Pengjie Wang
Query-Mixed Interest Extraction and Heterogeneous Interaction: A Scalable CTR Model for Industrial Recommender Systems
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Learning effective feature interactions is central to modern recommender systems, yet remains challenging in industrial settings due to sparse multi-field inputs and ultra-long user behavior sequences. While recent scaling efforts have improved model capacity, they often fail to construct both context-aware and context-independent user intent from the long-term and real-time behavior sequence. Meanwhile, recent work also suffers from inefficient and homogeneous interaction mechanisms, leading to suboptimal prediction performance. To address these limitations, we propose HeMix, a scalable ranking model that unifies adaptive sequence tokenization and heterogeneous interaction structure. Specifically, HeMix introduces a Query-Mixed Interest Extraction module that jointly models context-aware and context-independent user interests via dynamic and fixed queries over global and real-time behavior sequences. For interaction, we replace self-attention with the HeteroMixer block, enabling efficient, multi-granularity cross-feature interactions that adopt the multi-head token fusion, heterogeneous interaction and group-aligned reconstruction pipelines. HeMix demonstrates favorable scaling behavior, driven by the HeteroMixer block, where increasing model scale via parameter expansion leads to steady improvements in recommendation accuracy. Experiments on industrial-scale datasets show that HeMix scales effectively and consistently outperforms strong baselines. Most importantly, HeMix has been deployed on the AMAP platform, delivering significant online gains over DLRM: +3.61\% GMV, +2.78\% PV\_CTR, and +2.12\% UV\_CVR.
GeoGR: A Generative Retrieval Framework for Spatio-Temporal Aware POI Recommendation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Next Point-of-Interest (POI) prediction is a fundamental task in location-based services, especially critical for large-scale navigation platforms like AMAP that serve billions of users across diverse lifestyle scenarios. While recent POI recommendation approaches based on SIDs have achieved promising, they struggle in complex, sparse real-world environments due to two key limitations: (1) inadequate modeling of high-quality SIDs that capture cross-category spatio-temporal collaborative relationships, and (2) poor alignment between large language models (LLMs) and the POI recommendation task. To this end, we propose GeoGR, a geographic generative recommendation framework tailored for navigation-based LBS like AMAP, which perceives users' contextual state changes and enables intent-aware POI recommendation. GeoGR features a two-stage design: (i) a geo-aware SID tokenization pipeline that explicitly learns spatio-temporal collaborative semantic representations via geographically constrained co-visited POI pairs, contrastive learning, and iterative refinement; and (ii) a multi-stage LLM training strategy that aligns non-native SID tokens through multiple template-based continued pre-training(CPT) and enables autoregressive POI generation via supervised fine-tuning(SFT). Extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate GeoGR's superiority over state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, deployment on the AMAP platform, serving millions of users with multiple online metrics boosting, confirms its practical effectiveness and scalability in production.
RAIR: A Rule-Aware Benchmark Uniting Challenging Long-Tail and Visual Salience Subset for E-commerce Relevance Assessment
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Search relevance plays a central role in web e-commerce. While large language models (LLMs) have shown significant results on relevance task, existing benchmarks lack sufficient complexity for comprehensive model assessment, resulting in an absence of standardized relevance evaluation metrics across the industry. To address this limitation, we propose Rule-Aware benchmark with Image for Relevance assessment(RAIR), a Chinese dataset derived from real-world scenarios. RAIR established a standardized framework for relevance assessment and provides a set of universal rules, which forms the foundation for standardized evaluation. Additionally, RAIR analyzes essential capabilities required for current relevance models and introduces a comprehensive dataset consists of three subset: (1) a general subset with industry-balanced sampling to evaluate fundamental model competencies; (2) a long-tail hard subset focus on challenging cases to assess performance limits; (3) a visual salience subset for evaluating multimodal understanding capabilities. We conducted experiments on RAIR using 14 open and closed-source models. The results demonstrate that RAIR presents sufficient challenges even for GPT-5, which achieved the best performance. RAIR data are now available, serving as an industry benchmark for relevance assessment while providing new insights into general LLM and Visual Language Model(VLM) evaluation.
LoFT-LLM: Low-Frequency Time-Series Forecasting with Large Language Models
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Time-series forecasting in real-world applications such as finance and energy often faces challenges due to limited training data and complex, noisy temporal dynamics. Existing deep forecasting models typically supervise predictions using full-length temporal windows, which include substantial high-frequency noise and obscure long-term trends. Moreover, auxiliary variables containing rich domain-specific information are often underutilized, especially in few-shot settings. To address these challenges, we propose LoFT-LLM, a frequency-aware forecasting pipeline that integrates low-frequency learning with semantic calibration via a large language model (LLM). Firstly, a Patch Low-Frequency forecasting Module (PLFM) extracts stable low-frequency trends from localized spectral patches. Secondly, a residual learner then models high-frequency variations. Finally, a fine-tuned LLM refines the predictions by incorporating auxiliary context and domain knowledge through structured natural language prompts. Extensive experiments on financial and energy datasets demonstrate that LoFT-LLM significantly outperforms strong baselines under both full-data and few-shot regimes, delivering superior accuracy, robustness, and interpretability.
MOON Embedding: Multimodal Representation Learning for E-commerce Search Advertising
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce MOON, our comprehensive set of sustainable iterative practices for multimodal representation learning for e-commerce applications. MOON has already been fully deployed across all stages of Taobao search advertising system, including retrieval, relevance, ranking, and so on. The performance gains are particularly significant on click-through rate (CTR) prediction task, which achieves an overall +20.00% online CTR improvement. Over the past three years, this project has delivered the largest improvement on CTR prediction task and undergone five full-scale iterations. Throughout the exploration and iteration of our MOON, we have accumulated valuable insights and practical experience that we believe will benefit the research community. MOON contains a three-stage training paradigm of "Pretraining, Post-training, and Application", allowing effective integration of multimodal representations with downstream tasks. Notably, to bridge the misalignment between the objectives of multimodal representation learning and downstream training, we define the exchange rate to quantify how effectively improvements in an intermediate metric can translate into downstream gains. Through this analysis, we identify the image-based search recall as a critical intermediate metric guiding the optimization of multimodal models. Over three years and five iterations, MOON has evolved along four critical dimensions: data processing, training strategy, model architecture, and downstream application. The lessons and insights gained through the iterative improvements will also be shared. As part of our exploration into scaling effects in the e-commerce field, we further conduct a systematic study of the scaling laws governing multimodal representation learning, examining multiple factors such as the number of training tokens, negative samples, and the length of user behavior sequences.
MOON2.0: Dynamic Modality-balanced Multimodal Representation Learning for E-commerce Product Understanding
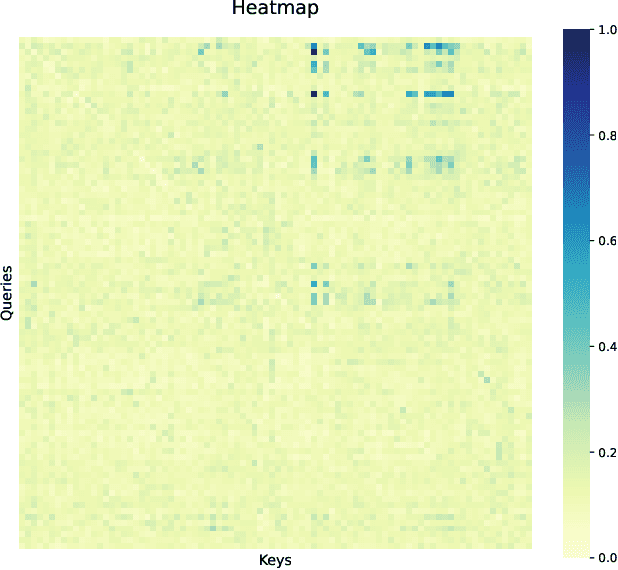
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of e-commerce calls for multimodal models that comprehend rich visual and textual product information. Although recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for product understanding exhibit strong capability in representation learning for e-commerce, they still face three challenges: (i) the modality imbalance induced by modality mixed training; (ii) underutilization of the intrinsic alignment relationships among visual and textual information within a product; and (iii) limited handling of noise in e-commerce multimodal data. To address these, we propose MOON2.0, a dynamic modality-balanced multimodal representation learning framework for e-commerce product understanding. MOON2.0 comprises: (1) a Modality-driven Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) module that adaptively processes input samples by their modality composition, enabling Multimodal Joint Learning to mitigate the modality imbalance; (2) a Dual-level Alignment method to better leverage semantic alignment properties inside individual products; and (3) an MLLM-based Image-text Co-augmentation strategy that integrates textual enrichment with visual expansion, coupled with Dynamic Sample Filtering to improve training data quality. We further introduce MBE2.0, a co-augmented multimodal representation benchmark for e-commerce representation learning and evaluation. Experiments show that MOON2.0 delivers state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on MBE2.0 and multiple public datasets. Furthermore, attention-based heatmap visualization provides qualitative evidence of improved multimodal alignment of MOON2.0.
From Scaling to Structured Expressivity: Rethinking Transformers for CTR Prediction
Nov 15, 2025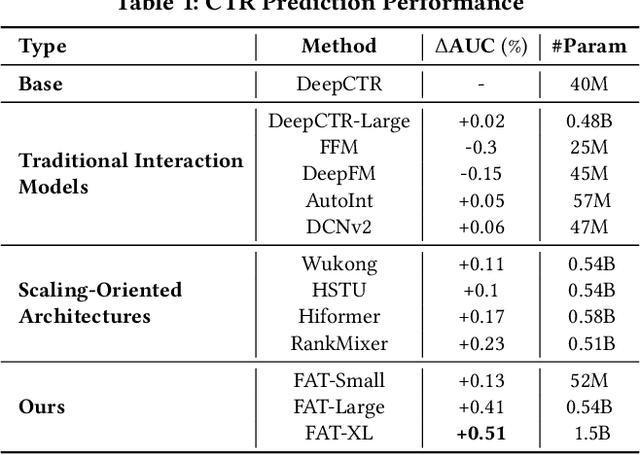


Abstract:Despite massive investments in scale, deep models for click-through rate (CTR) prediction often exhibit rapidly diminishing returns - a stark contrast to the smooth, predictable gains seen in large language models. We identify the root cause as a structural misalignment: Transformers assume sequential compositionality, while CTR data demand combinatorial reasoning over high-cardinality semantic fields. Unstructured attention spreads capacity indiscriminately, amplifying noise under extreme sparsity and breaking scalable learning. To restore alignment, we introduce the Field-Aware Transformer (FAT), which embeds field-based interaction priors into attention through decomposed content alignment and cross-field modulation. This design ensures model complexity scales with the number of fields F, not the total vocabulary size n >> F, leading to tighter generalization and, critically, observed power-law scaling in AUC as model width increases. We present the first formal scaling law for CTR models, grounded in Rademacher complexity, that explains and predicts this behavior. On large-scale benchmarks, FAT improves AUC by up to +0.51% over state-of-the-art methods. Deployed online, it delivers +2.33% CTR and +0.66% RPM. Our work establishes that effective scaling in recommendation arises not from size, but from structured expressivity-architectural coherence with data semantics.
Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces For Multi-task Learning
Mar 05, 2025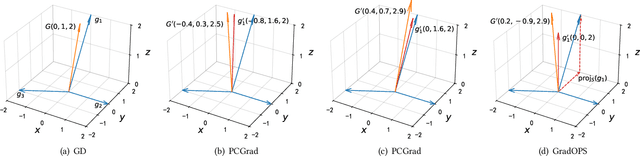
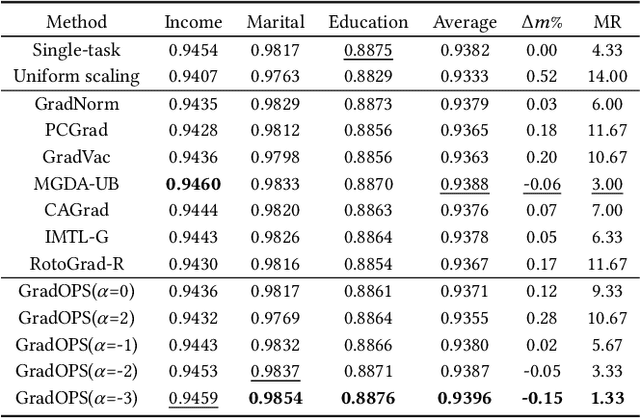
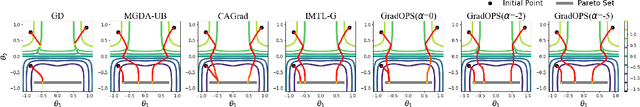
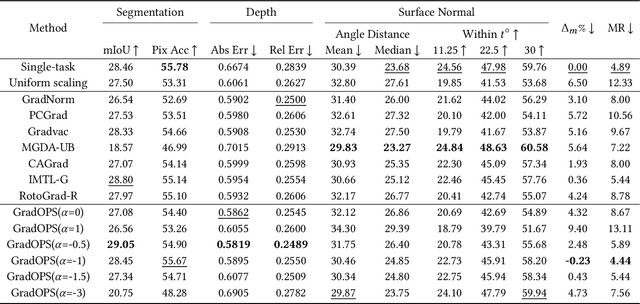
Abstract:Although multi-task learning (MTL) has been a preferred approach and successfully applied in many real-world scenarios, MTL models are not guaranteed to outperform single-task models on all tasks mainly due to the negative effects of conflicting gradients among the tasks. In this paper, we fully examine the influence of conflicting gradients and further emphasize the importance and advantages of achieving non-conflicting gradients which allows simple but effective trade-off strategies among the tasks with stable performance. Based on our findings, we propose the Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces (GradOPS) spanned by other task-specific gradients. Our method not only solves all conflicts among the tasks, but can also effectively search for diverse solutions towards different trade-off preferences among the tasks. Theoretical analysis on convergence is provided, and performance of our algorithm is fully testified on multiple benchmarks in various domains. Results demonstrate that our method can effectively find multiple state-of-the-art solutions with different trade-off strategies among the tasks on multiple datasets.
UQABench: Evaluating User Embedding for Prompting LLMs in Personalized Question Answering
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable success in natural language processing (NLP). In practical scenarios like recommendations, as users increasingly seek personalized experiences, it becomes crucial to incorporate user interaction history into the context of LLMs to enhance personalization. However, from a practical utility perspective, user interactions' extensive length and noise present challenges when used directly as text prompts. A promising solution is to compress and distill interactions into compact embeddings, serving as soft prompts to assist LLMs in generating personalized responses. Although this approach brings efficiency, a critical concern emerges: Can user embeddings adequately capture valuable information and prompt LLMs? To address this concern, we propose \name, a benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness of user embeddings in prompting LLMs for personalization. We establish a fair and standardized evaluation process, encompassing pre-training, fine-tuning, and evaluation stages. To thoroughly evaluate user embeddings, we design three dimensions of tasks: sequence understanding, action prediction, and interest perception. These evaluation tasks cover the industry's demands in traditional recommendation tasks, such as improving prediction accuracy, and its aspirations for LLM-based methods, such as accurately understanding user interests and enhancing the user experience. We conduct extensive experiments on various state-of-the-art methods for modeling user embeddings. Additionally, we reveal the scaling laws of leveraging user embeddings to prompt LLMs. The benchmark is available online.
Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation for E-Commerce Relevance Learning
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Effective query-item relevance modeling is pivotal for enhancing user experience and safeguarding user satisfaction in e-commerce search systems. Recently, benefiting from the vast inherent knowledge, Large Language Model (LLM) approach demonstrates strong performance and long-tail generalization ability compared with previous neural-based specialized relevance learning methods. Though promising, current LLM-based methods encounter the following inadequacies in practice: First, the massive parameters and computational demands make it difficult to be deployed online. Second, distilling LLM models to online models is a feasible direction, but the LLM relevance modeling is a black box, and its rich intrinsic knowledge is difficult to extract and apply online. To improve the interpretability of LLM and boost the performance of online relevance models via LLM, we propose an Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation framework for e-commerce relevance learning, which comprises two core components: (1) An Explainable LLM for relevance modeling (ELLM-rele), which decomposes the relevance learning into intermediate steps and models relevance learning as a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, thereby enhancing both interpretability and performance of LLM. (2) A Multi-dimensional Knowledge Distillation (MKD) architecture that transfers the knowledge of ELLM-rele to current deployable interaction-based and representation-based student models from both the relevance score distribution and CoT reasoning aspects. Through distilling the probabilistic and CoT reasoning knowledge, MKD improves both the semantic interaction and long-tail generalization abilities of student models. Extensive offline evaluations and online experiments on Taobao search ad scene demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly enhances e-commerce relevance learning performance and user experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge