation.
Personalized Context-aware Re-ranking for E-commerce Recommender Systems
Apr 15, 2019
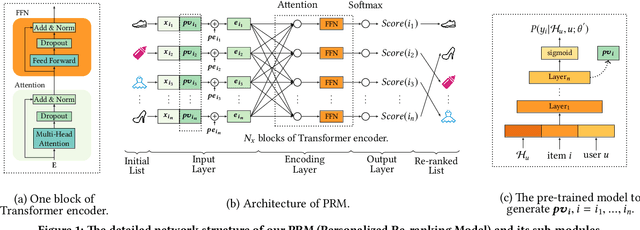

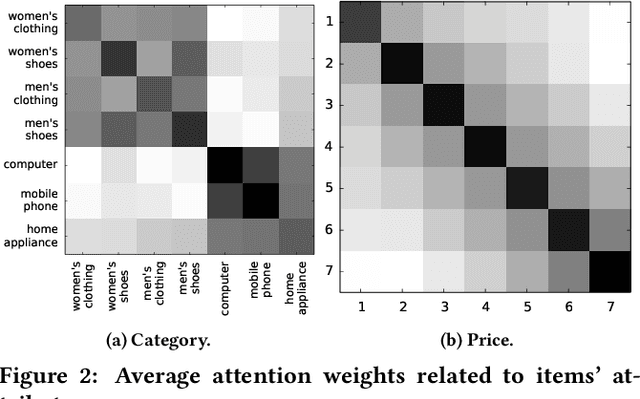
Abstract:Ranking is a core task in E-commerce recommender systems, which aims at providing an ordered list of items to users. Typically, a ranking function is learned from the labeled dataset to optimize the global performance, which produces a ranking score for each individual item. However, it may be sub-optimal because the scoring function applies to each item individually and does not explicitly consider the mutual influence between items, as well as the differences of users' preferences or intents. Therefore, we propose a personalized context-aware re-ranking model for E-commerce recommender systems. The proposed re-ranking model can be easily deployed as a follow-up modular after ranking by directly using the existing feature vectors of ranking. It directly optimizes the whole recommendation list by employing a transformer structure to efficiently encode the information of all items in the list. Specifically, the Transformer applies a self-attention mechanism that directly models the global relationships between any pair of items in the whole list. Besides, we introduce the personalized embedding to model the differences between feature distributions for different users. Experimental results on both offline benchmarks and real-world online E-commerce systems demonstrate the significant improvements of the proposed re-ranking model.
Multi-Source Pointer Network for Product Title Summarization
Oct 08, 2018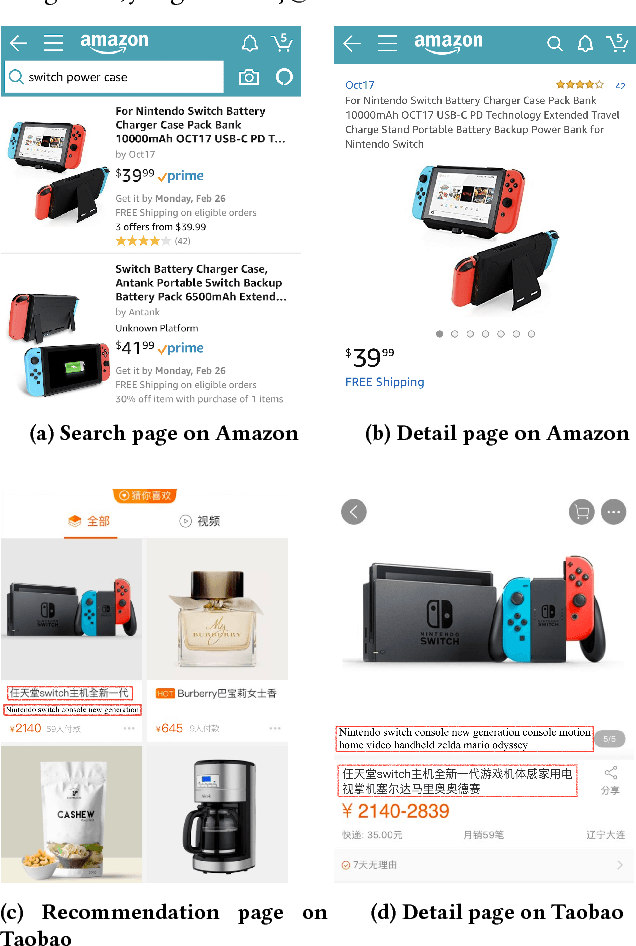

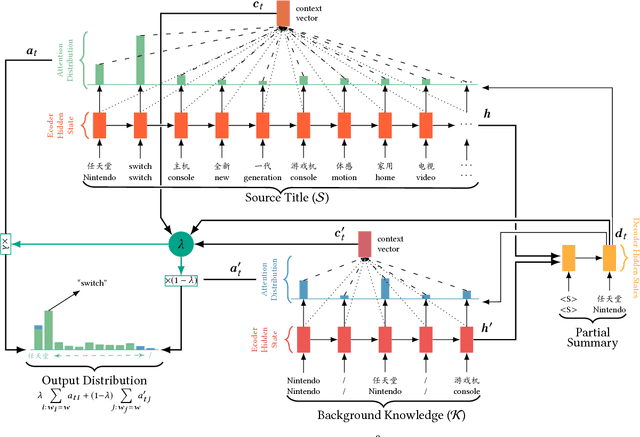
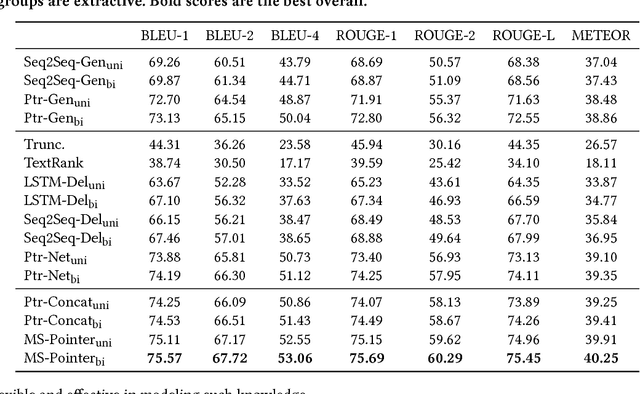
Abstract:In this paper, we study the product title summarization problem in E-commerce applications for display on mobile devices. Comparing with conventional sentence summarization, product title summarization has some extra and essential constraints. For example, factual errors or loss of the key information are intolerable for E-commerce applications. Therefore, we abstract two more constraints for product title summarization: (i) do not introduce irrelevant information; (ii) retain the key information (e.g., brand name and commodity name). To address these issues, we propose a novel multi-source pointer network by adding a new knowledge encoder for pointer network. The first constraint is handled by pointer mechanism. For the second constraint, we restore the key information by copying words from the knowledge encoder with the help of the soft gating mechanism. For evaluation, we build a large collection of real-world product titles along with human-written short titles. Experimental results demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms the other baselines. Finally, online deployment of our proposed model has yielded a significant business impact, as measured by the click-through rate.
Combination of Diverse Ranking Models for Personalized Expedia Hotel Searches
Nov 29, 2013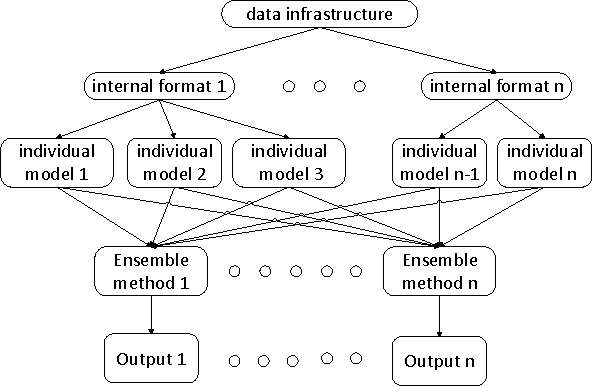
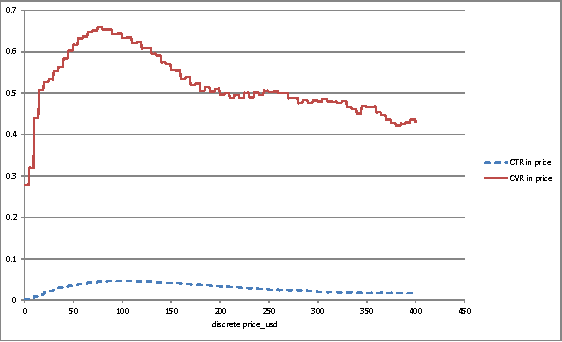
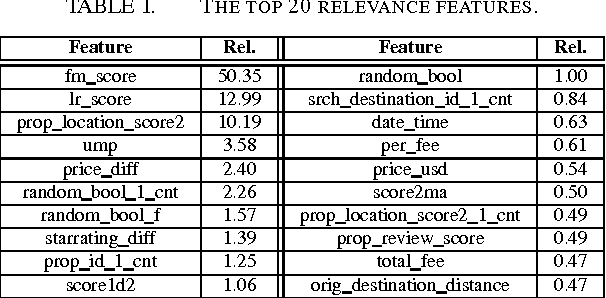

Abstract:The ICDM Challenge 2013 is to apply machine learning to the problem of hotel ranking, aiming to maximize purchases according to given hotel characteristics, location attractiveness of hotels, user's aggregated purchase history and competitive online travel agency information for each potential hotel choice. This paper describes the solution of team "binghsu & MLRush & BrickMover". We conduct simple feature engineering work and train different models by each individual team member. Afterwards, we use listwise ensemble method to combine each model's output. Besides describing effective model and features, we will discuss about the lessons we learned while using deep learning in this competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge