Bing Xu
DSFC-Net: A Dual-Encoder Spatial and Frequency Co-Awareness Network for Rural Road Extraction
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Accurate extraction of rural roads from high-resolution remote sensing imagery is essential for infrastructure planning and sustainable development. However, this task presents unique challenges in rural settings due to several factors. These include high intra-class variability and low inter-class separability from diverse surface materials, frequent vegetation occlusions that disrupt spatial continuity, and narrow road widths that exacerbate detection difficulties. Existing methods, primarily optimized for structured urban environments, often underperform in these scenarios as they overlook such distinctive characteristics. To address these challenges, we propose DSFC-Net, a dual-encoder framework that synergistically fuses spatial and frequency-domain information. Specifically, a CNN branch is employed to capture fine-grained local road boundaries and short-range continuity, while a novel Spatial-Frequency Hybrid Transformer (SFT) is introduced to robustly model global topological dependencies against vegetation occlusions. Distinct from standard attention mechanisms that suffer from frequency bias, the SFT incorporates a Cross-Frequency Interaction Attention (CFIA) module that explicitly decouples high- and low-frequency information via a Laplacian Pyramid strategy. This design enables the dynamic interaction between spatial details and frequency-aware global contexts, effectively preserving the connectivity of narrow roads. Furthermore, a Channel Feature Fusion Module (CFFM) is proposed to bridge the two branches by adaptively recalibrating channel-wise feature responses, seamlessly integrating local textures with global semantics for accurate segmentation. Comprehensive experiments on the WHU-RuR+, DeepGlobe, and Massachusetts datasets validate the superiority of DSFC-Net over state-of-the-art approaches.
VibeTensor: System Software for Deep Learning, Fully Generated by AI Agents
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:VIBETENSOR is an open-source research system software stack for deep learning, generated by LLM-powered coding agents under high-level human guidance. In this paper, "fully generated" refers to code provenance: implementation changes were produced and applied as agent-proposed diffs; validation relied on agent-run builds, tests, and differential checks, without per-change manual diff review. It implements a PyTorch-style eager tensor library with a C++20 core (CPU+CUDA), a torch-like Python overlay via nanobind, and an experimental Node.js/TypeScript interface. Unlike thin bindings, VIBETENSOR includes its own tensor/storage system, schema-lite dispatcher, reverse-mode autograd, CUDA runtime (streams/events/graphs), a stream-ordered caching allocator with diagnostics, and a stable C ABI for dynamically loaded operator plugins. We view this release as a milestone for AI-assisted software engineering: it shows coding agents can generate a coherent deep learning runtime spanning language bindings down to CUDA memory management, validated primarily by builds and tests. We describe the architecture, summarize the workflow used to produce and validate the system, and evaluate the artifact. We report repository scale and test-suite composition, and summarize reproducible microbenchmarks from an accompanying AI-generated kernel suite, including fused attention versus PyTorch SDPA/FlashAttention. We also report end-to-end training sanity checks on 3 small workloads (sequence reversal, ViT, miniGPT) on NVIDIA H100 (Hopper, SM90) and Blackwell-class GPUs; multi-GPU results are Blackwell-only and use an optional CUTLASS-based ring-allreduce plugin gated on CUDA 13+ and sm103a toolchain support. Finally, we discuss failure modes in generated system software, including a "Frankenstein" composition effect where locally correct subsystems interact to yield globally suboptimal performance.
A Novel Modeling Framework and Data Product for Extended VIIRS-like Artificial Nighttime Light Image Reconstruction (1986-2024)
Aug 01, 2025
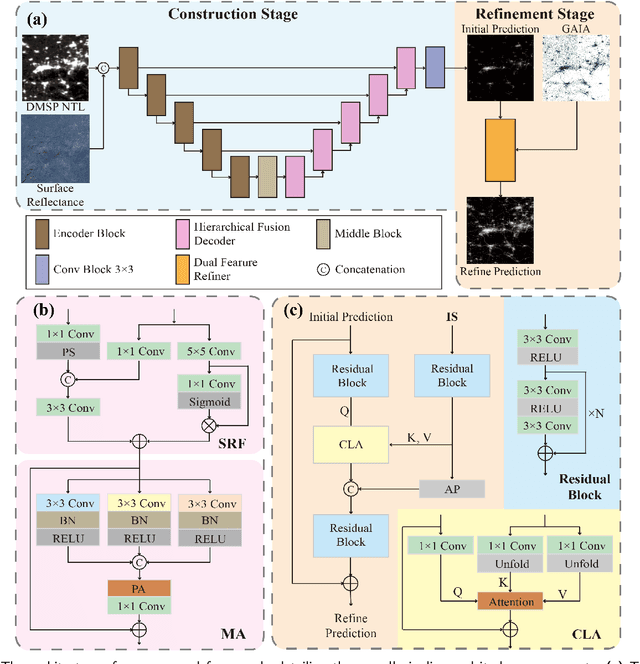
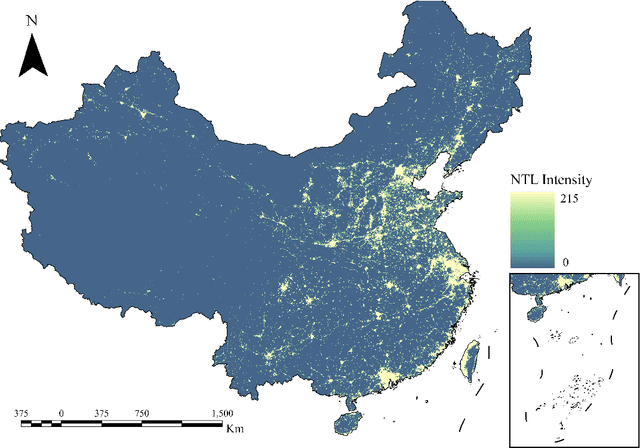

Abstract:Artificial Night-Time Light (NTL) remote sensing is a vital proxy for quantifying the intensity and spatial distribution of human activities. Although the NPP-VIIRS sensor provides high-quality NTL observations, its temporal coverage, which begins in 2012, restricts long-term time-series studies that extend to earlier periods. Despite the progress in extending VIIRS-like NTL time-series, current methods still suffer from two significant shortcomings: the underestimation of light intensity and the structural omission. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel reconstruction framework consisting of a two-stage process: construction and refinement. The construction stage features a Hierarchical Fusion Decoder (HFD) designed to enhance the fidelity of the initial reconstruction. The refinement stage employs a Dual Feature Refiner (DFR), which leverages high-resolution impervious surface masks to guide and enhance fine-grained structural details. Based on this framework, we developed the Extended VIIRS-like Artificial Nighttime Light (EVAL) product for China, extending the standard data record backwards by 26 years to begin in 1986. Quantitative evaluation shows that EVAL significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art products, boosting the $\text{R}^2$ from 0.68 to 0.80 while lowering the RMSE from 1.27 to 0.99. Furthermore, EVAL exhibits excellent temporal consistency and maintains a high correlation with socioeconomic parameters, confirming its reliability for long-term analysis. The resulting EVAL dataset provides a valuable new resource for the research community and is publicly available at https://doi.org/10.11888/HumanNat.tpdc.302930.
Lost in Benchmarks? Rethinking Large Language Model Benchmarking with Item Response Theory
May 21, 2025



Abstract:The evaluation of large language models (LLMs) via benchmarks is widespread, yet inconsistencies between different leaderboards and poor separability among top models raise concerns about their ability to accurately reflect authentic model capabilities. This paper provides a critical analysis of benchmark effectiveness, examining main-stream prominent LLM benchmarks using results from diverse models. We first propose a new framework for accurate and reliable estimations of item characteristics and model abilities. Specifically, we propose Pseudo-Siamese Network for Item Response Theory (PSN-IRT), an enhanced Item Response Theory framework that incorporates a rich set of item parameters within an IRT-grounded architecture. Based on PSN-IRT, we conduct extensive analysis which reveals significant and varied shortcomings in the measurement quality of current benchmarks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that leveraging PSN-IRT is able to construct smaller benchmarks while maintaining stronger alignment with human preference.
Generalized Neighborhood Attention: Multi-dimensional Sparse Attention at the Speed of Light
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Many sparse attention mechanisms such as Neighborhood Attention have typically failed to consistently deliver speedup over the self attention baseline. This is largely due to the level of complexity in attention infrastructure, and the rapid evolution of AI hardware architecture. At the same time, many state-of-the-art foundational models, particularly in computer vision, are heavily bound by attention, and need reliable sparsity to escape the O(n^2) complexity. In this paper, we study a class of promising sparse attention mechanisms that focus on locality, and aim to develop a better analytical model of their performance improvements. We first introduce Generalized Neighborhood Attention (GNA), which can describe sliding window, strided sliding window, and blocked attention. We then consider possible design choices in implementing these approaches, and create a simulator that can provide much more realistic speedup upper bounds for any given setting. Finally, we implement GNA on top of a state-of-the-art fused multi-headed attention (FMHA) kernel designed for the NVIDIA Blackwell architecture in CUTLASS. Our implementation can fully realize the maximum speedup theoretically possible in many perfectly block-sparse cases, and achieves an effective utilization of 1.3 petaFLOPs/second in FP16. In addition, we plug various GNA configurations into off-the-shelf generative models, such as Cosmos-7B, HunyuanVideo, and FLUX, and show that it can deliver 28% to 46% end-to-end speedup on B200 without any fine-tuning. We will open source our simulator and Blackwell kernels directly through the NATTEN project.
SRLCG: Self-Rectified Large-Scale Code Generation with Multidimensional Chain-of-Thought and Dynamic Backtracking
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized code generation, significantly enhancing developer productivity. However, for a vast number of users with minimal coding knowledge, LLMs provide little support, as they primarily generate isolated code snippets rather than complete, large-scale project code. Without coding expertise, these users struggle to interpret, modify, and iteratively refine the outputs of LLMs, making it impossible to assemble a complete project. To address this issue, we propose Self-Rectified Large-Scale Code Generator (SRLCG), a framework that generates complete multi-file project code from a single prompt. SRLCG employs a novel multidimensional chain-of-thought (CoT) and self-rectification to guide LLMs in generating correct and robust code files, then integrates them into a complete and coherent project using our proposed dynamic backtracking algorithm. Experimental results show that SRLCG generates code 15x longer than DeepSeek-V3, 16x longer than GPT-4, and at least 10x longer than other leading CoT-based baselines. Furthermore, they confirm its improved correctness, robustness, and performance compared to baselines in large-scale code generation.
5G Direct Position Estimation for Precise Localization in Dense Urban Area
Feb 25, 2025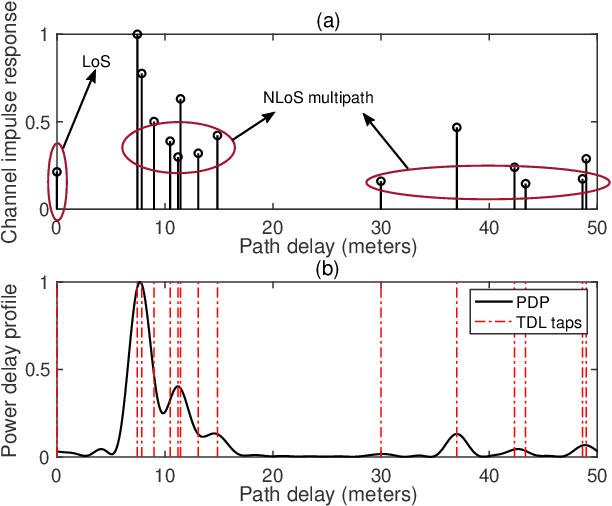
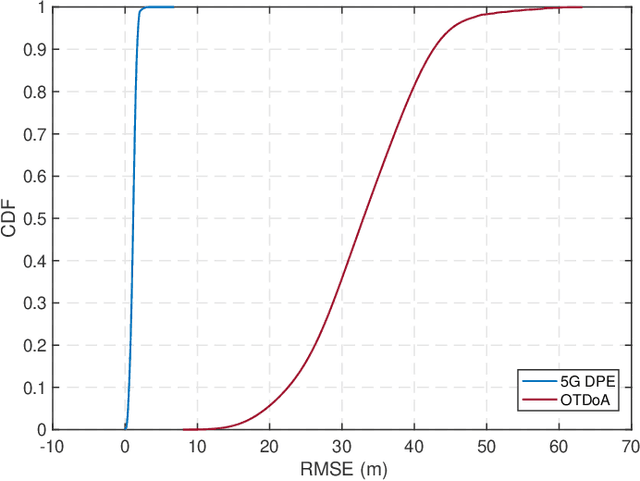
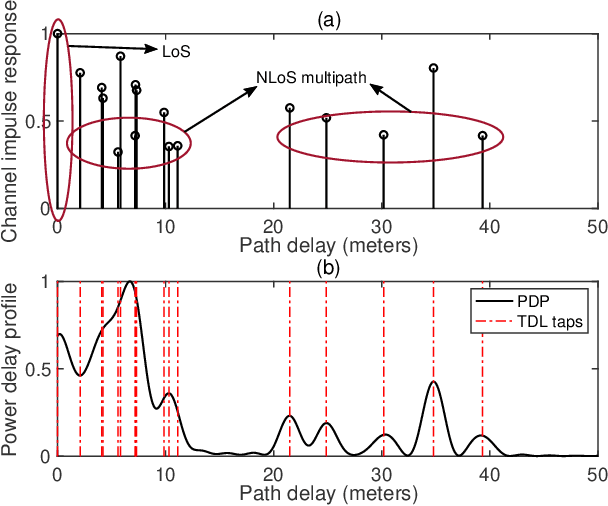
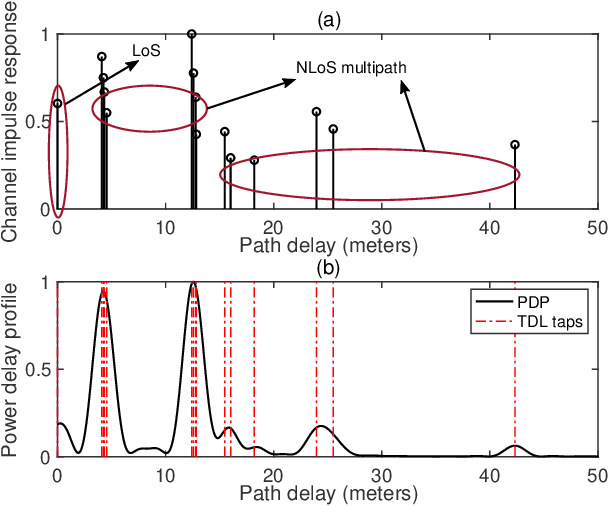
Abstract:In recent years, the fifth-generation (5G) new radio (NR) signals have emerged as a promising supplementary resource for urban navigation. However, a major challenge in utilizing 5G signals lies in their vulnerability to non-line-of-sight (NLoS) propagation effects, which are especially prevalent in urban street canyons. This paper applies the direct position estimation (DPE) method to 5G cellular signals to mitigate the NLoS bias as well as the multipath effects, thereby enabling precise localization in urbanized environments. The feasibility of applying the DPE method to NR positioning is analyzed, followed by a discussion of the tapped delay line (TDL) channel propagation model provided by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). The positioning performance is then evaluated through large-scale system-level simulations. The simulation results demonstrate that 5G DPE achieves satisfactory positioning accuracy in a 10 dB noisy channel, with an overall root mean square error (RMSE) constrained within 6 m. In addition, 5G DPE outperforms the observed time difference of arrival (OTDoA) method by 95.24% in terms of positioning accuracy in an NLoS-dominated propagation environment.
MuSC: Improving Complex Instruction Following with Multi-granularity Self-Contrastive Training
Feb 17, 2025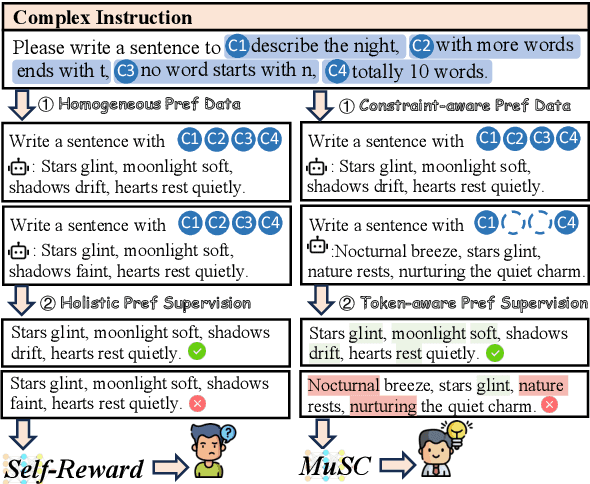



Abstract:Complex instruction-following with elaborate constraints is imperative for Large Language Models (LLMs). While existing methods have constructed data for complex instruction alignment, they all rely on a more advanced model, especially GPT-4, limiting their application. In this paper, we propose a Multi-granularity Self-Contrastive Training (MuSC) framework, to improve the complex instruction alignment without relying on a stronger model. Our method is conducted on both coarse and fine granularity. On coarse-granularity, we construct constraint-aware preference data based on instruction decomposition and recombination. On fine-granularity, we perform token-aware preference optimization with dynamic token-level supervision. Our method is evaluated on open-sourced models, and experiment results show our method achieves significant improvement on both complex and general instruction-following benchmarks, surpassing previous self-alignment methods.
Multipath Mitigation Technology-integrated GNSS Direct Position Estimation Plug-in Module
Nov 20, 2024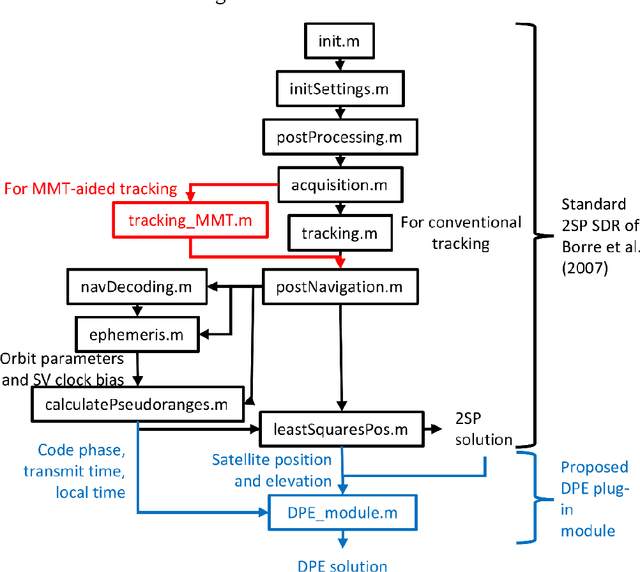
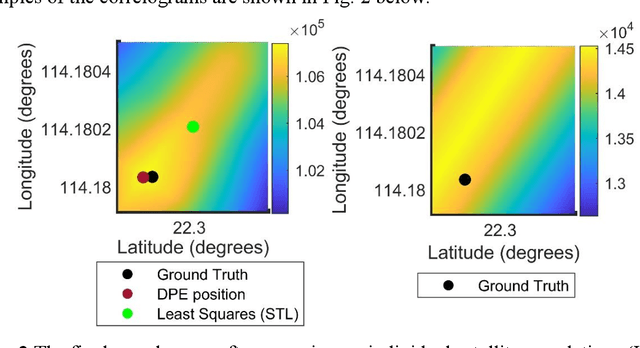
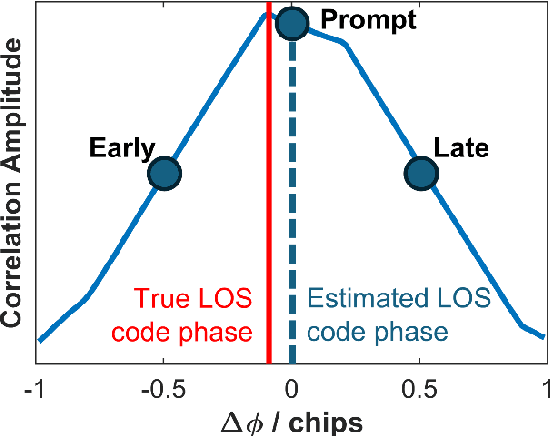
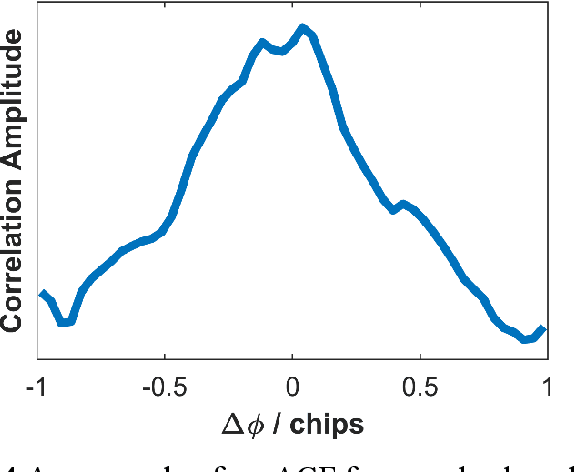
Abstract:Direct position estimation (DPE) is an effective solution to the MP issue at the signal processing level. Unlike two-step positioning (2SP) receivers, DPE directly solves for the receiver position, velocity, and time (PVT) in the navigation domain, without the estimation of intermediate measurements, thus allowing it to provide more robust and accurate PVT estimates in the presence of multipath (MP) and weak signals. But GNSS positioning with DPE is mostly left unapplied commercially, and continuing research into DPE has remained relatively stagnant over the past few years. To encourage further research on DPE by the GNSS community, we propose a DPE plug-in module that can be integrated into the conventional 2SP software-defined receivers (SDRs). Programmed in MATLAB, the proposed DPE plug-in module is aimed for better understanding and familiarity of a practical implementation of DPE. Its plug-in module architecture allows it to be incorporated with 2SP MATLAB SDRs, both vector tracking and scalar tracking with minimum changes, making it easy to use, and provides greater flexibility for researchers using various 2SP SDRs. Since the proposed DPE implementation makes use of tracking observables from 2SP to propagate the channel, we propose to further improve the performance of DPE against MP through using MP-compensated observables generated from Multipath Mitigation Technology (MMT)-aided tracking. Referred to as Multipath Mitigation Technology (MMT)-integrated DPE, it is proposed as a variant of DPE that is better suit for urban environment applications. Results show that while in MP-only conditions, an MMT-integrated 2SP has similar performance with MMT-integrated DPE, the proposed MMT-integrated DPE manages to show great superiority against non-line-of-sight (NLOS), making it the preferable option for applications in urban environments.
PMoL: Parameter Efficient MoE for Preference Mixing of LLM Alignment
Nov 02, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has been proven to be an effective method for preference alignment of large language models (LLMs) and is widely used in the post-training process of LLMs. However, RLHF struggles with handling multiple competing preferences. This leads to a decrease in the alignment of LLMs with human preferences. To address this issue, we propose Preference Mixture of LoRAs (PMoL) from the perspective of model architecture, which can adapt to any number of preferences to mix. PMoL combines Mixture of Experts (MoE) and Low Rank Adaptor (LoRA). This architecture is innovatively applied to the research of preference alignment and has achieved significant performance improvement. The expert group soft loss is used to enable MoE with the ability to mix preferences. Through comprehensive evaluation by the reward model and GPT-4o, the experiment results show that PMoL has superior preference mixing capabilities compared to baseline methods. PMoL achieves better preference alignment with lower training costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge