Xuguang Lan
Toward Reliable Sim-to-Real Predictability for MoE-based Robust Quadrupedal Locomotion
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has shown strong promise for quadrupedal agile locomotion, even with proprioception-only sensing. In practice, however, sim-to-real gap and reward overfitting in complex terrains can produce policies that fail to transfer, while physical validation remains risky and inefficient. To address these challenges, we introduce a unified framework encompassing a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) locomotion policy for robust multi-terrain representation with RoboGauge, a predictive assessment suite that quantifies sim-to-real transferability. The MoE policy employs a gated set of specialist experts to decompose latent terrain and command modeling, achieving superior deployment robustness and generalization via proprioception alone. RoboGauge further provides multi-dimensional proprioception-based metrics via sim-to-sim tests over terrains, difficulty levels, and domain randomizations, enabling reliable MoE policy selection without extensive physical trials. Experiments on a Unitree Go2 demonstrate robust locomotion on unseen challenging terrains, including snow, sand, stairs, slopes, and 30 cm obstacles. In dedicated high-speed tests, the robot reaches 4 m/s and exhibits an emergent narrow-width gait associated with improved stability at high velocity.
PRISM: Projection-based Reward Integration for Scene-Aware Real-to-Sim-to-Real Transfer with Few Demonstrations
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Learning from few demonstrations to develop policies robust to variations in robot initial positions and object poses is a problem of significant practical interest in robotics. Compared to imitation learning, which often struggles to generalize from limited samples, reinforcement learning (RL) can autonomously explore to obtain robust behaviors. Training RL agents through direct interaction with the real world is often impractical and unsafe, while building simulation environments requires extensive manual effort, such as designing scenes and crafting task-specific reward functions. To address these challenges, we propose an integrated real-to-sim-to-real pipeline that constructs simulation environments based on expert demonstrations by identifying scene objects from images and retrieving their corresponding 3D models from existing libraries. We introduce a projection-based reward model for RL policy training that is supervised by a vision-language model (VLM) using human-guided object projection relationships as prompts, with the policy further fine-tuned using expert demonstrations. In general, our work focuses on the construction of simulation environments and RL-based policy training, ultimately enabling the deployment of reliable robotic control policies in real-world scenarios.
Playing Non-Embedded Card-Based Games with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Significant progress has been made in AI for games, including board games, MOBA, and RTS games. However, complex agents are typically developed in an embedded manner, directly accessing game state information, unlike human players who rely on noisy visual data, leading to unfair competition. Developing complex non-embedded agents remains challenging, especially in card-based RTS games with complex features and large state spaces. We propose a non-embedded offline reinforcement learning training strategy using visual inputs to achieve real-time autonomous gameplay in the RTS game Clash Royale. Due to the lack of a object detection dataset for this game, we designed an efficient generative object detection dataset for training. We extract features using state-of-the-art object detection and optical character recognition models. Our method enables real-time image acquisition, perception feature fusion, decision-making, and control on mobile devices, successfully defeating built-in AI opponents. All code is open-sourced at https://github.com/wty-yy/katacr.
* Match videos: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xn4y1R7GQ, All code: https://github.com/wty-yy/katacr, Detection dataset: https://github.com/wty-yy/Clash-Royale-Detection-Dataset, Expert dataset: https://github.com/wty-yy/Clash-Royale-Replay-Dataset
MInCo: Mitigating Information Conflicts in Distracted Visual Model-based Reinforcement Learning
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:Existing visual model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) algorithms with observation reconstruction often suffer from information conflicts, making it difficult to learn compact representations and hence result in less robust policies, especially in the presence of task-irrelevant visual distractions. In this paper, we first reveal that the information conflicts in current visual MBRL algorithms stem from visual representation learning and latent dynamics modeling with an information-theoretic perspective. Based on this finding, we present a new algorithm to resolve information conflicts for visual MBRL, named MInCo, which mitigates information conflicts by leveraging negative-free contrastive learning, aiding in learning invariant representation and robust policies despite noisy observations. To prevent the dominance of visual representation learning, we introduce time-varying reweighting to bias the learning towards dynamics modeling as training proceeds. We evaluate our method on several robotic control tasks with dynamic background distractions. Our experiments demonstrate that MInCo learns invariant representations against background noise and consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art visual MBRL methods. Code is available at https://github.com/ShiguangSun/minco.
Bootstrapped Model Predictive Control
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Model Predictive Control (MPC) has been demonstrated to be effective in continuous control tasks. When a world model and a value function are available, planning a sequence of actions ahead of time leads to a better policy. Existing methods typically obtain the value function and the corresponding policy in a model-free manner. However, we find that such an approach struggles with complex tasks, resulting in poor policy learning and inaccurate value estimation. To address this problem, we leverage the strengths of MPC itself. In this work, we introduce Bootstrapped Model Predictive Control (BMPC), a novel algorithm that performs policy learning in a bootstrapped manner. BMPC learns a network policy by imitating an MPC expert, and in turn, uses this policy to guide the MPC process. Combined with model-based TD-learning, our policy learning yields better value estimation and further boosts the efficiency of MPC. We also introduce a lazy reanalyze mechanism, which enables computationally efficient imitation learning. Our method achieves superior performance over prior works on diverse continuous control tasks. In particular, on challenging high-dimensional locomotion tasks, BMPC significantly improves data efficiency while also enhancing asymptotic performance and training stability, with comparable training time and smaller network sizes. Code is available at https://github.com/wertyuilife2/bmpc.
Enhancing Decision Transformer with Diffusion-Based Trajectory Branch Generation
Nov 18, 2024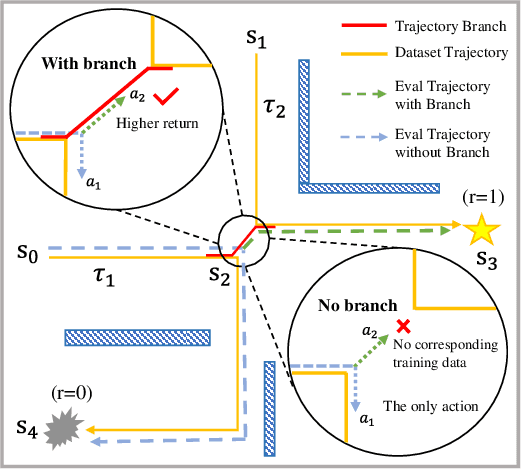
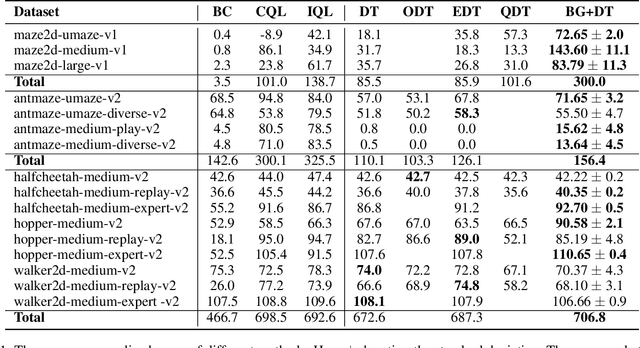
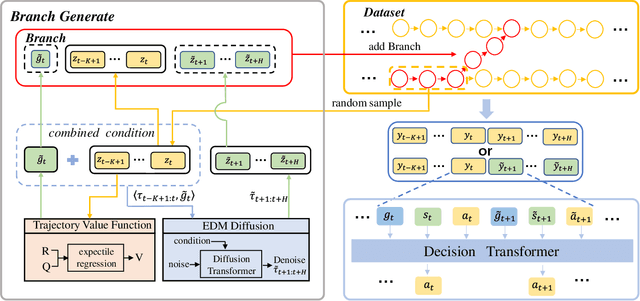
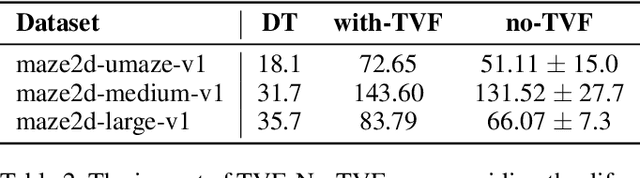
Abstract:Decision Transformer (DT) can learn effective policy from offline datasets by converting the offline reinforcement learning (RL) into a supervised sequence modeling task, where the trajectory elements are generated auto-regressively conditioned on the return-to-go (RTG).However, the sequence modeling learning approach tends to learn policies that converge on the sub-optimal trajectories within the dataset, for lack of bridging data to move to better trajectories, even if the condition is set to the highest RTG.To address this issue, we introduce Diffusion-Based Trajectory Branch Generation (BG), which expands the trajectories of the dataset with branches generated by a diffusion model.The trajectory branch is generated based on the segment of the trajectory within the dataset, and leads to trajectories with higher returns.We concatenate the generated branch with the trajectory segment as an expansion of the trajectory.After expanding, DT has more opportunities to learn policies to move to better trajectories, preventing it from converging to the sub-optimal trajectories.Empirically, after processing with BG, DT outperforms state-of-the-art sequence modeling methods on D4RL benchmark, demonstrating the effectiveness of adding branches to the dataset without further modifications.
Innovative Thinking, Infinite Humor: Humor Research of Large Language Models through Structured Thought Leaps
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Humor is a culturally nuanced aspect of human language that presents challenges for understanding and generation, requiring participants to possess good creativity and strong associative thinking. Similar to reasoning tasks like solving math problems, humor generation requires continuous reflection and revision to foster creative thinking, rather than relying on a sudden flash of inspiration like Creative Leap-of-Thought (CLoT) paradigm. Although CLoT can realize the ability of remote association generation, this paradigm fails to generate humor content. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a systematic way of thinking about generating humor and based on it, we built Creative Leap of Structured Thought (CLoST) frame. First, a reward model is necessary achieve the purpose of being able to correct errors, since there is currently no expert model of humor and a usable rule to determine whether a piece of content is humorous. Judgement-oriented instructions are designed to improve the capability of a model, and we also propose an open-domain instruction evolutionary method to fully unleash the potential. Then, through reinforcement learning, the model learns to hone its rationales of the thought chain and refine the strategies it uses. Thus, it learns to recognize and correct its mistakes, and finally generate the most humorous and creative answer. These findings deepen our understanding of the creative capabilities of LLMs and provide ways to enhance LLMs' creative abilities for cross-domain innovative applications.
REGNet V2: End-to-End REgion-based Grasp Detection Network for Grippers of Different Sizes in Point Clouds
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:Grasping has been a crucial but challenging problem in robotics for many years. One of the most important challenges is how to make grasping generalizable and robust to novel objects as well as grippers in unstructured environments. We present \regnet, a robotic grasping system that can adapt to different parallel jaws to grasp diversified objects. To support different grippers, \regnet embeds the gripper parameters into point clouds, based on which it predicts suitable grasp configurations. It includes three components: Score Network (SN), Grasp Region Network (GRN), and Refine Network (RN). In the first stage, SN is used to filter suitable points for grasping by grasp confidence scores. In the second stage, based on the selected points, GRN generates a set of grasp proposals. Finally, RN refines the grasp proposals for more accurate and robust predictions. We devise an analytic policy to choose the optimal grasp to be executed from the predicted grasp set. To train \regnet, we construct a large-scale grasp dataset containing collision-free grasp configurations using different parallel-jaw grippers. The experimental results demonstrate that \regnet with the analytic policy achieves the highest success rate of $74.98\%$ in real-world clutter scenes with $20$ objects, significantly outperforming several state-of-the-art methods, including GPD, PointNetGPD, and S4G. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/zhaobinglei/REGNet-V2.
Grounded Answers for Multi-agent Decision-making Problem through Generative World Model
Oct 03, 2024
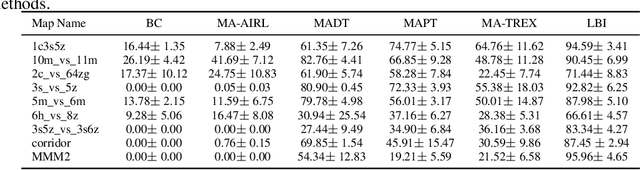


Abstract:Recent progress in generative models has stimulated significant innovations in many fields, such as image generation and chatbots. Despite their success, these models often produce sketchy and misleading solutions for complex multi-agent decision-making problems because they miss the trial-and-error experience and reasoning as humans. To address this limitation, we explore a paradigm that integrates a language-guided simulator into the multi-agent reinforcement learning pipeline to enhance the generated answer. The simulator is a world model that separately learns dynamics and reward, where the dynamics model comprises an image tokenizer as well as a causal transformer to generate interaction transitions autoregressively, and the reward model is a bidirectional transformer learned by maximizing the likelihood of trajectories in the expert demonstrations under language guidance. Given an image of the current state and the task description, we use the world model to train the joint policy and produce the image sequence as the answer by running the converged policy on the dynamics model. The empirical results demonstrate that this framework can improve the answers for multi-agent decision-making problems by showing superior performance on the training and unseen tasks of the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge benchmark. In particular, it can generate consistent interaction sequences and explainable reward functions at interaction states, opening the path for training generative models of the future.
DexDiff: Towards Extrinsic Dexterity Manipulation of Ungraspable Objects in Unrestricted Environments
Sep 09, 2024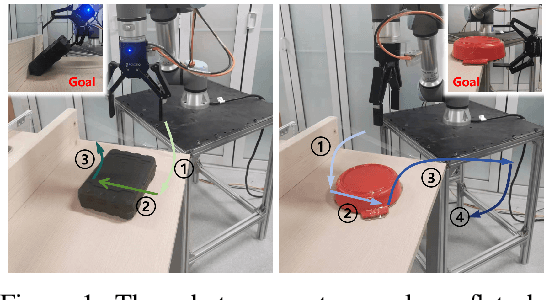
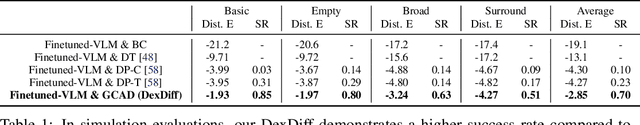
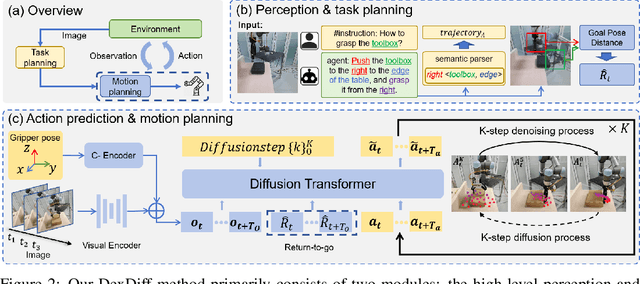
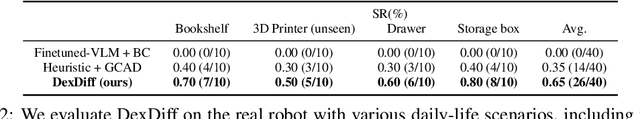
Abstract:Grasping large and flat objects (e.g. a book or a pan) is often regarded as an ungraspable task, which poses significant challenges due to the unreachable grasping poses. Previous works leverage Extrinsic Dexterity like walls or table edges to grasp such objects. However, they are limited to task-specific policies and lack task planning to find pre-grasp conditions. This makes it difficult to adapt to various environments and extrinsic dexterity constraints. Therefore, we present DexDiff, a robust robotic manipulation method for long-horizon planning with extrinsic dexterity. Specifically, we utilize a vision-language model (VLM) to perceive the environmental state and generate high-level task plans, followed by a goal-conditioned action diffusion (GCAD) model to predict the sequence of low-level actions. This model learns the low-level policy from offline data with the cumulative reward guided by high-level planning as the goal condition, which allows for improved prediction of robot actions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method not only effectively performs ungraspable tasks but also generalizes to previously unseen objects. It outperforms baselines by a 47% higher success rate in simulation and facilitates efficient deployment and manipulation in real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge