Sergio Vicenzo
5G Direct Position Estimation for Precise Localization in Dense Urban Area
Feb 25, 2025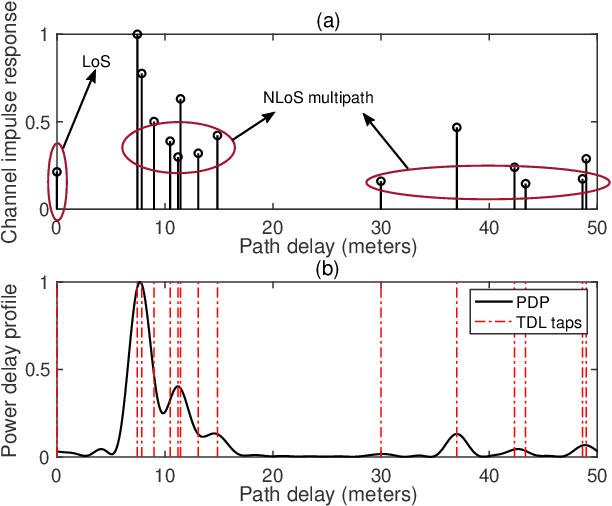
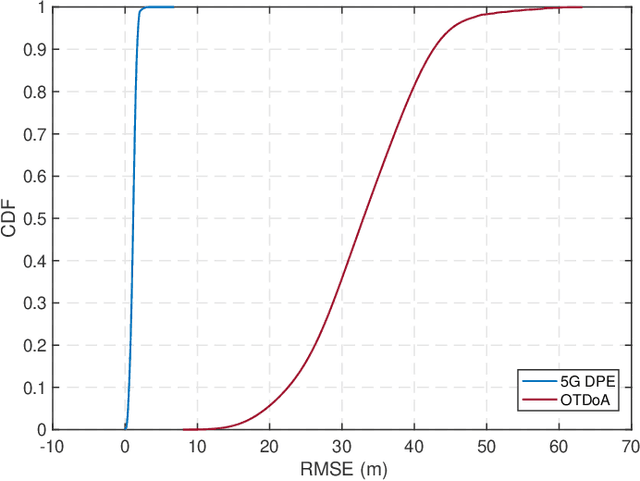
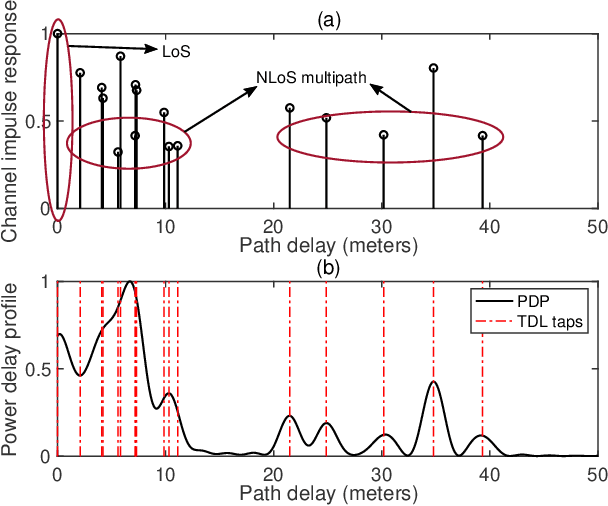
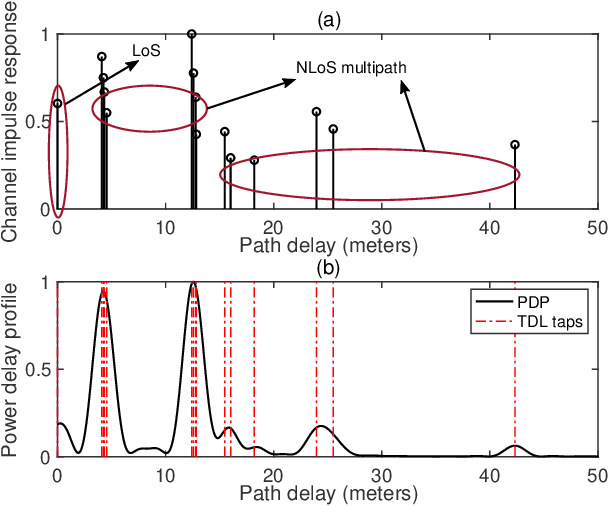
Abstract:In recent years, the fifth-generation (5G) new radio (NR) signals have emerged as a promising supplementary resource for urban navigation. However, a major challenge in utilizing 5G signals lies in their vulnerability to non-line-of-sight (NLoS) propagation effects, which are especially prevalent in urban street canyons. This paper applies the direct position estimation (DPE) method to 5G cellular signals to mitigate the NLoS bias as well as the multipath effects, thereby enabling precise localization in urbanized environments. The feasibility of applying the DPE method to NR positioning is analyzed, followed by a discussion of the tapped delay line (TDL) channel propagation model provided by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). The positioning performance is then evaluated through large-scale system-level simulations. The simulation results demonstrate that 5G DPE achieves satisfactory positioning accuracy in a 10 dB noisy channel, with an overall root mean square error (RMSE) constrained within 6 m. In addition, 5G DPE outperforms the observed time difference of arrival (OTDoA) method by 95.24% in terms of positioning accuracy in an NLoS-dominated propagation environment.
Multipath Mitigation Technology-integrated GNSS Direct Position Estimation Plug-in Module
Nov 20, 2024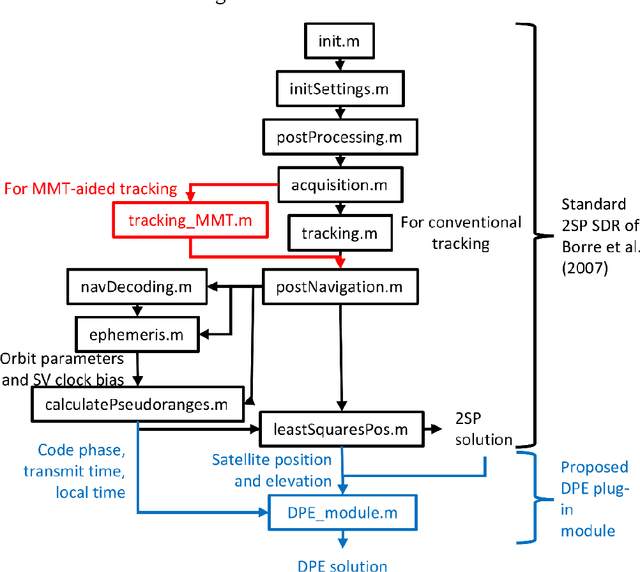
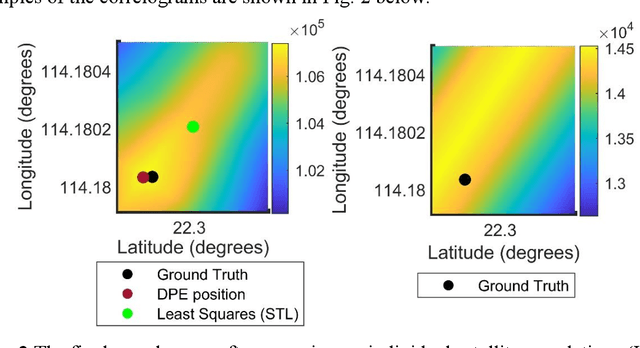
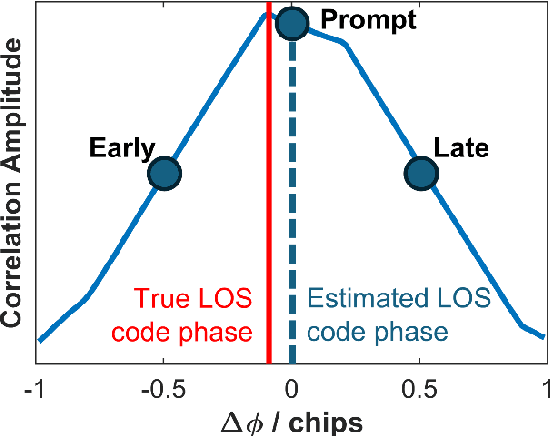
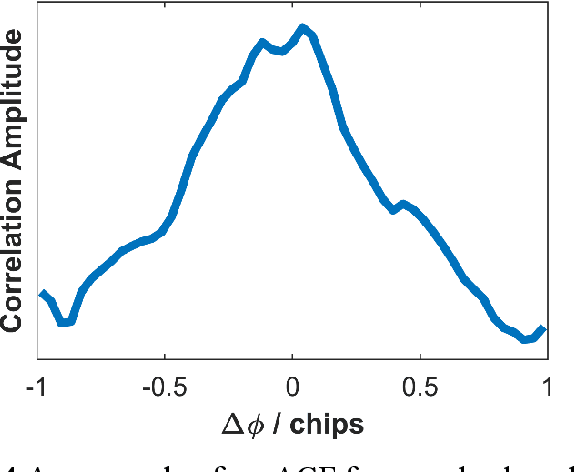
Abstract:Direct position estimation (DPE) is an effective solution to the MP issue at the signal processing level. Unlike two-step positioning (2SP) receivers, DPE directly solves for the receiver position, velocity, and time (PVT) in the navigation domain, without the estimation of intermediate measurements, thus allowing it to provide more robust and accurate PVT estimates in the presence of multipath (MP) and weak signals. But GNSS positioning with DPE is mostly left unapplied commercially, and continuing research into DPE has remained relatively stagnant over the past few years. To encourage further research on DPE by the GNSS community, we propose a DPE plug-in module that can be integrated into the conventional 2SP software-defined receivers (SDRs). Programmed in MATLAB, the proposed DPE plug-in module is aimed for better understanding and familiarity of a practical implementation of DPE. Its plug-in module architecture allows it to be incorporated with 2SP MATLAB SDRs, both vector tracking and scalar tracking with minimum changes, making it easy to use, and provides greater flexibility for researchers using various 2SP SDRs. Since the proposed DPE implementation makes use of tracking observables from 2SP to propagate the channel, we propose to further improve the performance of DPE against MP through using MP-compensated observables generated from Multipath Mitigation Technology (MMT)-aided tracking. Referred to as Multipath Mitigation Technology (MMT)-integrated DPE, it is proposed as a variant of DPE that is better suit for urban environment applications. Results show that while in MP-only conditions, an MMT-integrated 2SP has similar performance with MMT-integrated DPE, the proposed MMT-integrated DPE manages to show great superiority against non-line-of-sight (NLOS), making it the preferable option for applications in urban environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge