Wanqi Zhou
Reshaping Action Error Distributions for Reliable Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In robotic manipulation, vision-language-action (VLA) models have emerged as a promising paradigm for learning generalizable and scalable robot policies. Most existing VLA frameworks rely on standard supervised objectives, typically cross-entropy for discrete actions and mean squared error (MSE) for continuous action regression, which impose strong pointwise constraints on individual predictions. In this work, we focus on continuous-action VLA models and move beyond conventional MSE-based regression by reshaping action error distributions during training. Drawing on information-theoretic principles, we introduce Minimum Error Entropy (MEE) into modern VLA architectures and propose a trajectory-level MEE objective, together with two weighted variants, combined with MSE for continuous-action VLA training. We evaluate our approaches across standard, few-shot, and noisy settings on multiple representative VLA architectures, using simulation benchmarks such as LIBERO and SimplerEnv as well as real-world robotic manipulation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate consistent improvements in success rates and robustness across these settings. Under imbalanced data regimes, the gains persist within a well-characterized operating range, while incurring negligible additional training cost and no impact on inference efficiency. We further provide theoretical analyses that explain why MEE-based supervision is effective and characterize its practical range. Project Page: https://cognition2actionlab.github.io/VLA-TMEE.github.io/
Latent Reasoning VLA: Latent Thinking and Prediction for Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models benefit from chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, but existing approaches incur high inference overhead and rely on discrete reasoning representations that mismatch continuous perception and control. We propose Latent Reasoning VLA (\textbf{LaRA-VLA}), a unified VLA framework that internalizes multi-modal CoT reasoning into continuous latent representations for embodied action. LaRA-VLA performs unified reasoning and prediction in latent space, eliminating explicit CoT generation at inference time and enabling efficient, action-oriented control. To realize latent embodied reasoning, we introduce a curriculum-based training paradigm that progressively transitions from explicit textual and visual CoT supervision to latent reasoning, and finally adapts latent reasoning dynamics to condition action generation. We construct two structured CoT datasets and evaluate LaRA-VLA on both simulation benchmarks and long-horizon real-robot manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that LaRA-VLA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLA methods while reducing inference latency by up to 90\% compared to explicit CoT-based approaches, demonstrating latent reasoning as an effective and efficient paradigm for real-time embodied control. Project Page: \href{https://loveju1y.github.io/Latent-Reasoning-VLA/}{LaRA-VLA Website}.
Embodied Robot Manipulation in the Era of Foundation Models: Planning and Learning Perspectives
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in vision, language, and multimodal learning have substantially accelerated progress in robotic foundation models, with robot manipulation remaining a central and challenging problem. This survey examines robot manipulation from an algorithmic perspective and organizes recent learning-based approaches within a unified abstraction of high-level planning and low-level control. At the high level, we extend the classical notion of task planning to include reasoning over language, code, motion, affordances, and 3D representations, emphasizing their role in structured and long-horizon decision making. At the low level, we propose a training-paradigm-oriented taxonomy for learning-based control, organizing existing methods along input modeling, latent representation learning, and policy learning. Finally, we identify open challenges and prospective research directions related to scalability, data efficiency, multimodal physical interaction, and safety. Together, these analyses aim to clarify the design space of modern foundation models for robotic manipulation.
Dual-Path Stable Soft Prompt Generation for Domain Generalization
May 24, 2025Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) aims to learn a model using data from one or multiple related but distinct source domains that can generalize well to unseen out-of-distribution target domains. Inspired by the success of large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), prompt tuning has emerged as an effective generalization strategy. However, it often struggles to capture domain-specific features due to its reliance on manually or fixed prompt inputs. Recently, some prompt generation methods have addressed this limitation by dynamically generating instance-specific and domain-specific prompts for each input, enriching domain information and demonstrating potential for enhanced generalization. Through further investigation, we identify a notable issue in existing prompt generation methods: the same input often yields significantly different and suboptimal prompts across different random seeds, a phenomenon we term Prompt Variability. To address this, we introduce negative learning into the prompt generation process and propose Dual-Path Stable Soft Prompt Generation (DPSPG), a transformer-based framework designed to improve both the stability and generalization of prompts. Specifically, DPSPG incorporates a complementary prompt generator to produce negative prompts, thereby reducing the risk of introducing misleading information. Both theoretical and empirical analyses demonstrate that negative learning leads to more robust and effective prompts by increasing the effective margin and reducing the upper bound of the gradient norm. Extensive experiments on five DG benchmark datasets show that DPSPG consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods while maintaining prompt stability.
OpenHelix: A Short Survey, Empirical Analysis, and Open-Source Dual-System VLA Model for Robotic Manipulation
May 06, 2025



Abstract:Dual-system VLA (Vision-Language-Action) architectures have become a hot topic in embodied intelligence research, but there is a lack of sufficient open-source work for further performance analysis and optimization. To address this problem, this paper will summarize and compare the structural designs of existing dual-system architectures, and conduct systematic empirical evaluations on the core design elements of existing dual-system architectures. Ultimately, it will provide a low-cost open-source model for further exploration. Of course, this project will continue to update with more experimental conclusions and open-source models with improved performance for everyone to choose from. Project page: https://openhelix-robot.github.io/.
Rethinking Latent Representations in Behavior Cloning: An Information Bottleneck Approach for Robot Manipulation
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Behavior Cloning (BC) is a widely adopted visual imitation learning method in robot manipulation. Current BC approaches often enhance generalization by leveraging large datasets and incorporating additional visual and textual modalities to capture more diverse information. However, these methods overlook whether the learned representations contain redundant information and lack a solid theoretical foundation to guide the learning process. To address these limitations, we adopt an information-theoretic perspective and introduce mutual information to quantify and mitigate redundancy in latent representations. Building on this, we incorporate the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle into BC, which extends the idea of reducing redundancy by providing a structured framework for compressing irrelevant information while preserving task-relevant features. This work presents the first comprehensive study on redundancy in latent representations across various methods, backbones, and experimental settings, while extending the generalizability of the IB to BC. Extensive experiments and analyses on the CortexBench and LIBERO benchmarks demonstrate significant performance improvements with IB, underscoring the importance of reducing input data redundancy and highlighting its practical value for more practical applications. Project Page: https://baishuanghao.github.io/BC-IB.github.io.
PromptTA: Prompt-driven Text Adapter for Source-free Domain Generalization
Sep 21, 2024Abstract:Source-free domain generalization (SFDG) tackles the challenge of adapting models to unseen target domains without access to source domain data. To deal with this challenging task, recent advances in SFDG have primarily focused on leveraging the text modality of vision-language models such as CLIP. These methods involve developing a transferable linear classifier based on diverse style features extracted from the text and learned prompts or deriving domain-unified text representations from domain banks. However, both style features and domain banks have limitations in capturing comprehensive domain knowledge. In this work, we propose Prompt-Driven Text Adapter (PromptTA) method, which is designed to better capture the distribution of style features and employ resampling to ensure thorough coverage of domain knowledge. To further leverage this rich domain information, we introduce a text adapter that learns from these style features for efficient domain information storage. Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that PromptTA achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/zhanghr2001/PromptTA.
Jacobian Regularizer-based Neural Granger Causality
May 14, 2024



Abstract:With the advancement of neural networks, diverse methods for neural Granger causality have emerged, which demonstrate proficiency in handling complex data, and nonlinear relationships. However, the existing framework of neural Granger causality has several limitations. It requires the construction of separate predictive models for each target variable, and the relationship depends on the sparsity on the weights of the first layer, resulting in challenges in effectively modeling complex relationships between variables as well as unsatisfied estimation accuracy of Granger causality. Moreover, most of them cannot grasp full-time Granger causality. To address these drawbacks, we propose a Jacobian Regularizer-based Neural Granger Causality (JRNGC) approach, a straightforward yet highly effective method for learning multivariate summary Granger causality and full-time Granger causality by constructing a single model for all target variables. Specifically, our method eliminates the sparsity constraints of weights by leveraging an input-output Jacobian matrix regularizer, which can be subsequently represented as the weighted causal matrix in the post-hoc analysis. Extensive experiments show that our proposed approach achieves competitive performance with the state-of-the-art methods for learning summary Granger causality and full-time Granger causality while maintaining lower model complexity and high scalability.
Soft Prompt Generation for Domain Generalization
Apr 30, 2024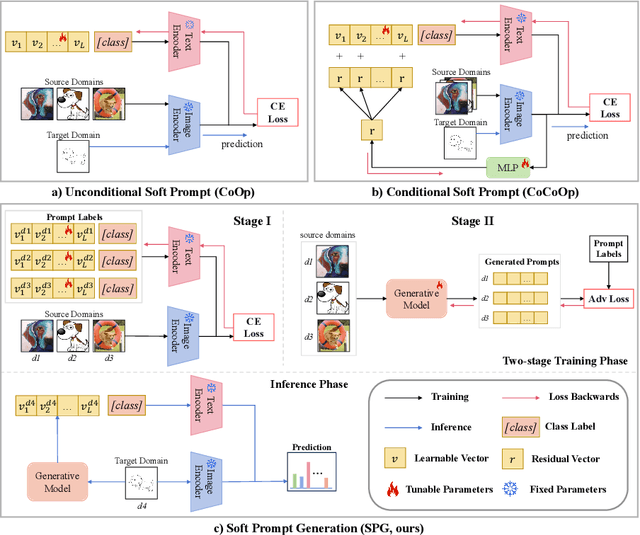
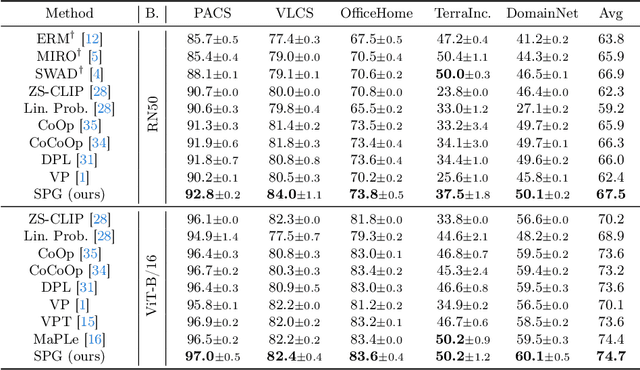
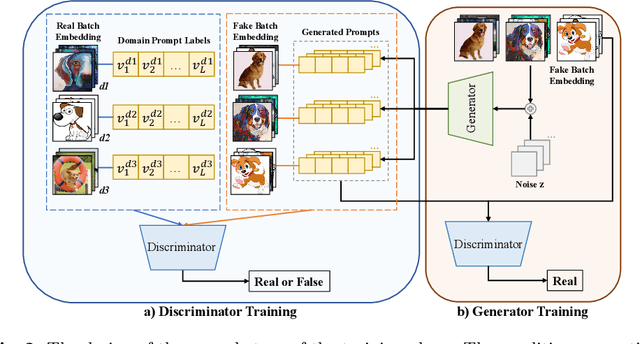
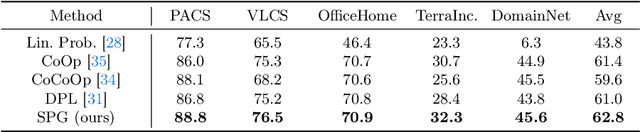
Abstract:Large pre-trained vision language models (VLMs) have shown impressive zero-shot ability on downstream tasks with manually designed prompt, which are not optimal for specific domains. To further adapt VLMs to downstream tasks, soft prompt is proposed to replace manually designed prompt, which acts as a learning vector that undergoes fine-tuning based on specific domain data. Prior prompt learning methods primarily learn a fixed prompt and residuled prompt from training samples. However, the learned prompts lack diversity and ignore information about unseen domains, potentially compromising the transferability of the prompts. In this paper, we reframe the prompt learning framework from a generative perspective and propose a simple yet efficient method for the Domain Generalization (DG) task, namely \textbf{S}oft \textbf{P}rompt \textbf{G}eneration (SPG). To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce the generative model into prompt learning in VLMs and explore its potential for producing soft prompts by relying solely on the generative model, ensuring the diversity of prompts. Specifically, SPG consists of a two-stage training phase and an inference phase. During the training phase, we introduce soft prompt labels for each domain, aiming to incorporate the generative model domain knowledge. During the inference phase, the generator of the generative model is employed to obtain instance-specific soft prompts for the unseen target domain. Extensive experiments on five domain generalization benchmarks of three DG tasks demonstrate that our proposed SPG achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code will be available soon.
Revisiting the Adversarial Robustness of Vision Language Models: a Multimodal Perspective
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have shown impressive generalization performance across various downstream tasks, yet they remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks. While prior research has primarily concentrated on improving the adversarial robustness of image encoders to guard against attacks on images, the exploration of text-based and multimodal attacks has largely been overlooked. In this work, we initiate the first known and comprehensive effort to study adapting vision-language models for adversarial robustness under the multimodal attack. Firstly, we introduce a multimodal attack strategy and investigate the impact of different attacks. We then propose a multimodal contrastive adversarial training loss, aligning the clean and adversarial text embeddings with the adversarial and clean visual features, to enhance the adversarial robustness of both image and text encoders of CLIP. Extensive experiments on 15 datasets across two tasks demonstrate that our method significantly improves the adversarial robustness of CLIP. Interestingly, we find that the model fine-tuned against multimodal adversarial attacks exhibits greater robustness than its counterpart fine-tuned solely against image-based attacks, even in the context of image attacks, which may open up new possibilities for enhancing the security of VLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge