Shanshan Lyu
Towards Computation- and Communication-efficient Computational Pathology
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Despite the impressive performance across a wide range of applications, current computational pathology models face significant diagnostic efficiency challenges due to their reliance on high-magnification whole-slide image analysis. This limitation severely compromises their clinical utility, especially in time-sensitive diagnostic scenarios and situations requiring efficient data transfer. To address these issues, we present a novel computation- and communication-efficient framework called Magnification-Aligned Global-Local Transformer (MAGA-GLTrans). Our approach significantly reduces computational time, file transfer requirements, and storage overhead by enabling effective analysis using low-magnification inputs rather than high-magnification ones. The key innovation lies in our proposed magnification alignment (MAGA) mechanism, which employs self-supervised learning to bridge the information gap between low and high magnification levels by effectively aligning their feature representations. Through extensive evaluation across various fundamental CPath tasks, MAGA-GLTrans demonstrates state-of-the-art classification performance while achieving remarkable efficiency gains: up to 10.7 times reduction in computational time and over 20 times reduction in file transfer and storage requirements. Furthermore, we highlight the versatility of our MAGA framework through two significant extensions: (1) its applicability as a feature extractor to enhance the efficiency of any CPath architecture, and (2) its compatibility with existing foundation models and histopathology-specific encoders, enabling them to process low-magnification inputs with minimal information loss. These advancements position MAGA-GLTrans as a particularly promising solution for time-sensitive applications, especially in the context of intraoperative frozen section diagnosis where both accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
Entire Space Learning Framework: Unbias Conversion Rate Prediction in Full Stages of Recommender System
Mar 01, 2023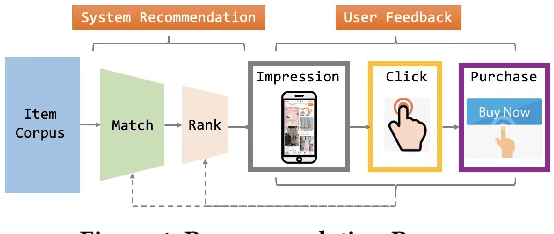

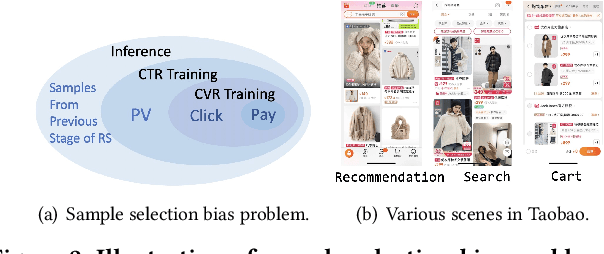

Abstract:Recommender system is an essential part of online services, especially for e-commerce platform. Conversion Rate (CVR) prediction in RS plays a significant role in optimizing Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV) goal of e-commerce. However, CVR suffers from well-known Sample Selection Bias (SSB) and Data Sparsity (DS) problems. Although existing methods ESMM and ESM2 train with all impression samples over the entire space by modeling user behavior paths, SSB and DS problems still exist. In real practice, the online inference space are samples from previous stage of RS process, rather than the impression space modeled by existing methods. Moreover, existing methods solve the DS problem mainly by building behavior paths of their own specific scene, ignoring the behaviors in various scenes of e-commerce platform. In this paper, we propose Entire Space Learning Framework: Unbias Conversion Rate Prediction in Full Stages of Recommender System, solving SSB and DS problems by reformulating GMV goal in a novel manner. Specifically, we rebuild the CVR on the entire data space with samples from previous stage of RS process, unifying training and online inference space. Moreover, we explicitly introduce purchase samples from other scenes of e-commerce platform in model learning process. Online A/B test and offline experiments show the superiority of our framework. Our framework has been deployed in rank stage of Taobao recommendation, providing recommendation service for hundreds of millions of consumers everyday.
GCN-ALP: Addressing Matching Collisions in Anchor Link Prediction
Mar 19, 2021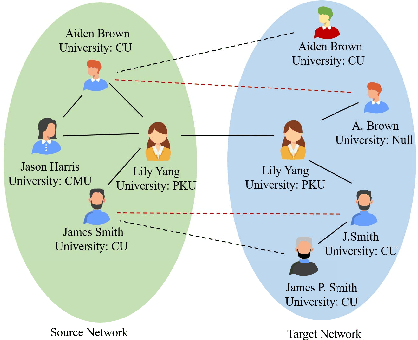
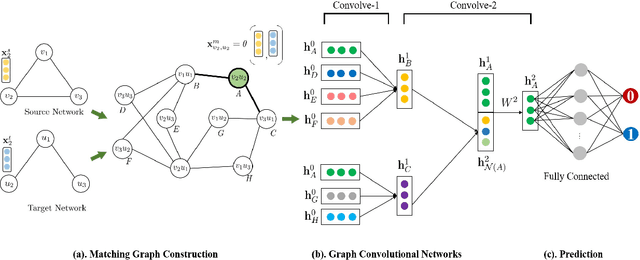
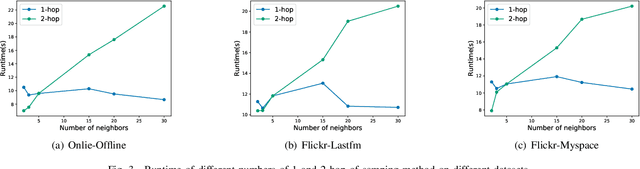
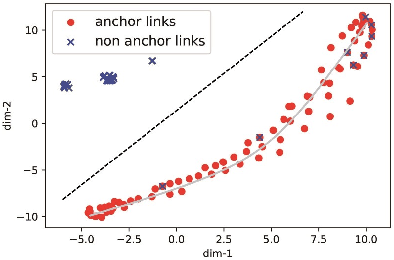
Abstract:Nowadays online users prefer to join multiple social media for the purpose of socialized online service. The problem \textit{anchor link prediction} is formalized to link user data with the common ground on user profile, content and network structure across social networks. Most of the traditional works concentrated on learning matching function with explicit or implicit features on observed user data. However, the low quality of observed user data confuses the judgment on anchor links, resulting in the matching collision problem in practice. In this paper, we explore local structure consistency and then construct a matching graph in order to circumvent matching collisions. Furthermore, we propose graph convolution networks with mini-batch strategy, efficiently solving anchor link prediction on matching graph. The experimental results on three real application scenarios show the great potentials of our proposed method in both prediction accuracy and efficiency. In addition, the visualization of learned embeddings provides us a qualitative way to understand the inference of anchor links on the matching graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge