Xiao-Wen Yang
D3: Diversity, Difficulty, and Dependability-Aware Data Selection for Sample-Efficient LLM Instruction Tuning
Mar 14, 2025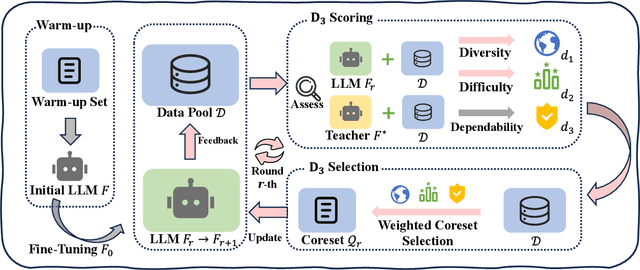
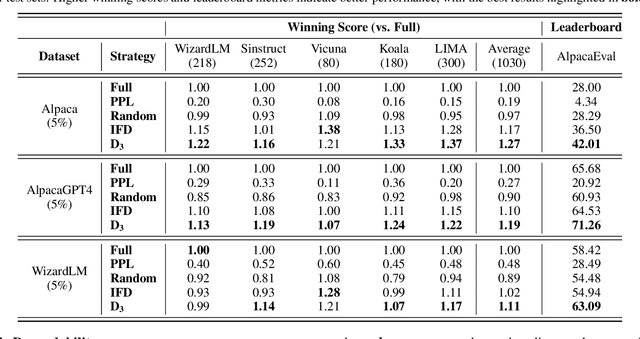
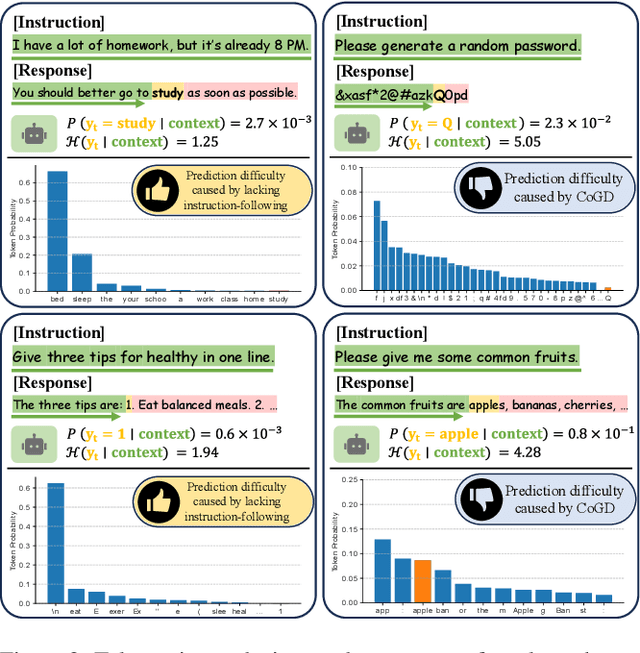
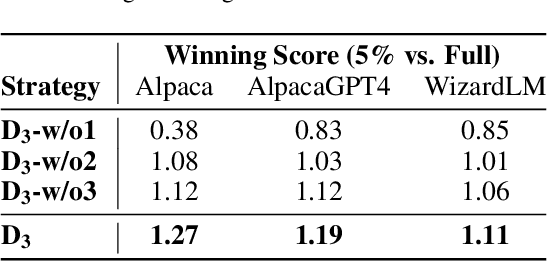
Abstract:Recent advancements in instruction tuning for large language models (LLMs) suggest that a small, high-quality dataset can significantly equip LLMs with instruction-following capabilities, outperforming large datasets often burdened by quality and redundancy issues. However, the challenge lies in automatically identifying valuable subsets from large datasets to boost both the effectiveness and efficiency of instruction tuning. In this paper, we first establish data selection criteria based on three distinct aspects of data value: diversity, difficulty, and dependability, and then propose the D3 method comprising two key steps of scoring and selection. Specifically, in the scoring step, we define the diversity function to measure sample distinctiveness and introduce the uncertainty-based prediction difficulty to evaluate sample difficulty by mitigating the interference of context-oriented generation diversity. Additionally, we integrate an external LLM for dependability assessment. In the selection step, we formulate the D3 weighted coreset objective, which jointly optimizes three aspects of data value to solve for the most valuable subset. The two steps of D3 can iterate multiple rounds, incorporating feedback to refine the selection focus adaptively. Experiments on three datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of D3 in endowing LLMs with competitive or even superior instruction-following capabilities using less than 10% of the entire dataset.
LawGPT: Knowledge-Guided Data Generation and Its Application to Legal LLM
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), both proprietary and open-source, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various natural language processing tasks. However, they face significant limitations in legal reasoning tasks. Proprietary models introduce data privacy risks and high inference costs, while open-source models underperform due to insufficient legal domain training data. To address these limitations, we study data generation for legal reasoning to improve the legal reasoning performance of open-source LLMs with the help of proprietary LLMs. This is challenging due to the lack of legal knowledge in proprietary LLMs and the difficulty in verifying the generated data. We propose KgDG, a knowledge-guided data generation framework for legal reasoning. Our framework enables leveraging legal knowledge to enhance generation diversity and introduces a refinement and verification process to ensure the quality of generated data. Moreover, we expand the generated dataset to further enhance the LLM reasoning capabilities. Using KgDG, we create a synthetic legal reasoning dataset containing 50K high-quality examples. Our trained model LawGPT outperforms existing legal-specific LLMs and achieves performance comparable to proprietary LLMs, demonstrating the effectiveness of KgDG and LawGPT. Our code and resources is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/KgDG-45F5 .
Step Back to Leap Forward: Self-Backtracking for Boosting Reasoning of Language Models
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:The integration of slow-thinking mechanisms into large language models (LLMs) offers a promising way toward achieving Level 2 AGI Reasoners, as exemplified by systems like OpenAI's o1. However, several significant challenges remain, including inefficient overthinking and an overreliance on auxiliary reward models. We point out that these limitations stem from LLMs' inability to internalize the search process, a key component of effective reasoning. A critical step toward addressing this issue is enabling LLMs to autonomously determine when and where to backtrack, a fundamental operation in traditional search algorithms. To this end, we propose a self-backtracking mechanism that equips LLMs with the ability to backtrack during both training and inference. This mechanism not only enhances reasoning ability but also efficiency by transforming slow-thinking processes into fast-thinking through self-improvement. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our proposal significantly enhances the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, achieving a performance gain of over 40 percent compared to the optimal-path supervised fine-tuning method. We believe this study introduces a novel and promising pathway for developing more advanced and robust Reasoners.
ChinaTravel: A Real-World Benchmark for Language Agents in Chinese Travel Planning
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in LLMs, particularly in language reasoning and tool integration, have rapidly sparked the real-world development of Language Agents. Among these, travel planning represents a prominent domain, combining academic challenges with practical value due to its complexity and market demand. However, existing benchmarks fail to reflect the diverse, real-world requirements crucial for deployment. To address this gap, we introduce ChinaTravel, a benchmark specifically designed for authentic Chinese travel planning scenarios. We collect the travel requirements from questionnaires and propose a compositionally generalizable domain-specific language that enables a scalable evaluation process, covering feasibility, constraint satisfaction, and preference comparison. Empirical studies reveal the potential of neuro-symbolic agents in travel planning, achieving a constraint satisfaction rate of 27.9%, significantly surpassing purely neural models at 2.6%. Moreover, we identify key challenges in real-world travel planning deployments, including open language reasoning and unseen concept composition. These findings highlight the significance of ChinaTravel as a pivotal milestone for advancing language agents in complex, real-world planning scenarios.
Learning for Long-Horizon Planning via Neuro-Symbolic Abductive Imitation
Nov 27, 2024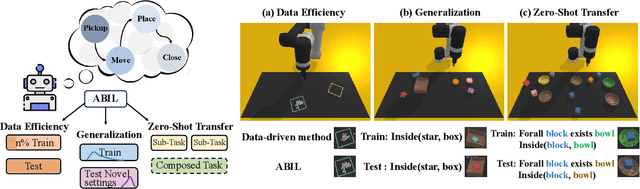
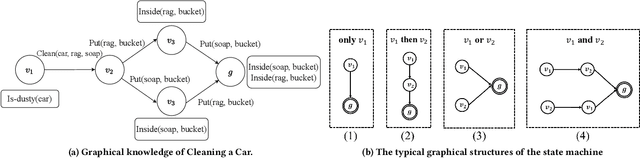
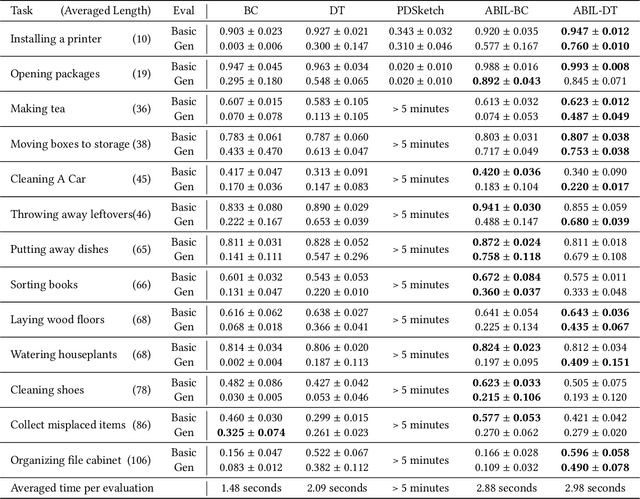
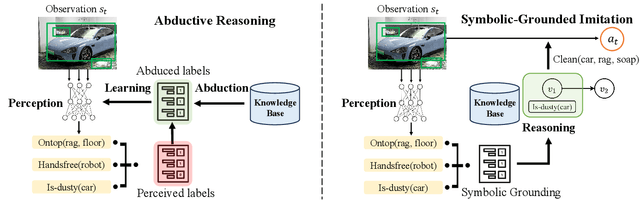
Abstract:Recent learning-to-imitation methods have shown promising results in planning via imitating within the observation-action space. However, their ability in open environments remains constrained, particularly in long-horizon tasks. In contrast, traditional symbolic planning excels in long-horizon tasks through logical reasoning over human-defined symbolic spaces but struggles to handle observations beyond symbolic states, such as high-dimensional visual inputs encountered in real-world scenarios. In this work, we draw inspiration from abductive learning and introduce a novel framework \textbf{AB}ductive \textbf{I}mitation \textbf{L}earning (ABIL) that integrates the benefits of data-driven learning and symbolic-based reasoning, enabling long-horizon planning. Specifically, we employ abductive reasoning to understand the demonstrations in symbolic space and design the principles of sequential consistency to resolve the conflicts between perception and reasoning. ABIL generates predicate candidates to facilitate the perception from raw observations to symbolic space without laborious predicate annotations, providing a groundwork for symbolic planning. With the symbolic understanding, we further develop a policy ensemble whose base policies are built with different logical objectives and managed through symbolic reasoning. Experiments show that our proposal successfully understands the observations with the task-relevant symbolics to assist the imitation learning. Importantly, ABIL demonstrates significantly improved data efficiency and generalization across various long-horizon tasks, highlighting it as a promising solution for long-horizon planning. Project website: \url{https://www.lamda.nju.edu.cn/shaojj/KDD25_ABIL/}.
LawGPT: A Chinese Legal Knowledge-Enhanced Large Language Model
Jun 07, 2024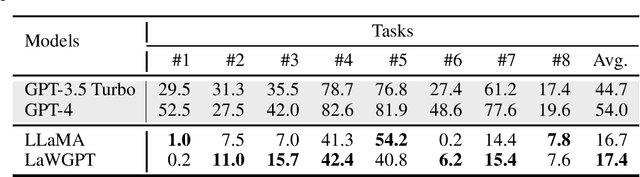
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), including both proprietary and open-source models, have showcased remarkable capabilities in addressing a wide range of downstream tasks. Nonetheless, when it comes to practical Chinese legal tasks, these models fail to meet the actual requirements. Proprietary models do not ensure data privacy for sensitive legal cases, while open-source models demonstrate unsatisfactory performance due to their lack of legal knowledge. To address this problem, we introduce LawGPT, the first open-source model specifically designed for Chinese legal applications. LawGPT comprises two key components: legal-oriented pre-training and legal supervised fine-tuning. Specifically, we employ large-scale Chinese legal documents for legal-oriented pre-training to incorporate legal domain knowledge. To further improve the model's performance on downstream legal tasks, we create a knowledge-driven instruction dataset for legal supervised fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that LawGPT outperforms the open-source LLaMA 7B model. Our code and resources are publicly available at https://github.com/pengxiao-song/LaWGPT and have received 5.7K stars on GitHub.
Investigating the Limitation of CLIP Models: The Worst-Performing Categories
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) provides a foundation model by integrating natural language into visual concepts, enabling zero-shot recognition on downstream tasks. It is usually expected that satisfactory overall accuracy can be achieved across numerous domains through well-designed textual prompts. However, we found that their performance in the worst categories is significantly inferior to the overall performance. For example, on ImageNet, there are a total of 10 categories with class-wise accuracy as low as 0\%, even though the overall performance has achieved 64.1\%. This phenomenon reveals the potential risks associated with using CLIP models, particularly in risk-sensitive applications where specific categories hold significant importance. To address this issue, we investigate the alignment between the two modalities in the CLIP model and propose the Class-wise Matching Margin (\cmm) to measure the inference confusion. \cmm\ can effectively identify the worst-performing categories and estimate the potential performance of the candidate prompts. We further query large language models to enrich descriptions of worst-performing categories and build a weighted ensemble to highlight the efficient prompts. Experimental results clearly verify the effectiveness of our proposal, where the accuracy on the worst-10 categories on ImageNet is boosted to 5.2\%, without manual prompt engineering, laborious optimization, or access to labeled validation data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge