MetaTool: Facilitating Large Language Models to Master Tools with Meta-task Augmentation
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2024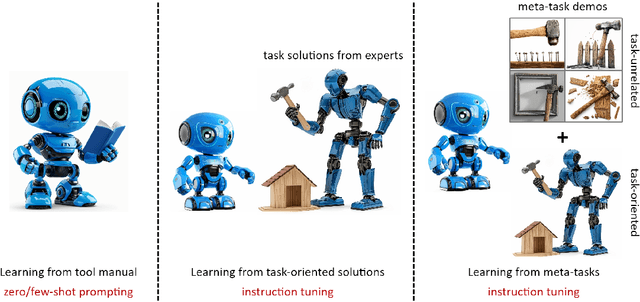
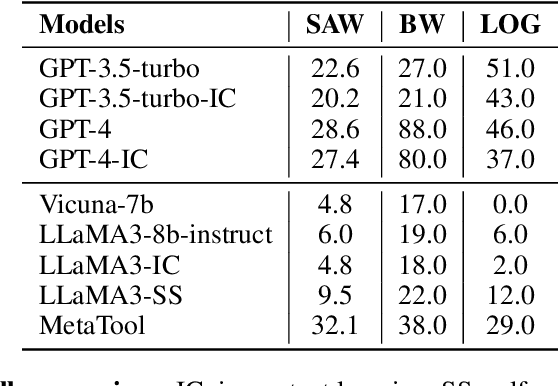
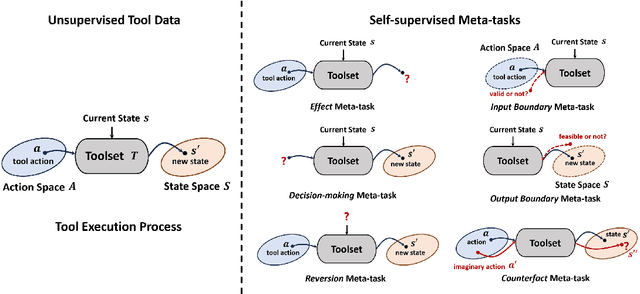
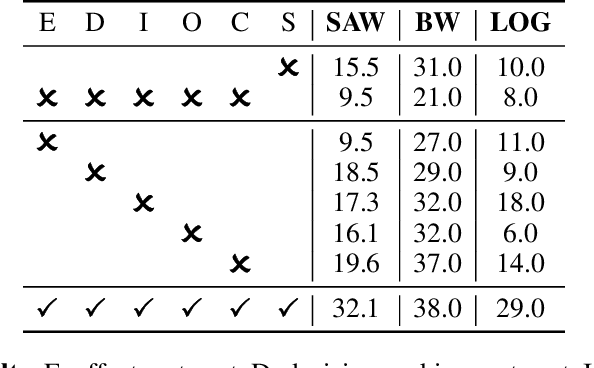
Utilizing complex tools with Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical component for grounding AI agents in various real-world scenarios. The core challenge of manipulating tools lies in understanding their usage and functionality. The prevailing approach involves few-shot prompting with demonstrations or fine-tuning on expert trajectories. However, for complex tools and tasks, mere in-context demonstrations may fail to cover sufficient knowledge. Training-based methods are also constrained by the high cost of dataset construction and limited generalizability. In this paper, we introduce a new tool learning methodology (MetaTool) that is generalizable for mastering any reusable toolset. Our approach includes a self-supervised data augmentation technique that enables LLMs to gain a comprehensive understanding of various tools, thereby improving their ability to complete tasks effectively. We develop a series of meta-tasks that involve predicting masked factors of tool execution. These self-supervised tasks enable the automatic generation of high-quality QA data concerning tool comprehension. By incorporating meta-task data into the instruction tuning process, the proposed MetaTool model achieves significant superiority to open-source models and is comparable to GPT-4/GPT-3.5 on multiple tool-oriented tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge