Bin Dai
UAV-Flow Colosseo: A Real-World Benchmark for Flying-on-a-Word UAV Imitation Learning
May 21, 2025Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are evolving into language-interactive platforms, enabling more intuitive forms of human-drone interaction. While prior works have primarily focused on high-level planning and long-horizon navigation, we shift attention to language-guided fine-grained trajectory control, where UAVs execute short-range, reactive flight behaviors in response to language instructions. We formalize this problem as the Flying-on-a-Word (Flow) task and introduce UAV imitation learning as an effective approach. In this framework, UAVs learn fine-grained control policies by mimicking expert pilot trajectories paired with atomic language instructions. To support this paradigm, we present UAV-Flow, the first real-world benchmark for language-conditioned, fine-grained UAV control. It includes a task formulation, a large-scale dataset collected in diverse environments, a deployable control framework, and a simulation suite for systematic evaluation. Our design enables UAVs to closely imitate the precise, expert-level flight trajectories of human pilots and supports direct deployment without sim-to-real gap. We conduct extensive experiments on UAV-Flow, benchmarking VLN and VLA paradigms. Results show that VLA models are superior to VLN baselines and highlight the critical role of spatial grounding in the fine-grained Flow setting.
SmartRAG: Jointly Learn RAG-Related Tasks From the Environment Feedback
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:RAG systems consist of multiple modules to work together. However, these modules are usually separately trained. We argue that a system like RAG that incorporates multiple modules should be jointly optimized to achieve optimal performance. To demonstrate this, we design a specific pipeline called \textbf{SmartRAG} that includes a policy network and a retriever. The policy network can serve as 1) a decision maker that decides when to retrieve, 2) a query rewriter to generate a query most suited to the retriever, and 3) an answer generator that produces the final response with/without the observations. We then propose to jointly optimize the whole system using a reinforcement learning algorithm, with the reward designed to encourage the system to achieve the best performance with minimal retrieval cost. When jointly optimized, all the modules can be aware of how other modules are working and thus find the best way to work together as a complete system. Empirical results demonstrate that the jointly optimized SmartRAG can achieve better performance than separately optimized counterparts.
Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments: How Far Have We Come?
Oct 10, 2024

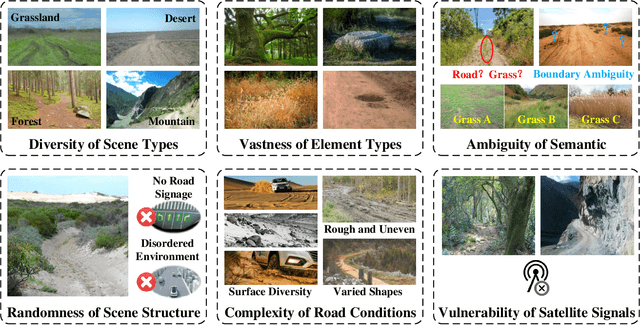
Abstract:Research on autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is less advanced than in structured urban settings due to challenges like environmental diversities and scene complexity. These environments-such as rural areas and rugged terrains-pose unique obstacles that are not common in structured urban areas. Despite these difficulties, autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is crucial for applications in agriculture, mining, and military operations. Our survey reviews over 250 papers for autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments, covering offline mapping, pose estimation, environmental perception, path planning, end-to-end autonomous driving, datasets, and relevant challenges. We also discuss emerging trends and future research directions. This review aims to consolidate knowledge and encourage further research for autonomous driving in unstructured environments. To support ongoing work, we maintain an active repository with up-to-date literature and open-source projects at: https://github.com/chaytonmin/Survey-Autonomous-Driving-in-Unstructured-Environments.
Deep-Learning-Based Adaptive Error-Correction Decoding for Spin-Torque Transfer Magnetic Random Access Memory (STT-MRAM)
Oct 07, 2024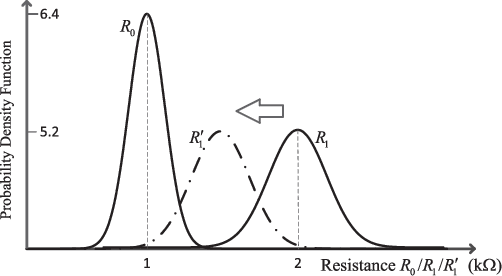
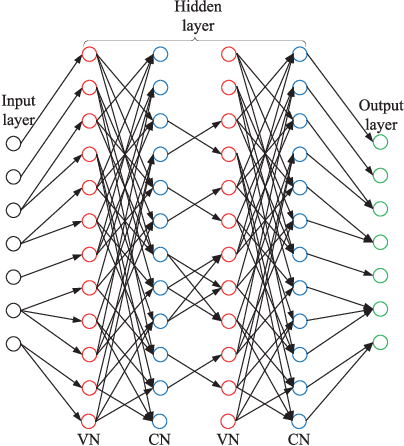
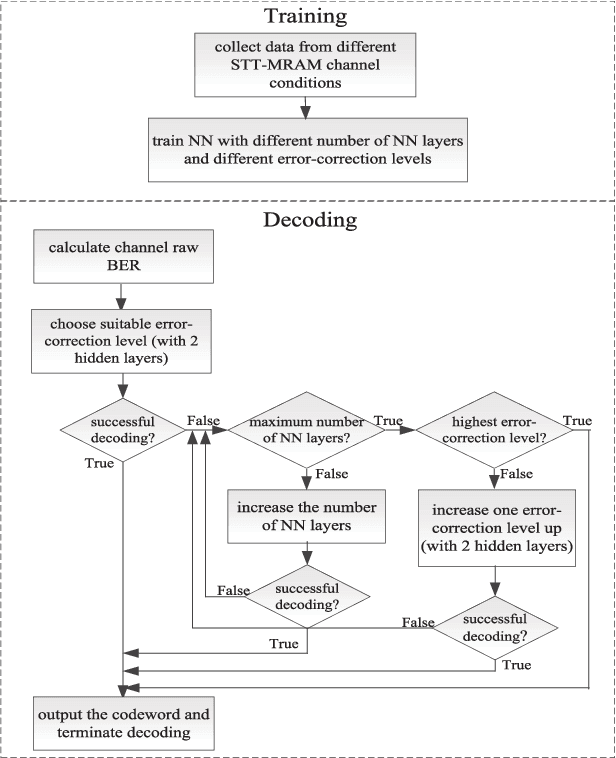
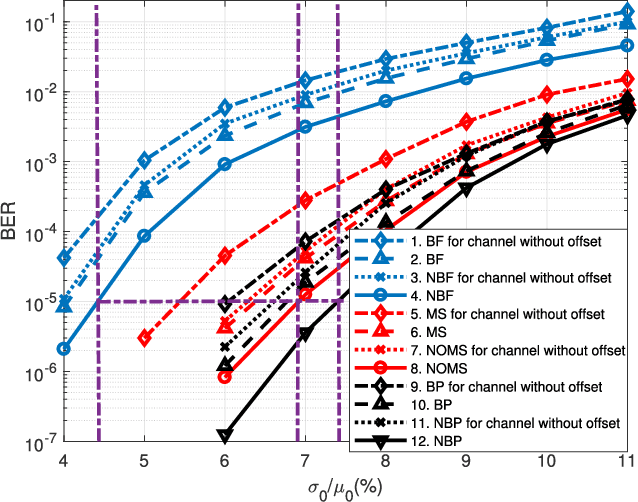
Abstract:Spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory (STT-MRAM) is a promising emerging non-volatile memory (NVM) technology with wide applications. However, the data recovery of STT-MRAM is affected by the diversity of channel raw bit error rate (BER) across different dies caused by process variations, as well as the unknown resistance offset due to temperature change. Therefore, it is critical to develop effective decoding algorithms of error correction codes (ECCs) for STT-MRAM. In this article, we first propose a neural bit-flipping (BF) decoding algorithm, which can share the same trellis representation as the state-of-the-art neural decoding algorithms, such as the neural belief propagation (NBP) and neural offset min-sum (NOMS) algorithm. Hence, a neural network (NN) decoder with a uniform architecture but different NN parameters can realize all these neural decoding algorithms. Based on such a unified NN decoder architecture, we further propose a novel deep-learning (DL)-based adaptive decoding algorithm whose decoding complexity can be adjusted according to the change of the channel conditions of STT-MRAM. Extensive experimental evaluation results demonstrate that the proposed neural decoders can greatly improve the performance over the standard decoders, with similar decoding latency and energy consumption. Moreover, the DL-based adaptive decoder can work well over different channel conditions of STT-MRAM irrespective of the unknown resistance offset, with a 50% reduction of the decoding latency and energy consumption compared to the fixed decoder.
DriveWorld: 4D Pre-trained Scene Understanding via World Models for Autonomous Driving
May 07, 2024Abstract:Vision-centric autonomous driving has recently raised wide attention due to its lower cost. Pre-training is essential for extracting a universal representation. However, current vision-centric pre-training typically relies on either 2D or 3D pre-text tasks, overlooking the temporal characteristics of autonomous driving as a 4D scene understanding task. In this paper, we address this challenge by introducing a world model-based autonomous driving 4D representation learning framework, dubbed \emph{DriveWorld}, which is capable of pre-training from multi-camera driving videos in a spatio-temporal fashion. Specifically, we propose a Memory State-Space Model for spatio-temporal modelling, which consists of a Dynamic Memory Bank module for learning temporal-aware latent dynamics to predict future changes and a Static Scene Propagation module for learning spatial-aware latent statics to offer comprehensive scene contexts. We additionally introduce a Task Prompt to decouple task-aware features for various downstream tasks. The experiments demonstrate that DriveWorld delivers promising results on various autonomous driving tasks. When pre-trained with the OpenScene dataset, DriveWorld achieves a 7.5% increase in mAP for 3D object detection, a 3.0% increase in IoU for online mapping, a 5.0% increase in AMOTA for multi-object tracking, a 0.1m decrease in minADE for motion forecasting, a 3.0% increase in IoU for occupancy prediction, and a 0.34m reduction in average L2 error for planning.
Towards Objectively Benchmarking Social Intelligence for Language Agents at Action Level
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Prominent large language models have exhibited human-level performance in many domains, even enabling the derived agents to simulate human and social interactions. While practical works have substantiated the practicability of grounding language agents in sandbox simulation or embodied simulators, current social intelligence benchmarks either stay at the language level or use subjective metrics. In pursuit of a more realistic and objective evaluation, we introduce the Social Tasks in Sandbox Simulation (STSS) benchmark, which assesses language agents \textbf{objectively} at the \textbf{action level} by scrutinizing the goal achievements within the multi-agent simulation. Additionally, we sample conversation scenarios to build a language-level benchmark to provide an economically prudent preliminary evaluation and align with prevailing benchmarks. To gauge the significance of agent architecture, we implement a target-driven planning (TDP) module as an adjunct to the existing agent. Our evaluative findings highlight that the STSS benchmark is challenging for state-of-the-art language agents. Furthermore, it effectively discriminates between distinct language agents, suggesting its usefulness as a benchmark for evaluating both language models and agent architectures.
AgentAvatar: Disentangling Planning, Driving and Rendering for Photorealistic Avatar Agents
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:In this study, our goal is to create interactive avatar agents that can autonomously plan and animate nuanced facial movements realistically, from both visual and behavioral perspectives. Given high-level inputs about the environment and agent profile, our framework harnesses LLMs to produce a series of detailed text descriptions of the avatar agents' facial motions. These descriptions are then processed by our task-agnostic driving engine into motion token sequences, which are subsequently converted into continuous motion embeddings that are further consumed by our standalone neural-based renderer to generate the final photorealistic avatar animations. These streamlined processes allow our framework to adapt to a variety of non-verbal avatar interactions, both monadic and dyadic. Our extensive study, which includes experiments on both newly compiled and existing datasets featuring two types of agents -- one capable of monadic interaction with the environment, and the other designed for dyadic conversation -- validates the effectiveness and versatility of our approach. To our knowledge, we advanced a leap step by combining LLMs and neural rendering for generalized non-verbal prediction and photo-realistic rendering of avatar agents.
Fast and Accurate Deep Loop Closing and Relocalization for Reliable LiDAR SLAM
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Loop closing and relocalization are crucial techniques to establish reliable and robust long-term SLAM by addressing pose estimation drift and degeneration. This article begins by formulating loop closing and relocalization within a unified framework. Then, we propose a novel multi-head network LCR-Net to tackle both tasks effectively. It exploits novel feature extraction and pose-aware attention mechanism to precisely estimate similarities and 6-DoF poses between pairs of LiDAR scans. In the end, we integrate our LCR-Net into a SLAM system and achieve robust and accurate online LiDAR SLAM in outdoor driving environments. We thoroughly evaluate our LCR-Net through three setups derived from loop closing and relocalization, including candidate retrieval, closed-loop point cloud registration, and continuous relocalization using multiple datasets. The results demonstrate that LCR-Net excels in all three tasks, surpassing the state-of-the-art methods and exhibiting a remarkable generalization ability. Notably, our LCR-Net outperforms baseline methods without using a time-consuming robust pose estimator, rendering it suitable for online SLAM applications. To our best knowledge, the integration of LCR-Net yields the first LiDAR SLAM with the capability of deep loop closing and relocalization. The implementation of our methods will be made open-source.
UniWorld: Autonomous Driving Pre-training via World Models
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we draw inspiration from Alberto Elfes' pioneering work in 1989, where he introduced the concept of the occupancy grid as World Models for robots. We imbue the robot with a spatial-temporal world model, termed UniWorld, to perceive its surroundings and predict the future behavior of other participants. UniWorld involves initially predicting 4D geometric occupancy as the World Models for foundational stage and subsequently fine-tuning on downstream tasks. UniWorld can estimate missing information concerning the world state and predict plausible future states of the world. Besides, UniWorld's pre-training process is label-free, enabling the utilization of massive amounts of image-LiDAR pairs to build a Foundational Model.The proposed unified pre-training framework demonstrates promising results in key tasks such as motion prediction, multi-camera 3D object detection, and surrounding semantic scene completion. When compared to monocular pre-training methods on the nuScenes dataset, UniWorld shows a significant improvement of about 1.5% in IoU for motion prediction, 2.0% in mAP and 2.0% in NDS for multi-camera 3D object detection, as well as a 3% increase in mIoU for surrounding semantic scene completion. By adopting our unified pre-training method, a 25% reduction in 3D training annotation costs can be achieved, offering significant practical value for the implementation of real-world autonomous driving. Codes are publicly available at https://github.com/chaytonmin/UniWorld.
Controlling Character Motions without Observable Driving Source
Aug 11, 2023



Abstract:How to generate diverse, life-like, and unlimited long head/body sequences without any driving source? We argue that this under-investigated research problem is non-trivial at all, and has unique technical challenges behind it. Without semantic constraints from the driving sources, using the standard autoregressive model to generate infinitely long sequences would easily result in 1) out-of-distribution (OOD) issue due to the accumulated error, 2) insufficient diversity to produce natural and life-like motion sequences and 3) undesired periodic patterns along the time. To tackle the above challenges, we propose a systematic framework that marries the benefits of VQ-VAE and a novel token-level control policy trained with reinforcement learning using carefully designed reward functions. A high-level prior model can be easily injected on top to generate unlimited long and diverse sequences. Although we focus on no driving sources now, our framework can be generalized for controlled synthesis with explicit driving sources. Through comprehensive evaluations, we conclude that our proposed framework can address all the above-mentioned challenges and outperform other strong baselines very significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge