Huayu Li
Martingale Foresight Sampling: A Principled Approach to Inference-Time LLM Decoding
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Standard autoregressive decoding in large language models (LLMs) is inherently short-sighted, often failing to find globally optimal reasoning paths due to its token-by-token generation process. While inference-time strategies like foresight sampling attempt to mitigate this by simulating future steps, they typically rely on ad-hoc heuristics for valuing paths and pruning the search space. This paper introduces Martingale Foresight Sampling (MFS), a principled framework that reformulates LLM decoding as a problem of identifying an optimal stochastic process. By modeling the quality of a reasoning path as a stochastic process, we leverage Martingale theory to design a theoretically-grounded algorithm. Our approach replaces heuristic mechanisms with principles from probability theory: step valuation is derived from the Doob Decomposition Theorem to measure a path's predictable advantage, path selection uses Optional Stopping Theory for principled pruning of suboptimal candidates, and an adaptive stopping rule based on the Martingale Convergence Theorem terminates exploration once a path's quality has provably converged. Experiments on six reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that MFS surpasses state-of-the-art methods in accuracy while significantly improving computational efficiency. Code will be released at https://github.com/miraclehetech/EACL2026-Martingale-Foresight-Sampling.
Meta Lattice: Model Space Redesign for Cost-Effective Industry-Scale Ads Recommendations
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The rapidly evolving landscape of products, surfaces, policies, and regulations poses significant challenges for deploying state-of-the-art recommendation models at industry scale, primarily due to data fragmentation across domains and escalating infrastructure costs that hinder sustained quality improvements. To address this challenge, we propose Lattice, a recommendation framework centered around model space redesign that extends Multi-Domain, Multi-Objective (MDMO) learning beyond models and learning objectives. Lattice addresses these challenges through a comprehensive model space redesign that combines cross-domain knowledge sharing, data consolidation, model unification, distillation, and system optimizations to achieve significant improvements in both quality and cost-efficiency. Our deployment of Lattice at Meta has resulted in 10% revenue-driving top-line metrics gain, 11.5% user satisfaction improvement, 6% boost in conversion rate, with 20% capacity saving.
C2AL: Cohort-Contrastive Auxiliary Learning for Large-scale Recommendation Systems
Oct 02, 2025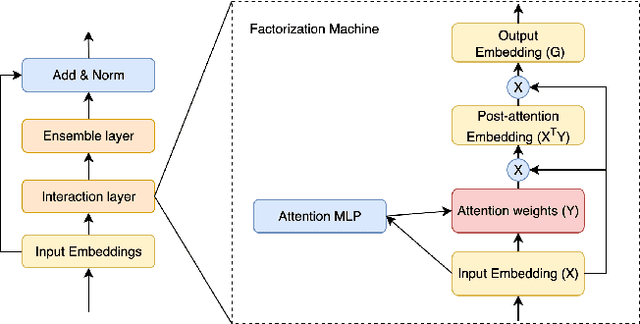
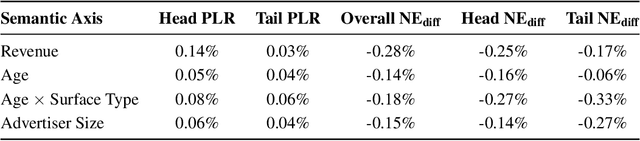
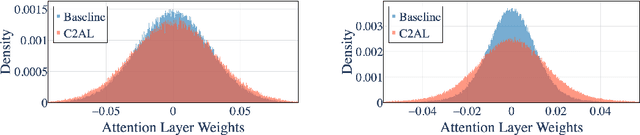

Abstract:Training large-scale recommendation models under a single global objective implicitly assumes homogeneity across user populations. However, real-world data are composites of heterogeneous cohorts with distinct conditional distributions. As models increase in scale and complexity and as more data is used for training, they become dominated by central distribution patterns, neglecting head and tail regions. This imbalance limits the model's learning ability and can result in inactive attention weights or dead neurons. In this paper, we reveal how the attention mechanism can play a key role in factorization machines for shared embedding selection, and propose to address this challenge by analyzing the substructures in the dataset and exposing those with strong distributional contrast through auxiliary learning. Unlike previous research, which heuristically applies weighted labels or multi-task heads to mitigate such biases, we leverage partially conflicting auxiliary labels to regularize the shared representation. This approach customizes the learning process of attention layers to preserve mutual information with minority cohorts while improving global performance. We evaluated C2AL on massive production datasets with billions of data points each for six SOTA models. Experiments show that the factorization machine is able to capture fine-grained user-ad interactions using the proposed method, achieving up to a 0.16% reduction in normalized entropy overall and delivering gains exceeding 0.30% on targeted minority cohorts.
DRA-GRPO: Exploring Diversity-Aware Reward Adjustment for R1-Zero-Like Training of Large Language Models
May 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning for language model post-training, such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), have shown promise in low-resource settings. However, GRPO typically relies on solution-level and scalar reward signals that fail to capture the semantic diversity among sampled completions. This leads to what we identify as a diversity-quality inconsistency, where distinct reasoning paths may receive indistinguishable rewards. To address this limitation, we propose $\textit{Diversity-aware Reward Adjustment}$ (DRA), a method that explicitly incorporates semantic diversity into the reward computation. DRA uses Submodular Mutual Information (SMI) to downweight redundant completions and amplify rewards for diverse ones. This encourages better exploration during learning, while maintaining stable exploitation of high-quality samples. Our method integrates seamlessly with both GRPO and its variant DR.~GRPO, resulting in $\textit{DRA-GRPO}$ and $\textit{DGA-DR.~GRPO}$. We evaluate our method on five mathematical reasoning benchmarks and find that it outperforms recent strong baselines. It achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average accuracy of 58.2%, using only 7,000 fine-tuning samples and a total training cost of approximately $55. The code is available at https://github.com/xiwenc1/DRA-GRPO.
FIC-TSC: Learning Time Series Classification with Fisher Information Constraint
May 09, 2025



Abstract:Analyzing time series data is crucial to a wide spectrum of applications, including economics, online marketplaces, and human healthcare. In particular, time series classification plays an indispensable role in segmenting different phases in stock markets, predicting customer behavior, and classifying worker actions and engagement levels. These aspects contribute significantly to the advancement of automated decision-making and system optimization in real-world applications. However, there is a large consensus that time series data often suffers from domain shifts between training and test sets, which dramatically degrades the classification performance. Despite the success of (reversible) instance normalization in handling the domain shifts for time series regression tasks, its performance in classification is unsatisfactory. In this paper, we propose \textit{FIC-TSC}, a training framework for time series classification that leverages Fisher information as the constraint. We theoretically and empirically show this is an efficient and effective solution to guide the model converge toward flatter minima, which enhances its generalizability to distribution shifts. We rigorously evaluate our method on 30 UEA multivariate and 85 UCR univariate datasets. Our empirical results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over 14 recent state-of-the-art methods.
Prompt-OT: An Optimal Transport Regularization Paradigm for Knowledge Preservation in Vision-Language Model Adaptation
Mar 11, 2025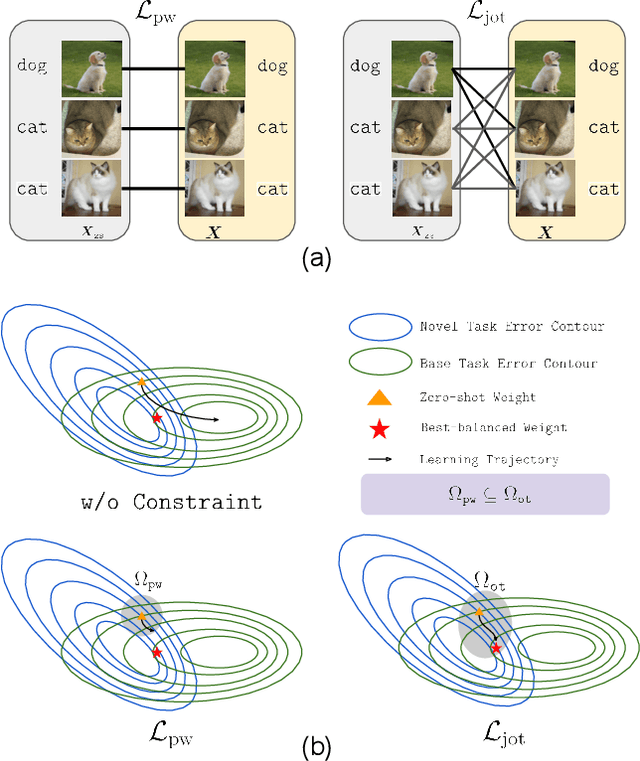



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP demonstrate strong performance but struggle when adapted to downstream tasks. Prompt learning has emerged as an efficient and effective strategy to adapt VLMs while preserving their pre-trained knowledge. However, existing methods still lead to overfitting and degrade zero-shot generalization. To address this challenge, we propose an optimal transport (OT)-guided prompt learning framework that mitigates forgetting by preserving the structural consistency of feature distributions between pre-trained and fine-tuned models. Unlike conventional point-wise constraints, OT naturally captures cross-instance relationships and expands the feasible parameter space for prompt tuning, allowing a better trade-off between adaptation and generalization. Our approach enforces joint constraints on both vision and text representations, ensuring a holistic feature alignment. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our simple yet effective method can outperform existing prompt learning strategies in base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset evaluation, and domain generalization without additional augmentation or ensemble techniques. The code is available at https://github.com/ChongQingNoSubway/Prompt-OT
External Large Foundation Model: How to Efficiently Serve Trillions of Parameters for Online Ads Recommendation
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Ads recommendation is a prominent service of online advertising systems and has been actively studied. Recent studies indicate that scaling-up and advanced design of the recommendation model can bring significant performance improvement. However, with a larger model scale, such prior studies have a significantly increasing gap from industry as they often neglect two fundamental challenges in industrial-scale applications. First, training and inference budgets are restricted for the model to be served, exceeding which may incur latency and impair user experience. Second, large-volume data arrive in a streaming mode with data distributions dynamically shifting, as new users/ads join and existing users/ads leave the system. We propose the External Large Foundation Model (ExFM) framework to address the overlooked challenges. Specifically, we develop external distillation and a data augmentation system (DAS) to control the computational cost of training/inference while maintaining high performance. We design the teacher in a way like a foundation model (FM) that can serve multiple students as vertical models (VMs) to amortize its building cost. We propose Auxiliary Head and Student Adapter to mitigate the data distribution gap between FM and VMs caused by the streaming data issue. Comprehensive experiments on internal industrial-scale applications and public datasets demonstrate significant performance gain by ExFM.
Enhancing Visual Inspection Capability of Multi-Modal Large Language Models on Medical Time Series with Supportive Conformalized and Interpretable Small Specialized Models
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in visual inspection of medical time-series data, achieving proficiency comparable to human clinicians. However, their broad scope limits domain-specific precision, and proprietary weights hinder fine-tuning for specialized datasets. In contrast, small specialized models (SSMs) excel in targeted tasks but lack the contextual reasoning required for complex clinical decision-making. To address these challenges, we propose ConMIL (Conformalized Multiple Instance Learning), a decision-support SSM that integrates seamlessly with LLMs. By using Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) to identify clinically significant signal segments and conformal prediction for calibrated set-valued outputs, ConMIL enhances LLMs' interpretative capabilities for medical time-series analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that ConMIL significantly improves the performance of state-of-the-art LLMs, such as ChatGPT4.0 and Qwen2-VL-7B. Specifically, \ConMIL{}-supported Qwen2-VL-7B achieves 94.92% and 96.82% precision for confident samples in arrhythmia detection and sleep staging, compared to standalone LLM accuracy of 46.13% and 13.16%. These findings highlight the potential of ConMIL to bridge task-specific precision and broader contextual reasoning, enabling more reliable and interpretable AI-driven clinical decision support.
Sequence Complementor: Complementing Transformers For Time Series Forecasting with Learnable Sequences
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Since its introduction, the transformer has shifted the development trajectory away from traditional models (e.g., RNN, MLP) in time series forecasting, which is attributed to its ability to capture global dependencies within temporal tokens. Follow-up studies have largely involved altering the tokenization and self-attention modules to better adapt Transformers for addressing special challenges like non-stationarity, channel-wise dependency, and variable correlation in time series. However, we found that the expressive capability of sequence representation is a key factor influencing Transformer performance in time forecasting after investigating several representative methods, where there is an almost linear relationship between sequence representation entropy and mean square error, with more diverse representations performing better. In this paper, we propose a novel attention mechanism with Sequence Complementors and prove feasible from an information theory perspective, where these learnable sequences are able to provide complementary information beyond current input to feed attention. We further enhance the Sequence Complementors via a diversification loss that is theoretically covered. The empirical evaluation of both long-term and short-term forecasting has confirmed its superiority over the recent state-of-the-art methods.
The Efficiency vs. Accuracy Trade-off: Optimizing RAG-Enhanced LLM Recommender Systems Using Multi-Head Early Exit
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in recommender systems for predicting Click-Through Rates (CTR) necessitates a delicate balance between computational efficiency and predictive accuracy. This paper presents an optimization framework that combines Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with an innovative multi-head early exit architecture to concurrently enhance both aspects. By integrating Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) as efficient retrieval mechanisms, we are able to significantly reduce data retrieval times while maintaining high model performance. The early exit strategy employed allows for dynamic termination of model inference, utilizing real-time predictive confidence assessments across multiple heads. This not only quickens the responsiveness of LLMs but also upholds or improves their accuracy, making it ideal for real-time application scenarios. Our experiments demonstrate how this architecture effectively decreases computation time without sacrificing the accuracy needed for reliable recommendation delivery, establishing a new standard for efficient, real-time LLM deployment in commercial systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge