Anssi Kanervisto
BFM-Zero: A Promptable Behavioral Foundation Model for Humanoid Control Using Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Building Behavioral Foundation Models (BFMs) for humanoid robots has the potential to unify diverse control tasks under a single, promptable generalist policy. However, existing approaches are either exclusively deployed on simulated humanoid characters, or specialized to specific tasks such as tracking. We propose BFM-Zero, a framework that learns an effective shared latent representation that embeds motions, goals, and rewards into a common space, enabling a single policy to be prompted for multiple downstream tasks without retraining. This well-structured latent space in BFM-Zero enables versatile and robust whole-body skills on a Unitree G1 humanoid in the real world, via diverse inference methods, including zero-shot motion tracking, goal reaching, and reward optimization, and few-shot optimization-based adaptation. Unlike prior on-policy reinforcement learning (RL) frameworks, BFM-Zero builds upon recent advancements in unsupervised RL and Forward-Backward (FB) models, which offer an objective-centric, explainable, and smooth latent representation of whole-body motions. We further extend BFM-Zero with critical reward shaping, domain randomization, and history-dependent asymmetric learning to bridge the sim-to-real gap. Those key design choices are quantitatively ablated in simulation. A first-of-its-kind model, BFM-Zero establishes a step toward scalable, promptable behavioral foundation models for whole-body humanoid control.
Zero-Shot Whole-Body Humanoid Control via Behavioral Foundation Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised reinforcement learning (RL) aims at pre-training agents that can solve a wide range of downstream tasks in complex environments. Despite recent advancements, existing approaches suffer from several limitations: they may require running an RL process on each downstream task to achieve a satisfactory performance, they may need access to datasets with good coverage or well-curated task-specific samples, or they may pre-train policies with unsupervised losses that are poorly correlated with the downstream tasks of interest. In this paper, we introduce a novel algorithm regularizing unsupervised RL towards imitating trajectories from unlabeled behavior datasets. The key technical novelty of our method, called Forward-Backward Representations with Conditional-Policy Regularization, is to train forward-backward representations to embed the unlabeled trajectories to the same latent space used to represent states, rewards, and policies, and use a latent-conditional discriminator to encourage policies to ``cover'' the states in the unlabeled behavior dataset. As a result, we can learn policies that are well aligned with the behaviors in the dataset, while retaining zero-shot generalization capabilities for reward-based and imitation tasks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this new approach in a challenging humanoid control problem: leveraging observation-only motion capture datasets, we train Meta Motivo, the first humanoid behavioral foundation model that can be prompted to solve a variety of whole-body tasks, including motion tracking, goal reaching, and reward optimization. The resulting model is capable of expressing human-like behaviors and it achieves competitive performance with task-specific methods while outperforming state-of-the-art unsupervised RL and model-based baselines.
Fast Adaptation with Behavioral Foundation Models
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised zero-shot reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for pretraining behavioral foundation models (BFMs), enabling agents to solve a wide range of downstream tasks specified via reward functions in a zero-shot fashion, i.e., without additional test-time learning or planning. This is achieved by learning self-supervised task embeddings alongside corresponding near-optimal behaviors and incorporating an inference procedure to directly retrieve the latent task embedding and associated policy for any given reward function. Despite promising results, zero-shot policies are often suboptimal due to errors induced by the unsupervised training process, the embedding, and the inference procedure. In this paper, we focus on devising fast adaptation strategies to improve the zero-shot performance of BFMs in a few steps of online interaction with the environment while avoiding any performance drop during the adaptation process. Notably, we demonstrate that existing BFMs learn a set of skills containing more performant policies than those identified by their inference procedure, making them well-suited for fast adaptation. Motivated by this observation, we propose both actor-critic and actor-only fast adaptation strategies that search in the low-dimensional task-embedding space of the pre-trained BFM to rapidly improve the performance of its zero-shot policies on any downstream task. Notably, our approach mitigates the initial "unlearning" phase commonly observed when fine-tuning pre-trained RL models. We evaluate our fast adaptation strategies on top of four state-of-the-art zero-shot RL methods in multiple navigation and locomotion domains. Our results show that they achieve 10-40% improvement over their zero-shot performance in a few tens of episodes, outperforming existing baselines.
Diffusion for World Modeling: Visual Details Matter in Atari
May 20, 2024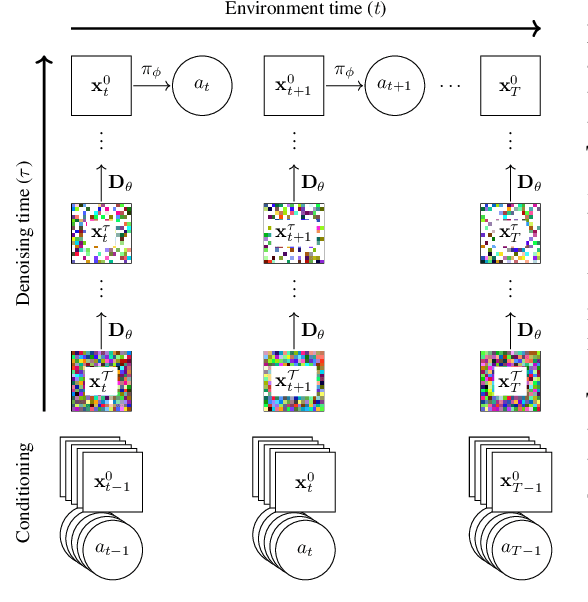
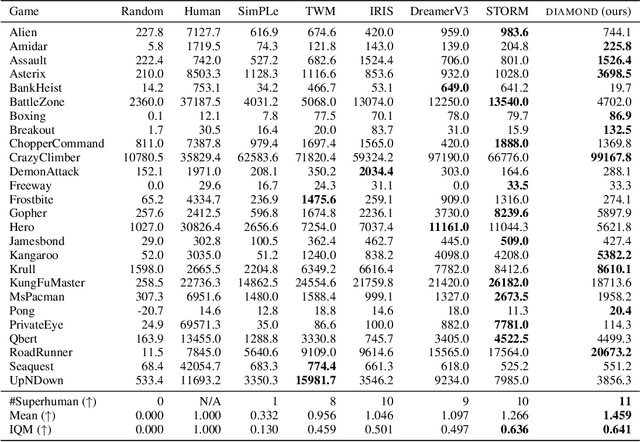
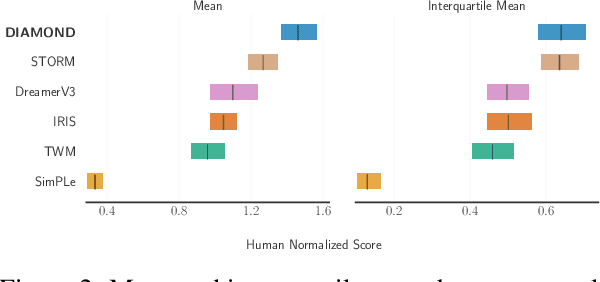
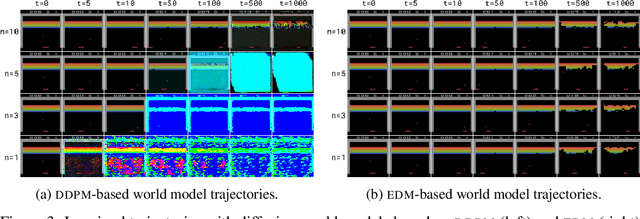
Abstract:World models constitute a promising approach for training reinforcement learning agents in a safe and sample-efficient manner. Recent world models predominantly operate on sequences of discrete latent variables to model environment dynamics. However, this compression into a compact discrete representation may ignore visual details that are important for reinforcement learning. Concurrently, diffusion models have become a dominant approach for image generation, challenging well-established methods modeling discrete latents. Motivated by this paradigm shift, we introduce DIAMOND (DIffusion As a Model Of eNvironment Dreams), a reinforcement learning agent trained in a diffusion world model. We analyze the key design choices that are required to make diffusion suitable for world modeling, and demonstrate how improved visual details can lead to improved agent performance. DIAMOND achieves a mean human normalized score of 1.46 on the competitive Atari 100k benchmark; a new best for agents trained entirely within a world model. To foster future research on diffusion for world modeling, we release our code, agents and playable world models at https://github.com/eloialonso/diamond.
Toward Human-AI Alignment in Large-Scale Multi-Player Games
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:Achieving human-AI alignment in complex multi-agent games is crucial for creating trustworthy AI agents that enhance gameplay. We propose a method to evaluate this alignment using an interpretable task-sets framework, focusing on high-level behavioral tasks instead of low-level policies. Our approach has three components. First, we analyze extensive human gameplay data from Xbox's Bleeding Edge (100K+ games), uncovering behavioral patterns in a complex task space. This task space serves as a basis set for a behavior manifold capturing interpretable axes: fight-flight, explore-exploit, and solo-multi-agent. Second, we train an AI agent to play Bleeding Edge using a Generative Pretrained Causal Transformer and measure its behavior. Third, we project human and AI gameplay to the proposed behavior manifold to compare and contrast. This allows us to interpret differences in policy as higher-level behavioral concepts, e.g., we find that while human players exhibit variability in fight-flight and explore-exploit behavior, AI players tend towards uniformity. Furthermore, AI agents predominantly engage in solo play, while humans often engage in cooperative and competitive multi-agent patterns. These stark differences underscore the need for interpretable evaluation, design, and integration of AI in human-aligned applications. Our study advances the alignment discussion in AI and especially generative AI research, offering a measurable framework for interpretable human-agent alignment in multiplayer gaming.
BEDD: The MineRL BASALT Evaluation and Demonstrations Dataset for Training and Benchmarking Agents that Solve Fuzzy Tasks
Dec 05, 2023



Abstract:The MineRL BASALT competition has served to catalyze advances in learning from human feedback through four hard-to-specify tasks in Minecraft, such as create and photograph a waterfall. Given the completion of two years of BASALT competitions, we offer to the community a formalized benchmark through the BASALT Evaluation and Demonstrations Dataset (BEDD), which serves as a resource for algorithm development and performance assessment. BEDD consists of a collection of 26 million image-action pairs from nearly 14,000 videos of human players completing the BASALT tasks in Minecraft. It also includes over 3,000 dense pairwise human evaluations of human and algorithmic agents. These comparisons serve as a fixed, preliminary leaderboard for evaluating newly-developed algorithms. To enable this comparison, we present a streamlined codebase for benchmarking new algorithms against the leaderboard. In addition to presenting these datasets, we conduct a detailed analysis of the data from both datasets to guide algorithm development and evaluation. The released code and data are available at https://github.com/minerllabs/basalt-benchmark .
Visual Encoders for Data-Efficient Imitation Learning in Modern Video Games
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Video games have served as useful benchmarks for the decision making community, but going beyond Atari games towards training agents in modern games has been prohibitively expensive for the vast majority of the research community. Recent progress in the research, development and open release of large vision models has the potential to amortize some of these costs across the community. However, it is currently unclear which of these models have learnt representations that retain information critical for sequential decision making. Towards enabling wider participation in the research of gameplaying agents in modern games, we present a systematic study of imitation learning with publicly available visual encoders compared to the typical, task-specific, end-to-end training approach in Minecraft, Minecraft Dungeons and Counter-Strike: Global Offensive.
Towards Solving Fuzzy Tasks with Human Feedback: A Retrospective of the MineRL BASALT 2022 Competition
Mar 23, 2023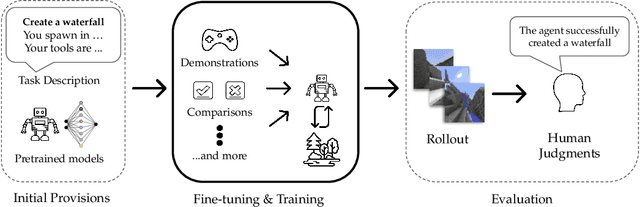

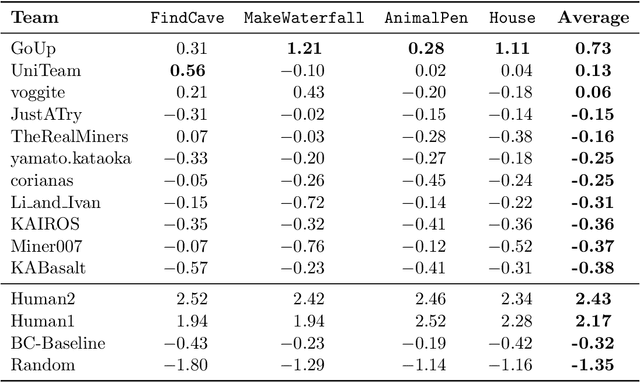
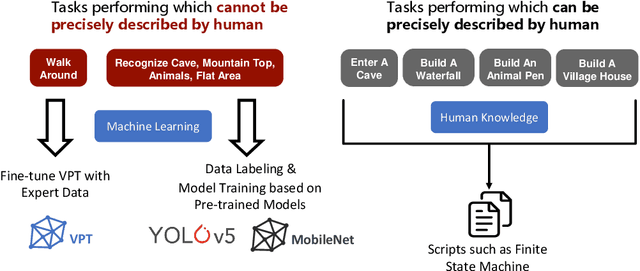
Abstract:To facilitate research in the direction of fine-tuning foundation models from human feedback, we held the MineRL BASALT Competition on Fine-Tuning from Human Feedback at NeurIPS 2022. The BASALT challenge asks teams to compete to develop algorithms to solve tasks with hard-to-specify reward functions in Minecraft. Through this competition, we aimed to promote the development of algorithms that use human feedback as channels to learn the desired behavior. We describe the competition and provide an overview of the top solutions. We conclude by discussing the impact of the competition and future directions for improvement.
Imitating Human Behaviour with Diffusion Models
Jan 25, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative models in the text-to-image domain. This paper studies their application as observation-to-action models for imitating human behaviour in sequential environments. Human behaviour is stochastic and multimodal, with structured correlations between action dimensions. Meanwhile, standard modelling choices in behaviour cloning are limited in their expressiveness and may introduce bias into the cloned policy. We begin by pointing out the limitations of these choices. We then propose that diffusion models are an excellent fit for imitating human behaviour, since they learn an expressive distribution over the joint action space. We introduce several innovations to make diffusion models suitable for sequential environments; designing suitable architectures, investigating the role of guidance, and developing reliable sampling strategies. Experimentally, diffusion models closely match human demonstrations in a simulated robotic control task and a modern 3D gaming environment.
* Published in ICLR 2023
A2C is a special case of PPO
May 18, 2022
Abstract:Advantage Actor-critic (A2C) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) are popular deep reinforcement learning algorithms used for game AI in recent years. A common understanding is that A2C and PPO are separate algorithms because PPO's clipped objective appears significantly different than A2C's objective. In this paper, however, we show A2C is a special case of PPO. We present theoretical justifications and pseudocode analysis to demonstrate why. To validate our claim, we conduct an empirical experiment using \texttt{Stable-baselines3}, showing A2C and PPO produce the \textit{exact} same models when other settings are controlled.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge