Huimin Yi
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
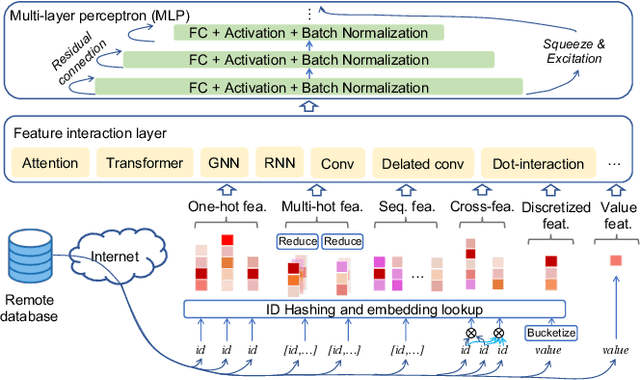
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommender systems face two fundamental limitations under the log-driven paradigm: (1) knowledge poverty in ID-based item representations that causes brittle interest modeling under data sparsity, and (2) systemic blindness to beyond-log user interests that constrains model performance within platform boundaries. These limitations stem from an over-reliance on shallow interaction statistics and close-looped feedback while neglecting the rich world knowledge about product semantics and cross-domain behavioral patterns that Large Language Models have learned from vast corpora. To address these challenges, we introduce ReaSeq, a reasoning-enhanced framework that leverages world knowledge in Large Language Models to address both limitations through explicit and implicit reasoning. Specifically, ReaSeq employs explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning via multi-agent collaboration to distill structured product knowledge into semantically enriched item representations, and latent reasoning via Diffusion Large Language Models to infer plausible beyond-log behaviors. Deployed on Taobao's ranking system serving hundreds of millions of users, ReaSeq achieves substantial gains: >6.0% in IPV and CTR, >2.9% in Orders, and >2.5% in GMV, validating the effectiveness of world-knowledge-enhanced reasoning over purely log-driven approaches.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-Scale Learning: An Efficient and User-Friendly Scaling Library
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce ROLL, an efficient, scalable, and user-friendly library designed for Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-scale Learning. ROLL caters to three primary user groups: tech pioneers aiming for cost-effective, fault-tolerant large-scale training, developers requiring flexible control over training workflows, and researchers seeking agile experimentation. ROLL is built upon several key modules to serve these user groups effectively. First, a single-controller architecture combined with an abstraction of the parallel worker simplifies the development of the training pipeline. Second, the parallel strategy and data transfer modules enable efficient and scalable training. Third, the rollout scheduler offers fine-grained management of each sample's lifecycle during the rollout stage. Fourth, the environment worker and reward worker support rapid and flexible experimentation with agentic RL algorithms and reward designs. Finally, AutoDeviceMapping allows users to assign resources to different models flexibly across various stages.
GBA: A Tuning-free Approach to Switch between Synchronous and Asynchronous Training for Recommendation Model
May 23, 2022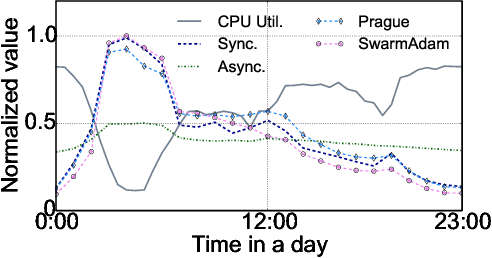
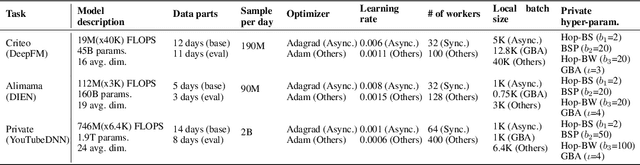
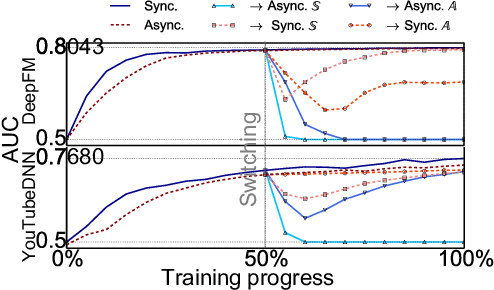

Abstract:High-concurrency asynchronous training upon parameter server (PS) architecture and high-performance synchronous training upon all-reduce (AR) architecture are the most commonly deployed distributed training modes for recommender systems. Although the synchronous AR training is designed to have higher training efficiency, the asynchronous PS training would be a better choice on training speed when there are stragglers (slow workers) in the shared cluster, especially under limited computing resources. To take full advantages of these two training modes, an ideal way is to switch between them upon the cluster status. We find two obstacles to a tuning-free approach: the different distribution of the gradient values and the stale gradients from the stragglers. In this paper, we propose Global Batch gradients Aggregation (GBA) over PS, which aggregates and applies gradients with the same global batch size as the synchronous training. A token-control process is implemented to assemble the gradients and decay the gradients with severe staleness. We provide the convergence analysis to demonstrate the robustness of GBA over the recommendation models against the gradient staleness. Experiments on three industrial-scale recommendation tasks show that GBA is an effective tuning-free approach for switching. Compared to the state-of-the-art derived asynchronous training, GBA achieves up to 0.2% improvement on the AUC metric, which is significant for the recommendation models. Meanwhile, under the strained hardware resource, GBA speeds up at least 2.4x compared to the synchronous training.
PICASSO: Unleashing the Potential of GPU-centric Training for Wide-and-deep Recommender Systems
Apr 17, 2022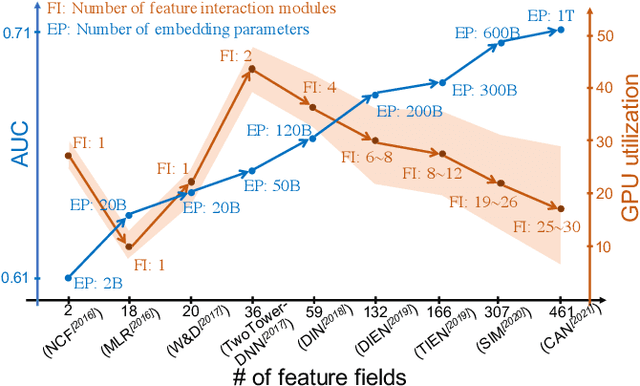
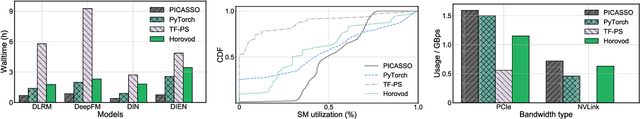
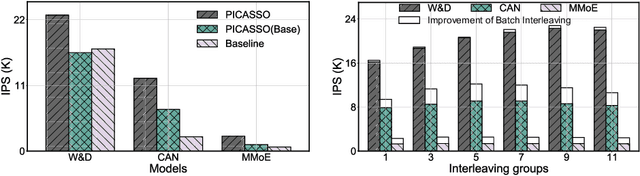
Abstract:The development of personalized recommendation has significantly improved the accuracy of information matching and the revenue of e-commerce platforms. Recently, it has 2 trends: 1) recommender systems must be trained timely to cope with ever-growing new products and ever-changing user interests from online marketing and social network; 2) SOTA recommendation models introduce DNN modules to improve prediction accuracy. Traditional CPU-based recommender systems cannot meet these two trends, and GPU- centric training has become a trending approach. However, we observe that GPU devices in training recommender systems are underutilized, and they cannot attain an expected throughput improvement as what it has achieved in CV and NLP areas. This issue can be explained by two characteristics of these recommendation models: First, they contain up to a thousand input feature fields, introducing fragmentary and memory-intensive operations; Second, the multiple constituent feature interaction submodules introduce substantial small-sized compute kernels. To remove this roadblock to the development of recommender systems, we propose a novel framework named PICASSO to accelerate the training of recommendation models on commodity hardware. Specifically, we conduct a systematic analysis to reveal the bottlenecks encountered in training recommendation models. We leverage the model structure and data distribution to unleash the potential of hardware through our packing, interleaving, and caching optimization. Experiments show that PICASSO increases the hardware utilization by an order of magnitude on the basis of SOTA baselines and brings up to 6x throughput improvement for a variety of industrial recommendation models. Using the same hardware budget in production, PICASSO on average shortens the walltime of daily training tasks by 7 hours, significantly reducing the delay of continuous delivery.
Image Matters: Visually modeling user behaviors using Advanced Model Server
Sep 04, 2018



Abstract:In Taobao, the largest e-commerce platform in China, billions of items are provided and typically displayed with their images. For better user experience and business effectiveness, Click Through Rate (CTR) prediction in online advertising system exploits abundant user historical behaviors to identify whether a user is interested in a candidate ad. Enhancing behavior representations with user behavior images will help understand user's visual preference and improve the accuracy of CTR prediction greatly. So we propose to model user preference jointly with user behavior ID features and behavior images. However, training with user behavior images brings tens to hundreds of images in one sample, giving rise to a great challenge in both communication and computation. To handle these challenges, we propose a novel and efficient distributed machine learning paradigm called Advanced Model Server (AMS). With the well known Parameter Server (PS) framework, each server node handles a separate part of parameters and updates them independently. AMS goes beyond this and is designed to be capable of learning a unified image descriptor model shared by all server nodes which embeds large images into low dimensional high level features before transmitting images to worker nodes. AMS thus dramatically reduces the communication load and enables the arduous joint training process. Based on AMS, the methods of effectively combining the images and ID features are carefully studied, and then we propose a Deep Image CTR Model. Our approach is shown to achieve significant improvements in both online and offline evaluations, and has been deployed in Taobao display advertising system serving the main traffic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge