Zhao-Yu Zhang
Towards Understanding the Overfitting Phenomenon of Deep Click-Through Rate Prediction Models
Sep 04, 2022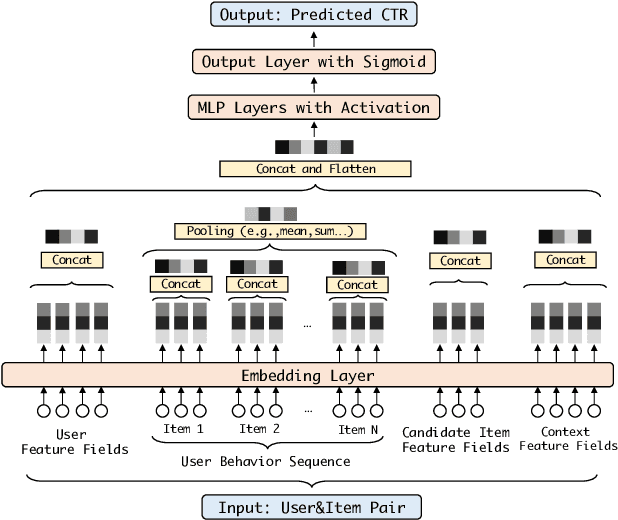
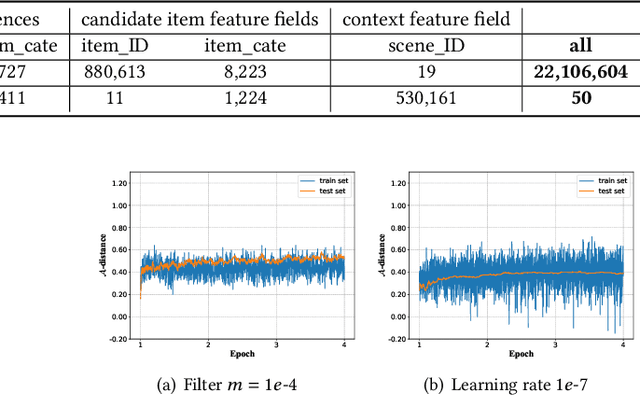
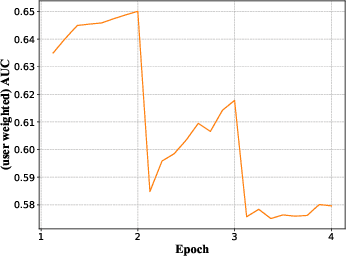
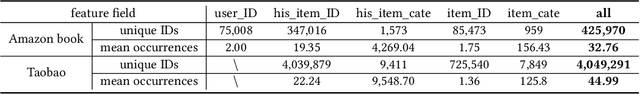
Abstract:Deep learning techniques have been applied widely in industrial recommendation systems. However, far less attention has been paid to the overfitting problem of models in recommendation systems, which, on the contrary, is recognized as a critical issue for deep neural networks. In the context of Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction, we observe an interesting one-epoch overfitting problem: the model performance exhibits a dramatic degradation at the beginning of the second epoch. Such a phenomenon has been witnessed widely in real-world applications of CTR models. Thereby, the best performance is usually achieved by training with only one epoch. To understand the underlying factors behind the one-epoch phenomenon, we conduct extensive experiments on the production data set collected from the display advertising system of Alibaba. The results show that the model structure, the optimization algorithm with a fast convergence rate, and the feature sparsity are closely related to the one-epoch phenomenon. We also provide a likely hypothesis for explaining such a phenomenon and conduct a set of proof-of-concept experiments. We hope this work can shed light on future research on training more epochs for better performance.
LIFE: Learning Individual Features for Multivariate Time Series Prediction with Missing Values
Oct 09, 2021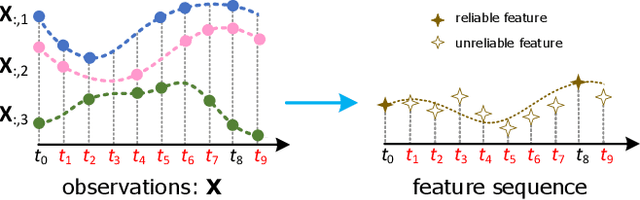

Abstract:Multivariate time series (MTS) prediction is ubiquitous in real-world fields, but MTS data often contains missing values. In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in using end-to-end models to handle MTS with missing values. To generate features for prediction, existing methods either merge all input dimensions of MTS or tackle each input dimension independently. However, both approaches are hard to perform well because the former usually produce many unreliable features and the latter lacks correlated information. In this paper, we propose a Learning Individual Features (LIFE) framework, which provides a new paradigm for MTS prediction with missing values. LIFE generates reliable features for prediction by using the correlated dimensions as auxiliary information and suppressing the interference from uncorrelated dimensions with missing values. Experiments on three real-world data sets verify the superiority of LIFE to existing state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge