Xinrui Yang
MInCo: Mitigating Information Conflicts in Distracted Visual Model-based Reinforcement Learning
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:Existing visual model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) algorithms with observation reconstruction often suffer from information conflicts, making it difficult to learn compact representations and hence result in less robust policies, especially in the presence of task-irrelevant visual distractions. In this paper, we first reveal that the information conflicts in current visual MBRL algorithms stem from visual representation learning and latent dynamics modeling with an information-theoretic perspective. Based on this finding, we present a new algorithm to resolve information conflicts for visual MBRL, named MInCo, which mitigates information conflicts by leveraging negative-free contrastive learning, aiding in learning invariant representation and robust policies despite noisy observations. To prevent the dominance of visual representation learning, we introduce time-varying reweighting to bias the learning towards dynamics modeling as training proceeds. We evaluate our method on several robotic control tasks with dynamic background distractions. Our experiments demonstrate that MInCo learns invariant representations against background noise and consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art visual MBRL methods. Code is available at https://github.com/ShiguangSun/minco.
Grounded Answers for Multi-agent Decision-making Problem through Generative World Model
Oct 03, 2024
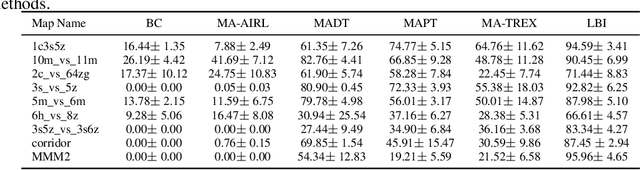


Abstract:Recent progress in generative models has stimulated significant innovations in many fields, such as image generation and chatbots. Despite their success, these models often produce sketchy and misleading solutions for complex multi-agent decision-making problems because they miss the trial-and-error experience and reasoning as humans. To address this limitation, we explore a paradigm that integrates a language-guided simulator into the multi-agent reinforcement learning pipeline to enhance the generated answer. The simulator is a world model that separately learns dynamics and reward, where the dynamics model comprises an image tokenizer as well as a causal transformer to generate interaction transitions autoregressively, and the reward model is a bidirectional transformer learned by maximizing the likelihood of trajectories in the expert demonstrations under language guidance. Given an image of the current state and the task description, we use the world model to train the joint policy and produce the image sequence as the answer by running the converged policy on the dynamics model. The empirical results demonstrate that this framework can improve the answers for multi-agent decision-making problems by showing superior performance on the training and unseen tasks of the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge benchmark. In particular, it can generate consistent interaction sequences and explainable reward functions at interaction states, opening the path for training generative models of the future.
Batch-Instructed Gradient for Prompt Evolution:Systematic Prompt Optimization for Enhanced Text-to-Image Synthesis
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image models have shown remarkable progress in generating high-quality images from user-provided prompts. Despite this, the quality of these images varies due to the models' sensitivity to human language nuances. With advancements in large language models, there are new opportunities to enhance prompt design for image generation tasks. Existing research primarily focuses on optimizing prompts for direct interaction, while less attention is given to scenarios involving intermediary agents, like the Stable Diffusion model. This study proposes a Multi-Agent framework to optimize input prompts for text-to-image generation models. Central to this framework is a prompt generation mechanism that refines initial queries using dynamic instructions, which evolve through iterative performance feedback. High-quality prompts are then fed into a state-of-the-art text-to-image model. A professional prompts database serves as a benchmark to guide the instruction modifier towards generating high-caliber prompts. A scoring system evaluates the generated images, and an LLM generates new instructions based on calculated gradients. This iterative process is managed by the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) algorithm and assessed using the Human Preference Score version 2 (HPS v2). Preliminary ablation studies highlight the effectiveness of various system components and suggest areas for future improvements.
Imagine, Initialize, and Explore: An Effective Exploration Method in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 01, 2024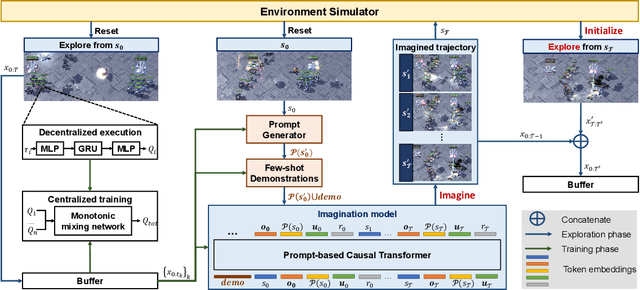
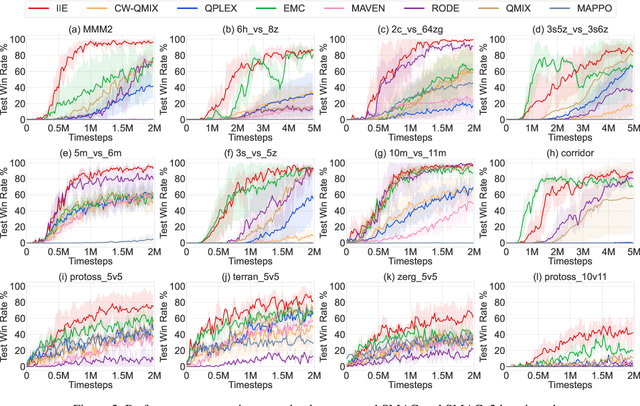
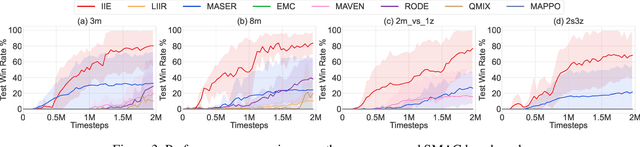
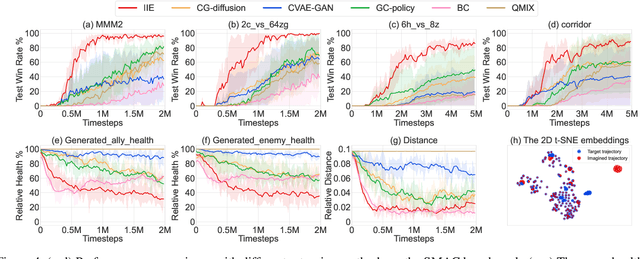
Abstract:Effective exploration is crucial to discovering optimal strategies for multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) in complex coordination tasks. Existing methods mainly utilize intrinsic rewards to enable committed exploration or use role-based learning for decomposing joint action spaces instead of directly conducting a collective search in the entire action-observation space. However, they often face challenges obtaining specific joint action sequences to reach successful states in long-horizon tasks. To address this limitation, we propose Imagine, Initialize, and Explore (IIE), a novel method that offers a promising solution for efficient multi-agent exploration in complex scenarios. IIE employs a transformer model to imagine how the agents reach a critical state that can influence each other's transition functions. Then, we initialize the environment at this state using a simulator before the exploration phase. We formulate the imagination as a sequence modeling problem, where the states, observations, prompts, actions, and rewards are predicted autoregressively. The prompt consists of timestep-to-go, return-to-go, influence value, and one-shot demonstration, specifying the desired state and trajectory as well as guiding the action generation. By initializing agents at the critical states, IIE significantly increases the likelihood of discovering potentially important under-explored regions. Despite its simplicity, empirical results demonstrate that our method outperforms multi-agent exploration baselines on the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge (SMAC) and SMACv2 environments. Particularly, IIE shows improved performance in the sparse-reward SMAC tasks and produces more effective curricula over the initialized states than other generative methods, such as CVAE-GAN and diffusion models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge