Hongjun Chen
Towards Geometry-Aware and Motion-Guided Video Human Mesh Recovery
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Existing video-based 3D Human Mesh Recovery (HMR) methods often produce physically implausible results, stemming from their reliance on flawed intermediate 3D pose anchors and their inability to effectively model complex spatiotemporal dynamics. To overcome these deep-rooted architectural problems, we introduce HMRMamba, a new paradigm for HMR that pioneers the use of Structured State Space Models (SSMs) for their efficiency and long-range modeling prowess. Our framework is distinguished by two core contributions. First, the Geometry-Aware Lifting Module, featuring a novel dual-scan Mamba architecture, creates a robust foundation for reconstruction. It directly grounds the 2D-to-3D pose lifting process with geometric cues from image features, producing a highly reliable 3D pose sequence that serves as a stable anchor. Second, the Motion-guided Reconstruction Network leverages this anchor to explicitly process kinematic patterns over time. By injecting this crucial temporal awareness, it significantly enhances the final mesh's coherence and robustness, particularly under occlusion and motion blur. Comprehensive evaluations on 3DPW, MPI-INF-3DHP, and Human3.6M benchmarks confirm that HMRMamba sets a new state-of-the-art, outperforming existing methods in both reconstruction accuracy and temporal consistency while offering superior computational efficiency.
From Human Intention to Action Prediction: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Intention-driven End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Current end-to-end autonomous driving systems operate at a level of intelligence akin to following simple steering commands. However, achieving genuinely intelligent autonomy requires a paradigm shift: moving from merely executing low-level instructions to understanding and fulfilling high-level, abstract human intentions. This leap from a command-follower to an intention-fulfiller, as illustrated in our conceptual framework, is hindered by a fundamental challenge: the absence of a standardized benchmark to measure and drive progress on this complex task. To address this critical gap, we introduce Intention-Drive, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the ability to translate high-level human intent into safe and precise driving actions. Intention-Drive features two core contributions: (1) a new dataset of complex scenarios paired with corresponding natural language intentions, and (2) a novel evaluation protocol centered on the Intent Success Rate (ISR), which assesses the semantic fulfillment of the human's goal beyond simple geometric accuracy. Through an extensive evaluation of a spectrum of baseline models on Intention-Drive, we reveal a significant performance deficit, showing that the baseline model struggle to achieve the comprehensive scene and intention understanding required for this advanced task.
RAWMamba: Unified sRGB-to-RAW De-rendering With State Space Model
Nov 18, 2024
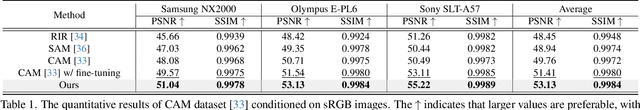
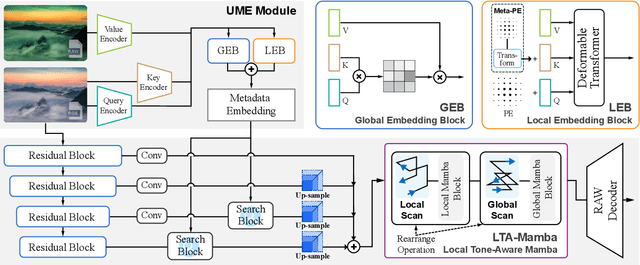
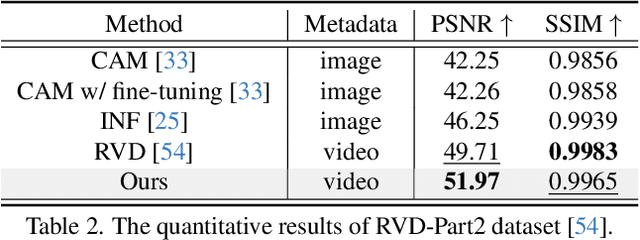
Abstract:Recent advancements in sRGB-to-RAW de-rendering have increasingly emphasized metadata-driven approaches to reconstruct RAW data from sRGB images, supplemented by partial RAW information. In image-based de-rendering, metadata is commonly obtained through sampling, whereas in video tasks, it is typically derived from the initial frame. The distinct metadata requirements necessitate specialized network architectures, leading to architectural incompatibilities that increase deployment complexity. In this paper, we propose RAWMamba, a Mamba-based unified framework developed for sRGB-to-RAW de-rendering across both image and video domains. The core of RAWMamba is the Unified Metadata Embedding (UME) module, which harmonizes diverse metadata types into a unified representation. In detail, a multi-perspective affinity modeling method is proposed to promote the extraction of reference information. In addition, we introduce the Local Tone-Aware Mamba (LTA-Mamba) module, which captures long-range dependencies to enable effective global propagation of metadata. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RAWMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance, yielding high-quality RAW data reconstruction.
Multi-Agent Path Finding with Prioritized Communication Learning
Feb 10, 2022Abstract:Multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) has been widely used to solve large-scale real-world problems, e.g., automation warehouses. The learning-based, fully decentralized framework has been introduced to alleviate real-time problems and simultaneously pursue optimal planning policy. However, existing methods might generate significantly more vertex conflicts (or collisions), which lead to a low success rate or more makespan. In this paper, we propose a PrIoritized COmmunication learning method (PICO), which incorporates the \textit{implicit} planning priorities into the communication topology within the decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning framework. Assembling with the classic coupled planners, the implicit priority learning module can be utilized to form the dynamic communication topology, which also builds an effective collision-avoiding mechanism. PICO performs significantly better in large-scale MAPF tasks in success rates and collision rates than state-of-the-art learning-based planners.
Seminar Learning for Click-Level Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Aug 30, 2021



Abstract:Annotation burden has become one of the biggest barriers to semantic segmentation. Approaches based on click-level annotations have therefore attracted increasing attention due to their superior trade-off between supervision and annotation cost. In this paper, we propose seminar learning, a new learning paradigm for semantic segmentation with click-level supervision. The fundamental rationale of seminar learning is to leverage the knowledge from different networks to compensate for insufficient information provided in click-level annotations. Mimicking a seminar, our seminar learning involves a teacher-student and a student-student module, where a student can learn from both skillful teachers and other students. The teacher-student module uses a teacher network based on the exponential moving average to guide the training of the student network. In the student-student module, heterogeneous pseudo-labels are proposed to bridge the transfer of knowledge among students to enhance each other's performance. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of seminar learning, which achieves the new state-of-the-art performance of 72.51% (mIOU), surpassing previous methods by a large margin of up to 16.88% on the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge