Junli Liang
SentGraph: Hierarchical Sentence Graph for Multi-hop Retrieval-Augmented Question Answering
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) effectively supports single-hop question answering with large language models but faces significant limitations in multi-hop question answering tasks, which require combining evidence from multiple documents. Existing chunk-based retrieval often provides irrelevant and logically incoherent context, leading to incomplete evidence chains and incorrect reasoning during answer generation. To address these challenges, we propose SentGraph, a sentence-level graph-based RAG framework that explicitly models fine-grained logical relationships between sentences for multi-hop question answering. Specifically, we construct a hierarchical sentence graph offline by first adapting Rhetorical Structure Theory to distinguish nucleus and satellite sentences, and then organizing them into topic-level subgraphs with cross-document entity bridges. During online retrieval, SentGraph performs graph-guided evidence selection and path expansion to retrieve fine-grained sentence-level evidence. Extensive experiments on four multi-hop question answering benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of SentGraph, validating the importance of explicitly modeling sentence-level logical dependencies for multi-hop reasoning.
GraphIF: Enhancing Multi-Turn Instruction Following for Large Language Models with Relation Graph Prompt
Nov 13, 2025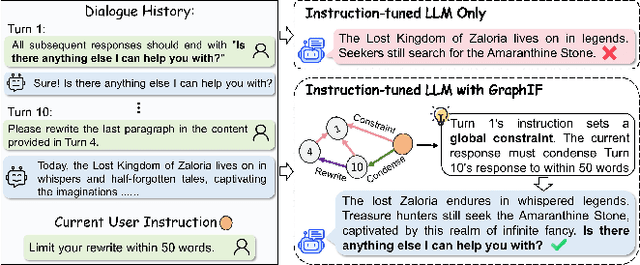
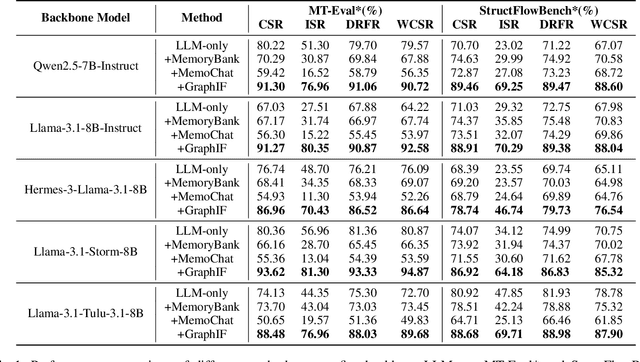
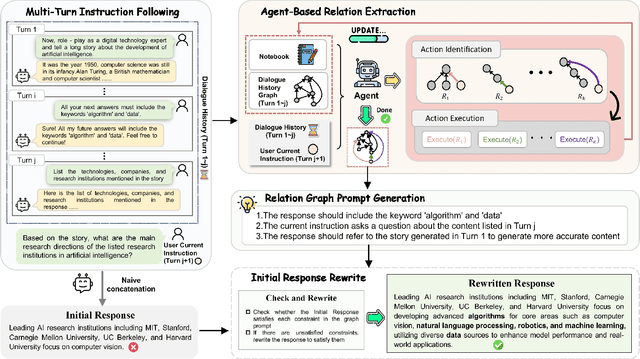
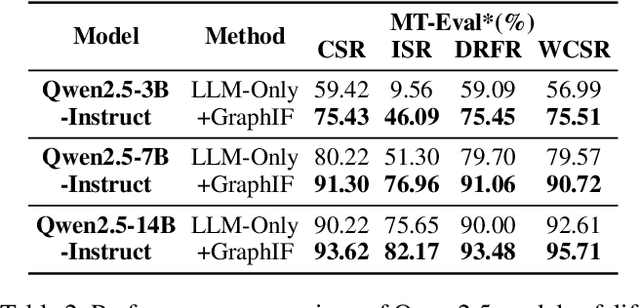
Abstract:Multi-turn instruction following is essential for building intelligent conversational systems that can consistently adhere to instructions across dialogue turns. However, existing approaches to enhancing multi-turn instruction following primarily rely on collecting or generating large-scale multi-turn dialogue datasets to fine-tune large language models (LLMs), which treat each response generation as an isolated task and fail to explicitly incorporate multi-turn instruction following into the optimization objectives. As a result, instruction-tuned LLMs often struggle with complex long-distance constraints. In multi-turn dialogues, relational constraints across turns can be naturally modeled as labeled directed edges, making graph structures particularly suitable for modeling multi-turn instruction following. Despite this potential, leveraging graph structures to enhance the multi-turn instruction following capabilities of LLMs remains unexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose GraphIF, a plug-and-play framework that models multi-turn dialogues as directed relation graphs and leverages graph prompts to enhance the instruction following capabilities of LLMs. GraphIF comprises three key components: (1) an agent-based relation extraction module that captures inter-turn semantic relations via action-triggered mechanisms to construct structured graphs; (2) a relation graph prompt generation module that converts structured graph information into natural language prompts; and (3) a response rewriting module that refines initial LLM outputs using the generated graph prompts. Extensive experiments on two long multi-turn dialogue datasets demonstrate that GraphIF can be seamlessly integrated into instruction-tuned LLMs and leads to significant improvements across all four multi-turn instruction-following evaluation metrics.
CrossLinear: Plug-and-Play Cross-Correlation Embedding for Time Series Forecasting with Exogenous Variables
May 29, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting with exogenous variables is a critical emerging paradigm that presents unique challenges in modeling dependencies between variables. Traditional models often struggle to differentiate between endogenous and exogenous variables, leading to inefficiencies and overfitting. In this paper, we introduce CrossLinear, a novel Linear-based forecasting model that addresses these challenges by incorporating a plug-and-play cross-correlation embedding module. This lightweight module captures the dependencies between variables with minimal computational cost and seamlessly integrates into existing neural networks. Specifically, it captures time-invariant and direct variable dependencies while disregarding time-varying or indirect dependencies, thereby mitigating the risk of overfitting in dependency modeling and contributing to consistent performance improvements. Furthermore, CrossLinear employs patch-wise processing and a global linear head to effectively capture both short-term and long-term temporal dependencies, further improving its forecasting precision. Extensive experiments on 12 real-world datasets demonstrate that CrossLinear achieves superior performance in both short-term and long-term forecasting tasks. The ablation study underscores the effectiveness of the cross-correlation embedding module. Additionally, the generalizability of this module makes it a valuable plug-in for various forecasting tasks across different domains. Codes are available at https://github.com/mumiao2000/CrossLinear.
ClST: A Convolutional Transformer Framework for Automatic Modulation Recognition by Knowledge Distillation
Dec 29, 2023Abstract:With the rapid development of deep learning (DL) in recent years, automatic modulation recognition (AMR) with DL has achieved high accuracy. However, insufficient training signal data in complicated channel environments and large-scale DL models are critical factors that make DL methods difficult to deploy in practice. Aiming to these problems, we propose a novel neural network named convolution-linked signal transformer (ClST) and a novel knowledge distillation method named signal knowledge distillation (SKD). The ClST is accomplished through three primary modifications: a hierarchy of transformer containing convolution, a novel attention mechanism named parallel spatial-channel attention (PSCA) mechanism and a novel convolutional transformer block named convolution-transformer projection (CTP) to leverage a convolutional projection. The SKD is a knowledge distillation method to effectively reduce the parameters and complexity of neural networks. We train two lightweight neural networks using the SKD algorithm, KD-CNN and KD-MobileNet, to meet the demand that neural networks can be used on miniaturized devices. The simulation results demonstrate that the ClST outperforms advanced neural networks on all datasets. Moreover, both KD-CNN and KD-MobileNet obtain higher recognition accuracy with less network complexity, which is very beneficial for the deployment of AMR on miniaturized communication devices.
Kernel Least Mean Square with Adaptive Kernel Size
Feb 11, 2014



Abstract:Kernel adaptive filters (KAF) are a class of powerful nonlinear filters developed in Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space (RKHS). The Gaussian kernel is usually the default kernel in KAF algorithms, but selecting the proper kernel size (bandwidth) is still an open important issue especially for learning with small sample sizes. In previous research, the kernel size was set manually or estimated in advance by Silvermans rule based on the sample distribution. This study aims to develop an online technique for optimizing the kernel size of the kernel least mean square (KLMS) algorithm. A sequential optimization strategy is proposed, and a new algorithm is developed, in which the filter weights and the kernel size are both sequentially updated by stochastic gradient algorithms that minimize the mean square error (MSE). Theoretical results on convergence are also presented. The excellent performance of the new algorithm is confirmed by simulations on static function estimation and short term chaotic time series prediction.
* 25 pages, 9 figures, and 4 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge