Dong Yao
Combining Incomplete Observational and Randomized Data for Heterogeneous Treatment Effects
Oct 28, 2024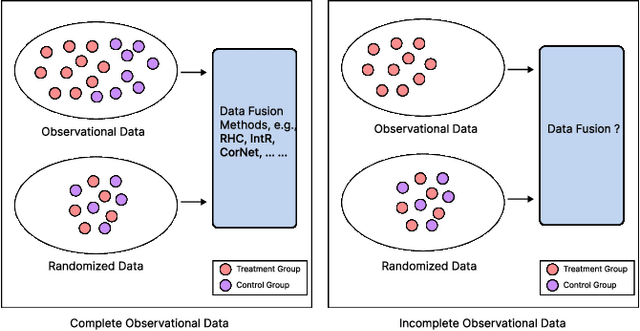
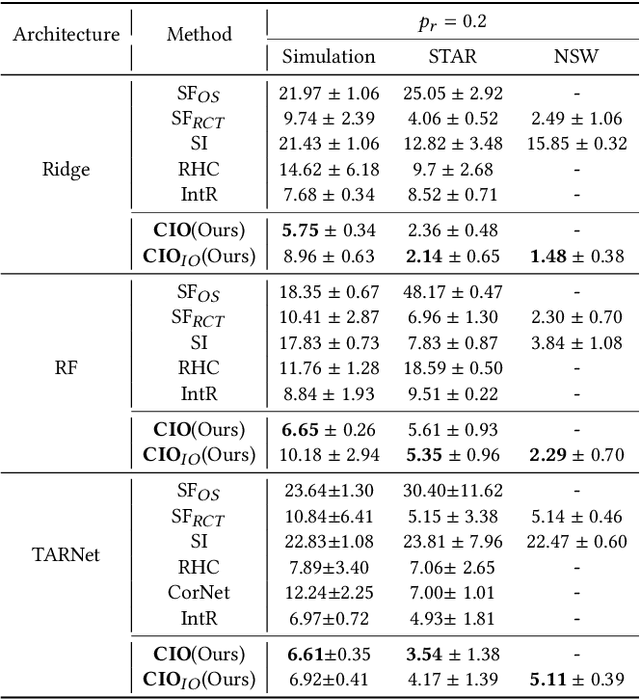
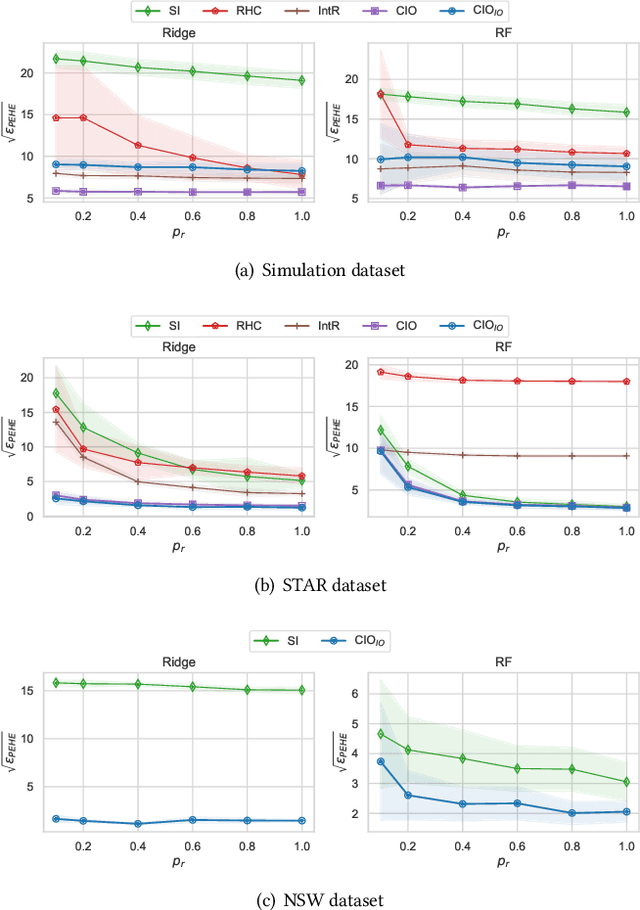
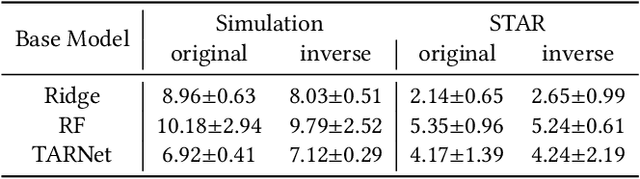
Abstract:Data from observational studies (OSs) is widely available and readily obtainable yet frequently contains confounding biases. On the other hand, data derived from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) helps to reduce these biases; however, it is expensive to gather, resulting in a tiny size of randomized data. For this reason, effectively fusing observational data and randomized data to better estimate heterogeneous treatment effects (HTEs) has gained increasing attention. However, existing methods for integrating observational data with randomized data must require \textit{complete} observational data, meaning that both treated subjects and untreated subjects must be included in OSs. This prerequisite confines the applicability of such methods to very specific situations, given that including all subjects, whether treated or untreated, in observational studies is not consistently achievable. In our paper, we propose a resilient approach to \textbf{C}ombine \textbf{I}ncomplete \textbf{O}bservational data and randomized data for HTE estimation, which we abbreviate as \textbf{CIO}. The CIO is capable of estimating HTEs efficiently regardless of the completeness of the observational data, be it full or partial. Concretely, a confounding bias function is first derived using the pseudo-experimental group from OSs, in conjunction with the pseudo-control group from RCTs, via an effect estimation procedure. This function is subsequently utilized as a corrective residual to rectify the observed outcomes of observational data during the HTE estimation by combining the available observational data and the all randomized data. To validate our approach, we have conducted experiments on a synthetic dataset and two semi-synthetic datasets.
A General and Flexible Multi-concept Parsing Framework for Multilingual Semantic Matching
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Sentence semantic matching is a research hotspot in natural language processing, which is considerably significant in various key scenarios, such as community question answering, searching, chatbot, and recommendation. Since most of the advanced models directly model the semantic relevance among words between two sentences while neglecting the \textit{keywords} and \textit{intents} concepts of them, DC-Match is proposed to disentangle keywords from intents and utilizes them to optimize the matching performance. Although DC-Match is a simple yet effective method for semantic matching, it highly depends on the external NER techniques to identify the keywords of sentences, which limits the performance of semantic matching for minor languages since satisfactory NER tools are usually hard to obtain. In this paper, we propose to generally and flexibly resolve the text into multi concepts for multilingual semantic matching to liberate the model from the reliance on NER models. To this end, we devise a \underline{M}ulti-\underline{C}oncept \underline{P}arsed \underline{S}emantic \underline{M}atching framework based on the pre-trained language models, abbreviated as \textbf{MCP-SM}, to extract various concepts and infuse them into the classification tokens. We conduct comprehensive experiments on English datasets QQP and MRPC, and Chinese dataset Medical-SM. Besides, we experiment on Arabic datasets MQ2Q and XNLI, the outstanding performance further prove MCP-SM's applicability in low-resource languages.
Music-PAW: Learning Music Representations via Hierarchical Part-whole Interaction and Contrast
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:The excellent performance of recent self-supervised learning methods on various downstream tasks has attracted great attention from academia and industry. Some recent research efforts have been devoted to self-supervised music representation learning. Nevertheless, most of them learn to represent equally-sized music clips in the waveform or a spectrogram. Despite being effective in some tasks, learning music representations in such a manner largely neglect the inherent part-whole hierarchies of music. Due to the hierarchical nature of the auditory cortex [24], understanding the bottom-up structure of music, i.e., how different parts constitute the whole at different levels, is essential for music understanding and representation learning. This work pursues hierarchical music representation learning and introduces the Music-PAW framework, which enables feature interactions of cropped music clips with part-whole hierarchies. From a technical perspective, we propose a transformer-based part-whole interaction module to progressively reason the structural relationships between part-whole music clips at adjacent levels. Besides, to create a multi-hierarchy representation space, we devise a hierarchical contrastive learning objective to align part-whole music representations in adjacent hierarchies. The merits of audio representation learning from part-whole hierarchies have been validated on various downstream tasks, including music classification (single-label and multi-label), cover song identification and acoustic scene classification.
Denoising Multi-modal Sequential Recommenders with Contrastive Learning
May 03, 2023



Abstract:There is a rapidly-growing research interest in engaging users with multi-modal data for accurate user modeling on recommender systems. Existing multimedia recommenders have achieved substantial improvements by incorporating various modalities and devising delicate modules. However, when users decide to interact with items, most of them do not fully read the content of all modalities. We refer to modalities that directly cause users' behaviors as point-of-interests, which are important aspects to capture users' interests. In contrast, modalities that do not cause users' behaviors are potential noises and might mislead the learning of a recommendation model. Not surprisingly, little research in the literature has been devoted to denoising such potential noises due to the inaccessibility of users' explicit feedback on their point-of-interests. To bridge the gap, we propose a weakly-supervised framework based on contrastive learning for denoising multi-modal recommenders (dubbed Demure). In a weakly-supervised manner, Demure circumvents the requirement of users' explicit feedback and identifies the noises by analyzing the modalities of all interacted items from a given user.
CCL4Rec: Contrast over Contrastive Learning for Micro-video Recommendation
Aug 17, 2022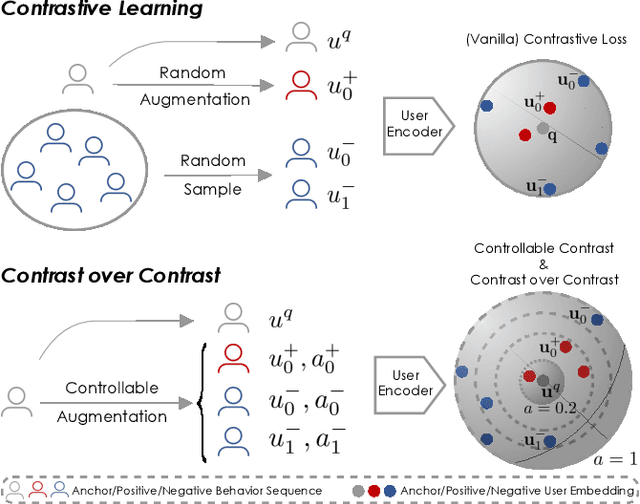
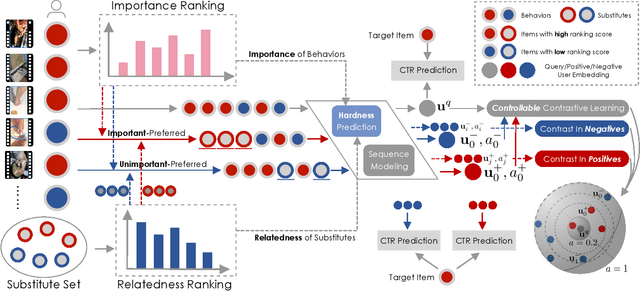
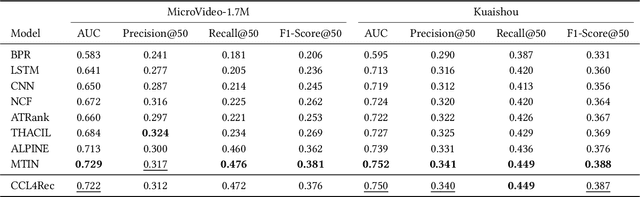
Abstract:Micro-video recommender systems suffer from the ubiquitous noises in users' behaviors, which might render the learned user representation indiscriminating, and lead to trivial recommendations (e.g., popular items) or even weird ones that are far beyond users' interests. Contrastive learning is an emergent technique for learning discriminating representations with random data augmentations. However, due to neglecting the noises in user behaviors and treating all augmented samples equally, the existing contrastive learning framework is insufficient for learning discriminating user representations in recommendation. To bridge this research gap, we propose the Contrast over Contrastive Learning framework for training recommender models, named CCL4Rec, which models the nuances of different augmented views by further contrasting augmented positives/negatives with adaptive pulling/pushing strengths, i.e., the contrast over (vanilla) contrastive learning. To accommodate these contrasts, we devise the hardness-aware augmentations that track the importance of behaviors being replaced in the query user and the relatedness of substitutes, and thus determining the quality of augmented positives/negatives. The hardness-aware augmentation also permits controllable contrastive learning, leading to performance gains and robust training. In this way, CCL4Rec captures the nuances of historical behaviors for a given user, which explicitly shields off the learned user representation from the effects of noisy behaviors. We conduct extensive experiments on two micro-video recommendation benchmarks, which demonstrate that CCL4Rec with far less model parameters could achieve comparable performance to existing state-of-the-art method, and improve the training/inference speed by several orders of magnitude.
Re4: Learning to Re-contrast, Re-attend, Re-construct for Multi-interest Recommendation
Aug 17, 2022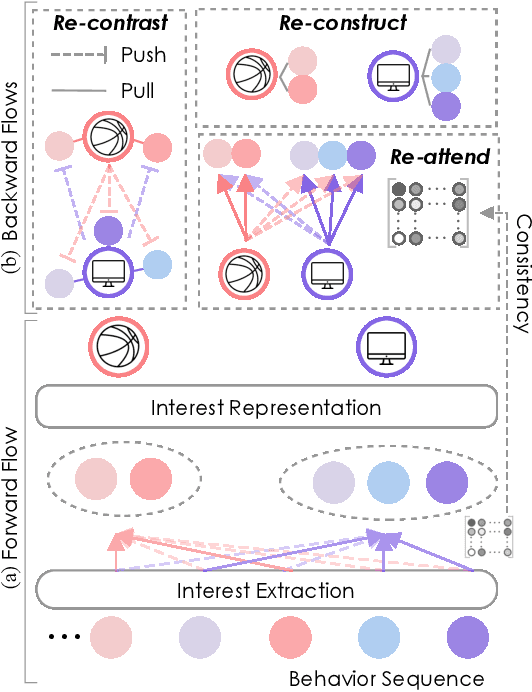
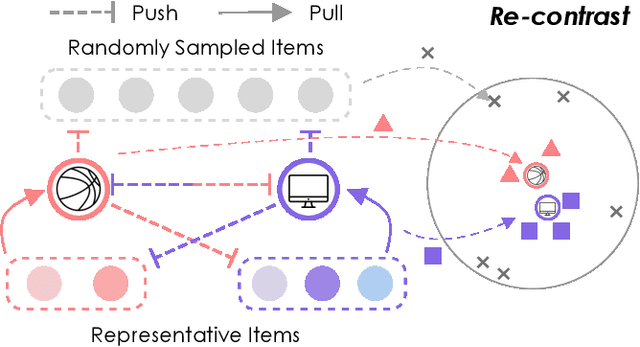
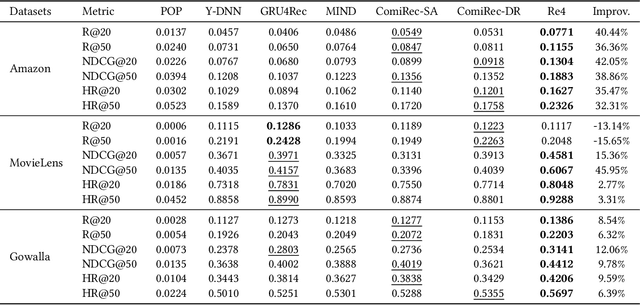
Abstract:Effectively representing users lie at the core of modern recommender systems. Since users' interests naturally exhibit multiple aspects, it is of increasing interest to develop multi-interest frameworks for recommendation, rather than represent each user with an overall embedding. Despite their effectiveness, existing methods solely exploit the encoder (the forward flow) to represent multiple aspects of interests. However, without explicit regularization, the interest embeddings may not be distinct from each other nor semantically reflect representative historical items. Towards this end, we propose the Re4 framework, which leverages the backward flow to reexamine each interest embedding. Specifically, Re4 encapsulates three backward flows, i.e., 1) Re-contrast, which drives each interest embedding to be distinct from other interests using contrastive learning; 2) Re-attend, which ensures the interest-item correlation estimation in the forward flow to be consistent with the criterion used in final recommendation; and 3) Re-construct, which ensures that each interest embedding can semantically reflect the information of representative items that relate to the corresponding interest. We demonstrate the novel forward-backward multi-interest paradigm on ComiRec, and perform extensive experiments on three real-world datasets. Empirical studies validate that Re4 helps to learn learning distinct and effective multi-interest representations.
Contrastive Learning with Positive-Negative Frame Mask for Music Representation
Apr 03, 2022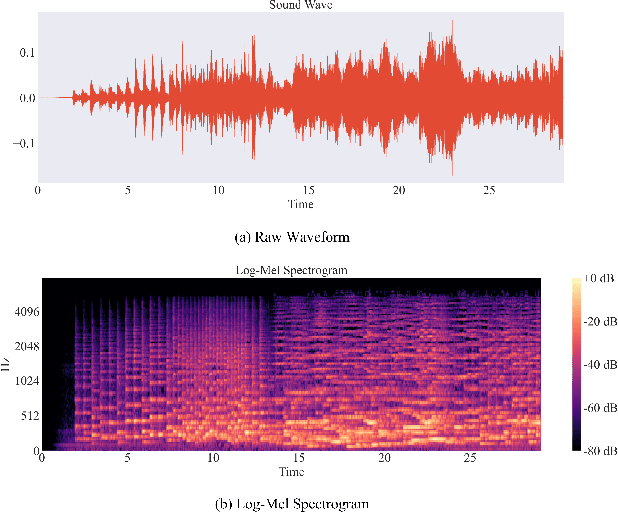
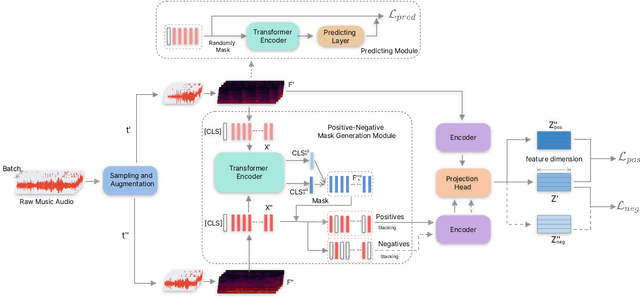
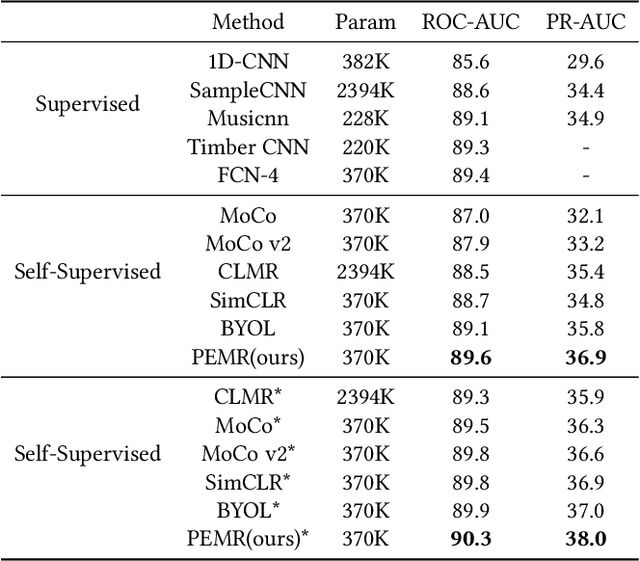
Abstract:Self-supervised learning, especially contrastive learning, has made an outstanding contribution to the development of many deep learning research fields. Recently, researchers in the acoustic signal processing field noticed its success and leveraged contrastive learning for better music representation. Typically, existing approaches maximize the similarity between two distorted audio segments sampled from the same music. In other words, they ensure a semantic agreement at the music level. However, those coarse-grained methods neglect some inessential or noisy elements at the frame level, which may be detrimental to the model to learn the effective representation of music. Towards this end, this paper proposes a novel Positive-nEgative frame mask for Music Representation based on the contrastive learning framework, abbreviated as PEMR. Concretely, PEMR incorporates a Positive-Negative Mask Generation module, which leverages transformer blocks to generate frame masks on the Log-Mel spectrogram. We can generate self-augmented negative and positive samples by masking important components or inessential components, respectively. We devise a novel contrastive learning objective to accommodate both self-augmented positives/negatives sampled from the same music. We conduct experiments on four public datasets. The experimental results of two music-related downstream tasks, music classification, and cover song identification, demonstrate the generalization ability and transferability of music representation learned by PEMR.
CauseRec: Counterfactual User Sequence Synthesis for Sequential Recommendation
Sep 11, 2021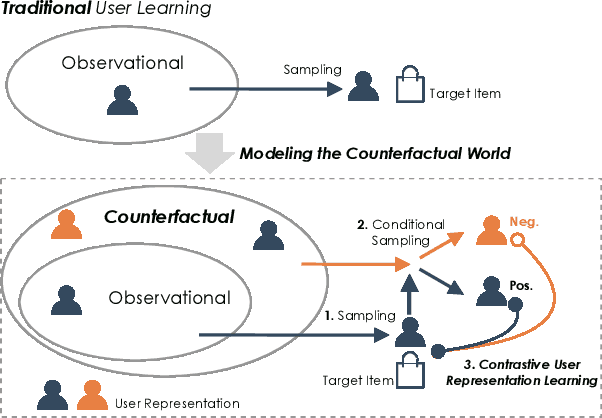
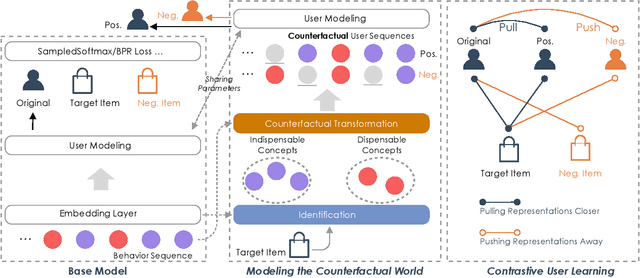
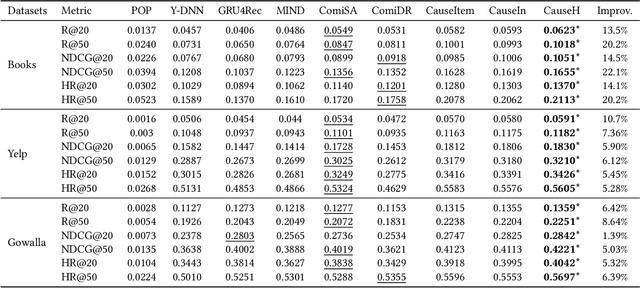
Abstract:Learning user representations based on historical behaviors lies at the core of modern recommender systems. Recent advances in sequential recommenders have convincingly demonstrated high capability in extracting effective user representations from the given behavior sequences. Despite significant progress, we argue that solely modeling the observational behaviors sequences may end up with a brittle and unstable system due to the noisy and sparse nature of user interactions logged. In this paper, we propose to learn accurate and robust user representations, which are required to be less sensitive to (attack on) noisy behaviors and trust more on the indispensable ones, by modeling counterfactual data distribution. Specifically, given an observed behavior sequence, the proposed CauseRec framework identifies dispensable and indispensable concepts at both the fine-grained item level and the abstract interest level. CauseRec conditionally samples user concept sequences from the counterfactual data distributions by replacing dispensable and indispensable concepts within the original concept sequence. With user representations obtained from the synthesized user sequences, CauseRec performs contrastive user representation learning by contrasting the counterfactual with the observational. We conduct extensive experiments on real-world public recommendation benchmarks and justify the effectiveness of CauseRec with multi-aspects model analysis. The results demonstrate that the proposed CauseRec outperforms state-of-the-art sequential recommenders by learning accurate and robust user representations.
Modeling High-order Interactions across Multi-interests for Micro-video Reommendation
Apr 01, 2021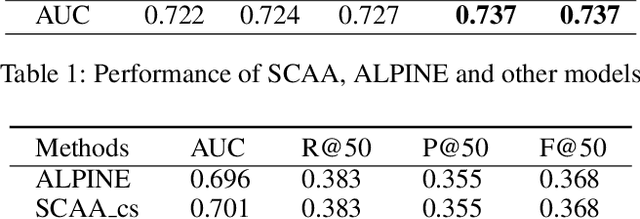
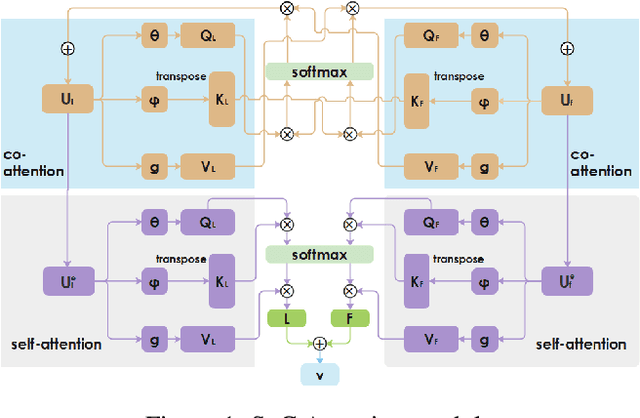
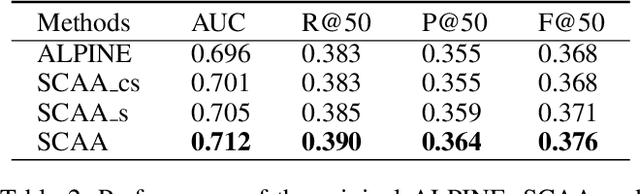
Abstract:Personalized recommendation system has become pervasive in various video platform. Many effective methods have been proposed, but most of them didn't capture the user's multi-level interest trait and dependencies between their viewed micro-videos well. To solve these problems, we propose a Self-over-Co Attention module to enhance user's interest representation. In particular, we first use co-attention to model correlation patterns across different levels and then use self-attention to model correlation patterns within a specific level. Experimental results on filtered public datasets verify that our presented module is useful.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge