Huan Zheng
Towards Geometry-Aware and Motion-Guided Video Human Mesh Recovery
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Existing video-based 3D Human Mesh Recovery (HMR) methods often produce physically implausible results, stemming from their reliance on flawed intermediate 3D pose anchors and their inability to effectively model complex spatiotemporal dynamics. To overcome these deep-rooted architectural problems, we introduce HMRMamba, a new paradigm for HMR that pioneers the use of Structured State Space Models (SSMs) for their efficiency and long-range modeling prowess. Our framework is distinguished by two core contributions. First, the Geometry-Aware Lifting Module, featuring a novel dual-scan Mamba architecture, creates a robust foundation for reconstruction. It directly grounds the 2D-to-3D pose lifting process with geometric cues from image features, producing a highly reliable 3D pose sequence that serves as a stable anchor. Second, the Motion-guided Reconstruction Network leverages this anchor to explicitly process kinematic patterns over time. By injecting this crucial temporal awareness, it significantly enhances the final mesh's coherence and robustness, particularly under occlusion and motion blur. Comprehensive evaluations on 3DPW, MPI-INF-3DHP, and Human3.6M benchmarks confirm that HMRMamba sets a new state-of-the-art, outperforming existing methods in both reconstruction accuracy and temporal consistency while offering superior computational efficiency.
From Human Intention to Action Prediction: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Intention-driven End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Current end-to-end autonomous driving systems operate at a level of intelligence akin to following simple steering commands. However, achieving genuinely intelligent autonomy requires a paradigm shift: moving from merely executing low-level instructions to understanding and fulfilling high-level, abstract human intentions. This leap from a command-follower to an intention-fulfiller, as illustrated in our conceptual framework, is hindered by a fundamental challenge: the absence of a standardized benchmark to measure and drive progress on this complex task. To address this critical gap, we introduce Intention-Drive, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the ability to translate high-level human intent into safe and precise driving actions. Intention-Drive features two core contributions: (1) a new dataset of complex scenarios paired with corresponding natural language intentions, and (2) a novel evaluation protocol centered on the Intent Success Rate (ISR), which assesses the semantic fulfillment of the human's goal beyond simple geometric accuracy. Through an extensive evaluation of a spectrum of baseline models on Intention-Drive, we reveal a significant performance deficit, showing that the baseline model struggle to achieve the comprehensive scene and intention understanding required for this advanced task.
Semantic Causality-Aware Vision-Based 3D Occupancy Prediction
Sep 10, 2025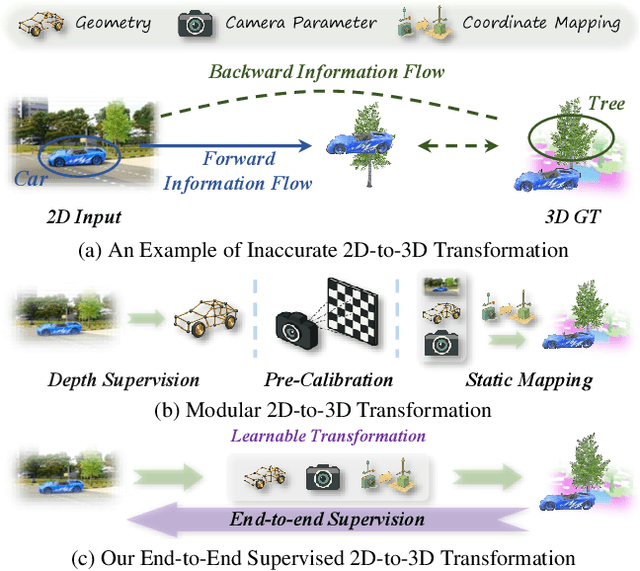
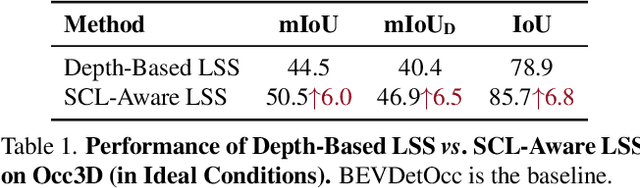
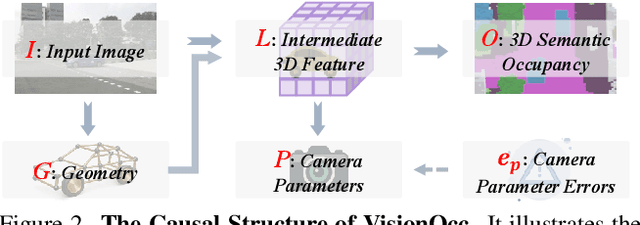
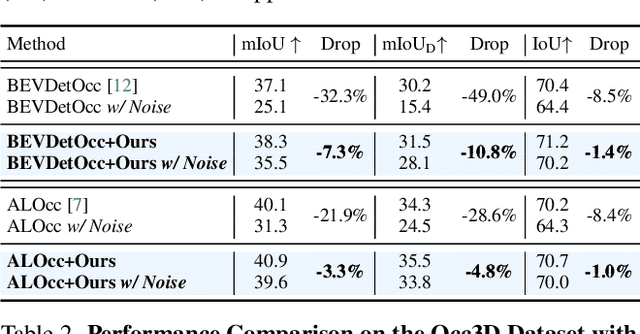
Abstract:Vision-based 3D semantic occupancy prediction is a critical task in 3D vision that integrates volumetric 3D reconstruction with semantic understanding. Existing methods, however, often rely on modular pipelines. These modules are typically optimized independently or use pre-configured inputs, leading to cascading errors. In this paper, we address this limitation by designing a novel causal loss that enables holistic, end-to-end supervision of the modular 2D-to-3D transformation pipeline. Grounded in the principle of 2D-to-3D semantic causality, this loss regulates the gradient flow from 3D voxel representations back to the 2D features. Consequently, it renders the entire pipeline differentiable, unifying the learning process and making previously non-trainable components fully learnable. Building on this principle, we propose the Semantic Causality-Aware 2D-to-3D Transformation, which comprises three components guided by our causal loss: Channel-Grouped Lifting for adaptive semantic mapping, Learnable Camera Offsets for enhanced robustness against camera perturbations, and Normalized Convolution for effective feature propagation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Occ3D benchmark, demonstrating significant robustness to camera perturbations and improved 2D-to-3D semantic consistency.
Geometry-aware Temporal Aggregation Network for Monocular 3D Lane Detection
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Monocular 3D lane detection aims to estimate 3D position of lanes from frontal-view (FV) images. However, current monocular 3D lane detection methods suffer from two limitations, including inaccurate geometric information of the predicted 3D lanes and difficulties in maintaining lane integrity. To address these issues, we seek to fully exploit the potential of multiple input frames. First, we aim at enhancing the ability to perceive the geometry of scenes by leveraging temporal geometric consistency. Second, we strive to improve the integrity of lanes by revealing more instance information from temporal sequences. Therefore, we propose a novel Geometry-aware Temporal Aggregation Network (GTA-Net) for monocular 3D lane detection. On one hand, we develop the Temporal Geometry Enhancement Module (TGEM), which exploits geometric consistency across successive frames, facilitating effective geometry perception. On the other hand, we present the Temporal Instance-aware Query Generation (TIQG), which strategically incorporates temporal cues into query generation, thereby enabling the exploration of comprehensive instance information. Experiments demonstrate that our GTA-Net achieves SoTA results, surpassing existing monocular 3D lane detection solutions.
Rethinking Temporal Fusion with a Unified Gradient Descent View for 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:We present GDFusion, a temporal fusion method for vision-based 3D semantic occupancy prediction (VisionOcc). GDFusion opens up the underexplored aspects of temporal fusion within the VisionOcc framework, focusing on both temporal cues and fusion strategies. It systematically examines the entire VisionOcc pipeline, identifying three fundamental yet previously overlooked temporal cues: scene-level consistency, motion calibration, and geometric complementation. These cues capture diverse facets of temporal evolution and make distinct contributions across various modules in the VisionOcc framework. To effectively fuse temporal signals across heterogeneous representations, we propose a novel fusion strategy by reinterpreting the formulation of vanilla RNNs. This reinterpretation leverages gradient descent on features to unify the integration of diverse temporal information, seamlessly embedding the proposed temporal cues into the network. Extensive experiments on nuScenes demonstrate that GDFusion significantly outperforms established baselines. Notably, on Occ3D benchmark, it achieves 1.4\%-4.8\% mIoU improvements and reduces memory consumption by 27\%-72\%.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
CubeFormer: A Simple yet Effective Baseline for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Lightweight image super-resolution (SR) methods aim at increasing the resolution and restoring the details of an image using a lightweight neural network. However, current lightweight SR methods still suffer from inferior performance and unpleasant details. Our analysis reveals that these methods are hindered by constrained feature diversity, which adversely impacts feature representation and detail recovery. To respond this issue, we propose a simple yet effective baseline called CubeFormer, designed to enhance feature richness by completing holistic information aggregation. To be specific, we introduce cube attention, which expands 2D attention to 3D space, facilitating exhaustive information interactions, further encouraging comprehensive information extraction and promoting feature variety. In addition, we inject block and grid sampling strategies to construct intra-cube transformer blocks (Intra-CTB) and inter-cube transformer blocks (Inter-CTB), which perform local and global modeling, respectively. Extensive experiments show that our CubeFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on commonly used SR benchmarks. Our source code and models will be publicly available.
RAWMamba: Unified sRGB-to-RAW De-rendering With State Space Model
Nov 18, 2024
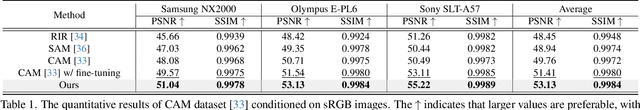
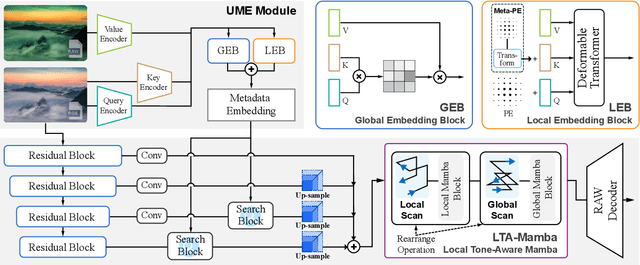
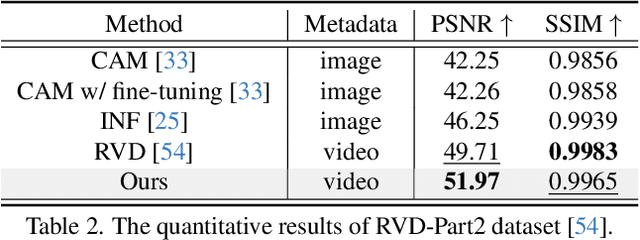
Abstract:Recent advancements in sRGB-to-RAW de-rendering have increasingly emphasized metadata-driven approaches to reconstruct RAW data from sRGB images, supplemented by partial RAW information. In image-based de-rendering, metadata is commonly obtained through sampling, whereas in video tasks, it is typically derived from the initial frame. The distinct metadata requirements necessitate specialized network architectures, leading to architectural incompatibilities that increase deployment complexity. In this paper, we propose RAWMamba, a Mamba-based unified framework developed for sRGB-to-RAW de-rendering across both image and video domains. The core of RAWMamba is the Unified Metadata Embedding (UME) module, which harmonizes diverse metadata types into a unified representation. In detail, a multi-perspective affinity modeling method is proposed to promote the extraction of reference information. In addition, we introduce the Local Tone-Aware Mamba (LTA-Mamba) module, which captures long-range dependencies to enable effective global propagation of metadata. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RAWMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance, yielding high-quality RAW data reconstruction.
Decoupling Fine Detail and Global Geometry for Compressed Depth Map Super-Resolution
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Recovering high-quality depth maps from compressed sources has gained significant attention due to the limitations of consumer-grade depth cameras and the bandwidth restrictions during data transmission. However, current methods still suffer from two challenges. First, bit-depth compression produces a uniform depth representation in regions with subtle variations, hindering the recovery of detailed information. Second, densely distributed random noise reduces the accuracy of estimating the global geometric structure of the scene. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, termed geometry-decoupled network (GDNet), for compressed depth map super-resolution that decouples the high-quality depth map reconstruction process by handling global and detailed geometric features separately. To be specific, we propose the fine geometry detail encoder (FGDE), which is designed to aggregate fine geometry details in high-resolution low-level image features while simultaneously enriching them with complementary information from low-resolution context-level image features. In addition, we develop the global geometry encoder (GGE) that aims at suppressing noise and extracting global geometric information effectively via constructing compact feature representation in a low-rank space. We conduct experiments on multiple benchmark datasets, demonstrating that our GDNet significantly outperforms current methods in terms of geometric consistency and detail recovery. In the ECCV 2024 AIM Compressed Depth Upsampling Challenge, our solution won the 1st place award. Our codes will be available.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Low Light Image Enhancement: Methods and Results
Apr 22, 2024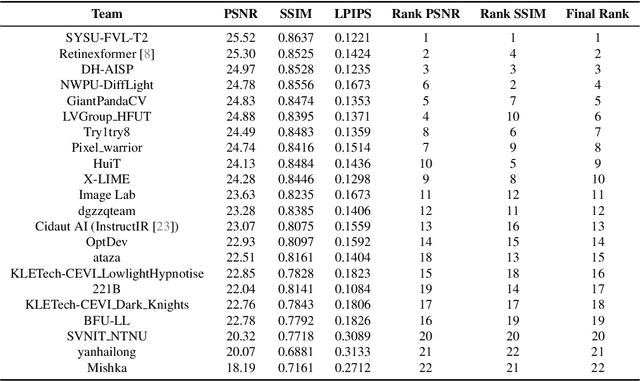

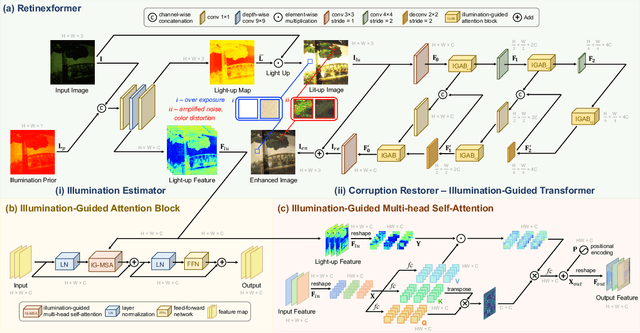

Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 low light image enhancement challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and results. The aim of this challenge is to discover an effective network design or solution capable of generating brighter, clearer, and visually appealing results when dealing with a variety of conditions, including ultra-high resolution (4K and beyond), non-uniform illumination, backlighting, extreme darkness, and night scenes. A notable total of 428 participants registered for the challenge, with 22 teams ultimately making valid submissions. This paper meticulously evaluates the state-of-the-art advancements in enhancing low-light images, reflecting the significant progress and creativity in this field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge