Hongbo Deng
Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces For Multi-task Learning
Mar 05, 2025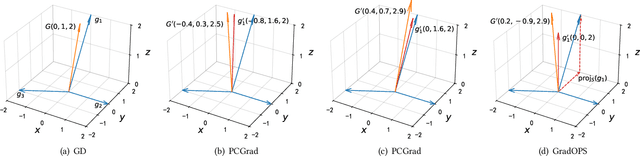
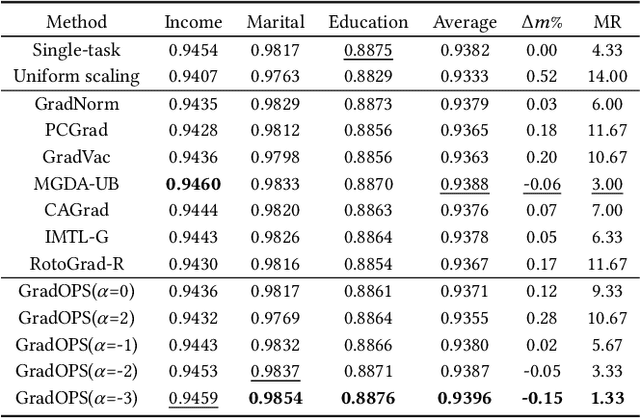
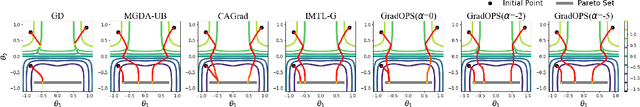
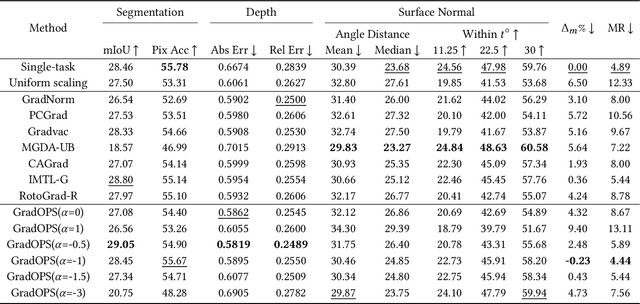
Abstract:Although multi-task learning (MTL) has been a preferred approach and successfully applied in many real-world scenarios, MTL models are not guaranteed to outperform single-task models on all tasks mainly due to the negative effects of conflicting gradients among the tasks. In this paper, we fully examine the influence of conflicting gradients and further emphasize the importance and advantages of achieving non-conflicting gradients which allows simple but effective trade-off strategies among the tasks with stable performance. Based on our findings, we propose the Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces (GradOPS) spanned by other task-specific gradients. Our method not only solves all conflicts among the tasks, but can also effectively search for diverse solutions towards different trade-off preferences among the tasks. Theoretical analysis on convergence is provided, and performance of our algorithm is fully testified on multiple benchmarks in various domains. Results demonstrate that our method can effectively find multiple state-of-the-art solutions with different trade-off strategies among the tasks on multiple datasets.
Multi-Scenario Ranking with Adaptive Feature Learning
Jun 29, 2023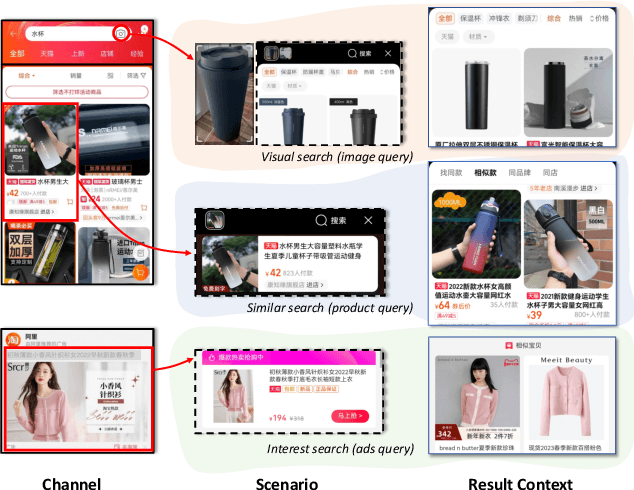
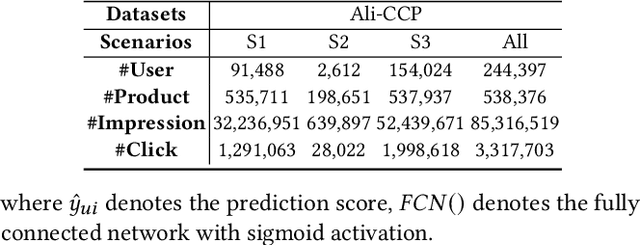
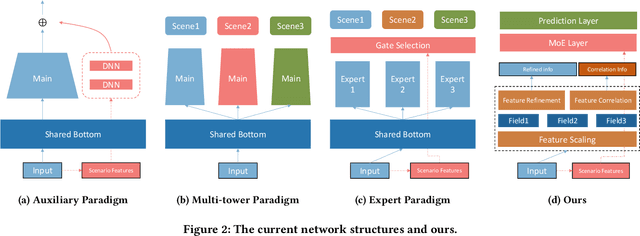
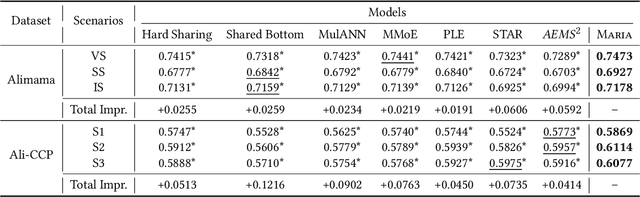
Abstract:Recently, Multi-Scenario Learning (MSL) is widely used in recommendation and retrieval systems in the industry because it facilitates transfer learning from different scenarios, mitigating data sparsity and reducing maintenance cost. These efforts produce different MSL paradigms by searching more optimal network structure, such as Auxiliary Network, Expert Network, and Multi-Tower Network. It is intuitive that different scenarios could hold their specific characteristics, activating the user's intents quite differently. In other words, different kinds of auxiliary features would bear varying importance under different scenarios. With more discriminative feature representations refined in a scenario-aware manner, better ranking performance could be easily obtained without expensive search for the optimal network structure. Unfortunately, this simple idea is mainly overlooked but much desired in real-world systems.Further analysis also validates the rationality of adaptive feature learning under a multi-scenario scheme. Moreover, our A/B test results on the Alibaba search advertising platform also demonstrate that Maria is superior in production environments.
Towards Understanding the Overfitting Phenomenon of Deep Click-Through Rate Prediction Models
Sep 04, 2022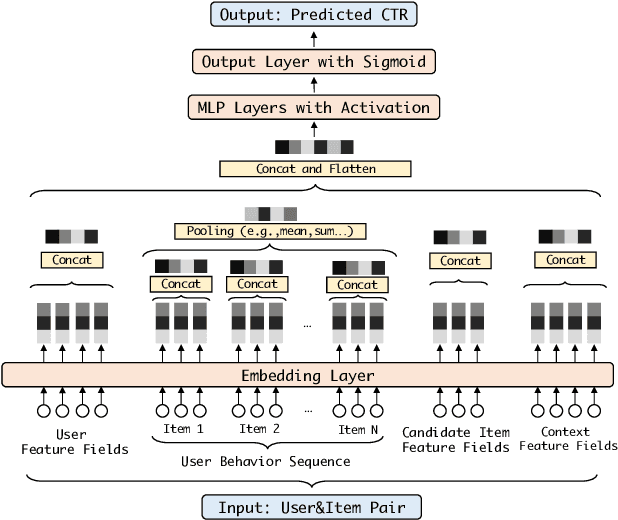
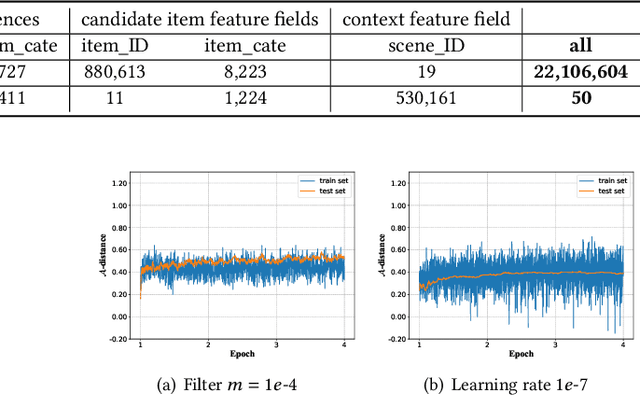
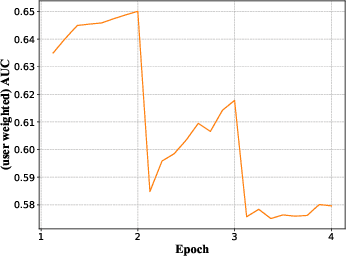
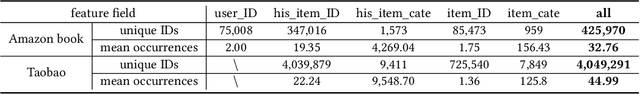
Abstract:Deep learning techniques have been applied widely in industrial recommendation systems. However, far less attention has been paid to the overfitting problem of models in recommendation systems, which, on the contrary, is recognized as a critical issue for deep neural networks. In the context of Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction, we observe an interesting one-epoch overfitting problem: the model performance exhibits a dramatic degradation at the beginning of the second epoch. Such a phenomenon has been witnessed widely in real-world applications of CTR models. Thereby, the best performance is usually achieved by training with only one epoch. To understand the underlying factors behind the one-epoch phenomenon, we conduct extensive experiments on the production data set collected from the display advertising system of Alibaba. The results show that the model structure, the optimization algorithm with a fast convergence rate, and the feature sparsity are closely related to the one-epoch phenomenon. We also provide a likely hypothesis for explaining such a phenomenon and conduct a set of proof-of-concept experiments. We hope this work can shed light on future research on training more epochs for better performance.
KEEP: An Industrial Pre-Training Framework for Online Recommendation via Knowledge Extraction and Plugging
Aug 22, 2022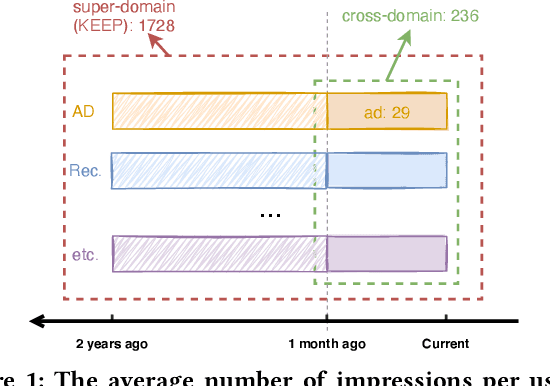

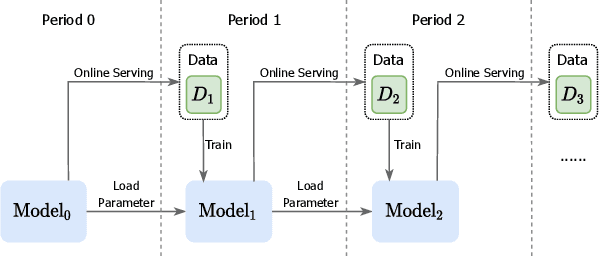
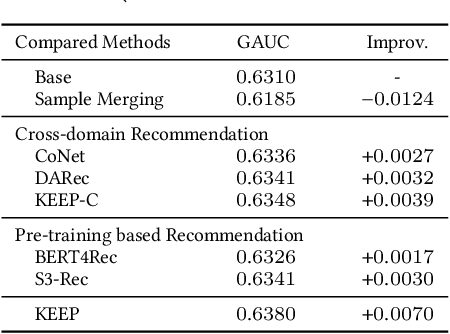
Abstract:An industrial recommender system generally presents a hybrid list that contains results from multiple subsystems. In practice, each subsystem is optimized with its own feedback data to avoid the disturbance among different subsystems. However, we argue that such data usage may lead to sub-optimal online performance because of the \textit{data sparsity}. To alleviate this issue, we propose to extract knowledge from the \textit{super-domain} that contains web-scale and long-time impression data, and further assist the online recommendation task (downstream task). To this end, we propose a novel industrial \textbf{K}nowl\textbf{E}dge \textbf{E}xtraction and \textbf{P}lugging (\textbf{KEEP}) framework, which is a two-stage framework that consists of 1) a supervised pre-training knowledge extraction module on super-domain, and 2) a plug-in network that incorporates the extracted knowledge into the downstream model. This makes it friendly for incremental training of online recommendation. Moreover, we design an efficient empirical approach for KEEP and introduce our hands-on experience during the implementation of KEEP in a large-scale industrial system. Experiments conducted on two real-world datasets demonstrate that KEEP can achieve promising results. It is notable that KEEP has also been deployed on the display advertising system in Alibaba, bringing a lift of $+5.4\%$ CTR and $+4.7\%$ RPM.
Joint Optimization of Ranking and Calibration with Contextualized Hybrid Model
Aug 12, 2022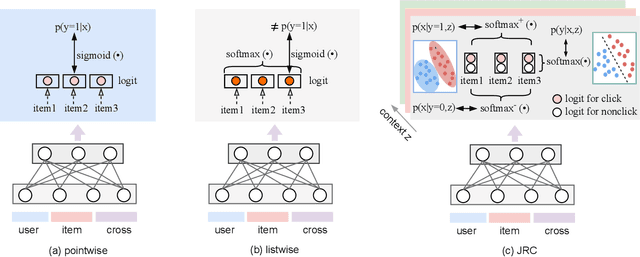
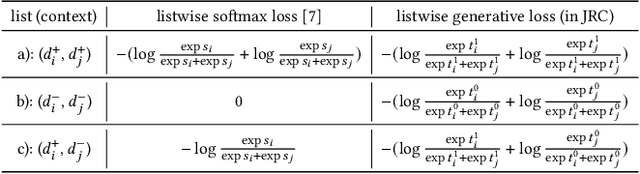

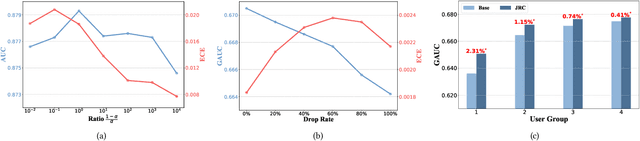
Abstract:Despite the development of ranking optimization techniques, the pointwise model remains the dominating approach for click-through rate (CTR) prediction. It can be attributed to the calibration ability of the pointwise model since the prediction can be viewed as the click probability. In practice, a CTR prediction model is also commonly assessed with the ranking ability, for which prediction models based on ranking losses (e.g., pairwise or listwise loss) usually achieve better performances than the pointwise loss. Previous studies have experimented with a direct combination of the two losses to obtain the benefit from both losses and observed an improved performance. However, previous studies break the meaning of output logit as the click-through rate, which may lead to sub-optimal solutions. To address this issue, we propose an approach that can Jointly optimize the Ranking and Calibration abilities (JRC for short). JRC improves the ranking ability by contrasting the logit value for the sample with different labels and constrains the predicted probability to be a function of the logit subtraction. We further show that JRC consolidates the interpretation of logits, where the logits model the joint distribution. With such an interpretation, we prove that JRC approximately optimizes the contextualized hybrid discriminative-generative objective. Experiments on public and industrial datasets and online A/B testing show that our approach improves both ranking and calibration abilities. Since May 2022, JRC has been deployed on the display advertising platform of Alibaba and has obtained significant performance improvements.
GBA: A Tuning-free Approach to Switch between Synchronous and Asynchronous Training for Recommendation Model
May 23, 2022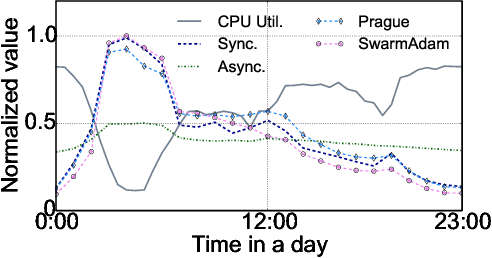
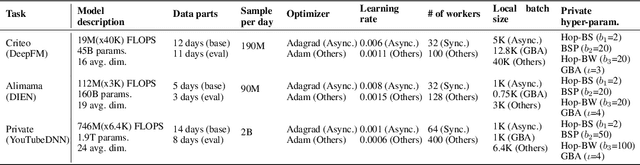
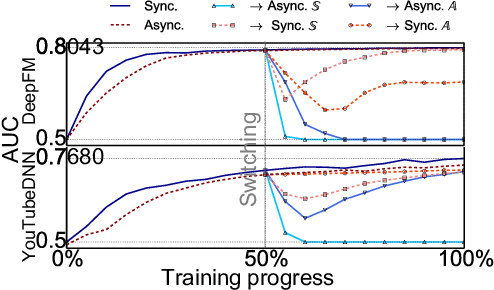

Abstract:High-concurrency asynchronous training upon parameter server (PS) architecture and high-performance synchronous training upon all-reduce (AR) architecture are the most commonly deployed distributed training modes for recommender systems. Although the synchronous AR training is designed to have higher training efficiency, the asynchronous PS training would be a better choice on training speed when there are stragglers (slow workers) in the shared cluster, especially under limited computing resources. To take full advantages of these two training modes, an ideal way is to switch between them upon the cluster status. We find two obstacles to a tuning-free approach: the different distribution of the gradient values and the stale gradients from the stragglers. In this paper, we propose Global Batch gradients Aggregation (GBA) over PS, which aggregates and applies gradients with the same global batch size as the synchronous training. A token-control process is implemented to assemble the gradients and decay the gradients with severe staleness. We provide the convergence analysis to demonstrate the robustness of GBA over the recommendation models against the gradient staleness. Experiments on three industrial-scale recommendation tasks show that GBA is an effective tuning-free approach for switching. Compared to the state-of-the-art derived asynchronous training, GBA achieves up to 0.2% improvement on the AUC metric, which is significant for the recommendation models. Meanwhile, under the strained hardware resource, GBA speeds up at least 2.4x compared to the synchronous training.
Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search under Neural Similarity Metric for Large-Scale Recommendation
Feb 28, 2022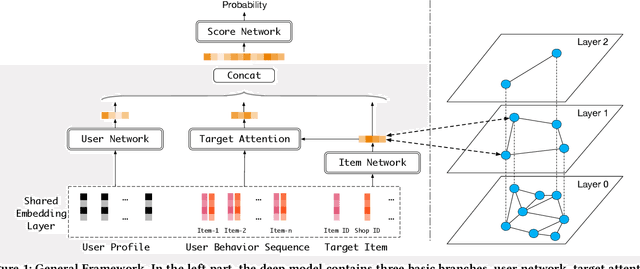

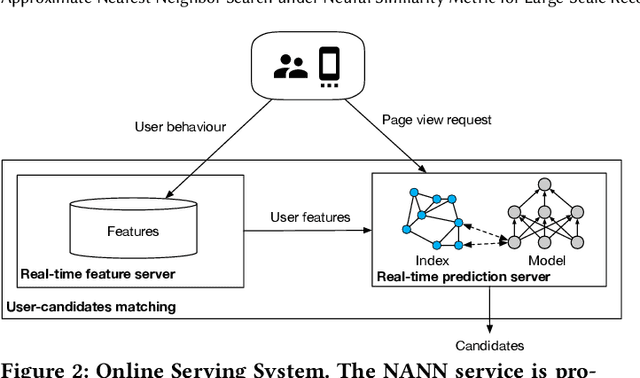
Abstract:Model-based methods for recommender systems have been studied extensively for years. Modern recommender systems usually resort to 1) representation learning models which define user-item preference as the distance between their embedding representations, and 2) embedding-based Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search to tackle the efficiency problem introduced by large-scale corpus. While providing efficient retrieval, the embedding-based retrieval pattern also limits the model capacity since the form of user-item preference measure is restricted to the distance between their embedding representations. However, for other more precise user-item preference measures, e.g., preference scores directly derived from a deep neural network, they are computationally intractable because of the lack of an efficient retrieval method, and an exhaustive search for all user-item pairs is impractical. In this paper, we propose a novel method to extend ANN search to arbitrary matching functions, e.g., a deep neural network. Our main idea is to perform a greedy walk with a matching function in a similarity graph constructed from all items. To solve the problem that the similarity measures of graph construction and user-item matching function are heterogeneous, we propose a pluggable adversarial training task to ensure the graph search with arbitrary matching function can achieve fairly high precision. Experimental results in both open source and industry datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The proposed method has been fully deployed in the Taobao display advertising platform and brings a considerable advertising revenue increase. We also summarize our detailed experiences in deployment in this paper.
Adversarial Gradient Driven Exploration for Deep Click-Through Rate Prediction
Dec 21, 2021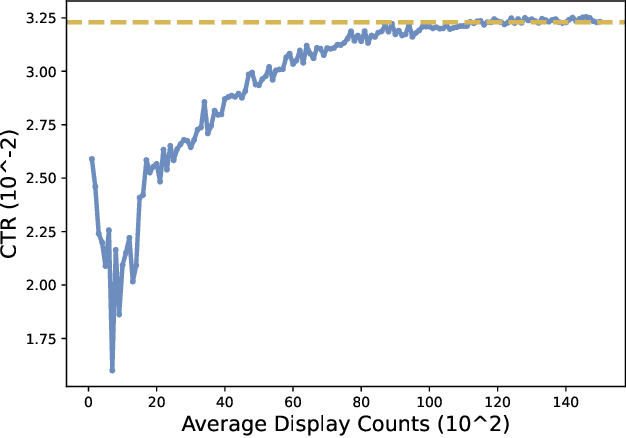
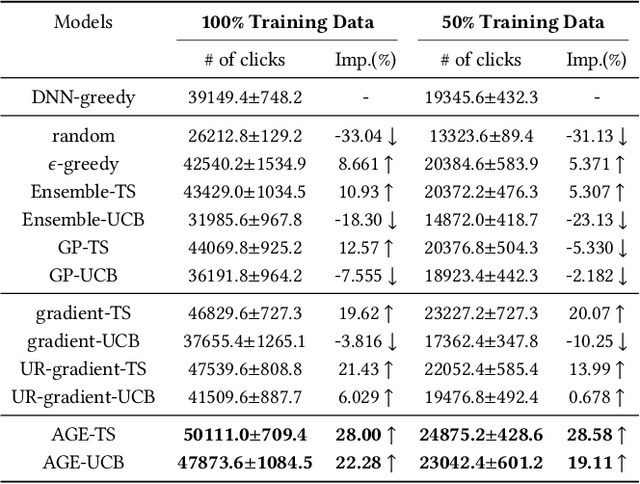
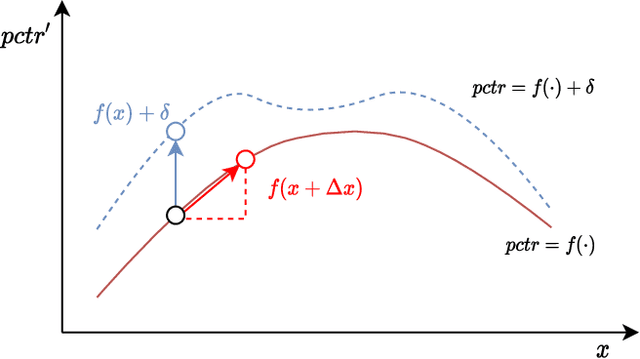
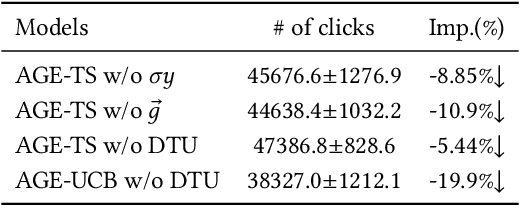
Abstract:Nowadays, data-driven deep neural models have already shown remarkable progress on Click-through Rate (CTR) prediction. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of such models may fail when there are insufficient data. To handle this issue, researchers often adopt exploration strategies to examine items based on the estimated reward, e.g., UCB or Thompson Sampling. In the context of Exploitation-and-Exploration for CTR prediction, recent studies have attempted to utilize the prediction uncertainty along with model prediction as the reward score. However, we argue that such an approach may make the final ranking score deviate from the original distribution, and thereby affect model performance in the online system. In this paper, we propose a novel exploration method called \textbf{A}dversarial \textbf{G}radient Driven \textbf{E}xploration (AGE). Specifically, we propose a Pseudo-Exploration Module to simulate the gradient updating process, which can approximate the influence of the samples of to-be-explored items for the model. In addition, for better exploration efficiency, we propose an Dynamic Threshold Unit to eliminate the effects of those samples with low potential CTR. The effectiveness of our approach was demonstrated on an open-access academic dataset. Meanwhile, AGE has also been deployed in a real-world display advertising platform and all online metrics have been significantly improved.
Comparative Explanations of Recommendations
Nov 01, 2021

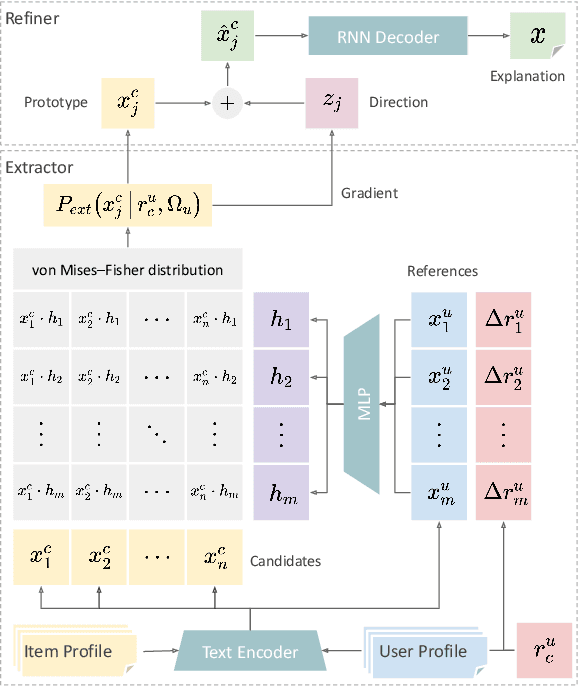
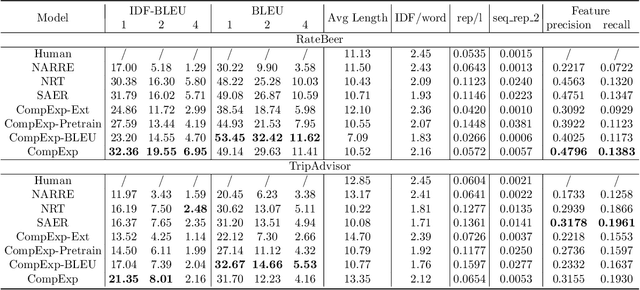
Abstract:As recommendation is essentially a comparative (or ranking) process, a good explanation should illustrate to users why an item is believed to be better than another, i.e., comparative explanations about the recommended items. Ideally, after reading the explanations, a user should reach the same ranking of items as the system's. Unfortunately, little research attention has yet been paid on such comparative explanations. In this work, we develop an extract-and-refine architecture to explain the relative comparisons among a set of ranked items from a recommender system. For each recommended item, we first extract one sentence from its associated reviews that best suits the desired comparison against a set of reference items. Then this extracted sentence is further articulated with respect to the target user through a generative model to better explain why the item is recommended. We design a new explanation quality metric based on BLEU to guide the end-to-end training of the extraction and refinement components, which avoids generation of generic content. Extensive offline evaluations on two large recommendation benchmark datasets and serious user studies against an array of state-of-the-art explainable recommendation algorithms demonstrate the necessity of comparative explanations and the effectiveness of our solution.
DemiNet: Dependency-Aware Multi-Interest Network with Self-Supervised Graph Learning for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Sep 26, 2021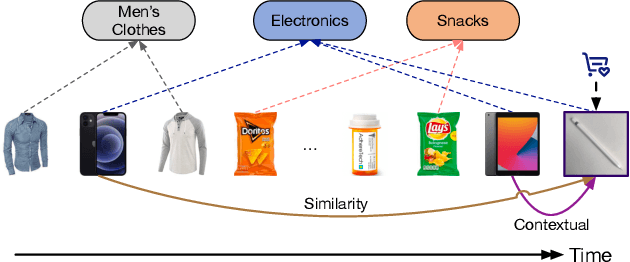

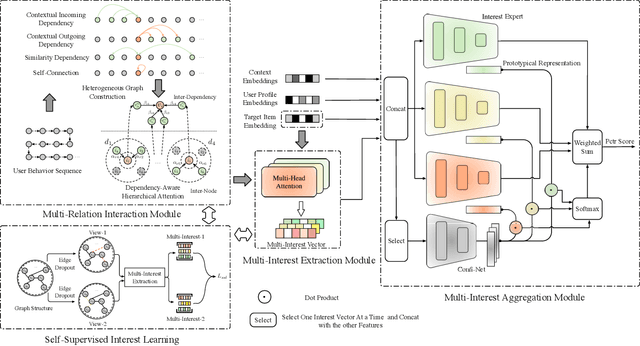
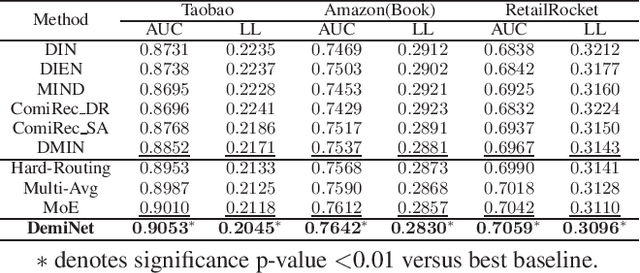
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel model named DemiNet (short for DEpendency-Aware Multi-Interest Network}) to address the above two issues. To be specific, we first consider various dependency types between item nodes and perform dependency-aware heterogeneous attention for denoising and obtaining accurate sequence item representations. Secondly, for multiple interests extraction, multi-head attention is conducted on top of the graph embedding. To filter out noisy inter-item correlations and enhance the robustness of extracted interests, self-supervised interest learning is introduced to the above two steps. Thirdly, to aggregate the multiple interests, interest experts corresponding to different interest routes give rating scores respectively, while a specialized network assigns the confidence of each score. Experimental results on three real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed DemiNet significantly improves the overall recommendation performance over several state-of-the-art baselines. Further studies verify the efficacy and interpretability benefits brought from the fine-grained user interest modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge