Yu Deng
IBM
Robot-DIFT: Distilling Diffusion Features for Geometrically Consistent Visuomotor Control
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:We hypothesize that a key bottleneck in generalizable robot manipulation is not solely data scale or policy capacity, but a structural mismatch between current visual backbones and the physical requirements of closed-loop control. While state-of-the-art vision encoders (including those used in VLAs) optimize for semantic invariance to stabilize classification, manipulation typically demands geometric sensitivity the ability to map millimeter-level pose shifts to predictable feature changes. Their discriminative objective creates a "blind spot" for fine-grained control, whereas generative diffusion models inherently encode geometric dependencies within their latent manifolds, encouraging the preservation of dense multi-scale spatial structure. However, directly deploying stochastic diffusion features for control is hindered by stochastic instability, inference latency, and representation drift during fine-tuning. To bridge this gap, we propose Robot-DIFT, a framework that decouples the source of geometric information from the process of inference via Manifold Distillation. By distilling a frozen diffusion teacher into a deterministic Spatial-Semantic Feature Pyramid Network (S2-FPN), we retain the rich geometric priors of the generative model while ensuring temporal stability, real-time execution, and robustness against drift. Pretrained on the large-scale DROID dataset, Robot-DIFT demonstrates superior geometric consistency and control performance compared to leading discriminative baselines, supporting the view that how a model learns to see dictates how well it can learn to act.
Think Locally, Explain Globally: Graph-Guided LLM Investigations via Local Reasoning and Belief Propagation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:LLM agents excel when environments are mostly static and the needed information fits in a model's context window, but they often fail in open-ended investigations where explanations must be constructed by iteratively mining evidence from massive, heterogeneous operational data. These investigations exhibit hidden dependency structure: entities interact, signals co-vary, and the importance of a fact may only become clear after other evidence is discovered. Because the context window is bounded, agents must summarize intermediate findings before their significance is known, increasing the risk of discarding key evidence. ReAct-style agents are especially brittle in this regime. Their retrieve-summarize-reason loop makes conclusions sensitive to exploration order and introduces run-to-run non-determinism, producing a reliability gap where Pass-at-k may be high but Majority-at-k remains low. Simply sampling more rollouts or generating longer reasoning traces does not reliably stabilize results, since hypotheses cannot be autonomously checked as new evidence arrives and there is no explicit mechanism for belief bookkeeping and revision. In addition, ReAct entangles semantic reasoning with controller duties such as tool orchestration and state tracking, so execution errors and plan drift degrade reasoning while consuming scarce context. We address these issues by formulating investigation as abductive reasoning over a dependency graph and proposing EoG (Explanations over Graphs), a disaggregated framework in which an LLM performs bounded local evidence mining and labeling (cause vs symptom) while a deterministic controller manages traversal, state, and belief propagation to compute a minimal explanatory frontier. On a representative ITBench diagnostics task, EoG improves both accuracy and run-to-run consistency over ReAct baselines, including a 7x average gain in Majority-at-k entity F1.
LLM-powered Real-time Patent Citation Recommendation for Financial Technologies
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Rapid financial innovation has been accompanied by a sharp increase in patenting activity, making timely and comprehensive prior-art discovery more difficult. This problem is especially evident in financial technologies, where innovations develop quickly, patent collections grow continuously, and citation recommendation systems must be updated as new applications arrive. Existing patent retrieval and citation recommendation methods typically rely on static indexes or periodic retraining, which limits their ability to operate effectively in such dynamic settings. In this study, we propose a real-time patent citation recommendation framework designed for large and fast-changing financial patent corpora. Using a dataset of 428,843 financial patents granted by the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) between 2000 and 2024, we build a three-stage recommendation pipeline. The pipeline uses large language model (LLM) embeddings to represent the semantic content of patent abstracts, applies efficient approximate nearest-neighbor search to construct a manageable candidate set, and ranks candidates by semantic similarity to produce top-k citation recommendations. In addition to improving recommendation accuracy, the proposed framework directly addresses the dynamic nature of patent systems. By using an incremental indexing strategy based on hierarchical navigable small-world (HNSW) graphs, newly issued patents can be added without rebuilding the entire index. A rolling day-by-day update experiment shows that incremental updating improves recall while substantially reducing computational cost compared with rebuild-based indexing. The proposed method also consistently outperforms traditional text-based baselines and alternative nearest-neighbor retrieval approaches.
VASA-3D: Lifelike Audio-Driven Gaussian Head Avatars from a Single Image
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:We propose VASA-3D, an audio-driven, single-shot 3D head avatar generator. This research tackles two major challenges: capturing the subtle expression details present in real human faces, and reconstructing an intricate 3D head avatar from a single portrait image. To accurately model expression details, VASA-3D leverages the motion latent of VASA-1, a method that yields exceptional realism and vividness in 2D talking heads. A critical element of our work is translating this motion latent to 3D, which is accomplished by devising a 3D head model that is conditioned on the motion latent. Customization of this model to a single image is achieved through an optimization framework that employs numerous video frames of the reference head synthesized from the input image. The optimization takes various training losses robust to artifacts and limited pose coverage in the generated training data. Our experiment shows that VASA-3D produces realistic 3D talking heads that cannot be achieved by prior art, and it supports the online generation of 512x512 free-viewpoint videos at up to 75 FPS, facilitating more immersive engagements with lifelike 3D avatars.
Native and Compact Structured Latents for 3D Generation
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D generative modeling have significantly improved the generation realism, yet the field is still hampered by existing representations, which struggle to capture assets with complex topologies and detailed appearance. This paper present an approach for learning a structured latent representation from native 3D data to address this challenge. At its core is a new sparse voxel structure called O-Voxel, an omni-voxel representation that encodes both geometry and appearance. O-Voxel can robustly model arbitrary topology, including open, non-manifold, and fully-enclosed surfaces, while capturing comprehensive surface attributes beyond texture color, such as physically-based rendering parameters. Based on O-Voxel, we design a Sparse Compression VAE which provides a high spatial compression rate and a compact latent space. We train large-scale flow-matching models comprising 4B parameters for 3D generation using diverse public 3D asset datasets. Despite their scale, inference remains highly efficient. Meanwhile, the geometry and material quality of our generated assets far exceed those of existing models. We believe our approach offers a significant advancement in 3D generative modeling.
Depth-Consistent 3D Gaussian Splatting via Physical Defocus Modeling and Multi-View Geometric Supervision
Nov 13, 2025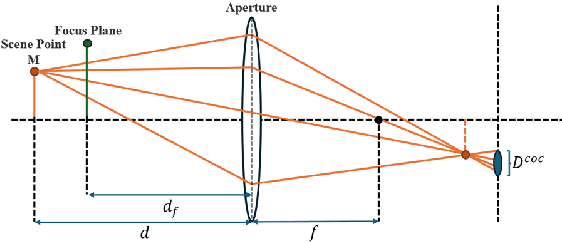
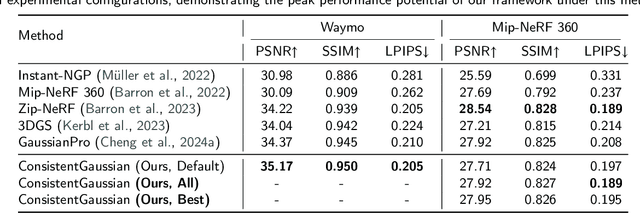
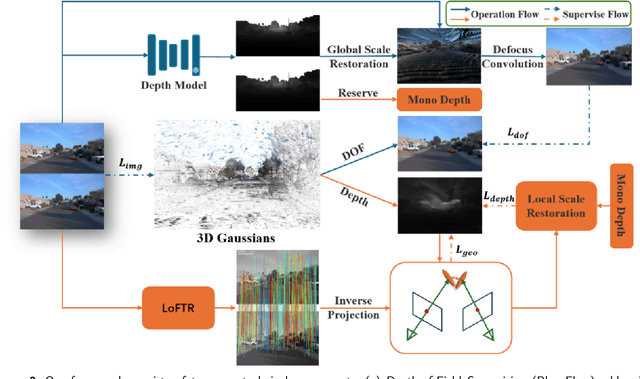
Abstract:Three-dimensional reconstruction in scenes with extreme depth variations remains challenging due to inconsistent supervisory signals between near-field and far-field regions. Existing methods fail to simultaneously address inaccurate depth estimation in distant areas and structural degradation in close-range regions. This paper proposes a novel computational framework that integrates depth-of-field supervision and multi-view consistency supervision to advance 3D Gaussian Splatting. Our approach comprises two core components: (1) Depth-of-field Supervision employs a scale-recovered monocular depth estimator (e.g., Metric3D) to generate depth priors, leverages defocus convolution to synthesize physically accurate defocused images, and enforces geometric consistency through a novel depth-of-field loss, thereby enhancing depth fidelity in both far-field and near-field regions; (2) Multi-View Consistency Supervision employing LoFTR-based semi-dense feature matching to minimize cross-view geometric errors and enforce depth consistency via least squares optimization of reliable matched points. By unifying defocus physics with multi-view geometric constraints, our method achieves superior depth fidelity, demonstrating a 0.8 dB PSNR improvement over the state-of-the-art method on the Waymo Open Dataset. This framework bridges physical imaging principles and learning-based depth regularization, offering a scalable solution for complex depth stratification in urban environments.
STORM: Segment, Track, and Object Re-Localization from a Single 3D Model
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Accurate 6D pose estimation and tracking are fundamental capabilities for physical AI systems such as robots. However, existing approaches typically rely on a manually annotated segmentation mask of the target in the first frame, which is labor-intensive and leads to reduced performance when faced with occlusions or rapid movement. To address these limi- tations, we propose STORM (Segment, Track, and Object Re-localization from a single 3D Model), an open-source robust real-time 6D pose estimation system that requires no manual annotation. STORM employs a novel three-stage pipeline combining vision-language understanding with self-supervised feature matching: contextual object descriptions guide localization, self-cross-attention mechanisms identify candidate regions, and a segmentation model produces precise masks for accurate pose estimation. Another key innovation is our automatic re-registration mechanism that detects tracking failures through feature similarity monitoring and recovers from severe occlusions or rapid motion. STORM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on challenging industrial datasets featuring multi-object occlusions, high-speed motion, and varying illumination, while operating at real-time speeds without additional training. This annotation-free approach significantly reduces deployment overhead, providing a practical solution for modern applications, such as flexible manufacturing and intelligent quality control.
Scalable Vision-Language-Action Model Pretraining for Robotic Manipulation with Real-Life Human Activity Videos
Oct 24, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for pretraining robotic manipulation Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models using a large corpus of unscripted real-life video recordings of human hand activities. Treating human hand as dexterous robot end-effector, we show that "in-the-wild" egocentric human videos without any annotations can be transformed into data formats fully aligned with existing robotic V-L-A training data in terms of task granularity and labels. This is achieved by the development of a fully-automated holistic human activity analysis approach for arbitrary human hand videos. This approach can generate atomic-level hand activity segments and their language descriptions, each accompanied with framewise 3D hand motion and camera motion. We process a large volume of egocentric videos and create a hand-VLA training dataset containing 1M episodes and 26M frames. This training data covers a wide range of objects and concepts, dexterous manipulation tasks, and environment variations in real life, vastly exceeding the coverage of existing robot data. We design a dexterous hand VLA model architecture and pretrain the model on this dataset. The model exhibits strong zero-shot capabilities on completely unseen real-world observations. Additionally, fine-tuning it on a small amount of real robot action data significantly improves task success rates and generalization to novel objects in real robotic experiments. We also demonstrate the appealing scaling behavior of the model's task performance with respect to pretraining data scale. We believe this work lays a solid foundation for scalable VLA pretraining, advancing robots toward truly generalizable embodied intelligence.
MoGe-2: Accurate Monocular Geometry with Metric Scale and Sharp Details
Jul 03, 2025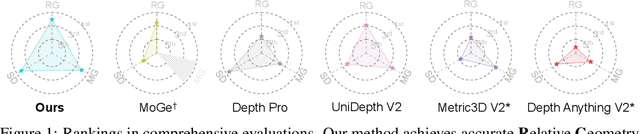
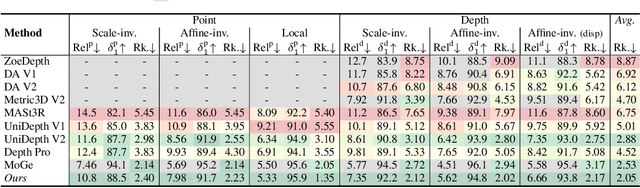
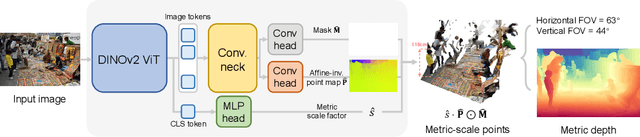
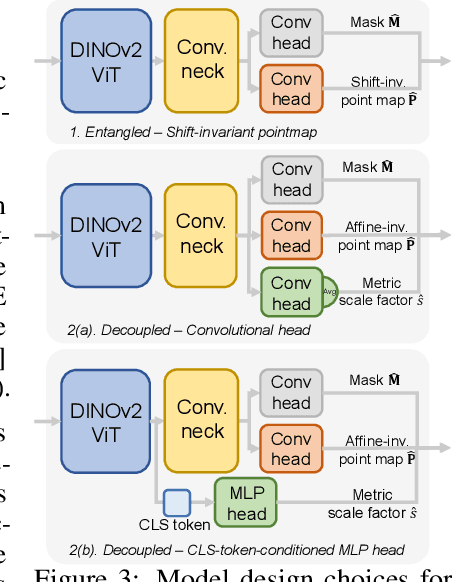
Abstract:We propose MoGe-2, an advanced open-domain geometry estimation model that recovers a metric scale 3D point map of a scene from a single image. Our method builds upon the recent monocular geometry estimation approach, MoGe, which predicts affine-invariant point maps with unknown scales. We explore effective strategies to extend MoGe for metric geometry prediction without compromising the relative geometry accuracy provided by the affine-invariant point representation. Additionally, we discover that noise and errors in real data diminish fine-grained detail in the predicted geometry. We address this by developing a unified data refinement approach that filters and completes real data from different sources using sharp synthetic labels, significantly enhancing the granularity of the reconstructed geometry while maintaining the overall accuracy. We train our model on a large corpus of mixed datasets and conducted comprehensive evaluations, demonstrating its superior performance in achieving accurate relative geometry, precise metric scale, and fine-grained detail recovery -- capabilities that no previous methods have simultaneously achieved.
Brain Imaging Foundation Models, Are We There Yet? A Systematic Review of Foundation Models for Brain Imaging and Biomedical Research
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation models (FMs), large neural networks pretrained on extensive and diverse datasets, have revolutionized artificial intelligence and shown significant promise in medical imaging by enabling robust performance with limited labeled data. Although numerous surveys have reviewed the application of FM in healthcare care, brain imaging remains underrepresented, despite its critical role in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases using modalities such as MRI, CT, and PET. Existing reviews either marginalize brain imaging or lack depth on the unique challenges and requirements of FM in this domain, such as multimodal data integration, support for diverse clinical tasks, and handling of heterogeneous, fragmented datasets. To address this gap, we present the first comprehensive and curated review of FMs for brain imaging. We systematically analyze 161 brain imaging datasets and 86 FM architectures, providing information on key design choices, training paradigms, and optimizations driving recent advances. Our review highlights the leading models for various brain imaging tasks, summarizes their innovations, and critically examines current limitations and blind spots in the literature. We conclude by outlining future research directions to advance FM applications in brain imaging, with the aim of fostering progress in both clinical and research settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge