Hui Zhao
RAIR: A Rule-Aware Benchmark Uniting Challenging Long-Tail and Visual Salience Subset for E-commerce Relevance Assessment
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Search relevance plays a central role in web e-commerce. While large language models (LLMs) have shown significant results on relevance task, existing benchmarks lack sufficient complexity for comprehensive model assessment, resulting in an absence of standardized relevance evaluation metrics across the industry. To address this limitation, we propose Rule-Aware benchmark with Image for Relevance assessment(RAIR), a Chinese dataset derived from real-world scenarios. RAIR established a standardized framework for relevance assessment and provides a set of universal rules, which forms the foundation for standardized evaluation. Additionally, RAIR analyzes essential capabilities required for current relevance models and introduces a comprehensive dataset consists of three subset: (1) a general subset with industry-balanced sampling to evaluate fundamental model competencies; (2) a long-tail hard subset focus on challenging cases to assess performance limits; (3) a visual salience subset for evaluating multimodal understanding capabilities. We conducted experiments on RAIR using 14 open and closed-source models. The results demonstrate that RAIR presents sufficient challenges even for GPT-5, which achieved the best performance. RAIR data are now available, serving as an industry benchmark for relevance assessment while providing new insights into general LLM and Visual Language Model(VLM) evaluation.
SA-WiSense: A Blind-Spot-Free Respiration Sensing Framework for Single-Antenna Wi-Fi Devices
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:Wi-Fi sensing offers a promising technique for contactless human respiration monitoring. A key challenge, however, is the blind spot problem caused by random phase offsets that corrupt the complementarity of respiratory signals. To address the challenge, we propose a single-antenna-Wi-Fi-sensing (SA-WiSense) framework to improve accuracy of human respiration monitoring, robust against random phase offsets. The proposed SA-WiSense framework is cost-efficient, as only a single antenna is used rather than multiple antennas as in the previous works. Therefore, the proposed framework is applicable to Internet of Thing (IoT), where most of sensors are equipped with a single antenna. On one hand, we propose a cross-subcarrier channel state information (CSI) ratio (CSCR) based blind spot mitigation approach for IoT, where the ratios of two values of CSI between subcarriers are leveraged to mitigate random phase offsets. We prove that the random phase offsets can be cancelled by the proposed CSCR approach, thereby restoring the inherent complementarity of signals for blind-spot-free sensing. On the other hand, we propose a genetic algorithm (GA) based subcarrier selection (GASS) approach by formulating an optimization problem in terms of the sensing-signal-to-noise ratio (SSNR) of CSCR between subcarriers. GA is utilized to solve the formulated optimization problem. We use commodity ESP32 microcontrollers to build an experiment test. The proposed works are validated to achieve an detection rate of 91.2% for respiration monitoring at distances up to 8.0 meters, substantially more accurate than the state-of-the-art methods with a single antenna.
Rethinking the Embodied Gap in Vision-and-Language Navigation: A Holistic Study of Physical and Visual Disparities
Jul 17, 2025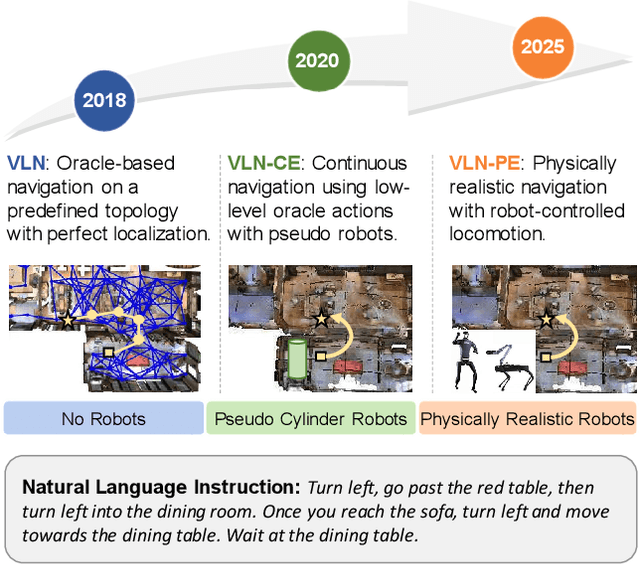
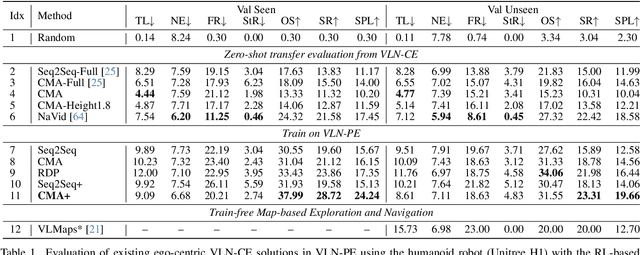
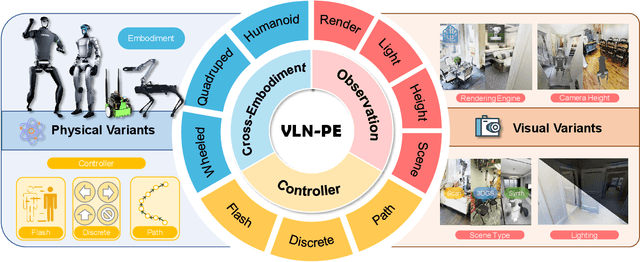
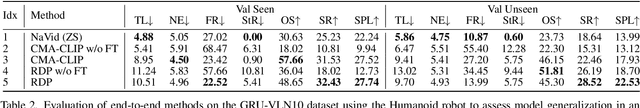
Abstract:Recent Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) advancements are promising, but their idealized assumptions about robot movement and control fail to reflect physically embodied deployment challenges. To bridge this gap, we introduce VLN-PE, a physically realistic VLN platform supporting humanoid, quadruped, and wheeled robots. For the first time, we systematically evaluate several ego-centric VLN methods in physical robotic settings across different technical pipelines, including classification models for single-step discrete action prediction, a diffusion model for dense waypoint prediction, and a train-free, map-based large language model (LLM) integrated with path planning. Our results reveal significant performance degradation due to limited robot observation space, environmental lighting variations, and physical challenges like collisions and falls. This also exposes locomotion constraints for legged robots in complex environments. VLN-PE is highly extensible, allowing seamless integration of new scenes beyond MP3D, thereby enabling more comprehensive VLN evaluation. Despite the weak generalization of current models in physical deployment, VLN-PE provides a new pathway for improving cross-embodiment's overall adaptability. We hope our findings and tools inspire the community to rethink VLN limitations and advance robust, practical VLN models. The code is available at https://crystalsixone.github.io/vln_pe.github.io/.
Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces For Multi-task Learning
Mar 05, 2025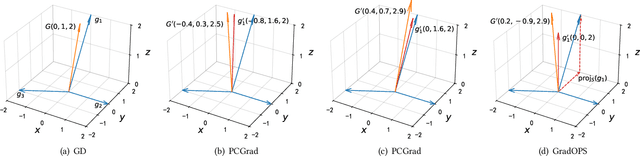
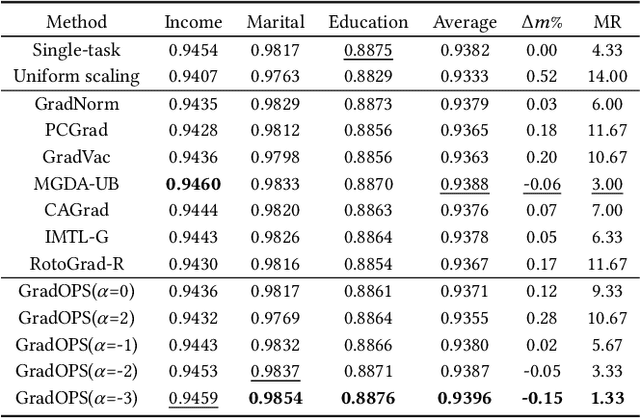
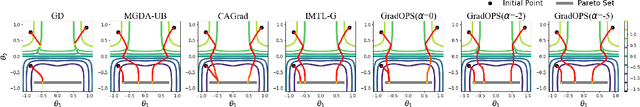
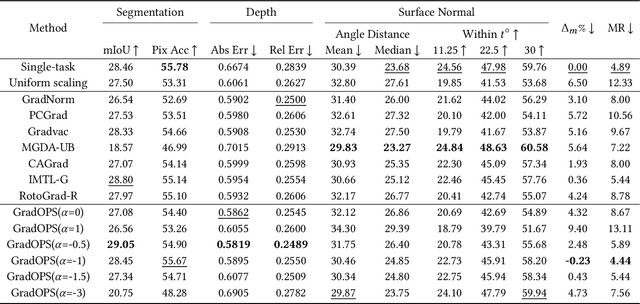
Abstract:Although multi-task learning (MTL) has been a preferred approach and successfully applied in many real-world scenarios, MTL models are not guaranteed to outperform single-task models on all tasks mainly due to the negative effects of conflicting gradients among the tasks. In this paper, we fully examine the influence of conflicting gradients and further emphasize the importance and advantages of achieving non-conflicting gradients which allows simple but effective trade-off strategies among the tasks with stable performance. Based on our findings, we propose the Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces (GradOPS) spanned by other task-specific gradients. Our method not only solves all conflicts among the tasks, but can also effectively search for diverse solutions towards different trade-off preferences among the tasks. Theoretical analysis on convergence is provided, and performance of our algorithm is fully testified on multiple benchmarks in various domains. Results demonstrate that our method can effectively find multiple state-of-the-art solutions with different trade-off strategies among the tasks on multiple datasets.
Error Classification of Large Language Models on Math Word Problems: A Dynamically Adaptive Framework
Jan 26, 2025
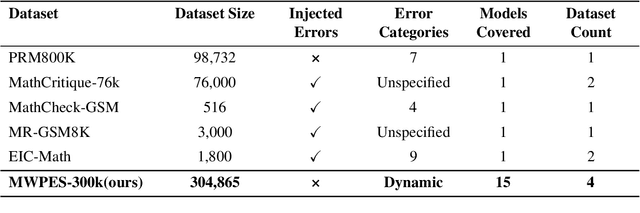

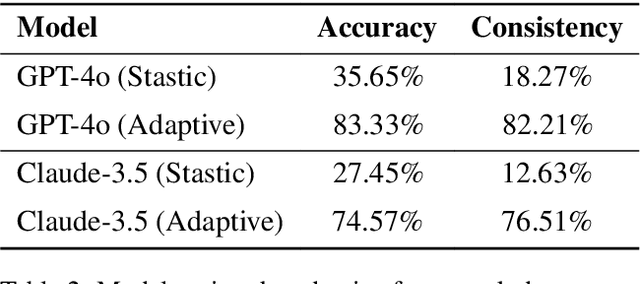
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various domains. Math Word Problems (MWPs) serve as a crucial benchmark for evaluating LLMs' reasoning abilities. While most research primarily focuses on improving accuracy, it often neglects understanding and addressing the underlying patterns of errors. Current error classification methods rely on static and predefined categories, which limit their ability to capture the full spectrum of error patterns in mathematical reasoning. To enable systematic error analysis, we collect error samples from 15 different LLMs of varying sizes across four distinct MWP datasets using multiple sampling strategies. Based on this extensive collection, we introduce MWPES-300K, a comprehensive dataset containing 304,865 error samples that cover diverse error patterns and reasoning paths. To reduce human bias and enable fine-grained analysis of error patterns, we propose a novel framework for automated dynamic error classification in mathematical reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that dataset characteristics significantly shape error patterns, which evolve from basic to complex manifestations as model capabilities increase. With deeper insights into error patterns, we propose error-aware prompting that incorporates common error patterns as explicit guidance, leading to significant improvements in mathematical reasoning performance.
Machine Learning Analysis of Anomalous Diffusion
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancements in machine learning have made its application to anomalous diffusion analysis both essential and inevitable. This review systematically introduces the integration of machine learning techniques for enhanced analysis of anomalous diffusion, focusing on two pivotal aspects: single trajectory characterization via machine learning and representation learning of anomalous diffusion. We extensively compare various machine learning methods, including both classical machine learning and deep learning, used for the inference of diffusion parameters and trajectory segmentation. Additionally, platforms such as the Anomalous Diffusion Challenge that serve as benchmarks for evaluating these methods are highlighted. On the other hand, we outline three primary strategies for representing anomalous diffusion: the combination of predefined features, the feature vector from the penultimate layer of neural network, and the latent representation from the autoencoder, analyzing their applicability across various scenarios. This investigation paves the way for future research, offering valuable perspectives that can further enrich the study of anomalous diffusion and advance the application of artificial intelligence in statistical physics and biophysics.
Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation for E-Commerce Relevance Learning
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Effective query-item relevance modeling is pivotal for enhancing user experience and safeguarding user satisfaction in e-commerce search systems. Recently, benefiting from the vast inherent knowledge, Large Language Model (LLM) approach demonstrates strong performance and long-tail generalization ability compared with previous neural-based specialized relevance learning methods. Though promising, current LLM-based methods encounter the following inadequacies in practice: First, the massive parameters and computational demands make it difficult to be deployed online. Second, distilling LLM models to online models is a feasible direction, but the LLM relevance modeling is a black box, and its rich intrinsic knowledge is difficult to extract and apply online. To improve the interpretability of LLM and boost the performance of online relevance models via LLM, we propose an Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation framework for e-commerce relevance learning, which comprises two core components: (1) An Explainable LLM for relevance modeling (ELLM-rele), which decomposes the relevance learning into intermediate steps and models relevance learning as a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, thereby enhancing both interpretability and performance of LLM. (2) A Multi-dimensional Knowledge Distillation (MKD) architecture that transfers the knowledge of ELLM-rele to current deployable interaction-based and representation-based student models from both the relevance score distribution and CoT reasoning aspects. Through distilling the probabilistic and CoT reasoning knowledge, MKD improves both the semantic interaction and long-tail generalization abilities of student models. Extensive offline evaluations and online experiments on Taobao search ad scene demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly enhances e-commerce relevance learning performance and user experience.
Think Before You Act: A Two-Stage Framework for Mitigating Gender Bias Towards Vision-Language Tasks
May 27, 2024
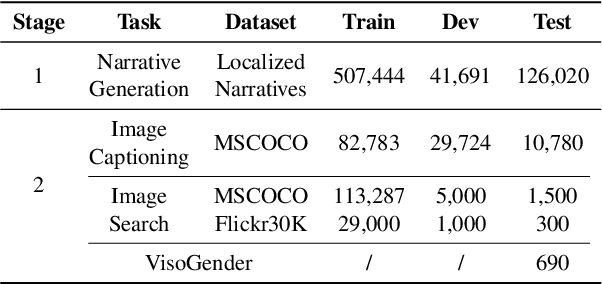
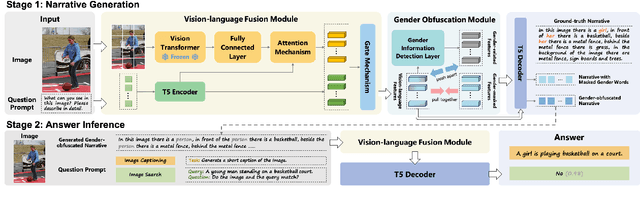
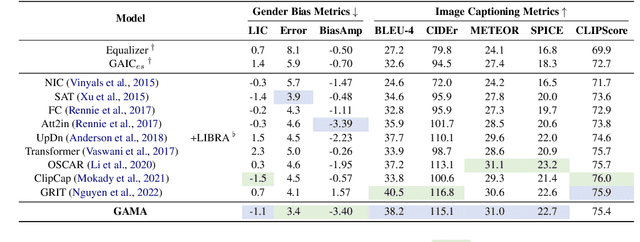
Abstract:Gender bias in vision-language models (VLMs) can reinforce harmful stereotypes and discrimination. In this paper, we focus on mitigating gender bias towards vision-language tasks. We identify object hallucination as the essence of gender bias in VLMs. Existing VLMs tend to focus on salient or familiar attributes in images but ignore contextualized nuances. Moreover, most VLMs rely on the co-occurrence between specific objects and gender attributes to infer the ignored features, ultimately resulting in gender bias. We propose GAMA, a task-agnostic generation framework to mitigate gender bias. GAMA consists of two stages: narrative generation and answer inference. During narrative generation, GAMA yields all-sided but gender-obfuscated narratives, which prevents premature concentration on localized image features, especially gender attributes. During answer inference, GAMA integrates the image, generated narrative, and a task-specific question prompt to infer answers for different vision-language tasks. This approach allows the model to rethink gender attributes and answers. We conduct extensive experiments on GAMA, demonstrating its debiasing and generalization ability.
A Novel Wide-Area Multiobject Detection System with High-Probability Region Searching
May 07, 2024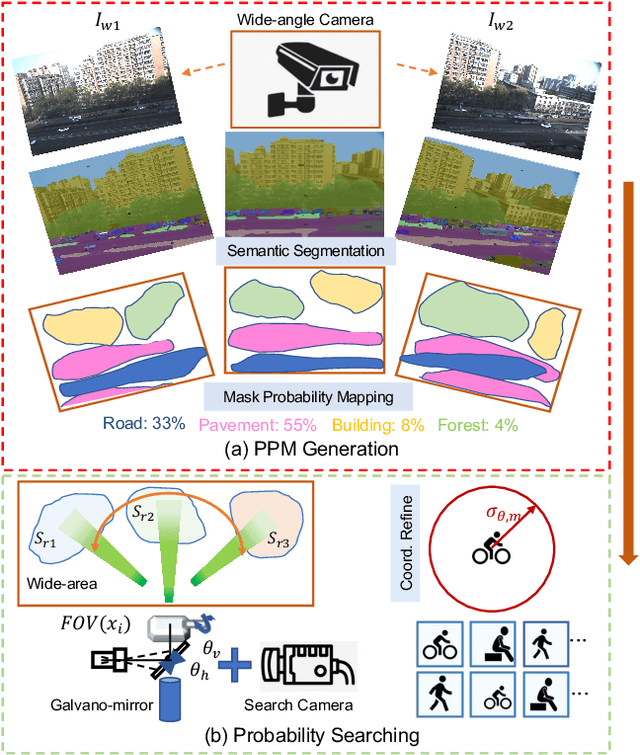
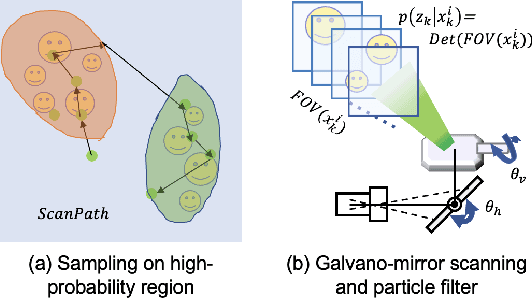
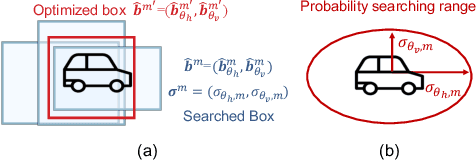
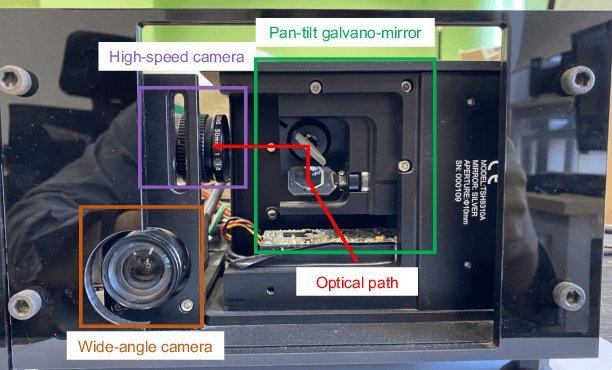
Abstract:In recent years, wide-area visual surveillance systems have been widely applied in various industrial and transportation scenarios. These systems, however, face significant challenges when implementing multi-object detection due to conflicts arising from the need for high-resolution imaging, efficient object searching, and accurate localization. To address these challenges, this paper presents a hybrid system that incorporates a wide-angle camera, a high-speed search camera, and a galvano-mirror. In this system, the wide-angle camera offers panoramic images as prior information, which helps the search camera capture detailed images of the targeted objects. This integrated approach enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of wide-area visual detection systems. Specifically, in this study, we introduce a wide-angle camera-based method to generate a panoramic probability map (PPM) for estimating high-probability regions of target object presence. Then, we propose a probability searching module that uses the PPM-generated prior information to dynamically adjust the sampling range and refine target coordinates based on uncertainty variance computed by the object detector. Finally, the integration of PPM and the probability searching module yields an efficient hybrid vision system capable of achieving 120 fps multi-object search and detection. Extensive experiments are conducted to verify the system's effectiveness and robustness.
* Accepted by ICRA 2024
InternLM2 Technical Report
Mar 26, 2024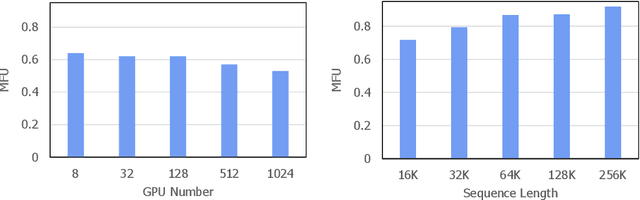
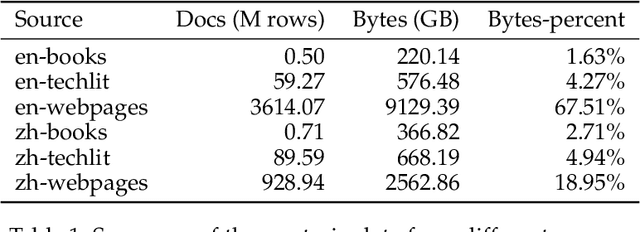

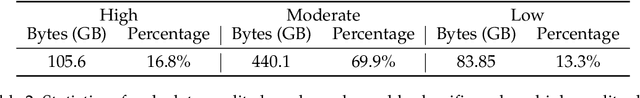
Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 has sparked discussions on the advent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, replicating such advancements in open-source models has been challenging. This paper introduces InternLM2, an open-source LLM that outperforms its predecessors in comprehensive evaluations across 6 dimensions and 30 benchmarks, long-context modeling, and open-ended subjective evaluations through innovative pre-training and optimization techniques. The pre-training process of InternLM2 is meticulously detailed, highlighting the preparation of diverse data types including text, code, and long-context data. InternLM2 efficiently captures long-term dependencies, initially trained on 4k tokens before advancing to 32k tokens in pre-training and fine-tuning stages, exhibiting remarkable performance on the 200k ``Needle-in-a-Haystack" test. InternLM2 is further aligned using Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and a novel Conditional Online Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (COOL RLHF) strategy that addresses conflicting human preferences and reward hacking. By releasing InternLM2 models in different training stages and model sizes, we provide the community with insights into the model's evolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge