Piyush Chawla
The Efficiency vs. Accuracy Trade-off: Optimizing RAG-Enhanced LLM Recommender Systems Using Multi-Head Early Exit
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in recommender systems for predicting Click-Through Rates (CTR) necessitates a delicate balance between computational efficiency and predictive accuracy. This paper presents an optimization framework that combines Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with an innovative multi-head early exit architecture to concurrently enhance both aspects. By integrating Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) as efficient retrieval mechanisms, we are able to significantly reduce data retrieval times while maintaining high model performance. The early exit strategy employed allows for dynamic termination of model inference, utilizing real-time predictive confidence assessments across multiple heads. This not only quickens the responsiveness of LLMs but also upholds or improves their accuracy, making it ideal for real-time application scenarios. Our experiments demonstrate how this architecture effectively decreases computation time without sacrificing the accuracy needed for reliable recommendation delivery, establishing a new standard for efficient, real-time LLM deployment in commercial systems.
Belittling the Source: Trustworthiness Indicators to Obfuscate Fake News on the Web
Sep 03, 2018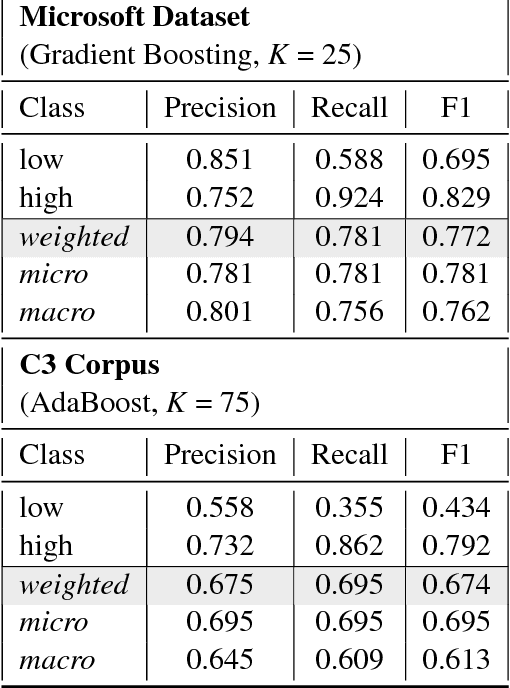
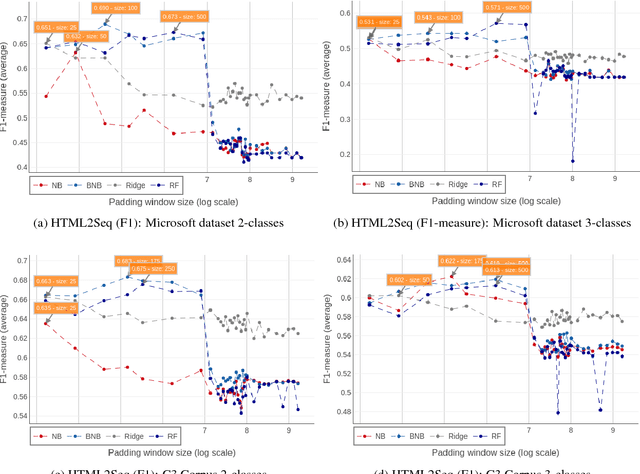
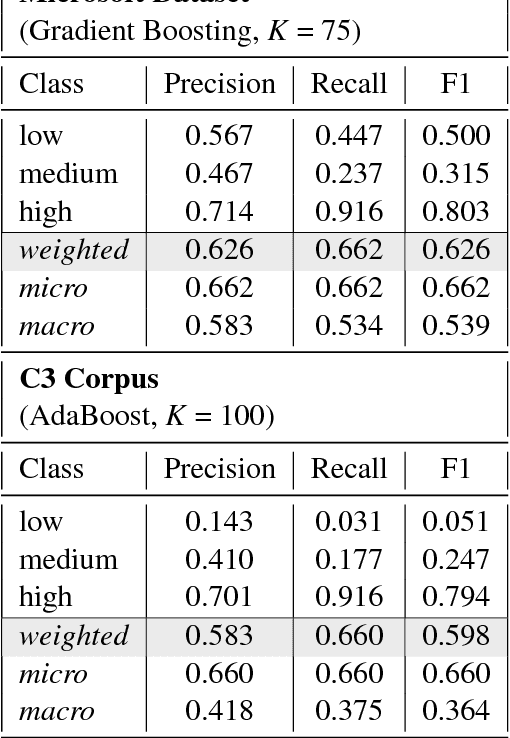
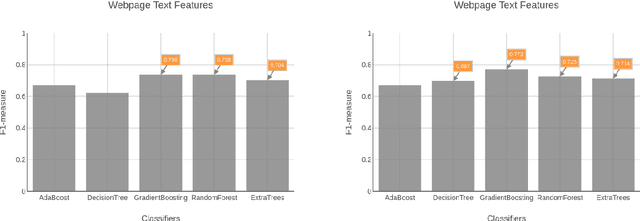
Abstract:With the growth of the internet, the number of fake-news online has been proliferating every year. The consequences of such phenomena are manifold, ranging from lousy decision-making process to bullying and violence episodes. Therefore, fact-checking algorithms became a valuable asset. To this aim, an important step to detect fake-news is to have access to a credibility score for a given information source. However, most of the widely used Web indicators have either been shut-down to the public (e.g., Google PageRank) or are not free for use (Alexa Rank). Further existing databases are short-manually curated lists of online sources, which do not scale. Finally, most of the research on the topic is theoretical-based or explore confidential data in a restricted simulation environment. In this paper we explore current research, highlight the challenges and propose solutions to tackle the problem of classifying websites into a credibility scale. The proposed model automatically extracts source reputation cues and computes a credibility factor, providing valuable insights which can help in belittling dubious and confirming trustful unknown websites. Experimental results outperform state of the art in the 2-classes and 5-classes setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge