Yilin Zhao
DGA-Net: Enhancing SAM with Depth Prompting and Graph-Anchor Guidance for Camouflaged Object Detection
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:To fully exploit depth cues in Camouflaged Object Detection (COD), we present DGA-Net, a specialized framework that adapts the Segment Anything Model (SAM) via a novel ``depth prompting" paradigm. Distinguished from existing approaches that primarily rely on sparse prompts (e.g., points or boxes), our method introduces a holistic mechanism for constructing and propagating dense depth prompts. Specifically, we propose a Cross-modal Graph Enhancement (CGE) module that synthesizes RGB semantics and depth geometric within a heterogeneous graph to form a unified guidance signal. Furthermore, we design an Anchor-Guided Refinement (AGR) module. To counteract the inherent information decay in feature hierarchies, AGR forges a global anchor and establishes direct non-local pathways to broadcast this guidance from deep to shallow layers, ensuring precise and consistent segmentation. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results demonstrate that our proposed DGA-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art COD methods.
Learning to Pose Problems: Reasoning-Driven and Solver-Adaptive Data Synthesis for Large Reasoning Models
Nov 13, 2025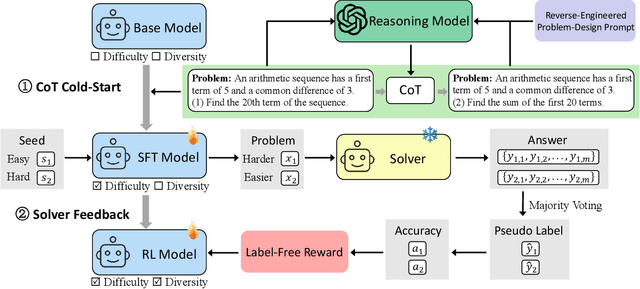
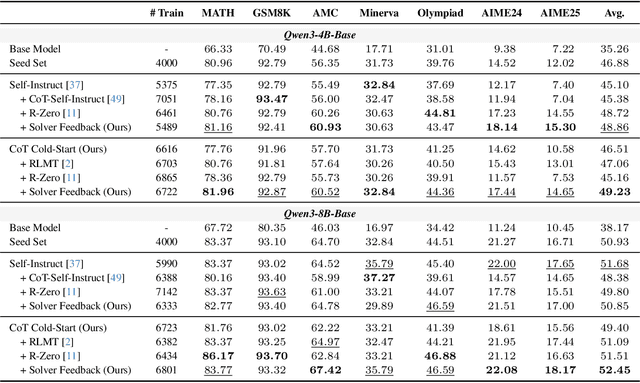

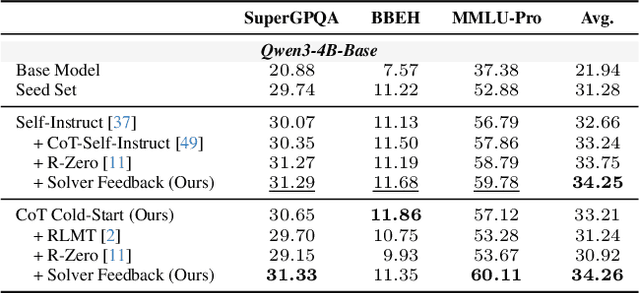
Abstract:Data synthesis for training large reasoning models offers a scalable alternative to limited, human-curated datasets, enabling the creation of high-quality data. However, existing approaches face several challenges: (i) indiscriminate generation that ignores the solver's ability and yields low-value problems, or reliance on complex data pipelines to balance problem difficulty; and (ii) a lack of reasoning in problem generation, leading to shallow problem variants. In this paper, we develop a problem generator that reasons explicitly to plan problem directions before synthesis and adapts difficulty to the solver's ability. Specifically, we construct related problem pairs and augment them with intermediate problem-design CoT produced by a reasoning model. These data bootstrap problem-design strategies from the generator. Then, we treat the solver's feedback on synthetic problems as a reward signal, enabling the generator to calibrate difficulty and produce complementary problems near the edge of the solver's competence. Extensive experiments on 10 mathematical and general reasoning benchmarks show that our method achieves an average improvement of 2.5% and generalizes to both language and vision-language models. Moreover, a solver trained on the synthesized data provides improved rewards for continued generator training, enabling co-evolution and yielding a further 0.7% performance gain. Our code will be made publicly available here.
VoxelFormer: Parameter-Efficient Multi-Subject Visual Decoding from fMRI
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in fMRI-based visual decoding have enabled compelling reconstructions of perceived images. However, most approaches rely on subject-specific training, limiting scalability and practical deployment. We introduce \textbf{VoxelFormer}, a lightweight transformer architecture that enables multi-subject training for visual decoding from fMRI. VoxelFormer integrates a Token Merging Transformer (ToMer) for efficient voxel compression and a query-driven Q-Former that produces fixed-size neural representations aligned with the CLIP image embedding space. Evaluated on the 7T Natural Scenes Dataset, VoxelFormer achieves competitive retrieval performance on subjects included during training with significantly fewer parameters than existing methods. These results highlight token merging and query-based transformers as promising strategies for parameter-efficient neural decoding.
Innovative Thinking, Infinite Humor: Humor Research of Large Language Models through Structured Thought Leaps
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Humor is a culturally nuanced aspect of human language that presents challenges for understanding and generation, requiring participants to possess good creativity and strong associative thinking. Similar to reasoning tasks like solving math problems, humor generation requires continuous reflection and revision to foster creative thinking, rather than relying on a sudden flash of inspiration like Creative Leap-of-Thought (CLoT) paradigm. Although CLoT can realize the ability of remote association generation, this paradigm fails to generate humor content. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a systematic way of thinking about generating humor and based on it, we built Creative Leap of Structured Thought (CLoST) frame. First, a reward model is necessary achieve the purpose of being able to correct errors, since there is currently no expert model of humor and a usable rule to determine whether a piece of content is humorous. Judgement-oriented instructions are designed to improve the capability of a model, and we also propose an open-domain instruction evolutionary method to fully unleash the potential. Then, through reinforcement learning, the model learns to hone its rationales of the thought chain and refine the strategies it uses. Thus, it learns to recognize and correct its mistakes, and finally generate the most humorous and creative answer. These findings deepen our understanding of the creative capabilities of LLMs and provide ways to enhance LLMs' creative abilities for cross-domain innovative applications.
MetaTool: Facilitating Large Language Models to Master Tools with Meta-task Augmentation
Jul 15, 2024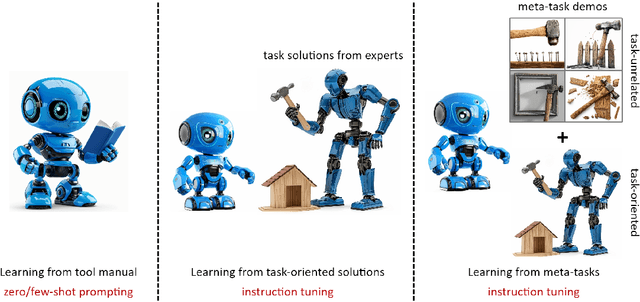
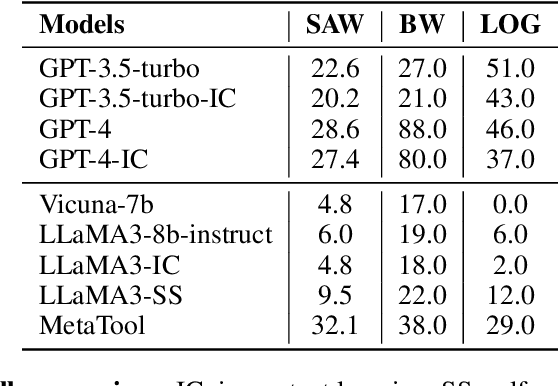
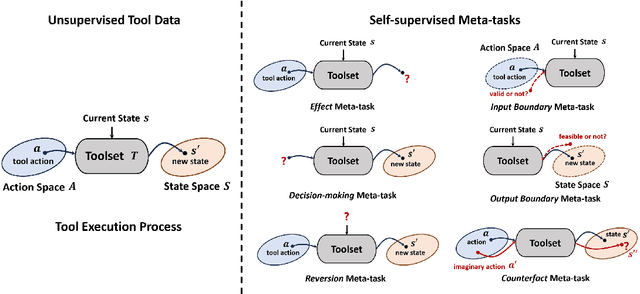
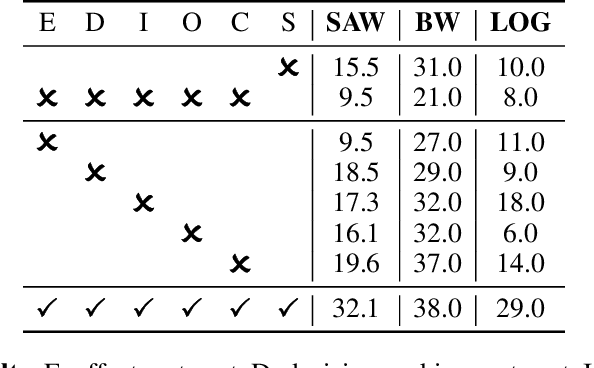
Abstract:Utilizing complex tools with Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical component for grounding AI agents in various real-world scenarios. The core challenge of manipulating tools lies in understanding their usage and functionality. The prevailing approach involves few-shot prompting with demonstrations or fine-tuning on expert trajectories. However, for complex tools and tasks, mere in-context demonstrations may fail to cover sufficient knowledge. Training-based methods are also constrained by the high cost of dataset construction and limited generalizability. In this paper, we introduce a new tool learning methodology (MetaTool) that is generalizable for mastering any reusable toolset. Our approach includes a self-supervised data augmentation technique that enables LLMs to gain a comprehensive understanding of various tools, thereby improving their ability to complete tasks effectively. We develop a series of meta-tasks that involve predicting masked factors of tool execution. These self-supervised tasks enable the automatic generation of high-quality QA data concerning tool comprehension. By incorporating meta-task data into the instruction tuning process, the proposed MetaTool model achieves significant superiority to open-source models and is comparable to GPT-4/GPT-3.5 on multiple tool-oriented tasks.
PLLaVA : Parameter-free LLaVA Extension from Images to Videos for Video Dense Captioning
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:Vision-language pre-training has significantly elevated performance across a wide range of image-language applications. Yet, the pre-training process for video-related tasks demands exceptionally large computational and data resources, which hinders the progress of video-language models. This paper investigates a straight-forward, highly efficient, and resource-light approach to adapting an existing image-language pre-trained model for dense video understanding. Our preliminary experiments reveal that directly fine-tuning pre-trained image-language models with multiple frames as inputs on video datasets leads to performance saturation or even a drop. Our further investigation reveals that it is largely attributed to the bias of learned high-norm visual features. Motivated by this finding, we propose a simple but effective pooling strategy to smooth the feature distribution along the temporal dimension and thus reduce the dominant impacts from the extreme features. The new model is termed Pooling LLaVA, or PLLaVA in short. PLLaVA achieves new state-of-the-art performance on modern benchmark datasets for both video question-answer and captioning tasks. Notably, on the recent popular VideoChatGPT benchmark, PLLaVA achieves a score of 3.48 out of 5 on average of five evaluated dimensions, exceeding the previous SOTA results from GPT4V (IG-VLM) by 9%. On the latest multi-choice benchmark MVBench, PLLaVA achieves 58.1% accuracy on average across 20 sub-tasks, 14.5% higher than GPT4V (IG-VLM). Code is available at https://pllava.github.io/
ChatAnything: Facetime Chat with LLM-Enhanced Personas
Nov 12, 2023



Abstract:In this technical report, we target generating anthropomorphized personas for LLM-based characters in an online manner, including visual appearance, personality and tones, with only text descriptions. To achieve this, we first leverage the in-context learning capability of LLMs for personality generation by carefully designing a set of system prompts. We then propose two novel concepts: the mixture of voices (MoV) and the mixture of diffusers (MoD) for diverse voice and appearance generation. For MoV, we utilize the text-to-speech (TTS) algorithms with a variety of pre-defined tones and select the most matching one based on the user-provided text description automatically. For MoD, we combine the recent popular text-to-image generation techniques and talking head algorithms to streamline the process of generating talking objects. We termed the whole framework as ChatAnything. With it, users could be able to animate anything with any personas that are anthropomorphic using just a few text inputs. However, we have observed that the anthropomorphic objects produced by current generative models are often undetectable by pre-trained face landmark detectors, leading to failure of the face motion generation, even if these faces possess human-like appearances because those images are nearly seen during the training (e.g., OOD samples). To address this issue, we incorporate pixel-level guidance to infuse human face landmarks during the image generation phase. To benchmark these metrics, we have built an evaluation dataset. Based on it, we verify that the detection rate of the face landmark is significantly increased from 57.0% to 92.5% thus allowing automatic face animation based on generated speech content. The code and more results can be found at https://chatanything.github.io/.
Multi-grained Evidence Inference for Multi-choice Reading Comprehension
Oct 27, 2023

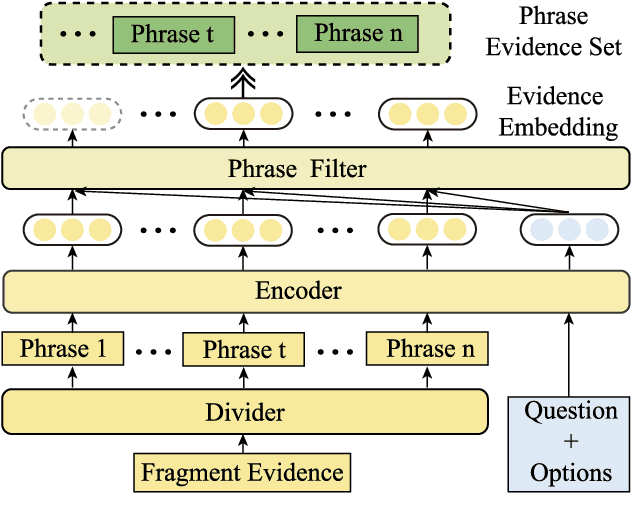

Abstract:Multi-choice Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) is a major and challenging task for machines to answer questions according to provided options. Answers in multi-choice MRC cannot be directly extracted in the given passages, and essentially require machines capable of reasoning from accurate extracted evidence. However, the critical evidence may be as simple as just one word or phrase, while it is hidden in the given redundant, noisy passage with multiple linguistic hierarchies from phrase, fragment, sentence until the entire passage. We thus propose a novel general-purpose model enhancement which integrates multi-grained evidence comprehensively, named Multi-grained evidence inferencer (Mugen), to make up for the inability. Mugen extracts three different granularities of evidence: coarse-, middle- and fine-grained evidence, and integrates evidence with the original passages, achieving significant and consistent performance improvement on four multi-choice MRC benchmarks.
* Accepted by TASLP 2023, vol. 31, pp. 3896-3907
Lite Unified Modeling for Discriminative Reading Comprehension
Mar 26, 2022
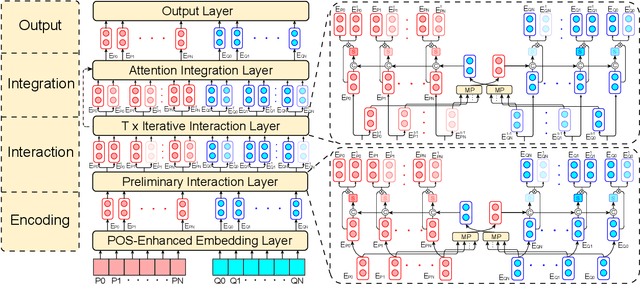
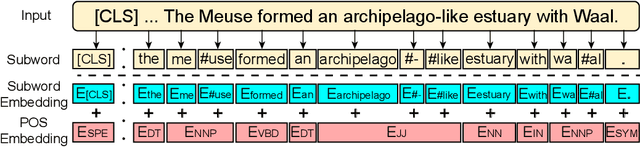
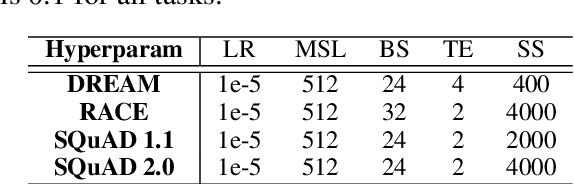
Abstract:As a broad and major category in machine reading comprehension (MRC), the generalized goal of discriminative MRC is answer prediction from the given materials. However, the focuses of various discriminative MRC tasks may be diverse enough: multi-choice MRC requires model to highlight and integrate all potential critical evidence globally; while extractive MRC focuses on higher local boundary preciseness for answer extraction. Among previous works, there lacks a unified design with pertinence for the overall discriminative MRC tasks. To fill in above gap, we propose a lightweight POS-Enhanced Iterative Co-Attention Network (POI-Net) as the first attempt of unified modeling with pertinence, to handle diverse discriminative MRC tasks synchronously. Nearly without introducing more parameters, our lite unified design brings model significant improvement with both encoder and decoder components. The evaluation results on four discriminative MRC benchmarks consistently indicate the general effectiveness and applicability of our model, and the code is available at https://github.com/Yilin1111/poi-net.
DocOIE: A Document-level Context-Aware Dataset for OpenIE
May 11, 2021



Abstract:Open Information Extraction (OpenIE) aims to extract structured relational tuples (subject, relation, object) from sentences and plays critical roles for many downstream NLP applications. Existing solutions perform extraction at sentence level, without referring to any additional contextual information. In reality, however, a sentence typically exists as part of a document rather than standalone; we often need to access relevant contextual information around the sentence before we can accurately interpret it. As there is no document-level context-aware OpenIE dataset available, we manually annotate 800 sentences from 80 documents in two domains (Healthcare and Transportation) to form a DocOIE dataset for evaluation. In addition, we propose DocIE, a novel document-level context-aware OpenIE model. Our experimental results based on DocIE demonstrate that incorporating document-level context is helpful in improving OpenIE performance. Both DocOIE dataset and DocIE model are released for public.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge