Xiuzhen Guo
Staged Voxel-Level Deep Reinforcement Learning for 3D Medical Image Segmentation with Noisy Annotations
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has achieved significant advancements in medical image segmentation. Currently, obtaining accurate segmentation outcomes is critically reliant on large-scale datasets with high-quality annotations. However, noisy annotations are frequently encountered owing to the complex morphological structures of organs in medical images and variations among different annotators, which can substantially limit the efficacy of segmentation models. Motivated by the fact that medical imaging annotator can correct labeling errors during segmentation based on prior knowledge, we propose an end-to-end Staged Voxel-Level Deep Reinforcement Learning (SVL-DRL) framework for robust medical image segmentation under noisy annotations. This framework employs a dynamic iterative update strategy to automatically mitigate the impact of erroneous labels without requiring manual intervention. The key advancements of SVL-DRL over existing works include: i) formulating noisy annotations as a voxel-dependent problem and addressing it through a novel staged reinforcement learning framework which guarantees robust model convergence; ii) incorporating a voxel-level asynchronous advantage actor-critic (vA3C) module that conceptualizes each voxel as an autonomous agent, which allows each agent to dynamically refine its own state representation during training, thereby directly mitigating the influence of erroneous labels; iii) designing a novel action space for the agents, along with a composite reward function that strategically combines the Dice value and a spatial continuity metric to significantly boost segmentation accuracy while maintain semantic integrity. Experiments on three public medical image datasets demonstrates State-of-The-Art (SoTA) performance under various experimental settings, with an average improvement of over 3\% in both Dice and IoU scores.
mmHRR: Monitoring Heart Rate Recovery with Millimeter Wave Radar
Mar 28, 2025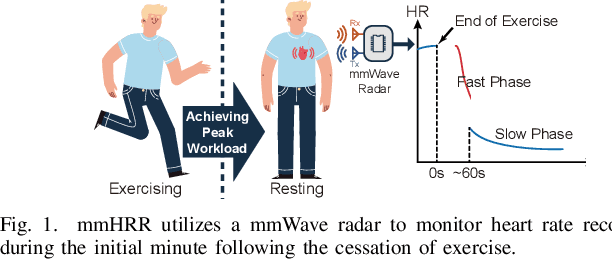
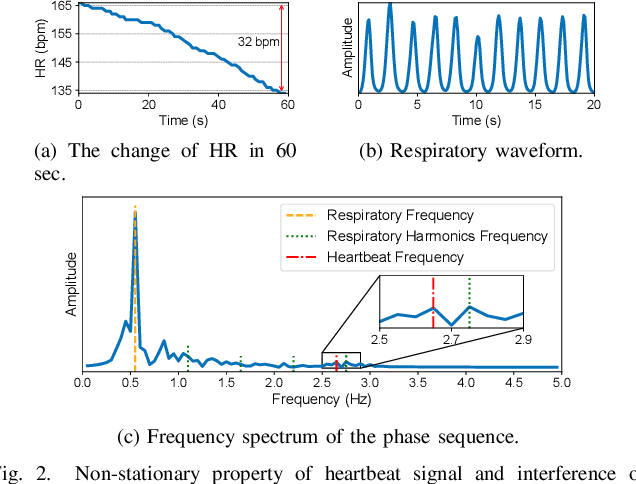
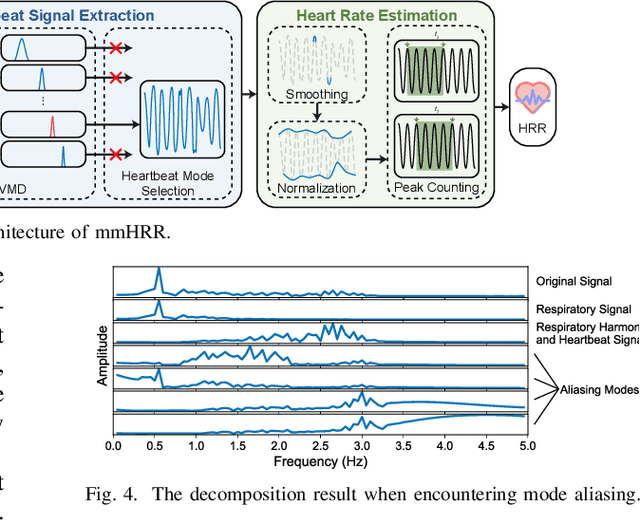
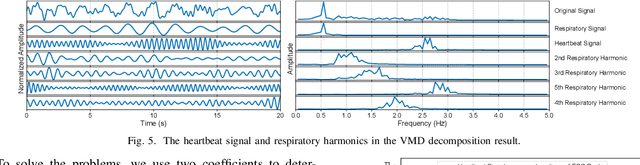
Abstract:Heart rate recovery (HRR) within the initial minute following exercise is a widely utilized metric for assessing cardiac autonomic function in individuals and predicting mortality risk in patients with cardiovascular disease. However, prevailing solutions for HRR monitoring typically involve the use of specialized medical equipment or contact wearable sensors, resulting in high costs and poor user experience. In this paper, we propose a contactless HRR monitoring technique, mmHRR, which achieves accurate heart rate (HR) estimation with a commercial mmWave radar. Unlike HR estimation at rest, the HR varies quickly after exercise and the heartbeat signal entangles with the respiration harmonics. To overcome these hurdles and effectively estimate the HR from the weak and non-stationary heartbeat signal, we propose a novel signal processing pipeline, including dynamic target tracking, adaptive heartbeat signal extraction, and accurate HR estimation with composite sliding windows. Real-world experiments demonstrate that mmHRR exhibits exceptional robustness across diverse environmental conditions, and achieves an average HR estimation error of 3.31 bpm (beats per minute), 71% lower than that of the state-of-the-art method.
GIGP: A Global Information Interacting and Geometric Priors Focusing Framework for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 12, 2025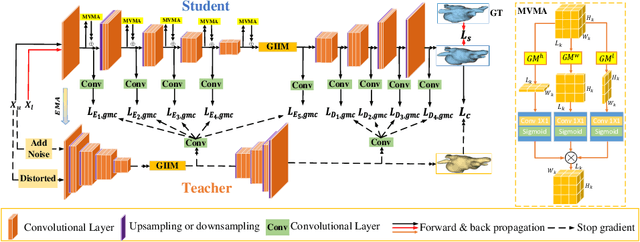
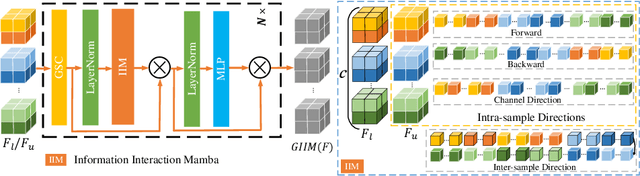
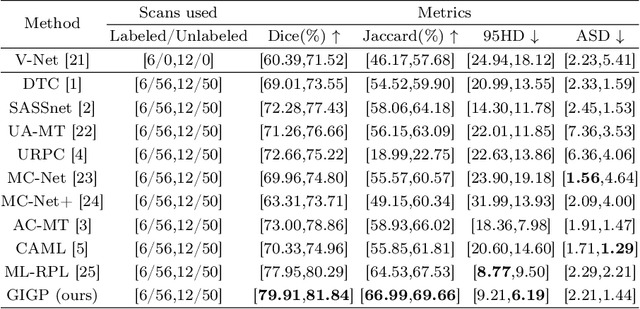
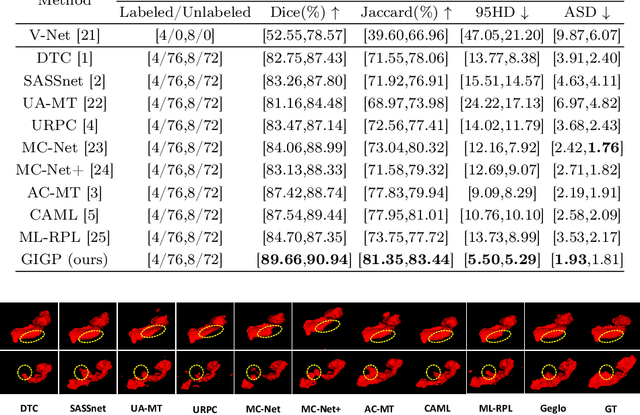
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning enhances medical image segmentation by leveraging unlabeled data, reducing reliance on extensive labeled datasets. On the one hand, the distribution discrepancy between limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data can hinder model generalization. Most existing methods rely on local similarity matching, which may introduce bias. In contrast, Mamba effectively models global context with linear complexity, learning more comprehensive data representations. On the other hand, medical images usually exhibit consistent anatomical structures defined by geometric features. Most existing methods fail to fully utilize global geometric priors, such as volumes, moments etc. In this work, we introduce a global information interaction and geometric priors focus framework (GIGP). Firstly, we present a Global Information Interaction Mamba module to reduce distribution discrepancy between labeled and unlabeled data. Secondly, we propose a Geometric Moment Attention Mechanism to extract richer global geometric features. Finally, we propose Global Geometric Perturbation Consistency to simulate organ dynamics and geometric variations, enhancing the ability of the model to learn generalized features. The superior performance on the NIH Pancreas and Left Atrium datasets demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach.
Diff-CL: A Novel Cross Pseudo-Supervision Method for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 12, 2025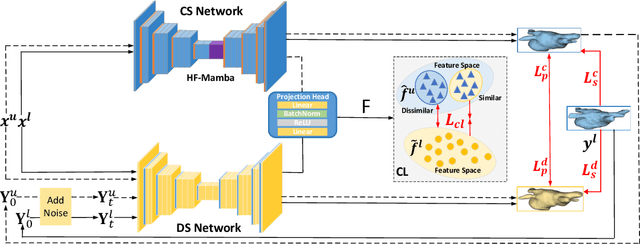
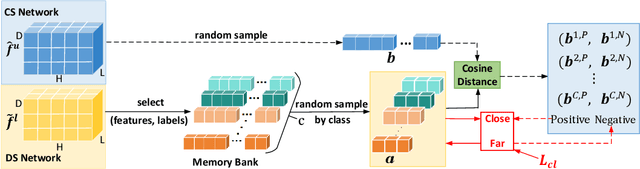

Abstract:Semi-supervised learning utilizes insights from unlabeled data to improve model generalization, thereby reducing reliance on large labeled datasets. Most existing studies focus on limited samples and fail to capture the overall data distribution. We contend that combining distributional information with detailed information is crucial for achieving more robust and accurate segmentation results. On the one hand, with its robust generative capabilities, diffusion models (DM) learn data distribution effectively. However, it struggles with fine detail capture, leading to generated images with misleading details. Combining DM with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) enables the former to learn data distribution while the latter corrects fine details. While capturing complete high-frequency details by CNNs requires substantial computational resources and is susceptible to local noise. On the other hand, given that both labeled and unlabeled data come from the same distribution, we believe that regions in unlabeled data similar to overall class semantics to labeled data are likely to belong to the same class, while regions with minimal similarity are less likely to. This work introduces a semi-supervised medical image segmentation framework from the distribution perspective (Diff-CL). Firstly, we propose a cross-pseudo-supervision learning mechanism between diffusion and convolution segmentation networks. Secondly, we design a high-frequency mamba module to capture boundary and detail information globally. Finally, we apply contrastive learning for label propagation from labeled to unlabeled data. Our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across three datasets, including left atrium, brain tumor, and NIH pancreas datasets.
Saiyan: Design and Implementation of a Low-power Demodulator for LoRa Backscatter Systems
Sep 30, 2022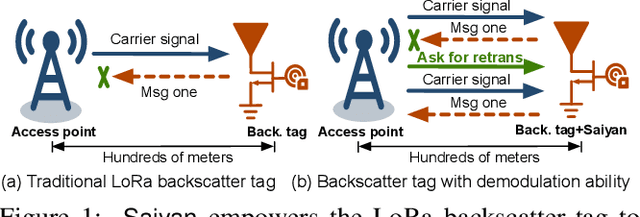
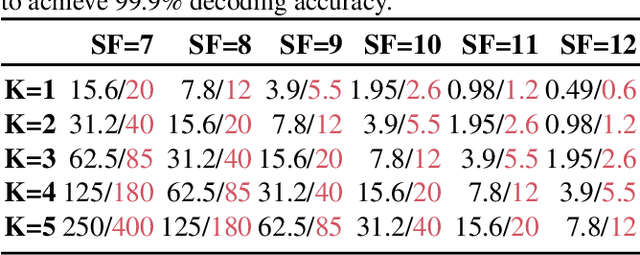
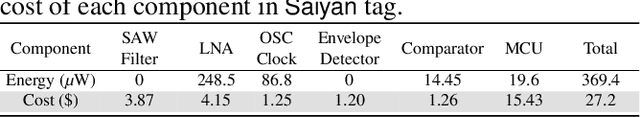
Abstract:The radio range of backscatter systems continues growing as new wireless communication primitives are continuously invented. Nevertheless, both the bit error rate and the packet loss rate of backscatter signals increase rapidly with the radio range, thereby necessitating the cooperation between the access point and the backscatter tags through a feedback loop. Unfortunately, the low-power nature of backscatter tags limits their ability to demodulate feedback signals from a remote access point and scales down to such circumstances. This paper presents Saiyan, an ultra-low-power demodulator for long-range LoRa backscatter systems. With Saiyan, a backscatter tag can demodulate feedback signals from a remote access point with moderate power consumption and then perform an immediate packet retransmission in the presence of packet loss. Moreover, Saiyan enables rate adaption and channel hopping-two PHY-layer operations that are important to channel efficiency yet unavailable on long-range backscatter systems. We prototype Saiyan on a two-layer PCB board and evaluate its performance in different environments. Results show that Saiyan achieves 5 gain on the demodulation range, compared with state-of-the-art systems. Our ASIC simulation shows that the power consumption of Saiyan is around 93.2 uW. Code and hardware schematics can be found at: https://github.com/ZangJac/Saiyan.
RF-Transformer: A Unified Backscatter Radio Hardware Abstraction
Sep 30, 2022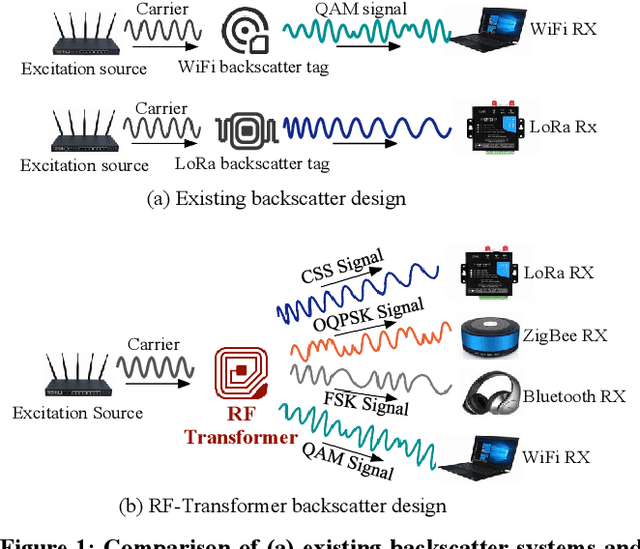
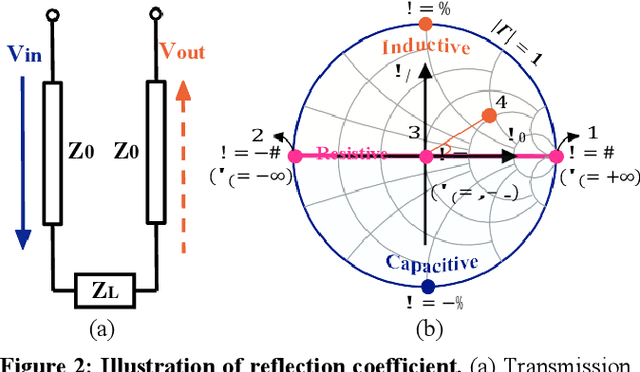
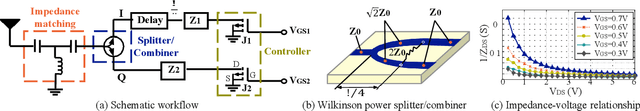
Abstract:This paper presents RF-Transformer, a unified backscatter radio hardware abstraction that allows a low-power IoT device to directly communicate with heterogeneous wireless receivers at the minimum power consumption. Unlike existing backscatter systems that are tailored to a specific wireless communication protocol, RF-Transformer provides a programmable interface to the micro-controller, allowing IoT devices to synthesize different types of protocol-compliant backscatter signals sharing radically different PHY-layer designs. To show the efficacy of our design, we implement a PCB prototype of RF-Transformer on 2.4 GHz ISM band and showcase its capability on generating standard ZigBee, Bluetooth, LoRa, and Wi-Fi 802.11b/g/n/ac packets. Our extensive field studies show that RF-Transformer achieves 23.8 Mbps, 247.1 Kbps, 986.5 Kbps, and 27.3 Kbps throughput when generating standard Wi-Fi, ZigBee, Bluetooth, and LoRa signals while consuming 7.6-74.2 less power than their active counterparts. Our ASIC simulation based on the 65-nm CMOS process shows that the power gain of RF-Transformer can further grow to 92-678. We further integrate RF-Transformer with pressure sensors and present a case study on detecting foot traffic density in hallways. Our 7-day case studies demonstrate RFTransformer can reliably transmit sensor data to a commodity gateway by synthesizing LoRa packets on top of Wi-Fi signals. Our experimental results also verify the compatibility of RF-Transformer with commodity receivers. Code and hardware schematics can be found at: https://github.com/LeFsCC/RF-Transformer.
Efficient Ambient LoRa Backscatter with On-Off Keying Modulation
Sep 30, 2022
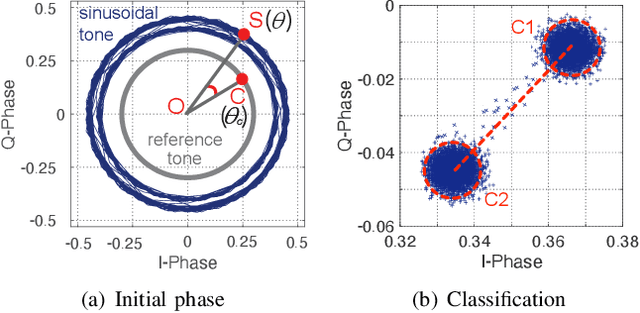
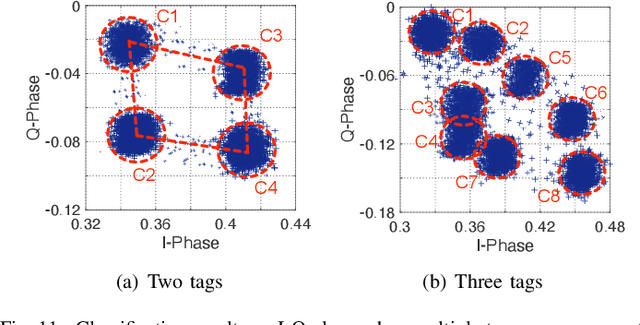
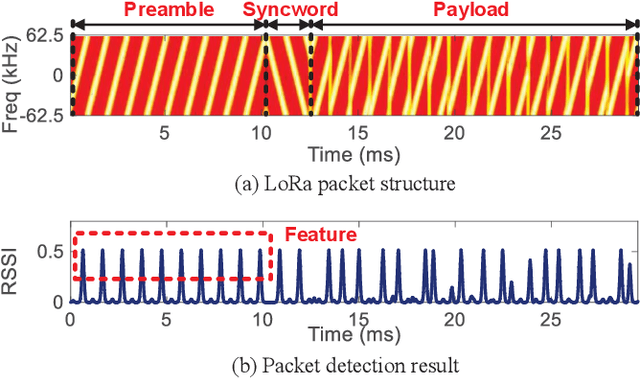
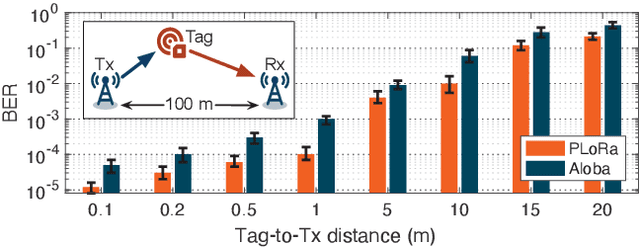
Abstract:Backscatter communication holds potential for ubiquitous and low-cost connectivity among low-power IoT devices. To avoid interference between the carrier signal and the backscatter signal, recent works propose a frequency-shifting technique to separate these two signals in the frequency domain. Such proposals, however, have to occupy the precious wireless spectrum that is already overcrowded, and increase the power, cost, and complexity of the backscatter tag. In this paper, we revisit the classic ON-OFF Keying (OOK) modulation and propose Aloba, a backscatter system that takes the ambient LoRa transmissions as the excitation and piggybacks the in-band OOK modulated signals over the LoRa transmissions. Our design enables the backsactter signal to work in the same frequency band of the carrier signal, meanwhile achieving flexible data rate at different transmission range. The key contributions of Aloba include: (1) the design of a low-power backscatter tag that can pick up the ambient LoRa signals from other signals. (2) a novel decoding algorithm to demodulate both the carrier signal and the backscatter signal from their superposition. We further adopt link coding mechanism and interleave operation to enhance the reliability of backscatter signal decoding. We implement Aloba and conduct head-to-head comparison with the state-of-the-art LoRa backscatter system PLoRa in various settings. The experiment results show Aloba can achieve 199.4 Kbps data rate at various distances, 52.4 times higher than PLoRa.
AdaComm: Tracing Channel Dynamics for Reliable Cross-Technology Communication
Sep 30, 2022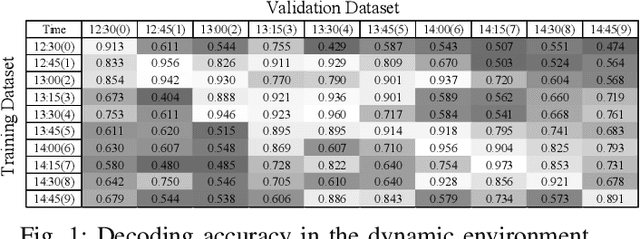
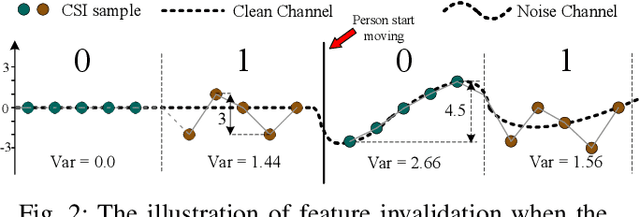
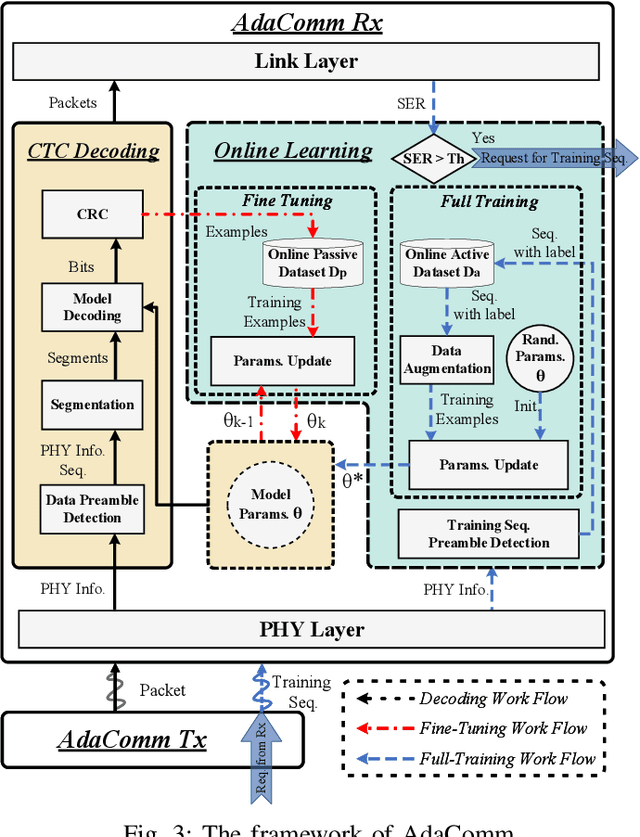
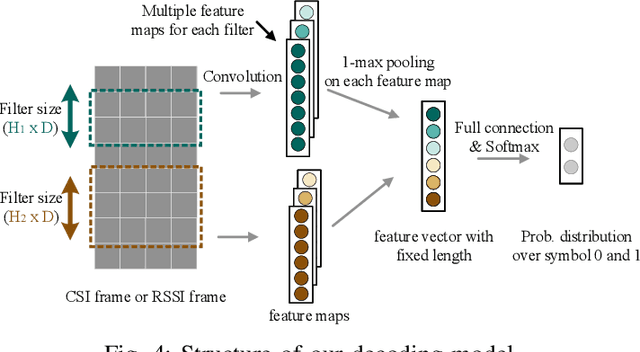
Abstract:Cross-Technology Communication (CTC) is an emerging technology to support direct communication between wireless devices that follow different standards. In spite of the many different proposals from the community to enable CTC, the performance aspect of CTC is an equally important problem but has seldom been studied before. We find this problem is extremely challenging, due to the following reasons: on one hand, a link for CTC is essentially different from a conventional wireless link. The conventional link indicators like RSSI (received signal strength indicator) and SNR (signal to noise ratio) cannot be used to directly characterize a CTC link. On the other hand, the indirect indicators like PER (packet error rate), which is adopted by many existing CTC proposals, cannot capture the short-term link behavior. As a result, the existing CTC proposals fail to keep reliable performance under dynamic channel conditions. In order to address the above challenge, we in this paper propose AdaComm, a generic framework to achieve self-adaptive CTC in dynamic channels. Instead of reactively adjusting the CTC sender, AdaComm adopts online learning mechanism to adaptively adjust the decoding model at the CTC receiver. The self-adaptive decoding model automatically learns the effective features directly from the raw received signals that are embedded with the current channel state. With the lossless channel information, AdaComm further adopts the fine tuning and full training modes to cope with the continuous and abrupt channel dynamics. We implement AdaComm and integrate it with two existing CTC approaches that respectively employ CSI (channel state information) and RSSI as the information carrier. The evaluation results demonstrate that AdaComm can significantly reduce the SER (symbol error rate) by 72.9% and 49.2%, respectively, compared with the existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge