Howard Zhang
WorldBench: Disambiguating Physics for Diagnostic Evaluation of World Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in generative foundational models, often termed "world models," have propelled interest in applying them to critical tasks like robotic planning and autonomous system training. For reliable deployment, these models must exhibit high physical fidelity, accurately simulating real-world dynamics. Existing physics-based video benchmarks, however, suffer from entanglement, where a single test simultaneously evaluates multiple physical laws and concepts, fundamentally limiting their diagnostic capability. We introduce WorldBench, a novel video-based benchmark specifically designed for concept-specific, disentangled evaluation, allowing us to rigorously isolate and assess understanding of a single physical concept or law at a time. To make WorldBench comprehensive, we design benchmarks at two different levels: 1) an evaluation of intuitive physical understanding with concepts such as object permanence or scale/perspective, and 2) an evaluation of low-level physical constants and material properties such as friction coefficients or fluid viscosity. When SOTA video-based world models are evaluated on WorldBench, we find specific patterns of failure in particular physics concepts, with all tested models lacking the physical consistency required to generate reliable real-world interactions. Through its concept-specific evaluation, WorldBench offers a more nuanced and scalable framework for rigorously evaluating the physical reasoning capabilities of video generation and world models, paving the way for more robust and generalizable world-model-driven learning.
InstantRestore: Single-Step Personalized Face Restoration with Shared-Image Attention
Dec 09, 2024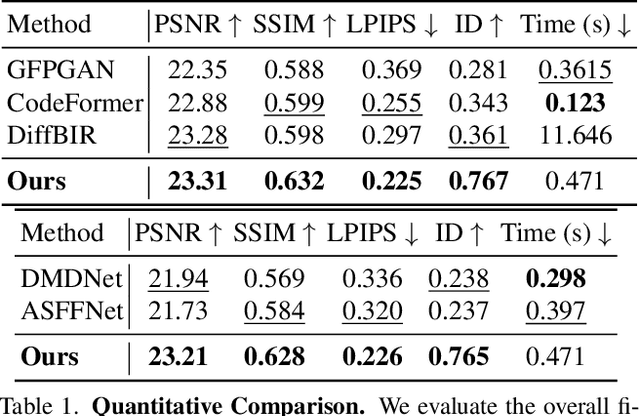
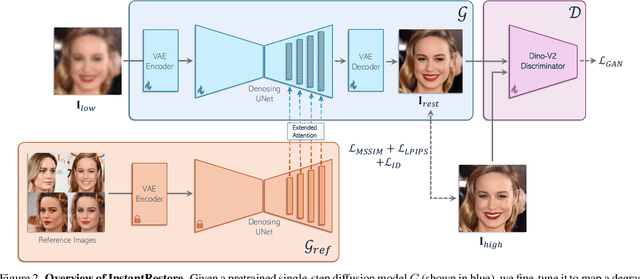
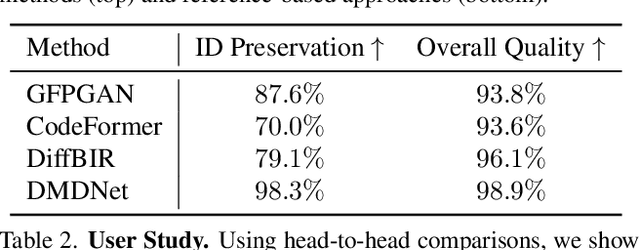
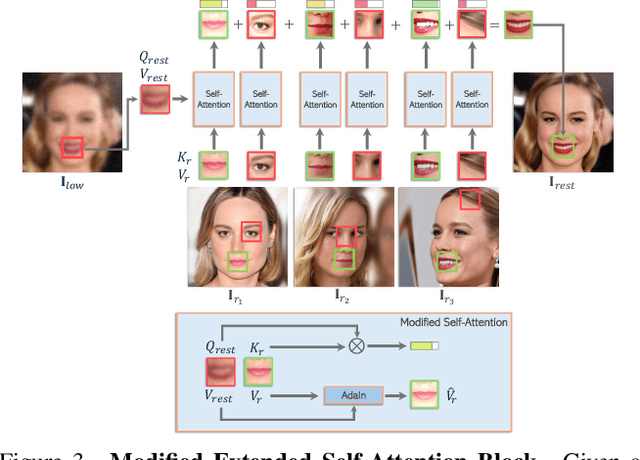
Abstract:Face image restoration aims to enhance degraded facial images while addressing challenges such as diverse degradation types, real-time processing demands, and, most crucially, the preservation of identity-specific features. Existing methods often struggle with slow processing times and suboptimal restoration, especially under severe degradation, failing to accurately reconstruct finer-level identity details. To address these issues, we introduce InstantRestore, a novel framework that leverages a single-step image diffusion model and an attention-sharing mechanism for fast and personalized face restoration. Additionally, InstantRestore incorporates a novel landmark attention loss, aligning key facial landmarks to refine the attention maps, enhancing identity preservation. At inference time, given a degraded input and a small (~4) set of reference images, InstantRestore performs a single forward pass through the network to achieve near real-time performance. Unlike prior approaches that rely on full diffusion processes or per-identity model tuning, InstantRestore offers a scalable solution suitable for large-scale applications. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InstantRestore outperforms existing methods in quality and speed, making it an appealing choice for identity-preserving face restoration.
All-day Depth Completion
May 27, 2024



Abstract:We propose a method for depth estimation under different illumination conditions, i.e., day and night time. As photometry is uninformative in regions under low-illumination, we tackle the problem through a multi-sensor fusion approach, where we take as input an additional synchronized sparse point cloud (i.e., from a LiDAR) projected onto the image plane as a sparse depth map, along with a camera image. The crux of our method lies in the use of the abundantly available synthetic data to first approximate the 3D scene structure by learning a mapping from sparse to (coarse) dense depth maps along with their predictive uncertainty - we term this, SpaDe. In poorly illuminated regions where photometric intensities do not afford the inference of local shape, the coarse approximation of scene depth serves as a prior; the uncertainty map is then used with the image to guide refinement through an uncertainty-driven residual learning (URL) scheme. The resulting depth completion network leverages complementary strengths from both modalities - depth is sparse but insensitive to illumination and in metric scale, and image is dense but sensitive with scale ambiguity. SpaDe can be used in a plug-and-play fashion, which allows for 25% improvement when augmented onto existing methods to preprocess sparse depth. We demonstrate URL on the nuScenes dataset where we improve over all baselines by an average 11.65% in all-day scenarios, 11.23% when tested specifically for daytime, and 13.12% for nighttime scenes.
WeatherProof: Leveraging Language Guidance for Semantic Segmentation in Adverse Weather
Mar 21, 2024
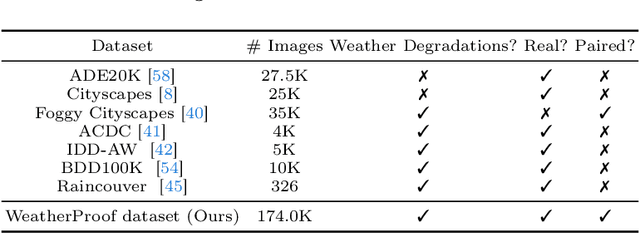


Abstract:We propose a method to infer semantic segmentation maps from images captured under adverse weather conditions. We begin by examining existing models on images degraded by weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow, and found that they exhibit a large performance drop as compared to those captured under clear weather. To control for changes in scene structures, we propose WeatherProof, the first semantic segmentation dataset with accurate clear and adverse weather image pairs that share an underlying scene. Through this dataset, we analyze the error modes in existing models and found that they were sensitive to the highly complex combination of different weather effects induced on the image during capture. To improve robustness, we propose a way to use language as guidance by identifying contributions of adverse weather conditions and injecting that as "side information". Models trained using our language guidance exhibit performance gains by up to 10.2% in mIoU on WeatherProof, up to 8.44% in mIoU on the widely used ACDC dataset compared to standard training techniques, and up to 6.21% in mIoU on the ACDC dataset as compared to previous SOTA methods.
GT-Rain Single Image Deraining Challenge Report
Mar 18, 2024


Abstract:This report reviews the results of the GT-Rain challenge on single image deraining at the UG2+ workshop at CVPR 2023. The aim of this competition is to study the rainy weather phenomenon in real world scenarios, provide a novel real world rainy image dataset, and to spark innovative ideas that will further the development of single image deraining methods on real images. Submissions were trained on the GT-Rain dataset and evaluated on an extension of the dataset consisting of 15 additional scenes. Scenes in GT-Rain are comprised of real rainy image and ground truth image captured moments after the rain had stopped. 275 participants were registered in the challenge and 55 competed in the final testing phase.
WeatherProof: A Paired-Dataset Approach to Semantic Segmentation in Adverse Weather
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:The introduction of large, foundational models to computer vision has led to drastically improved performance on the task of semantic segmentation. However, these existing methods exhibit a large performance drop when testing on images degraded by weather conditions such as rain, fog, or snow. We introduce a general paired-training method that can be applied to all current foundational model architectures that leads to improved performance on images in adverse weather conditions. To this end, we create the WeatherProof Dataset, the first semantic segmentation dataset with accurate clear and adverse weather image pairs, which not only enables our new training paradigm, but also improves the evaluation of the performance gap between clear and degraded segmentation. We find that training on these paired clear and adverse weather frames which share an underlying scene results in improved performance on adverse weather data. With this knowledge, we propose a training pipeline which accentuates the advantages of paired-data training using consistency losses and language guidance, which leads to performance improvements by up to 18.4% as compared to standard training procedures.
Enhancing Diffusion Models with 3D Perspective Geometry Constraints
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:While perspective is a well-studied topic in art, it is generally taken for granted in images. However, for the recent wave of high-quality image synthesis methods such as latent diffusion models, perspective accuracy is not an explicit requirement. Since these methods are capable of outputting a wide gamut of possible images, it is difficult for these synthesized images to adhere to the principles of linear perspective. We introduce a novel geometric constraint in the training process of generative models to enforce perspective accuracy. We show that outputs of models trained with this constraint both appear more realistic and improve performance of downstream models trained on generated images. Subjective human trials show that images generated with latent diffusion models trained with our constraint are preferred over images from the Stable Diffusion V2 model 70% of the time. SOTA monocular depth estimation models such as DPT and PixelFormer, fine-tuned on our images, outperform the original models trained on real images by up to 7.03% in RMSE and 19.3% in SqRel on the KITTI test set for zero-shot transfer.
Towards Ground Truth for Single Image Deraining
Jun 22, 2022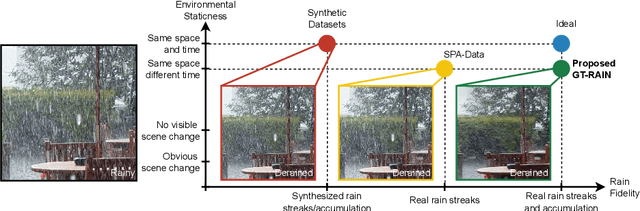
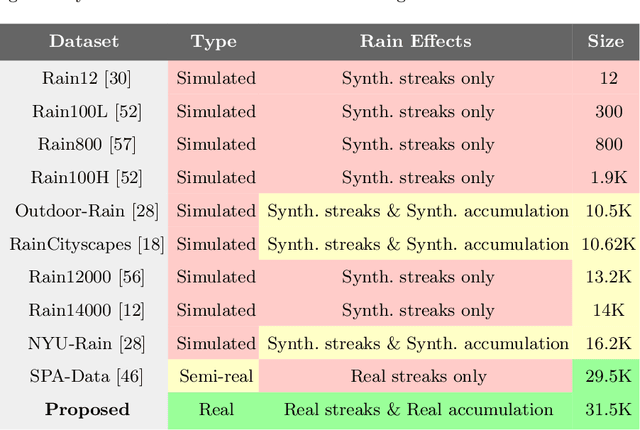
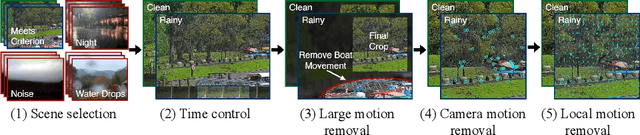
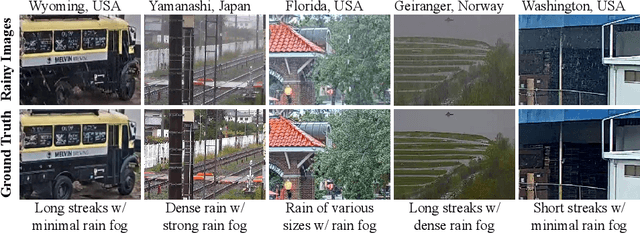
Abstract:We propose a large-scale dataset of real-world rainy and clean image pairs and a method to remove degradations, induced by rain streaks and rain accumulation, from the image. As there exists no real-world dataset for deraining, current state-of-the-art methods rely on synthetic data and thus are limited by the sim2real domain gap; moreover, rigorous evaluation remains a challenge due to the absence of a real paired dataset. We fill this gap by collecting the first real paired deraining dataset through meticulous control of non-rain variations. Our dataset enables paired training and quantitative evaluation for diverse real-world rain phenomena (e.g. rain streaks and rain accumulation). To learn a representation invariant to rain phenomena, we propose a deep neural network that reconstructs the underlying scene by minimizing a rain-invariant loss between rainy and clean images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed dataset benefits existing derainers, and our model can outperform the state-of-the-art deraining methods on real rainy images under various conditions.
Learning Accurate Long-term Dynamics for Model-based Reinforcement Learning
Dec 16, 2020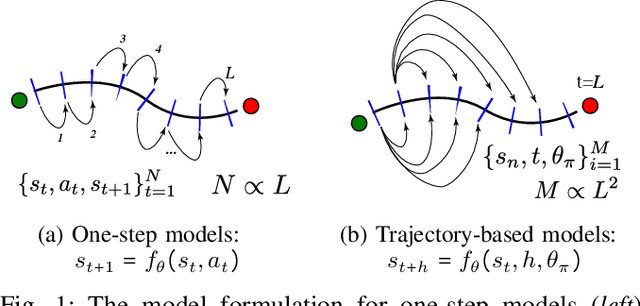
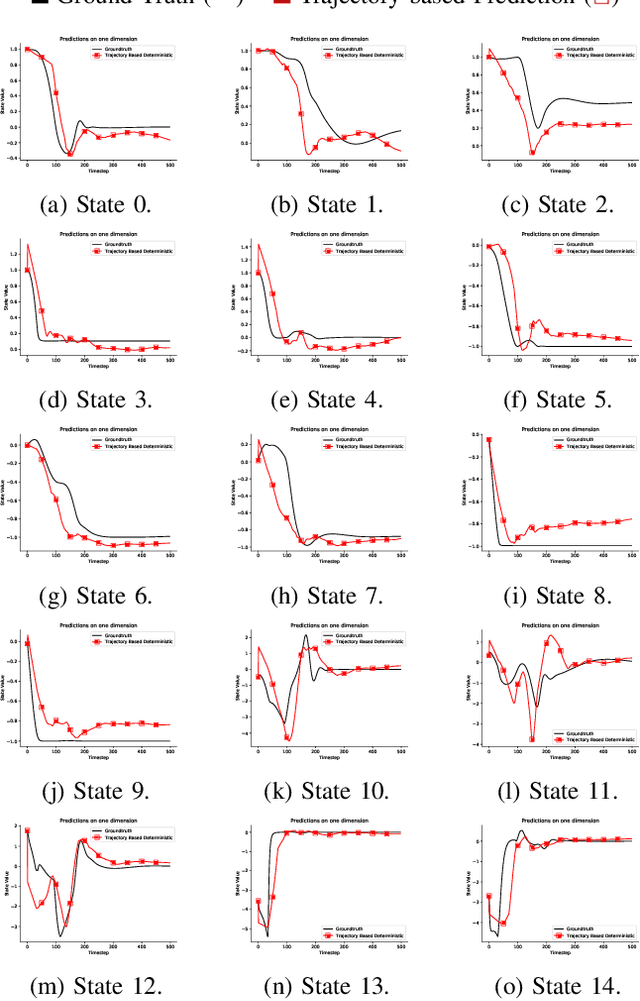
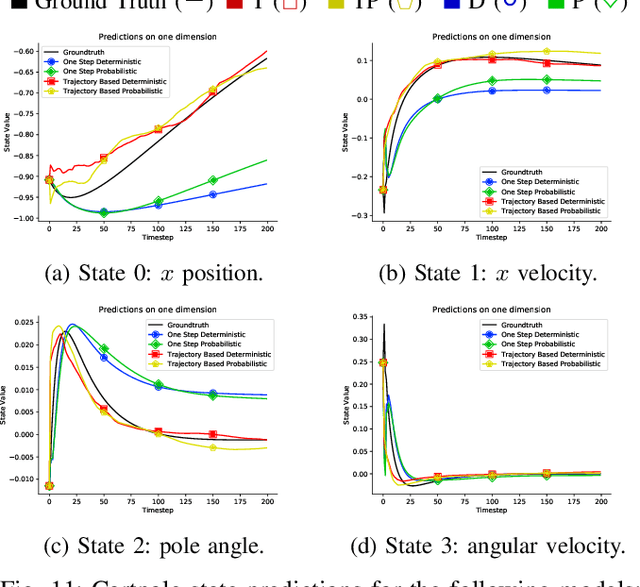
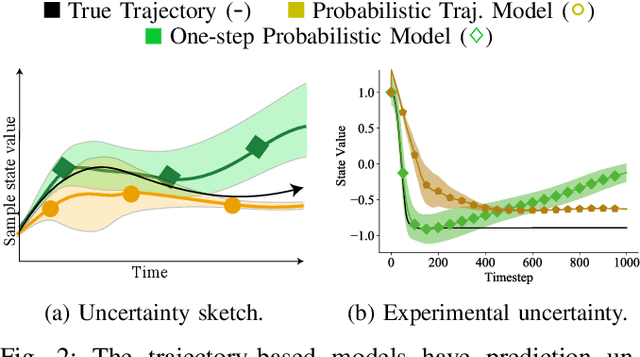
Abstract:Accurately predicting the dynamics of robotic systems is crucial for model-based control and reinforcement learning. The most common way to estimate dynamics is by fitting a one-step ahead prediction model and using it to recursively propagate the predicted state distribution over long horizons. Unfortunately, this approach is known to compound even small prediction errors, making long-term predictions inaccurate. In this paper, we propose a new parametrization to supervised learning on state-action data to stably predict at longer horizons -- that we call a trajectory-based model. This trajectory-based model takes an initial state, a future time index, and control parameters as inputs, and predicts the state at the future time. Our results in simulated and experimental robotic tasks show that our trajectory-based models yield significantly more accurate long term predictions, improved sample efficiency, and ability to predict task reward.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge