Jiang-Xin Shi
LIFT+: Lightweight Fine-Tuning for Long-Tail Learning
Apr 17, 2025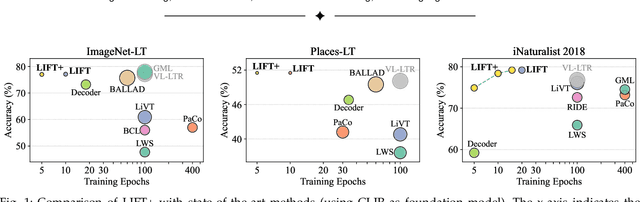
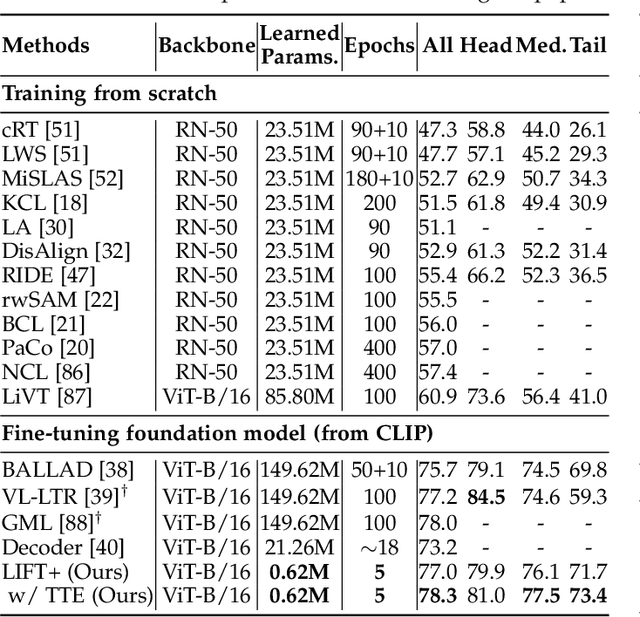
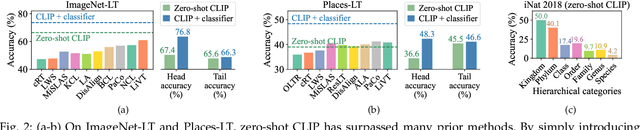
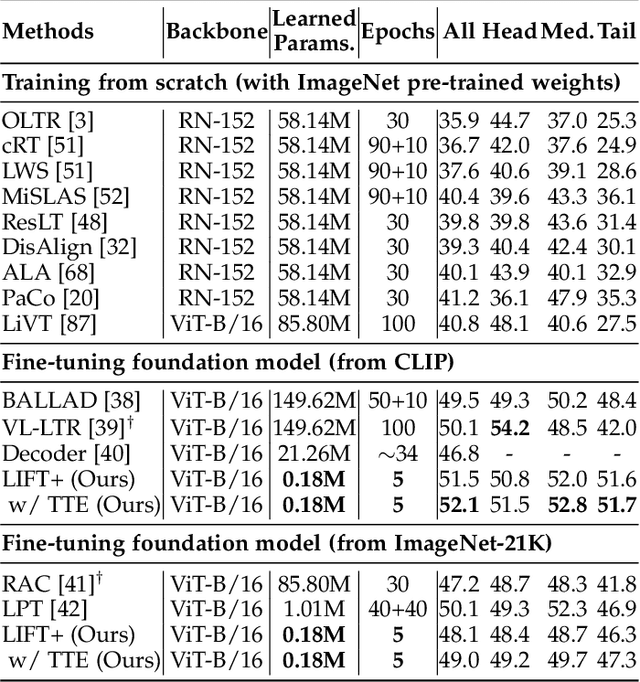
Abstract:The fine-tuning paradigm has emerged as a prominent approach for addressing long-tail learning tasks in the era of foundation models. However, the impact of fine-tuning strategies on long-tail learning performance remains unexplored. In this work, we disclose that existing paradigms exhibit a profound misuse of fine-tuning methods, leaving significant room for improvement in both efficiency and accuracy. Specifically, we reveal that heavy fine-tuning (fine-tuning a large proportion of model parameters) can lead to non-negligible performance deterioration on tail classes, whereas lightweight fine-tuning demonstrates superior effectiveness. Through comprehensive theoretical and empirical validation, we identify this phenomenon as stemming from inconsistent class conditional distributions induced by heavy fine-tuning. Building on this insight, we propose LIFT+, an innovative lightweight fine-tuning framework to optimize consistent class conditions. Furthermore, LIFT+ incorporates semantic-aware initialization, minimalist data augmentation, and test-time ensembling to enhance adaptation and generalization of foundation models. Our framework provides an efficient and accurate pipeline that facilitates fast convergence and model compactness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LIFT+ significantly reduces both training epochs (from $\sim$100 to $\leq$15) and learned parameters (less than 1%), while surpassing state-of-the-art approaches by a considerable margin. The source code is available at https://github.com/shijxcs/LIFT-plus.
LawGPT: Knowledge-Guided Data Generation and Its Application to Legal LLM
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), both proprietary and open-source, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various natural language processing tasks. However, they face significant limitations in legal reasoning tasks. Proprietary models introduce data privacy risks and high inference costs, while open-source models underperform due to insufficient legal domain training data. To address these limitations, we study data generation for legal reasoning to improve the legal reasoning performance of open-source LLMs with the help of proprietary LLMs. This is challenging due to the lack of legal knowledge in proprietary LLMs and the difficulty in verifying the generated data. We propose KgDG, a knowledge-guided data generation framework for legal reasoning. Our framework enables leveraging legal knowledge to enhance generation diversity and introduces a refinement and verification process to ensure the quality of generated data. Moreover, we expand the generated dataset to further enhance the LLM reasoning capabilities. Using KgDG, we create a synthetic legal reasoning dataset containing 50K high-quality examples. Our trained model LawGPT outperforms existing legal-specific LLMs and achieves performance comparable to proprietary LLMs, demonstrating the effectiveness of KgDG and LawGPT. Our code and resources is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/KgDG-45F5 .
Vision-Language Models are Strong Noisy Label Detectors
Sep 29, 2024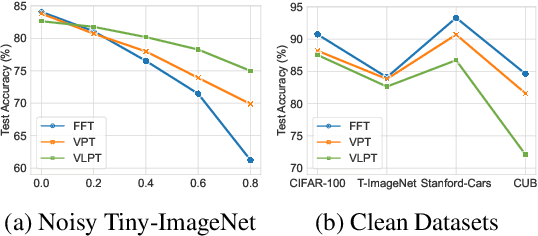



Abstract:Recent research on fine-tuning vision-language models has demonstrated impressive performance in various downstream tasks. However, the challenge of obtaining accurately labeled data in real-world applications poses a significant obstacle during the fine-tuning process. To address this challenge, this paper presents a Denoising Fine-Tuning framework, called DeFT, for adapting vision-language models. DeFT utilizes the robust alignment of textual and visual features pre-trained on millions of auxiliary image-text pairs to sieve out noisy labels. The proposed framework establishes a noisy label detector by learning positive and negative textual prompts for each class. The positive prompt seeks to reveal distinctive features of the class, while the negative prompt serves as a learnable threshold for separating clean and noisy samples. We employ parameter-efficient fine-tuning for the adaptation of a pre-trained visual encoder to promote its alignment with the learned textual prompts. As a general framework, DeFT can seamlessly fine-tune many pre-trained models to downstream tasks by utilizing carefully selected clean samples. Experimental results on seven synthetic and real-world noisy datasets validate the effectiveness of DeFT in both noisy label detection and image classification.
Efficient and Long-Tailed Generalization for Pre-trained Vision-Language Model
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP have shown powerful zero-shot inference ability via image-text matching and prove to be strong few-shot learners in various downstream tasks. However, in real-world scenarios, adapting CLIP to downstream tasks may encounter the following challenges: 1) data may exhibit long-tailed data distributions and might not have abundant samples for all the classes; 2) There might be emerging tasks with new classes that contain no samples at all. To overcome them, we propose a novel framework to achieve efficient and long-tailed generalization, which can be termed as Candle. During the training process, we propose compensating logit-adjusted loss to encourage large margins of prototypes and alleviate imbalance both within the base classes and between the base and new classes. For efficient adaptation, we treat the CLIP model as a black box and leverage the extracted features to obtain visual and textual prototypes for prediction. To make full use of multi-modal information, we also propose cross-modal attention to enrich the features from both modalities. For effective generalization, we introduce virtual prototypes for new classes to make up for their lack of training images. Candle achieves state-of-the-art performance over extensive experiments on 11 diverse datasets while substantially reducing the training time, demonstrating the superiority of our approach. The source code is available at https://github.com/shijxcs/Candle.
LawGPT: A Chinese Legal Knowledge-Enhanced Large Language Model
Jun 07, 2024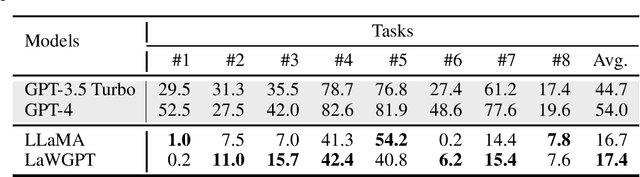
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), including both proprietary and open-source models, have showcased remarkable capabilities in addressing a wide range of downstream tasks. Nonetheless, when it comes to practical Chinese legal tasks, these models fail to meet the actual requirements. Proprietary models do not ensure data privacy for sensitive legal cases, while open-source models demonstrate unsatisfactory performance due to their lack of legal knowledge. To address this problem, we introduce LawGPT, the first open-source model specifically designed for Chinese legal applications. LawGPT comprises two key components: legal-oriented pre-training and legal supervised fine-tuning. Specifically, we employ large-scale Chinese legal documents for legal-oriented pre-training to incorporate legal domain knowledge. To further improve the model's performance on downstream legal tasks, we create a knowledge-driven instruction dataset for legal supervised fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that LawGPT outperforms the open-source LLaMA 7B model. Our code and resources are publicly available at https://github.com/pengxiao-song/LaWGPT and have received 5.7K stars on GitHub.
DeCoOp: Robust Prompt Tuning with Out-of-Distribution Detection
Jun 01, 2024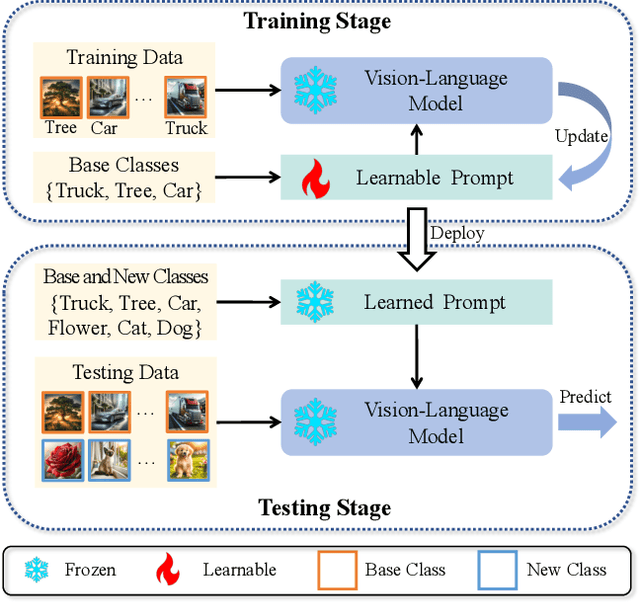
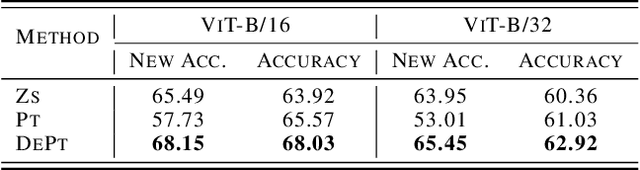
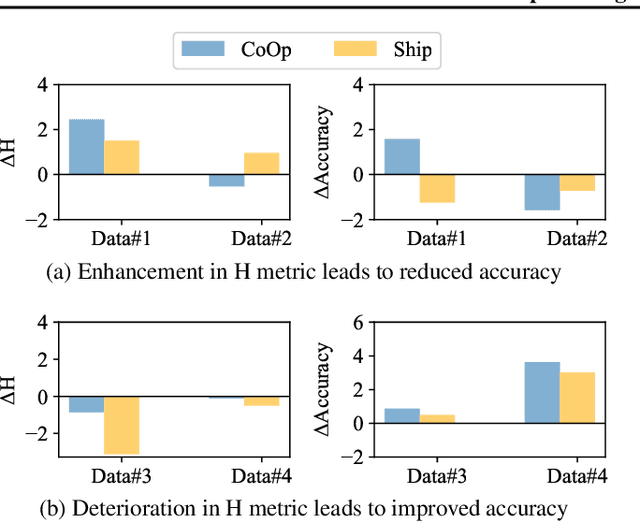
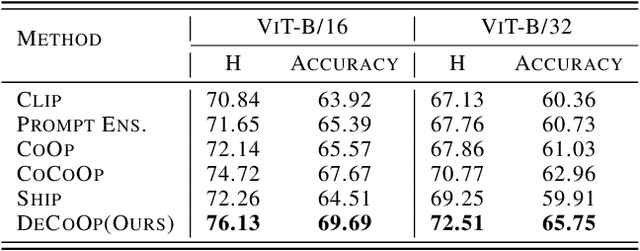
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated impressive zero-shot capabilities for various downstream tasks. Their performance can be further enhanced through few-shot prompt tuning methods. However, current studies evaluate the performance of learned prompts separately on base and new classes. This evaluation lacks practicality for real-world applications since downstream tasks cannot determine whether the data belongs to base or new classes in advance. In this paper, we explore a problem setting called Open-world Prompt Tuning (OPT), which involves tuning prompts on base classes and evaluating on a combination of base and new classes. By introducing Decomposed Prompt Tuning framework (DePT), we theoretically demonstrate that OPT can be solved by incorporating out-of-distribution detection into prompt tuning, thereby enhancing the base-to-new discriminability. Based on DePT, we present a novel prompt tuning approach, namely, Decomposed Context Optimization (DeCoOp), which introduces new-class detectors and sub-classifiers to further enhance the base-class and new-class discriminability. Experimental results on 11 benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of DePT and demonstrate that DeCoOp outperforms current state-of-the-art methods, providing a significant 2% average accuracy improvement.
How Re-sampling Helps for Long-Tail Learning?
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Long-tail learning has received significant attention in recent years due to the challenge it poses with extremely imbalanced datasets. In these datasets, only a few classes (known as the head classes) have an adequate number of training samples, while the rest of the classes (known as the tail classes) are infrequent in the training data. Re-sampling is a classical and widely used approach for addressing class imbalance issues. Unfortunately, recent studies claim that re-sampling brings negligible performance improvements in modern long-tail learning tasks. This paper aims to investigate this phenomenon systematically. Our research shows that re-sampling can considerably improve generalization when the training images do not contain semantically irrelevant contexts. In other scenarios, however, it can learn unexpected spurious correlations between irrelevant contexts and target labels. We design experiments on two homogeneous datasets, one containing irrelevant context and the other not, to confirm our findings. To prevent the learning of spurious correlations, we propose a new context shift augmentation module that generates diverse training images for the tail class by maintaining a context bank extracted from the head-class images. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed module can boost the generalization and outperform other approaches, including class-balanced re-sampling, decoupled classifier re-training, and data augmentation methods. The source code is available at https://www.lamda.nju.edu.cn/code_CSA.ashx.
Investigating the Limitation of CLIP Models: The Worst-Performing Categories
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) provides a foundation model by integrating natural language into visual concepts, enabling zero-shot recognition on downstream tasks. It is usually expected that satisfactory overall accuracy can be achieved across numerous domains through well-designed textual prompts. However, we found that their performance in the worst categories is significantly inferior to the overall performance. For example, on ImageNet, there are a total of 10 categories with class-wise accuracy as low as 0\%, even though the overall performance has achieved 64.1\%. This phenomenon reveals the potential risks associated with using CLIP models, particularly in risk-sensitive applications where specific categories hold significant importance. To address this issue, we investigate the alignment between the two modalities in the CLIP model and propose the Class-wise Matching Margin (\cmm) to measure the inference confusion. \cmm\ can effectively identify the worst-performing categories and estimate the potential performance of the candidate prompts. We further query large language models to enrich descriptions of worst-performing categories and build a weighted ensemble to highlight the efficient prompts. Experimental results clearly verify the effectiveness of our proposal, where the accuracy on the worst-10 categories on ImageNet is boosted to 5.2\%, without manual prompt engineering, laborious optimization, or access to labeled validation data.
Parameter-Efficient Long-Tailed Recognition
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:The "pre-training and fine-tuning" paradigm in addressing long-tailed recognition tasks has sparked significant interest since the emergence of large vision-language models like the contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP). While previous studies have shown promise in adapting pre-trained models for these tasks, they often undesirably require extensive training epochs or additional training data to maintain good performance. In this paper, we propose PEL, a fine-tuning method that can effectively adapt pre-trained models to long-tailed recognition tasks in fewer than 20 epochs without the need for extra data. We first empirically find that commonly used fine-tuning methods, such as full fine-tuning and classifier fine-tuning, suffer from overfitting, resulting in performance deterioration on tail classes. To mitigate this issue, PEL introduces a small number of task-specific parameters by adopting the design of any existing parameter-efficient fine-tuning method. Additionally, to expedite convergence, PEL presents a novel semantic-aware classifier initialization technique derived from the CLIP textual encoder without adding any computational overhead. Our experimental results on four long-tailed datasets demonstrate that PEL consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches. The source code is available at https://github.com/shijxcs/PEL.
A Survey on Extreme Multi-label Learning
Oct 08, 2022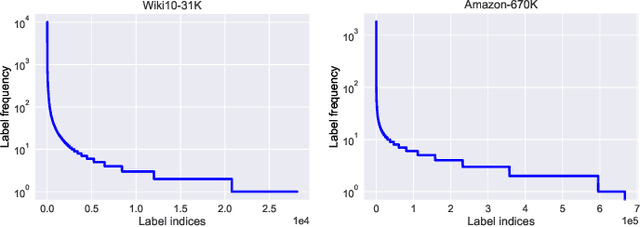

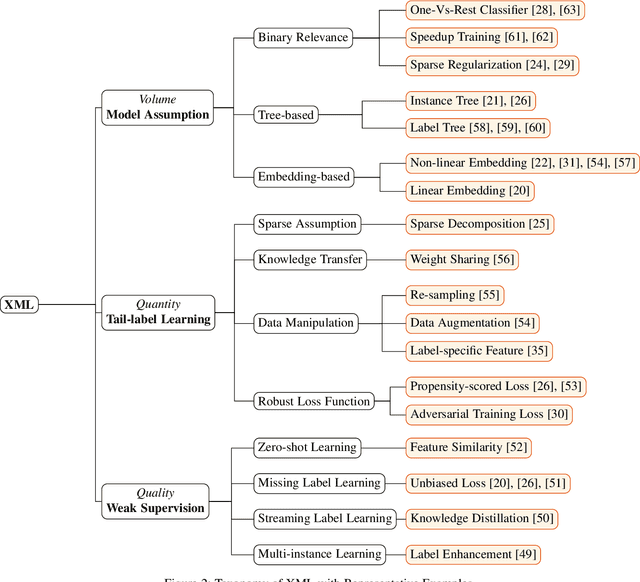
Abstract:Multi-label learning has attracted significant attention from both academic and industry field in recent decades. Although existing multi-label learning algorithms achieved good performance in various tasks, they implicitly assume the size of target label space is not huge, which can be restrictive for real-world scenarios. Moreover, it is infeasible to directly adapt them to extremely large label space because of the compute and memory overhead. Therefore, eXtreme Multi-label Learning (XML) is becoming an important task and many effective approaches are proposed. To fully understand XML, we conduct a survey study in this paper. We first clarify a formal definition for XML from the perspective of supervised learning. Then, based on different model architectures and challenges of the problem, we provide a thorough discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of each category of methods. For the benefit of conducting empirical studies, we collect abundant resources regarding XML, including code implementations, and useful tools. Lastly, we propose possible research directions in XML, such as new evaluation metrics, the tail label problem, and weakly supervised XML.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge