Luxin Liu
Distilling Task-specific Logical Rules from Large Pre-trained Models
Oct 06, 2022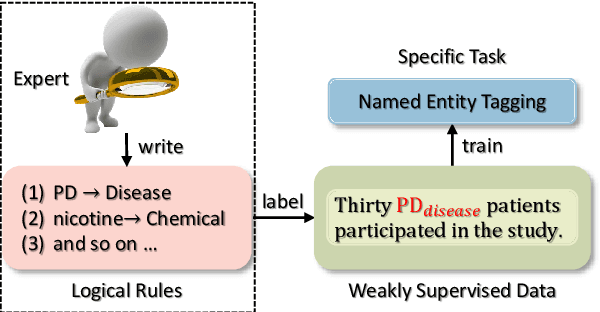
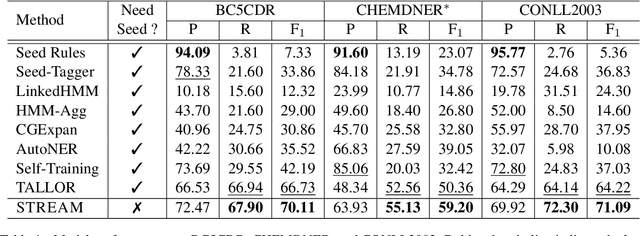
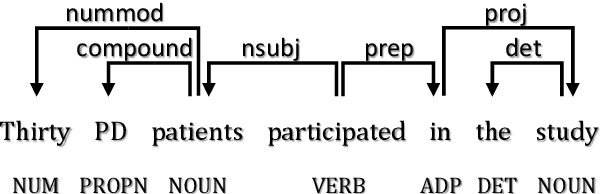
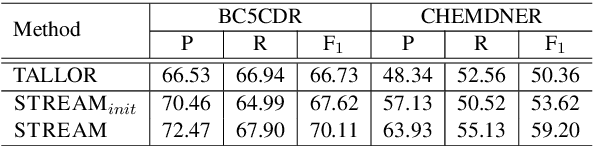
Abstract:Logical rules, both transferable and explainable, are widely used as weakly supervised signals for many downstream tasks such as named entity tagging. To reduce the human effort of writing rules, previous researchers adopt an iterative approach to automatically learn logical rules from several seed rules. However, obtaining more seed rules can only be accomplished by extra human annotation with heavy costs. Limited by the size and quality of the seed rules, the model performance of previous systems is bounded. In this paper, we develop a novel framework STREAM to distill task-specific logical rules from large pre-trained models. Specifically, we borrow recent prompt-based language models as the knowledge expert to yield initial seed rules, and based on the formed high-quality instance pool that acts as an intermediary role, we keep teaching the expert to fit our task and learning task-specific logical rules. Experiments on three public named entity tagging benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework. With several predefined prompt templates, our system has gained significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods.
Commonsense Knowledge Graph Reasoning by Selection or Generation? Why?
Aug 13, 2020



Abstract:Commonsense knowledge graph reasoning(CKGR) is the task of predicting a missing entity given one existing and the relation in a commonsense knowledge graph (CKG). Existing methods can be classified into two categories generation method and selection method. Each method has its own advantage. We theoretically and empirically compare the two methods, finding the selection method is more suitable than the generation method in CKGR. Given the observation, we further combine the structure of neural Text Encoder and Knowledge Graph Embedding models to solve the selection method's two problems, achieving competitive results. We provide a basic framework and baseline model for subsequent CKGR tasks by selection methods.
AliCoCo: Alibaba E-commerce Cognitive Concept Net
Mar 30, 2020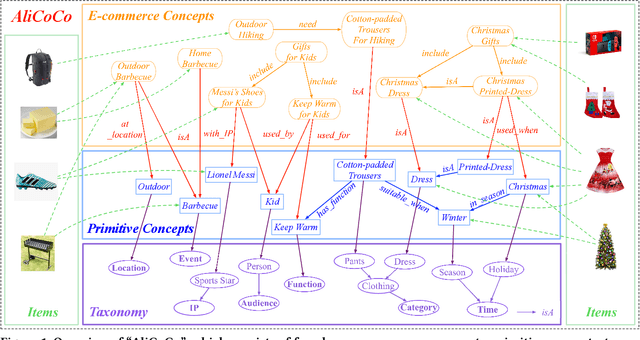
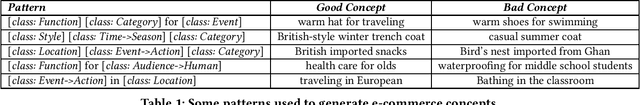
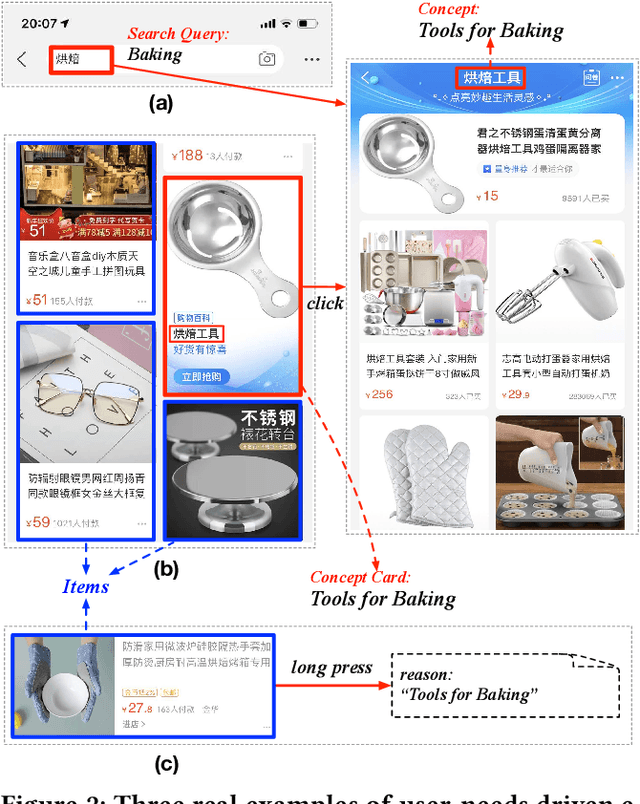
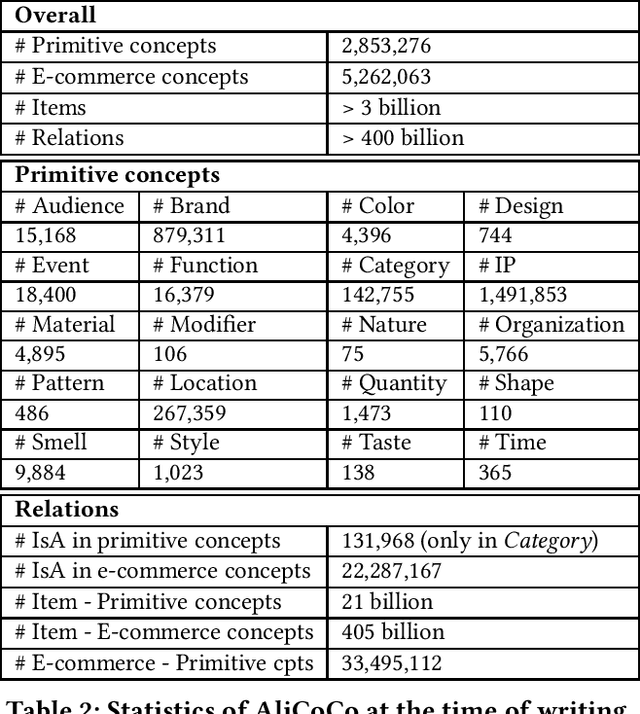
Abstract:One of the ultimate goals of e-commerce platforms is to satisfy various shopping needs for their customers. Much efforts are devoted to creating taxonomies or ontologies in e-commerce towards this goal. However, user needs in e-commerce are still not well defined, and none of the existing ontologies has the enough depth and breadth for universal user needs understanding. The semantic gap in-between prevents shopping experience from being more intelligent. In this paper, we propose to construct a large-scale e-commerce cognitive concept net named "AliCoCo", which is practiced in Alibaba, the largest Chinese e-commerce platform in the world. We formally define user needs in e-commerce, then conceptualize them as nodes in the net. We present details on how AliCoCo is constructed semi-automatically and its successful, ongoing and potential applications in e-commerce.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge