Bofang Li
Multi-Scenario Ranking with Adaptive Feature Learning
Jun 29, 2023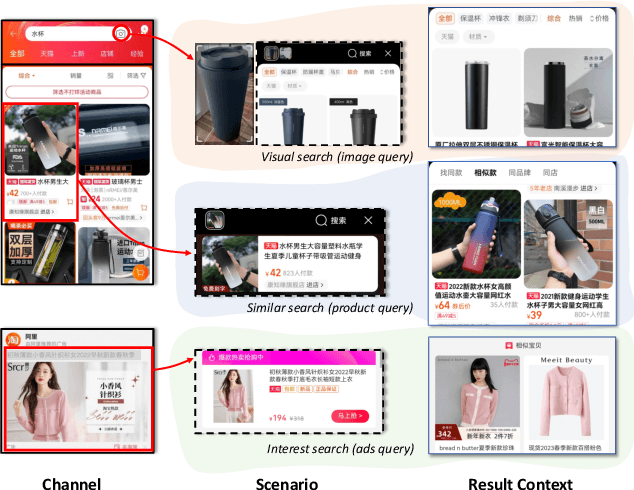
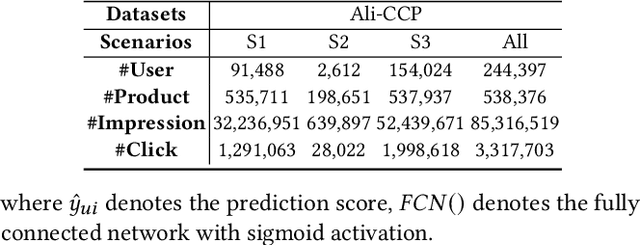
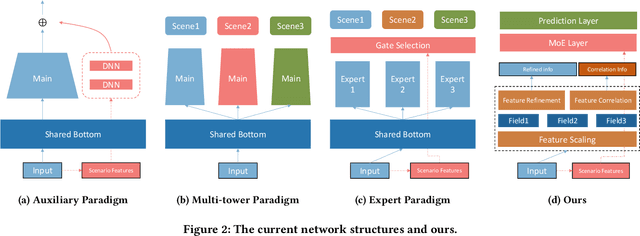
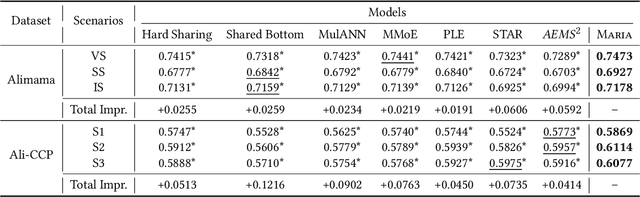
Abstract:Recently, Multi-Scenario Learning (MSL) is widely used in recommendation and retrieval systems in the industry because it facilitates transfer learning from different scenarios, mitigating data sparsity and reducing maintenance cost. These efforts produce different MSL paradigms by searching more optimal network structure, such as Auxiliary Network, Expert Network, and Multi-Tower Network. It is intuitive that different scenarios could hold their specific characteristics, activating the user's intents quite differently. In other words, different kinds of auxiliary features would bear varying importance under different scenarios. With more discriminative feature representations refined in a scenario-aware manner, better ranking performance could be easily obtained without expensive search for the optimal network structure. Unfortunately, this simple idea is mainly overlooked but much desired in real-world systems.Further analysis also validates the rationality of adaptive feature learning under a multi-scenario scheme. Moreover, our A/B test results on the Alibaba search advertising platform also demonstrate that Maria is superior in production environments.
CCL4Rec: Contrast over Contrastive Learning for Micro-video Recommendation
Aug 17, 2022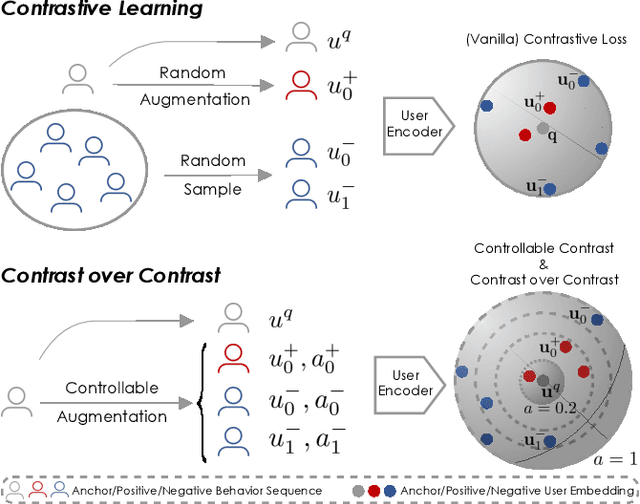
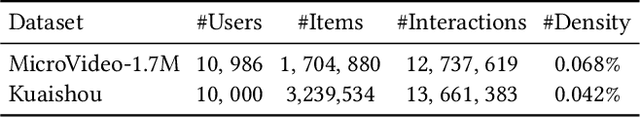
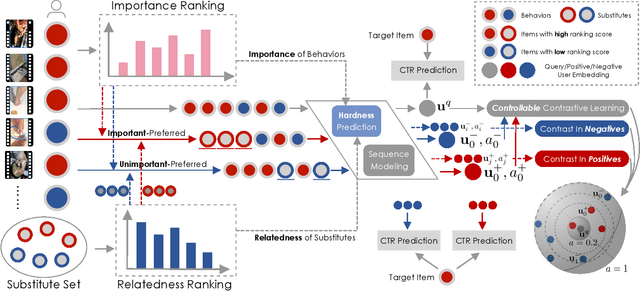
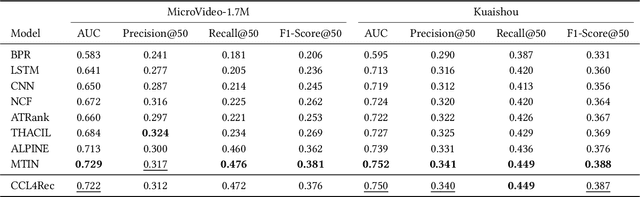
Abstract:Micro-video recommender systems suffer from the ubiquitous noises in users' behaviors, which might render the learned user representation indiscriminating, and lead to trivial recommendations (e.g., popular items) or even weird ones that are far beyond users' interests. Contrastive learning is an emergent technique for learning discriminating representations with random data augmentations. However, due to neglecting the noises in user behaviors and treating all augmented samples equally, the existing contrastive learning framework is insufficient for learning discriminating user representations in recommendation. To bridge this research gap, we propose the Contrast over Contrastive Learning framework for training recommender models, named CCL4Rec, which models the nuances of different augmented views by further contrasting augmented positives/negatives with adaptive pulling/pushing strengths, i.e., the contrast over (vanilla) contrastive learning. To accommodate these contrasts, we devise the hardness-aware augmentations that track the importance of behaviors being replaced in the query user and the relatedness of substitutes, and thus determining the quality of augmented positives/negatives. The hardness-aware augmentation also permits controllable contrastive learning, leading to performance gains and robust training. In this way, CCL4Rec captures the nuances of historical behaviors for a given user, which explicitly shields off the learned user representation from the effects of noisy behaviors. We conduct extensive experiments on two micro-video recommendation benchmarks, which demonstrate that CCL4Rec with far less model parameters could achieve comparable performance to existing state-of-the-art method, and improve the training/inference speed by several orders of magnitude.
AdaBERT: Task-Adaptive BERT Compression with Differentiable Neural Architecture Search
Jan 13, 2020



Abstract:Large pre-trained language models such as BERT have shown their effectiveness in various natural language processing tasks. However, the huge parameter size makes them difficult to be deployed in real-time applications that require quick inference with limited resources. Existing methods compress BERT into small models while such compression is task-independent, i.e., the same compressed BERT for all different downstream tasks. Motivated by the necessity and benefits of task-oriented BERT compression, we propose a novel compression method, AdaBERT, that leverages differentiable Neural Architecture Search to automatically compress BERT into task-adaptive small models for specific tasks. We incorporate a task-oriented knowledge distillation loss to provide search hints and an efficiency-aware loss as search constraints, which enables a good trade-off between efficiency and effectiveness for task-adaptive BERT compression. We evaluate AdaBERT on several NLP tasks, and the results demonstrate that those task-adaptive compressed models are 12.7x to 29.3x faster than BERT in inference time and 11.5x to 17.0x smaller in terms of parameter size, while comparable performance is maintained.
Learning Document Embeddings by Predicting N-grams for Sentiment Classification of Long Movie Reviews
Apr 23, 2016



Abstract:Despite the loss of semantic information, bag-of-ngram based methods still achieve state-of-the-art results for tasks such as sentiment classification of long movie reviews. Many document embeddings methods have been proposed to capture semantics, but they still can't outperform bag-of-ngram based methods on this task. In this paper, we modify the architecture of the recently proposed Paragraph Vector, allowing it to learn document vectors by predicting not only words, but n-gram features as well. Our model is able to capture both semantics and word order in documents while keeping the expressive power of learned vectors. Experimental results on IMDB movie review dataset shows that our model outperforms previous deep learning models and bag-of-ngram based models due to the above advantages. More robust results are also obtained when our model is combined with other models. The source code of our model will be also published together with this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge