Haihong Tang
Alibaba Group
TaoSearchEmb: A Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning Framework for Dense Retrieval in Taobao Search
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Dense retrieval, as the core component of e-commerce search engines, maps user queries and items into a unified semantic space through pre-trained embedding models to enable large-scale real-time semantic retrieval. Despite the rapid advancement of LLMs gradually replacing traditional BERT architectures for embedding, their training paradigms still adhere to BERT-like supervised fine-tuning and hard negative mining strategies. This approach relies on complex offline hard negative sample construction pipelines, which constrain model iteration efficiency and hinder the evolutionary potential of semantic representation capabilities. Besides, existing multi-task learning frameworks face the seesaw effect when simultaneously optimizing semantic relevance and non-relevance objectives. In this paper, we propose Retrieval-GRPO, a multi-objective reinforcement learning-based dense retrieval framework designed to address these challenges. The method eliminates offline hard negative sample construction by dynamically retrieving Top-K candidate products for each query during training, while introducing a relevance LLM as a reward model to generate real-time feedback. Specifically, the retrieval model dynamically optimizes embedding representations through reinforcement learning, with reward signals combining LLM-generated relevance scores, product quality scores, and multi-way exclusivity metrics to achieve multi-objective user preference alignment and real-time error correction. This mechanism not only removes dependency on hard negatives but also mitigates the seesaw effect through collaborative multi-objective optimization, significantly enhancing the model's semantic generalization capability for complex long-tail queries. Extensive offline and online experiments validate the effectiveness of Retrieval-GRPO, which has been deployed on China's largest e-commerce platform.
TaoSR-SHE: Stepwise Hybrid Examination Reinforcement Learning Framework for E-commerce Search Relevance
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Query-product relevance analysis is a foundational technology in e-commerce search engines and has become increasingly important in AI-driven e-commerce. The recent emergence of large language models (LLMs), particularly their chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning capabilities, offers promising opportunities for developing relevance systems that are both more interpretable and more robust. However, existing training paradigms have notable limitations: SFT and DPO suffer from poor generalization on long-tail queries and from a lack of fine-grained, stepwise supervision to enforce rule-aligned reasoning. In contrast, reinforcement learning with verification rewards (RLVR) suffers from sparse feedback, which provides insufficient signal to correct erroneous intermediate steps, thereby undermining logical consistency and limiting performance in complex inference scenarios. To address these challenges, we introduce the Stepwise Hybrid Examination Reinforcement Learning framework for Taobao Search Relevance (TaoSR-SHE). At its core is Stepwise Reward Policy Optimization (SRPO), a reinforcement learning algorithm that leverages step-level rewards generated by a hybrid of a high-quality generative stepwise reward model and a human-annotated offline verifier, prioritizing learning from critical correct and incorrect reasoning steps. TaoSR-SHE further incorporates two key techniques: diversified data filtering to encourage exploration across varied reasoning paths and mitigate policy entropy collapse, and multi-stage curriculum learning to foster progressive capability growth. Extensive experiments on real-world search benchmarks show that TaoSR-SHE improves both reasoning quality and relevance-prediction accuracy in large-scale e-commerce settings, outperforming SFT, DPO, GRPO, and other baselines, while also enhancing interpretability and robustness.
TaoSR-AGRL: Adaptive Guided Reinforcement Learning Framework for E-commerce Search Relevance
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Query-product relevance prediction is fundamental to e-commerce search and has become even more critical in the era of AI-powered shopping, where semantic understanding and complex reasoning directly shape the user experience and business conversion. Large Language Models (LLMs) enable generative, reasoning-based approaches, typically aligned via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or preference optimization methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). However, the increasing complexity of business rules and user queries exposes the inability of existing methods to endow models with robust reasoning capacity for long-tail and challenging cases. Efforts to address this via reinforcement learning strategies like Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) often suffer from sparse terminal rewards, offering insufficient guidance for multi-step reasoning and slowing convergence. To address these challenges, we propose TaoSR-AGRL, an Adaptive Guided Reinforcement Learning framework for LLM-based relevance prediction in Taobao Search Relevance. TaoSR-AGRL introduces two key innovations: (1) Rule-aware Reward Shaping, which decomposes the final relevance judgment into dense, structured rewards aligned with domain-specific relevance criteria; and (2) Adaptive Guided Replay, which identifies low-accuracy rollouts during training and injects targeted ground-truth guidance to steer the policy away from stagnant, rule-violating reasoning patterns toward compliant trajectories. TaoSR-AGRL was evaluated on large-scale real-world datasets and through online side-by-side human evaluations on Taobao Search. It consistently outperforms DPO and standard GRPO baselines in offline experiments, improving relevance accuracy, rule adherence, and training stability. The model trained with TaoSR-AGRL has been successfully deployed in the main search scenario on Taobao, serving hundreds of millions of users.
TaoSR1: The Thinking Model for E-commerce Relevance Search
Aug 17, 2025



Abstract:Query-product relevance prediction is a core task in e-commerce search. BERT-based models excel at semantic matching but lack complex reasoning capabilities. While Large Language Models (LLMs) are explored, most still use discriminative fine-tuning or distill to smaller models for deployment. We propose a framework to directly deploy LLMs for this task, addressing key challenges: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) error accumulation, discriminative hallucination, and deployment feasibility. Our framework, TaoSR1, involves three stages: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with CoT to instill reasoning; (2) Offline sampling with a pass@N strategy and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to improve generation quality; and (3) Difficulty-based dynamic sampling with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to mitigate discriminative hallucination. Additionally, post-CoT processing and a cumulative probability-based partitioning method enable efficient online deployment. TaoSR1 significantly outperforms baselines on offline datasets and achieves substantial gains in online side-by-side human evaluations, introducing a novel paradigm for applying CoT reasoning to relevance classification.
PUMGPT: A Large Vision-Language Model for Product Understanding
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Recent developments of multi-modal large language models have demonstrated its strong ability in solving vision-language tasks. In this paper, we focus on the product understanding task, which plays an essential role in enhancing online shopping experience. Product understanding task includes a variety of sub-tasks, which require models to respond diverse queries based on multi-modal product information. Traditional methods design distinct model architectures for each sub-task. On the contrary, we present PUMGPT, a large vision-language model aims at unifying all product understanding tasks under a singular model structure. To bridge the gap between vision and text representations, we propose Layer-wise Adapters (LA), an approach that provides enhanced alignment with fewer visual tokens and enables parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Moreover, the inherent parameter-efficient fine-tuning ability allows PUMGPT to be readily adapted to new product understanding tasks and emerging products. We design instruction templates to generate diverse product instruction datasets. Simultaneously, we utilize open-domain datasets during training to improve the performance of PUMGPT and its generalization ability. Through extensive evaluations, PUMGPT demonstrates its superior performance across multiple product understanding tasks, including product captioning, category question-answering, attribute extraction, attribute question-answering, and even free-form question-answering about products.
Improving Text Matching in E-Commerce Search with A Rationalizable, Intervenable and Fast Entity-Based Relevance Model
Jul 01, 2023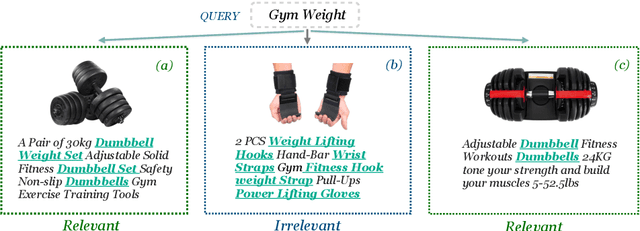
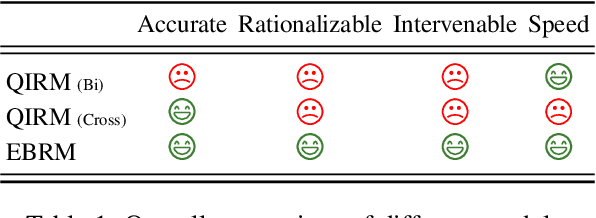
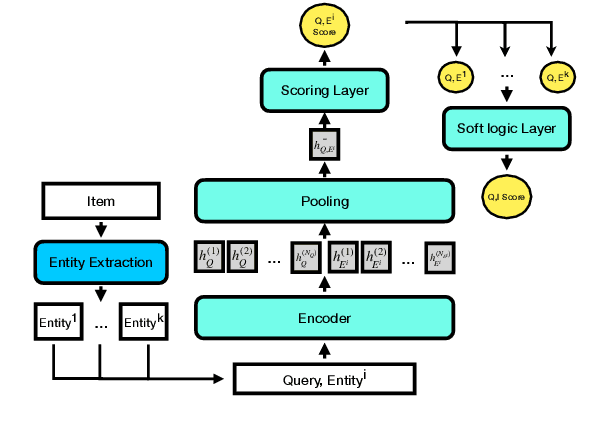
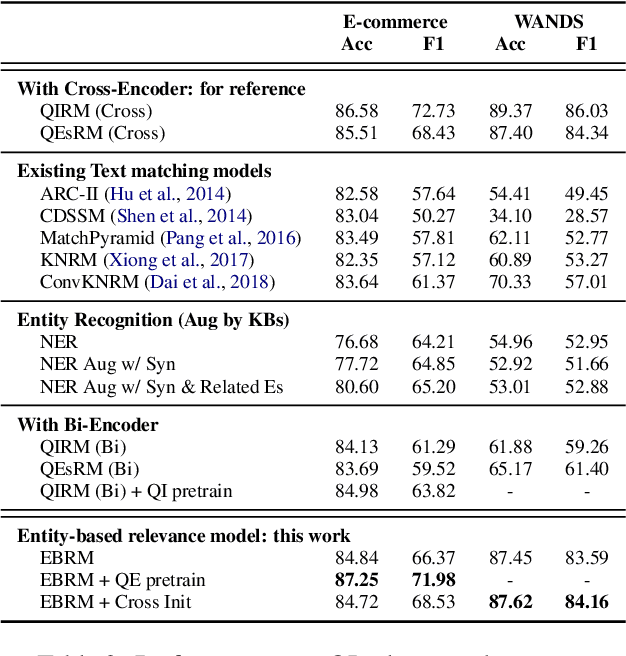
Abstract:Discovering the intended items of user queries from a massive repository of items is one of the main goals of an e-commerce search system. Relevance prediction is essential to the search system since it helps improve performance. When online serving a relevance model, the model is required to perform fast and accurate inference. Currently, the widely used models such as Bi-encoder and Cross-encoder have their limitations in accuracy or inference speed respectively. In this work, we propose a novel model called the Entity-Based Relevance Model (EBRM). We identify the entities contained in an item and decompose the QI (query-item) relevance problem into multiple QE (query-entity) relevance problems; we then aggregate their results to form the QI prediction using a soft logic formulation. The decomposition allows us to use a Cross-encoder QE relevance module for high accuracy as well as cache QE predictions for fast online inference. Utilizing soft logic makes the prediction procedure interpretable and intervenable. We also show that pretraining the QE module with auto-generated QE data from user logs can further improve the overall performance. The proposed method is evaluated on labeled data from e-commerce websites. Empirical results show that it achieves promising improvements with computation efficiency.
Non-stationary Projection-free Online Learning with Dynamic and Adaptive Regret Guarantees
May 19, 2023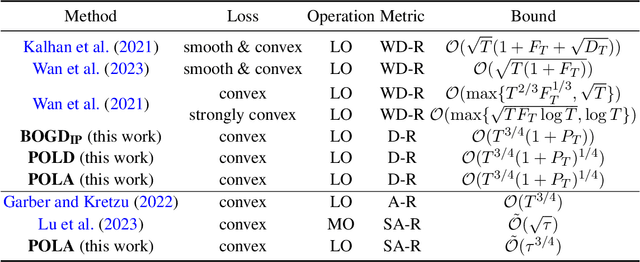
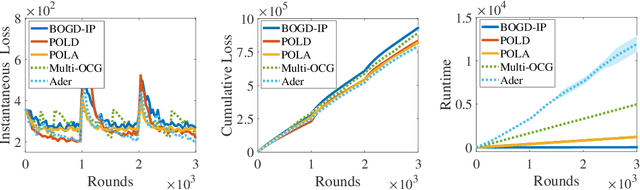
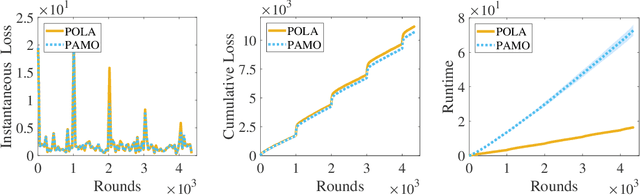
Abstract:Projection-free online learning has drawn increasing interest due to its efficiency in solving high-dimensional problems with complicated constraints. However, most existing projection-free online methods focus on minimizing the static regret, which unfortunately fails to capture the challenge of changing environments. In this paper, we investigate non-stationary projection-free online learning, and choose dynamic regret and adaptive regret to measure the performance. Specifically, we first provide a novel dynamic regret analysis for an existing projection-free method named $\text{BOGD}_\text{IP}$, and establish an $\mathcal{O}(T^{3/4}(1+P_T))$ dynamic regret bound, where $P_T$ denotes the path-length of the comparator sequence. Then, we improve the upper bound to $\mathcal{O}(T^{3/4}(1+P_T)^{1/4})$ by running multiple $\text{BOGD}_\text{IP}$ algorithms with different step sizes in parallel, and tracking the best one on the fly. Our results are the first general-case dynamic regret bounds for projection-free online learning, and can recover the existing $\mathcal{O}(T^{3/4})$ static regret by setting $P_T = 0$. Furthermore, we propose a projection-free method to attain an $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(\tau^{3/4})$ adaptive regret bound for any interval with length $\tau$, which nearly matches the static regret over that interval. The essential idea is to maintain a set of $\text{BOGD}_\text{IP}$ algorithms dynamically, and combine them by a meta algorithm. Moreover, we demonstrate that it is also equipped with an $\mathcal{O}(T^{3/4}(1+P_T)^{1/4})$ dynamic regret bound. Finally, empirical studies verify our theoretical findings.
Distilling Task-specific Logical Rules from Large Pre-trained Models
Oct 06, 2022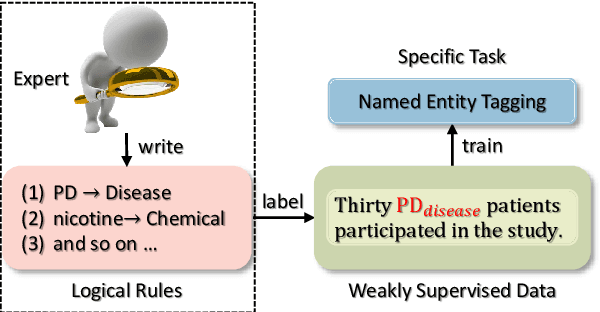
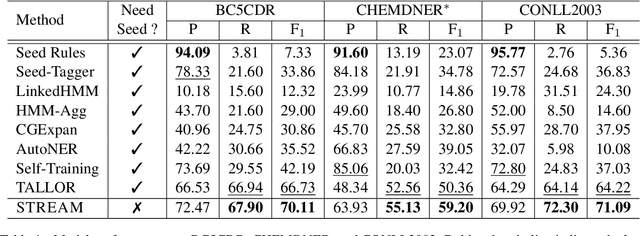
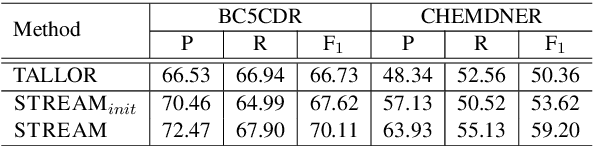
Abstract:Logical rules, both transferable and explainable, are widely used as weakly supervised signals for many downstream tasks such as named entity tagging. To reduce the human effort of writing rules, previous researchers adopt an iterative approach to automatically learn logical rules from several seed rules. However, obtaining more seed rules can only be accomplished by extra human annotation with heavy costs. Limited by the size and quality of the seed rules, the model performance of previous systems is bounded. In this paper, we develop a novel framework STREAM to distill task-specific logical rules from large pre-trained models. Specifically, we borrow recent prompt-based language models as the knowledge expert to yield initial seed rules, and based on the formed high-quality instance pool that acts as an intermediary role, we keep teaching the expert to fit our task and learning task-specific logical rules. Experiments on three public named entity tagging benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework. With several predefined prompt templates, our system has gained significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods.
Shape Controllable Virtual Try-on for Underwear Models
Jul 28, 2021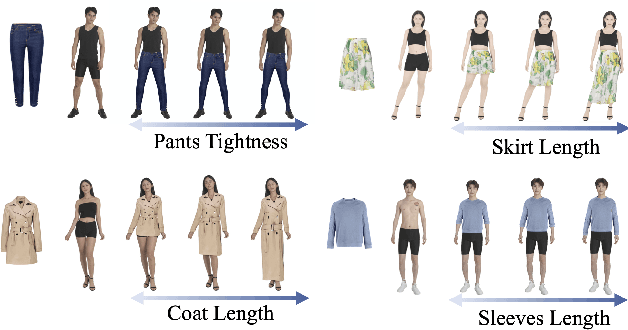
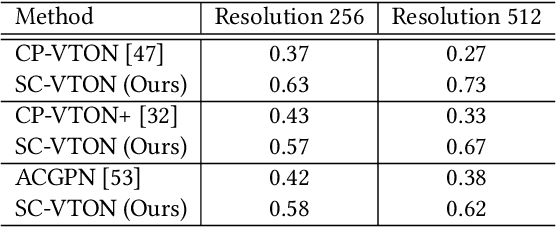
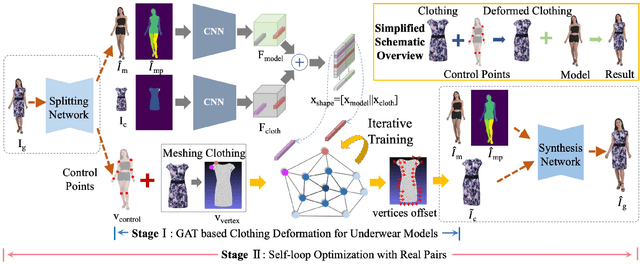
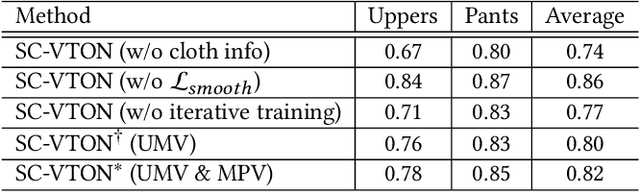
Abstract:Image virtual try-on task has abundant applications and has become a hot research topic recently. Existing 2D image-based virtual try-on methods aim to transfer a target clothing image onto a reference person, which has two main disadvantages: cannot control the size and length precisely; unable to accurately estimate the user's figure in the case of users wearing thick clothes, resulting in inaccurate dressing effect. In this paper, we put forward an akin task that aims to dress clothing for underwear models. %, which is also an urgent need in e-commerce scenarios. To solve the above drawbacks, we propose a Shape Controllable Virtual Try-On Network (SC-VTON), where a graph attention network integrates the information of model and clothing to generate the warped clothing image. In addition, the control points are incorporated into SC-VTON for the desired clothing shape. Furthermore, by adding a Splitting Network and a Synthesis Network, we can use clothing/model pair data to help optimize the deformation module and generalize the task to the typical virtual try-on task. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method can achieve accurate shape control. Meanwhile, compared with other methods, our method can generate high-resolution results with detailed textures.
SGPT: Semantic Graphs based Pre-training for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
May 26, 2021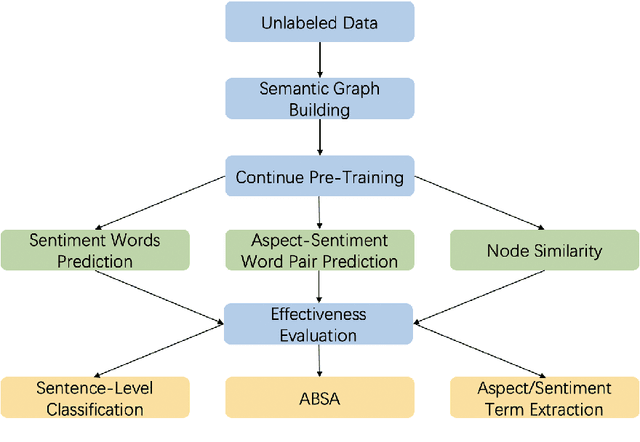
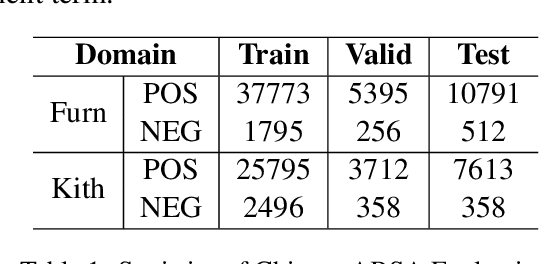
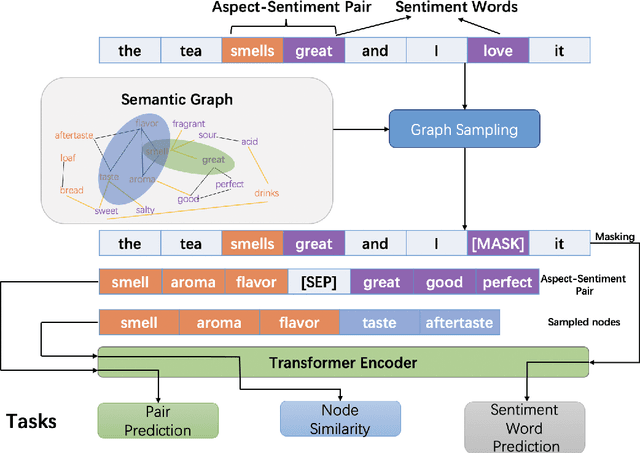
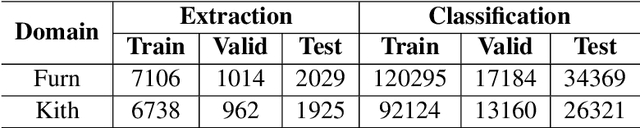
Abstract:Previous studies show effective of pre-trained language models for sentiment analysis. However, most of these studies ignore the importance of sentimental information for pre-trained models.Therefore, we fully investigate the sentimental information for pre-trained models and enhance pre-trained language models with semantic graphs for sentiment analysis.In particular, we introduce Semantic Graphs based Pre-training(SGPT) using semantic graphs to obtain synonym knowledge for aspect-sentiment pairs and similar aspect/sentiment terms.We then optimize the pre-trained language model with the semantic graphs.Empirical studies on several downstream tasks show that proposed model outperforms strong pre-trained baselines. The results also show the effectiveness of proposed semantic graphs for pre-trained model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge