Badong Chen
Reshaping Action Error Distributions for Reliable Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In robotic manipulation, vision-language-action (VLA) models have emerged as a promising paradigm for learning generalizable and scalable robot policies. Most existing VLA frameworks rely on standard supervised objectives, typically cross-entropy for discrete actions and mean squared error (MSE) for continuous action regression, which impose strong pointwise constraints on individual predictions. In this work, we focus on continuous-action VLA models and move beyond conventional MSE-based regression by reshaping action error distributions during training. Drawing on information-theoretic principles, we introduce Minimum Error Entropy (MEE) into modern VLA architectures and propose a trajectory-level MEE objective, together with two weighted variants, combined with MSE for continuous-action VLA training. We evaluate our approaches across standard, few-shot, and noisy settings on multiple representative VLA architectures, using simulation benchmarks such as LIBERO and SimplerEnv as well as real-world robotic manipulation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate consistent improvements in success rates and robustness across these settings. Under imbalanced data regimes, the gains persist within a well-characterized operating range, while incurring negligible additional training cost and no impact on inference efficiency. We further provide theoretical analyses that explain why MEE-based supervision is effective and characterize its practical range. Project Page: https://cognition2actionlab.github.io/VLA-TMEE.github.io/
Latent Reasoning VLA: Latent Thinking and Prediction for Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models benefit from chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, but existing approaches incur high inference overhead and rely on discrete reasoning representations that mismatch continuous perception and control. We propose Latent Reasoning VLA (\textbf{LaRA-VLA}), a unified VLA framework that internalizes multi-modal CoT reasoning into continuous latent representations for embodied action. LaRA-VLA performs unified reasoning and prediction in latent space, eliminating explicit CoT generation at inference time and enabling efficient, action-oriented control. To realize latent embodied reasoning, we introduce a curriculum-based training paradigm that progressively transitions from explicit textual and visual CoT supervision to latent reasoning, and finally adapts latent reasoning dynamics to condition action generation. We construct two structured CoT datasets and evaluate LaRA-VLA on both simulation benchmarks and long-horizon real-robot manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that LaRA-VLA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLA methods while reducing inference latency by up to 90\% compared to explicit CoT-based approaches, demonstrating latent reasoning as an effective and efficient paradigm for real-time embodied control. Project Page: \href{https://loveju1y.github.io/Latent-Reasoning-VLA/}{LaRA-VLA Website}.
Embodied Robot Manipulation in the Era of Foundation Models: Planning and Learning Perspectives
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in vision, language, and multimodal learning have substantially accelerated progress in robotic foundation models, with robot manipulation remaining a central and challenging problem. This survey examines robot manipulation from an algorithmic perspective and organizes recent learning-based approaches within a unified abstraction of high-level planning and low-level control. At the high level, we extend the classical notion of task planning to include reasoning over language, code, motion, affordances, and 3D representations, emphasizing their role in structured and long-horizon decision making. At the low level, we propose a training-paradigm-oriented taxonomy for learning-based control, organizing existing methods along input modeling, latent representation learning, and policy learning. Finally, we identify open challenges and prospective research directions related to scalability, data efficiency, multimodal physical interaction, and safety. Together, these analyses aim to clarify the design space of modern foundation models for robotic manipulation.
Long-VLA: Unleashing Long-Horizon Capability of Vision Language Action Model for Robot Manipulation
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have become a cornerstone in robotic policy learning, leveraging large-scale multimodal data for robust and scalable control. However, existing VLA frameworks primarily address short-horizon tasks, and their effectiveness on long-horizon, multi-step robotic manipulation remains limited due to challenges in skill chaining and subtask dependencies. In this work, we introduce Long-VLA, the first end-to-end VLA model specifically designed for long-horizon robotic tasks. Our approach features a novel phase-aware input masking strategy that adaptively segments each subtask into moving and interaction phases, enabling the model to focus on phase-relevant sensory cues and enhancing subtask compatibility. This unified strategy preserves the scalability and data efficiency of VLA training, and our architecture-agnostic module can be seamlessly integrated into existing VLA models. We further propose the L-CALVIN benchmark to systematically evaluate long-horizon manipulation. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real-world tasks demonstrate that Long-VLA significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods, establishing a new baseline for long-horizon robotic control.
Dual-Path Stable Soft Prompt Generation for Domain Generalization
May 24, 2025Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) aims to learn a model using data from one or multiple related but distinct source domains that can generalize well to unseen out-of-distribution target domains. Inspired by the success of large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), prompt tuning has emerged as an effective generalization strategy. However, it often struggles to capture domain-specific features due to its reliance on manually or fixed prompt inputs. Recently, some prompt generation methods have addressed this limitation by dynamically generating instance-specific and domain-specific prompts for each input, enriching domain information and demonstrating potential for enhanced generalization. Through further investigation, we identify a notable issue in existing prompt generation methods: the same input often yields significantly different and suboptimal prompts across different random seeds, a phenomenon we term Prompt Variability. To address this, we introduce negative learning into the prompt generation process and propose Dual-Path Stable Soft Prompt Generation (DPSPG), a transformer-based framework designed to improve both the stability and generalization of prompts. Specifically, DPSPG incorporates a complementary prompt generator to produce negative prompts, thereby reducing the risk of introducing misleading information. Both theoretical and empirical analyses demonstrate that negative learning leads to more robust and effective prompts by increasing the effective margin and reducing the upper bound of the gradient norm. Extensive experiments on five DG benchmark datasets show that DPSPG consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods while maintaining prompt stability.
Spiking Neural Networks with Temporal Attention-Guided Adaptive Fusion for imbalanced Multi-modal Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Multimodal spiking neural networks (SNNs) hold significant potential for energy-efficient sensory processing but face critical challenges in modality imbalance and temporal misalignment. Current approaches suffer from uncoordinated convergence speeds across modalities and static fusion mechanisms that ignore time-varying cross-modal interactions. We propose the temporal attention-guided adaptive fusion framework for multimodal SNNs with two synergistic innovations: 1) The Temporal Attention-guided Adaptive Fusion (TAAF) module that dynamically assigns importance scores to fused spiking features at each timestep, enabling hierarchical integration of temporally heterogeneous spike-based features; 2) The temporal adaptive balanced fusion loss that modulates learning rates per modality based on the above attention scores, preventing dominant modalities from monopolizing optimization. The proposed framework implements adaptive fusion, especially in the temporal dimension, and alleviates the modality imbalance during multimodal learning, mimicking cortical multisensory integration principles. Evaluations on CREMA-D, AVE, and EAD datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance (77.55\%, 70.65\% and 97.5\%accuracy, respectively) with energy efficiency. The system resolves temporal misalignment through learnable time-warping operations and faster modality convergence coordination than baseline SNNs. This work establishes a new paradigm for temporally coherent multimodal learning in neuromorphic systems, bridging the gap between biological sensory processing and efficient machine intelligence.
Rethinking Latent Representations in Behavior Cloning: An Information Bottleneck Approach for Robot Manipulation
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Behavior Cloning (BC) is a widely adopted visual imitation learning method in robot manipulation. Current BC approaches often enhance generalization by leveraging large datasets and incorporating additional visual and textual modalities to capture more diverse information. However, these methods overlook whether the learned representations contain redundant information and lack a solid theoretical foundation to guide the learning process. To address these limitations, we adopt an information-theoretic perspective and introduce mutual information to quantify and mitigate redundancy in latent representations. Building on this, we incorporate the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle into BC, which extends the idea of reducing redundancy by providing a structured framework for compressing irrelevant information while preserving task-relevant features. This work presents the first comprehensive study on redundancy in latent representations across various methods, backbones, and experimental settings, while extending the generalizability of the IB to BC. Extensive experiments and analyses on the CortexBench and LIBERO benchmarks demonstrate significant performance improvements with IB, underscoring the importance of reducing input data redundancy and highlighting its practical value for more practical applications. Project Page: https://baishuanghao.github.io/BC-IB.github.io.
Generalized Trusted Multi-view Classification Framework with Hierarchical Opinion Aggregation
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Recently, multi-view learning has witnessed a considerable interest on the research of trusted decision-making. Previous methods are mainly inspired from an important paper published by Han et al. in 2021, which formulates a Trusted Multi-view Classification (TMC) framework that aggregates evidence from different views based on Dempster's combination rule. All these methods only consider inter-view aggregation, yet lacking exploitation of intra-view information. In this paper, we propose a generalized trusted multi-view classification framework with hierarchical opinion aggregation. This hierarchical framework includes a two-phase aggregation process: the intra-view and inter-view aggregation hierarchies. In the intra aggregation, we assume that each view is comprised of common information shared with other views, as well as its specific information. We then aggregate both the common and specific information. This aggregation phase is useful to eliminate the feature noise inherent to view itself, thereby improving the view quality. In the inter-view aggregation, we design an attention mechanism at the evidence level to facilitate opinion aggregation from different views. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the pioneering efforts to formulate a hierarchical aggregation framework in the trusted multi-view learning domain. Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms some state-of-art trust-related baselines.
PromptTA: Prompt-driven Text Adapter for Source-free Domain Generalization
Sep 21, 2024Abstract:Source-free domain generalization (SFDG) tackles the challenge of adapting models to unseen target domains without access to source domain data. To deal with this challenging task, recent advances in SFDG have primarily focused on leveraging the text modality of vision-language models such as CLIP. These methods involve developing a transferable linear classifier based on diverse style features extracted from the text and learned prompts or deriving domain-unified text representations from domain banks. However, both style features and domain banks have limitations in capturing comprehensive domain knowledge. In this work, we propose Prompt-Driven Text Adapter (PromptTA) method, which is designed to better capture the distribution of style features and employ resampling to ensure thorough coverage of domain knowledge. To further leverage this rich domain information, we introduce a text adapter that learns from these style features for efficient domain information storage. Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that PromptTA achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/zhanghr2001/PromptTA.
Correntropy-Based Improper Likelihood Model for Robust Electrophysiological Source Imaging
Aug 27, 2024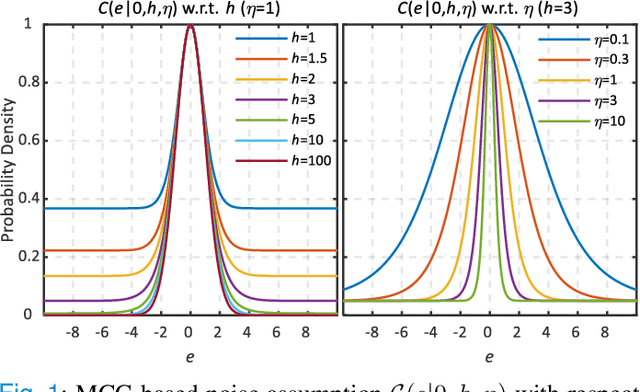
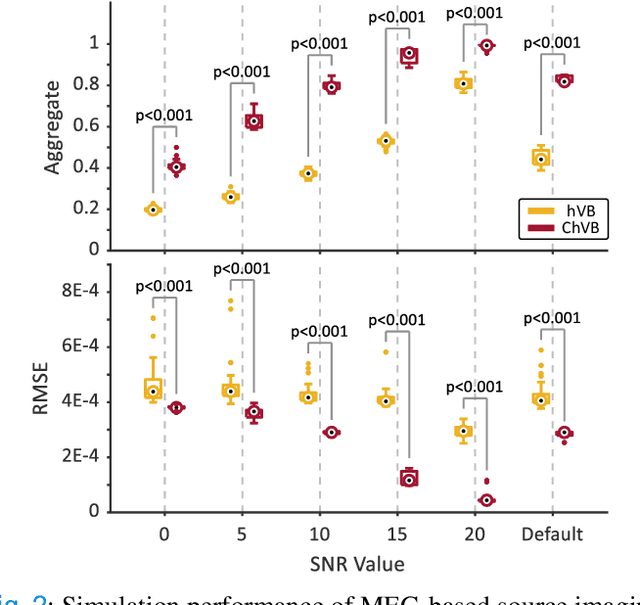
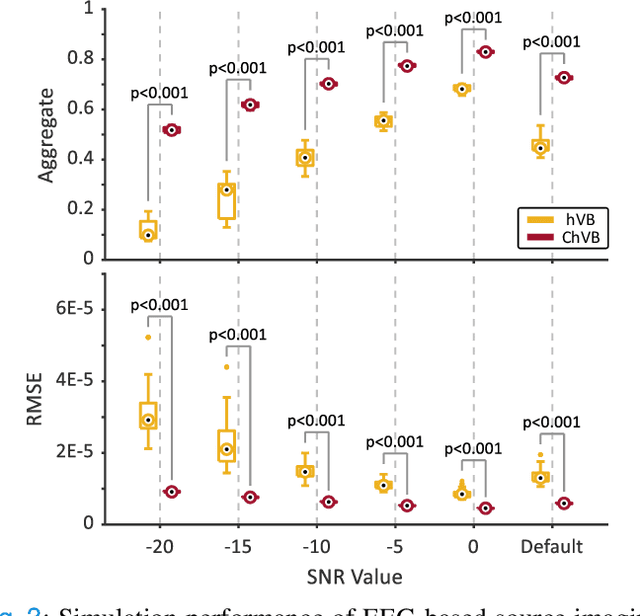
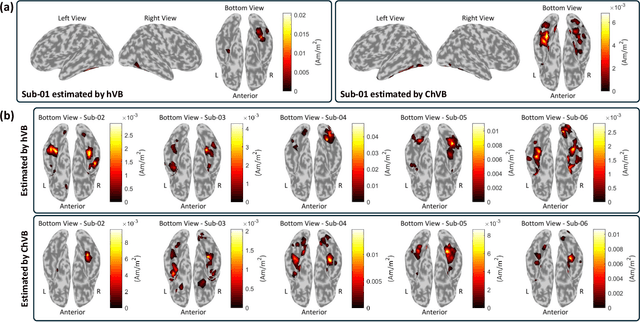
Abstract:Bayesian learning provides a unified skeleton to solve the electrophysiological source imaging task. From this perspective, existing source imaging algorithms utilize the Gaussian assumption for the observation noise to build the likelihood function for Bayesian inference. However, the electromagnetic measurements of brain activity are usually affected by miscellaneous artifacts, leading to a potentially non-Gaussian distribution for the observation noise. Hence the conventional Gaussian likelihood model is a suboptimal choice for the real-world source imaging task. In this study, we aim to solve this problem by proposing a new likelihood model which is robust with respect to non-Gaussian noises. Motivated by the robust maximum correntropy criterion, we propose a new improper distribution model concerning the noise assumption. This new noise distribution is leveraged to structure a robust likelihood function and integrated with hierarchical prior distributions to estimate source activities by variational inference. In particular, the score matching is adopted to determine the hyperparameters for the improper likelihood model. A comprehensive performance evaluation is performed to compare the proposed noise assumption to the conventional Gaussian model. Simulation results show that, the proposed method can realize more precise source reconstruction by designing known ground-truth. The real-world dataset also demonstrates the superiority of our new method with the visual perception task. This study provides a new backbone for Bayesian source imaging, which would facilitate its application using real-world noisy brain signal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge