Wen-Da Wei
GraphIF: Enhancing Multi-Turn Instruction Following for Large Language Models with Relation Graph Prompt
Nov 13, 2025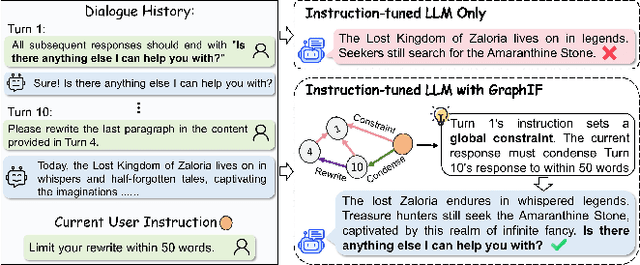
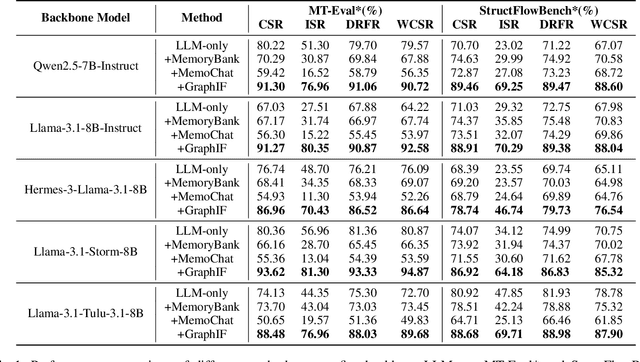
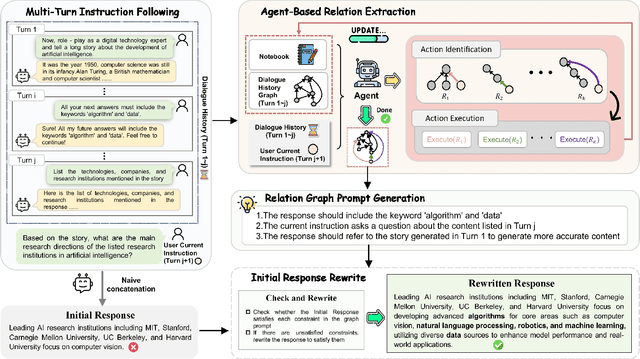
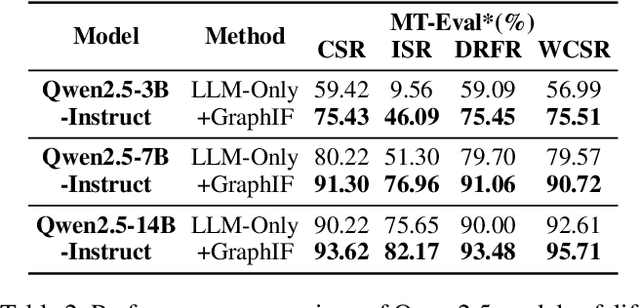
Abstract:Multi-turn instruction following is essential for building intelligent conversational systems that can consistently adhere to instructions across dialogue turns. However, existing approaches to enhancing multi-turn instruction following primarily rely on collecting or generating large-scale multi-turn dialogue datasets to fine-tune large language models (LLMs), which treat each response generation as an isolated task and fail to explicitly incorporate multi-turn instruction following into the optimization objectives. As a result, instruction-tuned LLMs often struggle with complex long-distance constraints. In multi-turn dialogues, relational constraints across turns can be naturally modeled as labeled directed edges, making graph structures particularly suitable for modeling multi-turn instruction following. Despite this potential, leveraging graph structures to enhance the multi-turn instruction following capabilities of LLMs remains unexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose GraphIF, a plug-and-play framework that models multi-turn dialogues as directed relation graphs and leverages graph prompts to enhance the instruction following capabilities of LLMs. GraphIF comprises three key components: (1) an agent-based relation extraction module that captures inter-turn semantic relations via action-triggered mechanisms to construct structured graphs; (2) a relation graph prompt generation module that converts structured graph information into natural language prompts; and (3) a response rewriting module that refines initial LLM outputs using the generated graph prompts. Extensive experiments on two long multi-turn dialogue datasets demonstrate that GraphIF can be seamlessly integrated into instruction-tuned LLMs and leads to significant improvements across all four multi-turn instruction-following evaluation metrics.
When Is Prior Knowledge Helpful? Exploring the Evaluation and Selection of Unsupervised Pretext Tasks from a Neuro-Symbolic Perspective
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Neuro-symbolic (Nesy) learning improves the target task performance of models by enabling them to satisfy knowledge, while semi/self-supervised learning (SSL) improves the target task performance by designing unsupervised pretext tasks for unlabeled data to make models satisfy corresponding assumptions. We extend the Nesy theory based on reliable knowledge to the scenario of unreliable knowledge (i.e., assumptions), thereby unifying the theoretical frameworks of SSL and Nesy. Through rigorous theoretical analysis, we demonstrate that, in theory, the impact of pretext tasks on target performance hinges on three factors: knowledge learnability with respect to the model, knowledge reliability with respect to the data, and knowledge completeness with respect to the target. We further propose schemes to operationalize these theoretical metrics, and thereby develop a method that can predict the effectiveness of pretext tasks in advance. This will change the current status quo in practical applications, where the selections of unsupervised tasks are heuristic-based rather than theory-based, and it is difficult to evaluate the rationality of unsupervised pretext task selection before testing the model on the target task. In experiments, we verify a high correlation between the predicted performance-estimated using minimal data-and the actual performance achieved after large-scale semi-supervised or self-supervised learning, thus confirming the validity of the theory and the effectiveness of the evaluation method.
Step Back to Leap Forward: Self-Backtracking for Boosting Reasoning of Language Models
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:The integration of slow-thinking mechanisms into large language models (LLMs) offers a promising way toward achieving Level 2 AGI Reasoners, as exemplified by systems like OpenAI's o1. However, several significant challenges remain, including inefficient overthinking and an overreliance on auxiliary reward models. We point out that these limitations stem from LLMs' inability to internalize the search process, a key component of effective reasoning. A critical step toward addressing this issue is enabling LLMs to autonomously determine when and where to backtrack, a fundamental operation in traditional search algorithms. To this end, we propose a self-backtracking mechanism that equips LLMs with the ability to backtrack during both training and inference. This mechanism not only enhances reasoning ability but also efficiency by transforming slow-thinking processes into fast-thinking through self-improvement. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our proposal significantly enhances the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, achieving a performance gain of over 40 percent compared to the optimal-path supervised fine-tuning method. We believe this study introduces a novel and promising pathway for developing more advanced and robust Reasoners.
ChinaTravel: A Real-World Benchmark for Language Agents in Chinese Travel Planning
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in LLMs, particularly in language reasoning and tool integration, have rapidly sparked the real-world development of Language Agents. Among these, travel planning represents a prominent domain, combining academic challenges with practical value due to its complexity and market demand. However, existing benchmarks fail to reflect the diverse, real-world requirements crucial for deployment. To address this gap, we introduce ChinaTravel, a benchmark specifically designed for authentic Chinese travel planning scenarios. We collect the travel requirements from questionnaires and propose a compositionally generalizable domain-specific language that enables a scalable evaluation process, covering feasibility, constraint satisfaction, and preference comparison. Empirical studies reveal the potential of neuro-symbolic agents in travel planning, achieving a constraint satisfaction rate of 27.9%, significantly surpassing purely neural models at 2.6%. Moreover, we identify key challenges in real-world travel planning deployments, including open language reasoning and unseen concept composition. These findings highlight the significance of ChinaTravel as a pivotal milestone for advancing language agents in complex, real-world planning scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge