Shijie Zhu
Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces For Multi-task Learning
Mar 05, 2025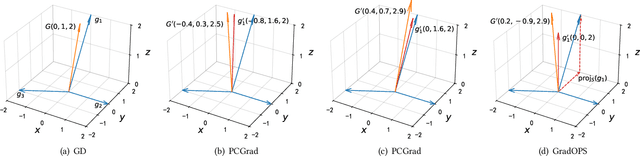
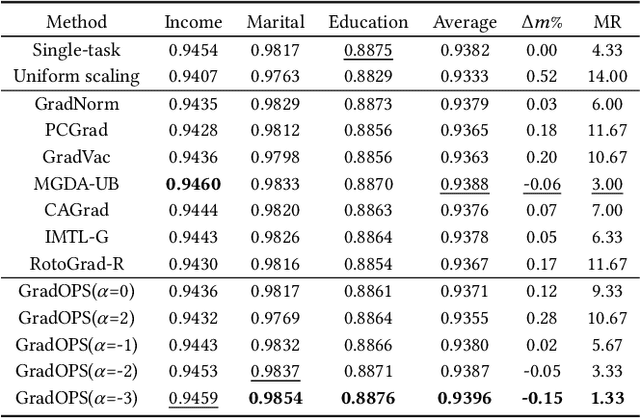
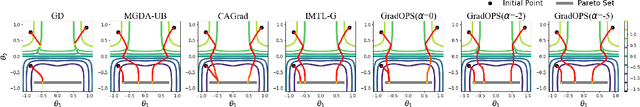
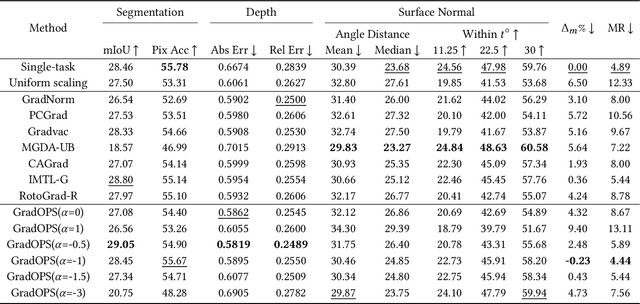
Abstract:Although multi-task learning (MTL) has been a preferred approach and successfully applied in many real-world scenarios, MTL models are not guaranteed to outperform single-task models on all tasks mainly due to the negative effects of conflicting gradients among the tasks. In this paper, we fully examine the influence of conflicting gradients and further emphasize the importance and advantages of achieving non-conflicting gradients which allows simple but effective trade-off strategies among the tasks with stable performance. Based on our findings, we propose the Gradient Deconfliction via Orthogonal Projections onto Subspaces (GradOPS) spanned by other task-specific gradients. Our method not only solves all conflicts among the tasks, but can also effectively search for diverse solutions towards different trade-off preferences among the tasks. Theoretical analysis on convergence is provided, and performance of our algorithm is fully testified on multiple benchmarks in various domains. Results demonstrate that our method can effectively find multiple state-of-the-art solutions with different trade-off strategies among the tasks on multiple datasets.
A Robust and Generalized Framework for Adversarial Graph Embedding
May 22, 2021



Abstract:Graph embedding is essential for graph mining tasks. With the prevalence of graph data in real-world applications, many methods have been proposed in recent years to learn high-quality graph embedding vectors various types of graphs. However, most existing methods usually randomly select the negative samples from the original graph to enhance the training data without considering the noise. In addition, most of these methods only focus on the explicit graph structures and cannot fully capture complex semantics of edges such as various relationships or asymmetry. In order to address these issues, we propose a robust and generalized framework for adversarial graph embedding based on generative adversarial networks. Inspired by generative adversarial network, we propose a robust and generalized framework for adversarial graph embedding, named AGE. AGE generates the fake neighbor nodes as the enhanced negative samples from the implicit distribution, and enables the discriminator and generator to jointly learn each node's robust and generalized representation. Based on this framework, we propose three models to handle three types of graph data and derive the corresponding optimization algorithms, i.e., UG-AGE and DG-AGE for undirected and directed homogeneous graphs, respectively, and HIN-AGE for heterogeneous information networks. Extensive experiments show that our methods consistently and significantly outperform existing state-of-the-art methods across multiple graph mining tasks, including link prediction, node classification, and graph reconstruction.
Adversarial Directed Graph Embedding
Aug 09, 2020



Abstract:Node representation learning for directed graphs is critically important to facilitate many graph mining tasks. To capture the directed edges between nodes, existing methods mostly learn two embedding vectors for each node, source vector and target vector. However, these methods learn the source and target vectors separately. For the node with very low indegree or outdegree, the corresponding target vector or source vector cannot be effectively learned. In this paper, we propose a novel Directed Graph embedding framework based on Generative Adversarial Network, called DGGAN. The main idea is to use adversarial mechanisms to deploy a discriminator and two generators that jointly learn each node's source and target vectors. For a given node, the two generators are trained to generate its fake target and source neighbor nodes from the same underlying distribution, and the discriminator aims to distinguish whether a neighbor node is real or fake. The two generators are formulated into a unified framework and could mutually reinforce each other to learn more robust source and target vectors. Extensive experiments show that DGGAN consistently and significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across multiple graph mining tasks on directed graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge