Jia Zhang
LatentChem: From Textual CoT to Latent Thinking in Chemical Reasoning
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Chemical large language models (LLMs) predominantly rely on explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in natural language to perform complex reasoning. However, chemical reasoning is inherently continuous and structural, and forcing it into discrete linguistic tokens introduces a fundamental representation mismatch that constrains both efficiency and performance. We introduce LatentChem, a latent reasoning interface that decouples chemical computation from textual generation, enabling models to perform multi-step reasoning directly in continuous latent space while emitting language only for final outputs. Remarkably, we observe a consistent emergent behavior: when optimized solely for task success, models spontaneously internalize reasoning, progressively abandoning verbose textual derivations in favor of implicit latent computation. This shift is not merely stylistic but computationally advantageous. Across diverse chemical reasoning benchmarks, LatentChem achieves a 59.88\% non-tie win rate over strong CoT-based baselines on ChemCoTBench, while delivering a 10.84$\times$ average inference speedup. Our results provide empirical evidence that chemical reasoning is more naturally and effectively realized as continuous latent dynamics rather than discretized linguistic trajectories.
E2Former-V2: On-the-Fly Equivariant Attention with Linear Activation Memory
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Equivariant Graph Neural Networks (EGNNs) have become a widely used approach for modeling 3D atomistic systems. However, mainstream architectures face critical scalability bottlenecks due to the explicit construction of geometric features or dense tensor products on \textit{every} edge. To overcome this, we introduce \textbf{E2Former-V2}, a scalable architecture that integrates algebraic sparsity with hardware-aware execution. We first propose \textbf{E}quivariant \textbf{A}xis-\textbf{A}ligned \textbf{S}parsification (EAAS). EAAS builds on Wigner-$6j$ convolution by exploiting an $\mathrm{SO}(3) \rightarrow \mathrm{SO}(2)$ change of basis to transform computationally expensive dense tensor contractions into efficient, sparse parity re-indexing operations. Building on this representation, we introduce \textbf{On-the-Fly Equivariant Attention}, a fully node-centric mechanism implemented via a custom fused Triton kernel. By eliminating materialized edge tensors and maximizing SRAM utilization, our kernel achieves a \textbf{20$\times$ improvement in TFLOPS} compared to standard implementations. Extensive experiments on the SPICE and OMol25 datasets demonstrate that E2Former-V2 maintains comparable predictive performance while notably accelerating inference. This work demonstrates that large equivariant transformers can be trained efficiently using widely accessible GPU platforms. The code is avalible at https://github.com/IQuestLab/UBio-MolFM/tree/e2formerv2.
Scalable Machine Learning Force Fields for Macromolecular Systems Through Long-Range Aware Message Passing
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Machine learning force fields (MLFFs) have revolutionized molecular simulations by providing quantum mechanical accuracy at the speed of molecular mechanical computations. However, a fundamental reliance of these models on fixed-cutoff architectures limits their applicability to macromolecular systems where long-range interactions dominate. We demonstrate that this locality constraint causes force prediction errors to scale monotonically with system size, revealing a critical architectural bottleneck. To overcome this, we establish the systematically designed MolLR25 ({Mol}ecules with {L}ong-{R}ange effect) benchmark up to 1200 atoms, generated using high-fidelity DFT, and introduce E2Former-LSR, an equivariant transformer that explicitly integrates long-range attention blocks. E2Former-LSR exhibits stable error scaling, achieves superior fidelity in capturing non-covalent decay, and maintains precision on complex protein conformations. Crucially, its efficient design provides up to 30% speedup compared to purely local models. This work validates the necessity of non-local architectures for generalizable MLFFs, enabling high-fidelity molecular dynamics for large-scale chemical and biological systems.
Tibetan Language and AI: A Comprehensive Survey of Resources, Methods and Challenges
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Tibetan, one of the major low-resource languages in Asia, presents unique linguistic and sociocultural characteristics that pose both challenges and opportunities for AI research. Despite increasing interest in developing AI systems for underrepresented languages, Tibetan has received limited attention due to a lack of accessible data resources, standardized benchmarks, and dedicated tools. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the current state of Tibetan AI in the AI domain, covering textual and speech data resources, NLP tasks, machine translation, speech recognition, and recent developments in LLMs. We systematically categorize existing datasets and tools, evaluate methods used across different tasks, and compare performance where possible. We also identify persistent bottlenecks such as data sparsity, orthographic variation, and the lack of unified evaluation metrics. Additionally, we discuss the potential of cross-lingual transfer, multi-modal learning, and community-driven resource creation. This survey aims to serve as a foundational reference for future work on Tibetan AI research and encourages collaborative efforts to build an inclusive and sustainable AI ecosystem for low-resource languages.
Beyond Single: A Data Selection Principle for LLM Alignment via Fine-Grained Preference Signals
Aug 11, 2025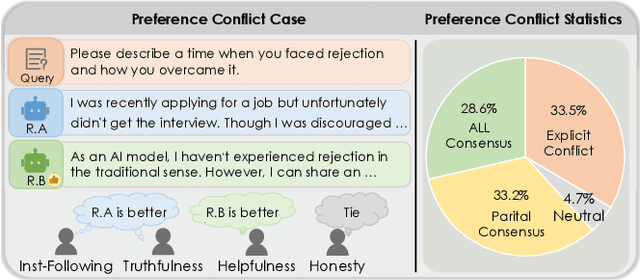
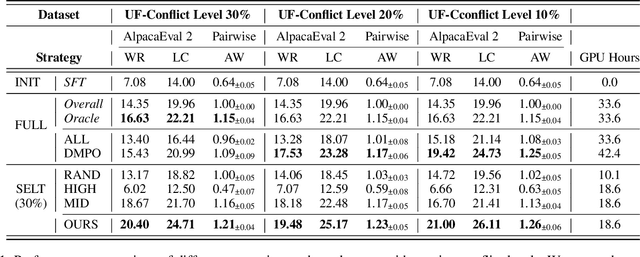
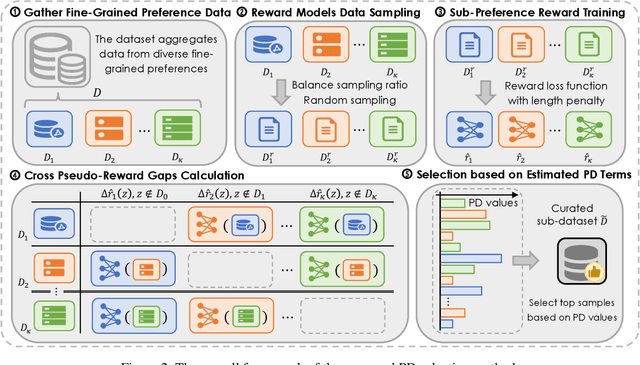
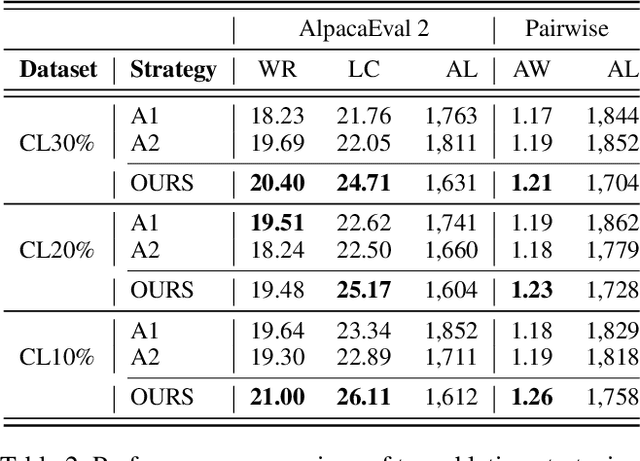
Abstract:Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with diverse human values requires moving beyond a single holistic "better-than" preference criterion. While collecting fine-grained, aspect-specific preference data is more reliable and scalable, existing methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) struggle with the severe noise and conflicts inherent in such aggregated datasets. In this paper, we tackle this challenge from a data-centric perspective. We first derive the Direct Multi-Preference Optimization (DMPO) objective, and uncover a key Preference Divergence (PD) term that quantifies inter-aspect preference conflicts. Instead of using this term for direct optimization, we leverage it to formulate a novel, theoretically-grounded data selection principle. Our principle advocates for selecting a subset of high-consensus data-identified by the most negative PD values-for efficient DPO training. We prove the optimality of this strategy by analyzing the loss bounds of the DMPO objective in the selection problem. To operationalize our approach, we introduce practical methods of PD term estimation and length bias mitigation, thereby proposing our PD selection method. Evaluation on the UltraFeedback dataset with three varying conflict levels shows that our simple yet effective strategy achieves over 10% relative improvement against both the standard holistic preference and a stronger oracle using aggregated preference signals, all while boosting training efficiency and obviating the need for intractable holistic preference annotating, unlocking the potential of robust LLM alignment via fine-grained preference signals.
eMotions: A Large-Scale Dataset and Audio-Visual Fusion Network for Emotion Analysis in Short-form Videos
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Short-form videos (SVs) have become a vital part of our online routine for acquiring and sharing information. Their multimodal complexity poses new challenges for video analysis, highlighting the need for video emotion analysis (VEA) within the community. Given the limited availability of SVs emotion data, we introduce eMotions, a large-scale dataset consisting of 27,996 videos with full-scale annotations. To ensure quality and reduce subjective bias, we emphasize better personnel allocation and propose a multi-stage annotation procedure. Additionally, we provide the category-balanced and test-oriented variants through targeted sampling to meet diverse needs. While there have been significant studies on videos with clear emotional cues (e.g., facial expressions), analyzing emotions in SVs remains a challenging task. The challenge arises from the broader content diversity, which introduces more distinct semantic gaps and complicates the representations learning of emotion-related features. Furthermore, the prevalence of audio-visual co-expressions in SVs leads to the local biases and collective information gaps caused by the inconsistencies in emotional expressions. To tackle this, we propose AV-CANet, an end-to-end audio-visual fusion network that leverages video transformer to capture semantically relevant representations. We further introduce the Local-Global Fusion Module designed to progressively capture the correlations of audio-visual features. Besides, EP-CE Loss is constructed to globally steer optimizations with tripolar penalties. Extensive experiments across three eMotions-related datasets and four public VEA datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed AV-CANet, while providing broad insights for future research. Moreover, we conduct ablation studies to examine the critical components of our method. Dataset and code will be made available at Github.
HOLA: Enhancing Audio-visual Deepfake Detection via Hierarchical Contextual Aggregations and Efficient Pre-training
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Advances in Generative AI have made video-level deepfake detection increasingly challenging, exposing the limitations of current detection techniques. In this paper, we present HOLA, our solution to the Video-Level Deepfake Detection track of 2025 1M-Deepfakes Detection Challenge. Inspired by the success of large-scale pre-training in the general domain, we first scale audio-visual self-supervised pre-training in the multimodal video-level deepfake detection, which leverages our self-built dataset of 1.81M samples, thereby leading to a unified two-stage framework. To be specific, HOLA features an iterative-aware cross-modal learning module for selective audio-visual interactions, hierarchical contextual modeling with gated aggregations under the local-global perspective, and a pyramid-like refiner for scale-aware cross-grained semantic enhancements. Moreover, we propose the pseudo supervised singal injection strategy to further boost model performance. Extensive experiments across expert models and MLLMs impressivly demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed HOLA. We also conduct a series of ablation studies to explore the crucial design factors of our introduced components. Remarkably, our HOLA ranks 1st, outperforming the second by 0.0476 AUC on the TestA set.
Probability Distribution Alignment and Low-Rank Weight Decomposition for Source-Free Domain Adaptive Brain Decoding
Apr 15, 2025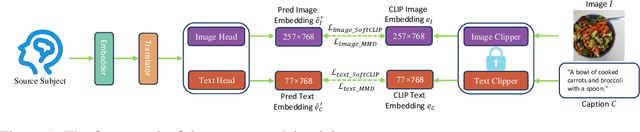


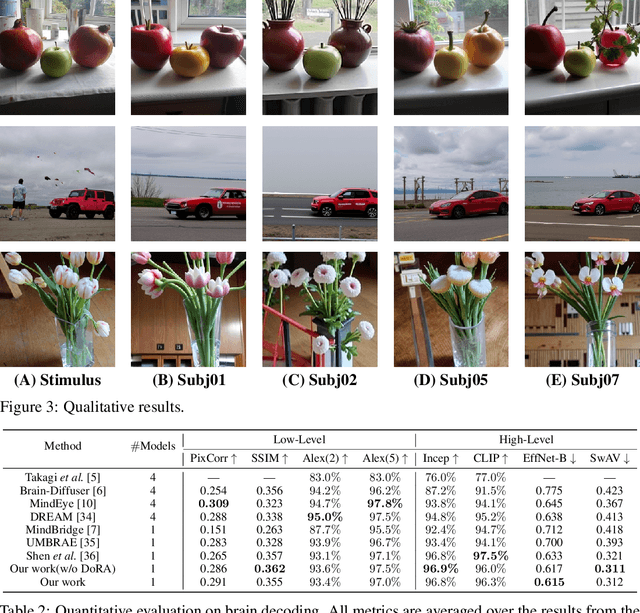
Abstract:Brain decoding currently faces significant challenges in individual differences, modality alignment, and high-dimensional embeddings. To address individual differences, researchers often use source subject data, which leads to issues such as privacy leakage and heavy data storage burdens. In modality alignment, current works focus on aligning the softmax probability distribution but neglect the alignment of marginal probability distributions, resulting in modality misalignment. Additionally, images and text are aligned separately with fMRI without considering the complex interplay between images and text, leading to poor image reconstruction. Finally, the enormous dimensionality of CLIP embeddings causes significant computational costs. Although the dimensionality of CLIP embeddings can be reduced by ignoring the number of patches obtained from images and the number of tokens acquired from text, this comes at the cost of a significant drop in model performance, creating a dilemma. To overcome these limitations, we propose a source-free domain adaptation-based brain decoding framework.
Artifact detection and localization in single-channel mobile EEG for sleep research using deep learning and attention mechanisms
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Artifacts in the electroencephalogram (EEG) degrade signal quality and impact the analysis of brain activity. Current methods for detecting artifacts in sleep EEG rely on simple threshold-based algorithms that require manual intervention, which is time-consuming and impractical due to the vast volume of data that novel mobile recording systems generate. We propose a convolutional neural network (CNN) model incorporating a convolutional block attention module (CNN-CBAM) to detect and identify the location of artifacts in the sleep EEG with attention maps. We benchmarked this model against six other machine learning and signal processing approaches. We trained/tuned all models on 72 manually annotated EEG recordings obtained during home-based monitoring from 18 healthy participants with a mean (SD) age of 68.05 y ($\pm$5.02). We tested them on 26 separate recordings from 6 healthy participants with a mean (SD) age of 68.33 y ($\pm$4.08), with contained artifacts in 4\% of epochs. CNN-CBAM achieved the highest area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.88), sensitivity (0.81), and specificity (0.86) when compared to the other approaches. The attention maps from CNN-CBAM localized artifacts within the epoch with a sensitivity of 0.71 and specificity of 0.67. This work demonstrates the feasibility of automating the detection and localization of artifacts in wearable sleep EEG.
mmHRR: Monitoring Heart Rate Recovery with Millimeter Wave Radar
Mar 28, 2025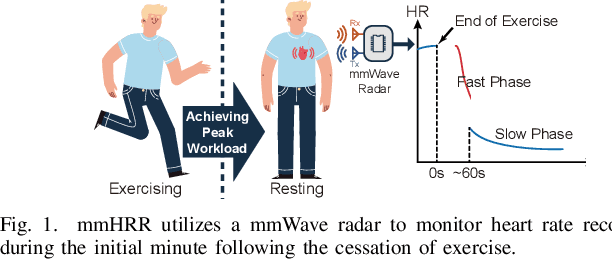
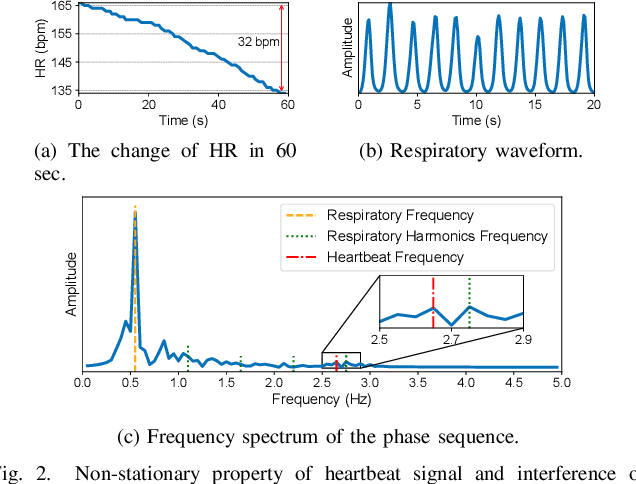
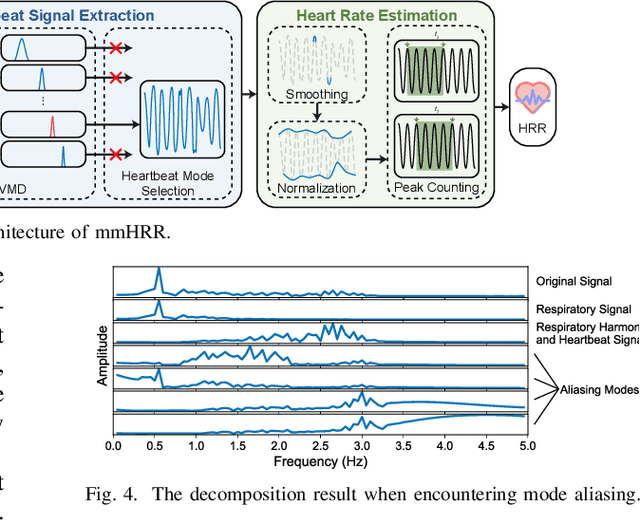
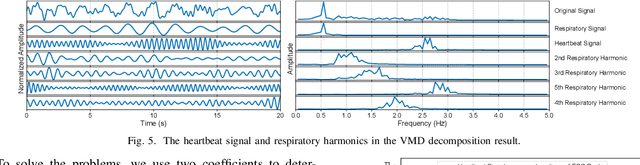
Abstract:Heart rate recovery (HRR) within the initial minute following exercise is a widely utilized metric for assessing cardiac autonomic function in individuals and predicting mortality risk in patients with cardiovascular disease. However, prevailing solutions for HRR monitoring typically involve the use of specialized medical equipment or contact wearable sensors, resulting in high costs and poor user experience. In this paper, we propose a contactless HRR monitoring technique, mmHRR, which achieves accurate heart rate (HR) estimation with a commercial mmWave radar. Unlike HR estimation at rest, the HR varies quickly after exercise and the heartbeat signal entangles with the respiration harmonics. To overcome these hurdles and effectively estimate the HR from the weak and non-stationary heartbeat signal, we propose a novel signal processing pipeline, including dynamic target tracking, adaptive heartbeat signal extraction, and accurate HR estimation with composite sliding windows. Real-world experiments demonstrate that mmHRR exhibits exceptional robustness across diverse environmental conditions, and achieves an average HR estimation error of 3.31 bpm (beats per minute), 71% lower than that of the state-of-the-art method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge