Gang Zhao
Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation for E-Commerce Relevance Learning
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Effective query-item relevance modeling is pivotal for enhancing user experience and safeguarding user satisfaction in e-commerce search systems. Recently, benefiting from the vast inherent knowledge, Large Language Model (LLM) approach demonstrates strong performance and long-tail generalization ability compared with previous neural-based specialized relevance learning methods. Though promising, current LLM-based methods encounter the following inadequacies in practice: First, the massive parameters and computational demands make it difficult to be deployed online. Second, distilling LLM models to online models is a feasible direction, but the LLM relevance modeling is a black box, and its rich intrinsic knowledge is difficult to extract and apply online. To improve the interpretability of LLM and boost the performance of online relevance models via LLM, we propose an Explainable LLM-driven Multi-dimensional Distillation framework for e-commerce relevance learning, which comprises two core components: (1) An Explainable LLM for relevance modeling (ELLM-rele), which decomposes the relevance learning into intermediate steps and models relevance learning as a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, thereby enhancing both interpretability and performance of LLM. (2) A Multi-dimensional Knowledge Distillation (MKD) architecture that transfers the knowledge of ELLM-rele to current deployable interaction-based and representation-based student models from both the relevance score distribution and CoT reasoning aspects. Through distilling the probabilistic and CoT reasoning knowledge, MKD improves both the semantic interaction and long-tail generalization abilities of student models. Extensive offline evaluations and online experiments on Taobao search ad scene demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly enhances e-commerce relevance learning performance and user experience.
Dance of the ADS: Orchestrating Failures through Historically-Informed Scenario Fuzzing
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:As autonomous driving systems (ADS) advance towards higher levels of autonomy, orchestrating their safety verification becomes increasingly intricate. This paper unveils ScenarioFuzz, a pioneering scenario-based fuzz testing methodology. Designed like a choreographer who understands the past performances, it uncovers vulnerabilities in ADS without the crutch of predefined scenarios. Leveraging map road networks, such as OPENDRIVE, we extract essential data to form a foundational scenario seed corpus. This corpus, enriched with pertinent information, provides the necessary boundaries for fuzz testing in the absence of starting scenarios. Our approach integrates specialized mutators and mutation techniques, combined with a graph neural network model, to predict and filter out high-risk scenario seeds, optimizing the fuzzing process using historical test data. Compared to other methods, our approach reduces the time cost by an average of 60.3%, while the number of error scenarios discovered per unit of time increases by 103%. Furthermore, we propose a self-supervised collision trajectory clustering method, which aids in identifying and summarizing 54 high-risk scenario categories prone to inducing ADS faults. Our experiments have successfully uncovered 58 bugs across six tested systems, emphasizing the critical safety concerns of ADS.
K-ESConv: Knowledge Injection for Emotional Support Dialogue Systems via Prompt Learning
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Automatic psychological counseling requires mass of professional knowledge that can be found in online counseling forums. Motivated by this, we propose K-ESConv, a novel prompt learning based knowledge injection method for emotional support dialogue system, transferring forum knowledge to response generation. We evaluate our model on an emotional support dataset ESConv, where the model retrieves and incorporates knowledge from external professional emotional Q\&A forum. Experiment results show that the proposed method outperforms existing baselines on both automatic evaluation and human evaluation, which shows that our approach significantly improves the correlation and diversity of responses and provides more comfort and better suggestion for the seeker.
DemoNSF: A Multi-task Demonstration-based Generative Framework for Noisy Slot Filling Task
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Recently, prompt-based generative frameworks have shown impressive capabilities in sequence labeling tasks. However, in practical dialogue scenarios, relying solely on simplistic templates and traditional corpora presents a challenge for these methods in generalizing to unknown input perturbations. To address this gap, we propose a multi-task demonstration based generative framework for noisy slot filling, named DemoNSF. Specifically, we introduce three noisy auxiliary tasks, namely noisy recovery (NR), random mask (RM), and hybrid discrimination (HD), to implicitly capture semantic structural information of input perturbations at different granularities. In the downstream main task, we design a noisy demonstration construction strategy for the generative framework, which explicitly incorporates task-specific information and perturbed distribution during training and inference. Experiments on two benchmarks demonstrate that DemoNSF outperforms all baseline methods and achieves strong generalization. Further analysis provides empirical guidance for the practical application of generative frameworks. Our code is released at https://github.com/dongguanting/Demo-NSF.
Type-aware Decoding via Explicitly Aggregating Event Information for Document-level Event Extraction
Oct 16, 2023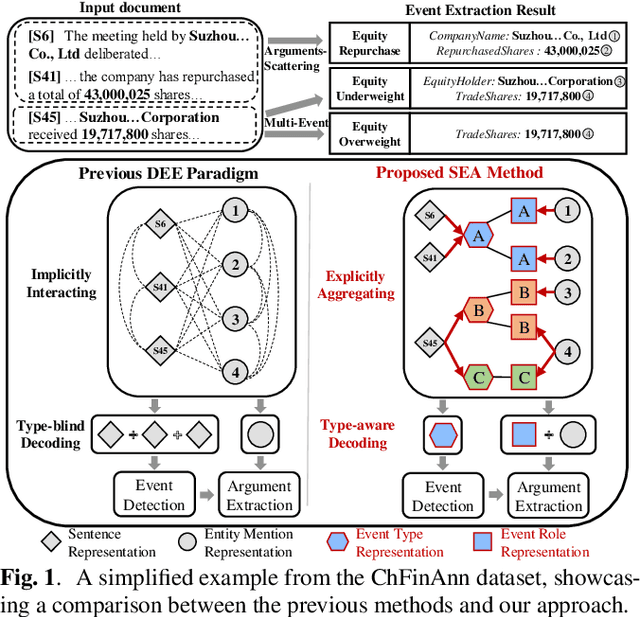



Abstract:Document-level event extraction (DEE) faces two main challenges: arguments-scattering and multi-event. Although previous methods attempt to address these challenges, they overlook the interference of event-unrelated sentences during event detection and neglect the mutual interference of different event roles during argument extraction. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel Schema-based Explicitly Aggregating~(SEA) model to address these limitations. SEA aggregates event information into event type and role representations, enabling the decoding of event records based on specific type-aware representations. By detecting each event based on its event type representation, SEA mitigates the interference caused by event-unrelated information. Furthermore, SEA extracts arguments for each role based on its role-aware representations, reducing mutual interference between different roles. Experimental results on the ChFinAnn and DuEE-fin datasets show that SEA outperforms the SOTA methods.
DemoSG: Demonstration-enhanced Schema-guided Generation for Low-resource Event Extraction
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Most current Event Extraction (EE) methods focus on the high-resource scenario, which requires a large amount of annotated data and can hardly be applied to low-resource domains. To address EE more effectively with limited resources, we propose the Demonstration-enhanced Schema-guided Generation (DemoSG) model, which benefits low-resource EE from two aspects: Firstly, we propose the demonstration-based learning paradigm for EE to fully use the annotated data, which transforms them into demonstrations to illustrate the extraction process and help the model learn effectively. Secondly, we formulate EE as a natural language generation task guided by schema-based prompts, thereby leveraging label semantics and promoting knowledge transfer in low-resource scenarios. We conduct extensive experiments under in-domain and domain adaptation low-resource settings on three datasets, and study the robustness of DemoSG. The results show that DemoSG significantly outperforms current methods in low-resource scenarios.
A Multi-Task Semantic Decomposition Framework with Task-specific Pre-training for Few-Shot NER
Aug 28, 2023
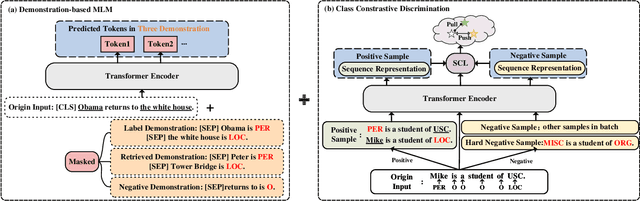

Abstract:The objective of few-shot named entity recognition is to identify named entities with limited labeled instances. Previous works have primarily focused on optimizing the traditional token-wise classification framework, while neglecting the exploration of information based on NER data characteristics. To address this issue, we propose a Multi-Task Semantic Decomposition Framework via Joint Task-specific Pre-training (MSDP) for few-shot NER. Drawing inspiration from demonstration-based and contrastive learning, we introduce two novel pre-training tasks: Demonstration-based Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and Class Contrastive Discrimination. These tasks effectively incorporate entity boundary information and enhance entity representation in Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). In the downstream main task, we introduce a multi-task joint optimization framework with the semantic decomposing method, which facilitates the model to integrate two different semantic information for entity classification. Experimental results of two few-shot NER benchmarks demonstrate that MSDP consistently outperforms strong baselines by a large margin. Extensive analyses validate the effectiveness and generalization of MSDP.
PCRED: Zero-shot Relation Triplet Extraction with Potential Candidate Relation Selection and Entity Boundary Detection
Dec 13, 2022



Abstract:Zero-shot relation triplet extraction (ZeroRTE) aims to extract relation triplets from unstructured texts under the zero-shot setting, where the relation sets at the training and testing stages are disjoint. Previous state-of-the-art method handles this challenging task by leveraging pretrained language models to generate data as additional training samples, which increases the training cost and severely constrains the model performance. To address the above issues, we propose a novel method named PCRED for ZeroRTE with Potential Candidate Relation Selection and Entity Boundary Detection. The remarkable characteristic of PCRED is that it does not rely on additional data and still achieves promising performance. The model adopts a relation-first paradigm, recognizing unseen relations through candidate relation selection. With this approach, the semantics of relations are naturally infused in the context. Entities are extracted based on the context and the semantics of relations subsequently. We evaluate our model on two ZeroRTE datasets. The experiment results show that our method consistently outperforms previous works. Our code will be available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PCRED.
Applications of BERT Based Sequence Tagging Models on Chinese Medical Text Attributes Extraction
Aug 22, 2020
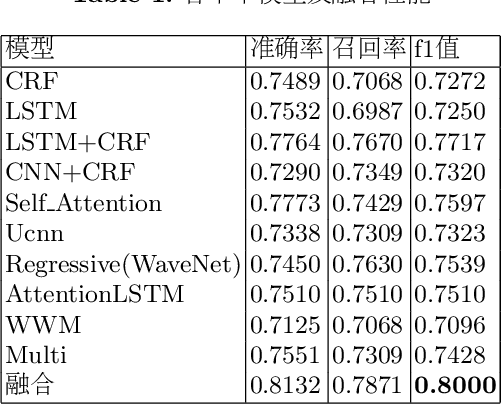


Abstract:We convert the Chinese medical text attributes extraction task into a sequence tagging or machine reading comprehension task. Based on BERT pre-trained models, we have not only tried the widely used LSTM-CRF sequence tagging model, but also other sequence models, such as CNN, UCNN, WaveNet, SelfAttention, etc, which reaches similar performance as LSTM+CRF. This sheds a light on the traditional sequence tagging models. Since the aspect of emphasis for different sequence tagging models varies substantially, ensembling these models adds diversity to the final system. By doing so, our system achieves good performance on the task of Chinese medical text attributes extraction (subtask 2 of CCKS 2019 task 1).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge