Brandon Houghton
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
BEDD: The MineRL BASALT Evaluation and Demonstrations Dataset for Training and Benchmarking Agents that Solve Fuzzy Tasks
Dec 05, 2023



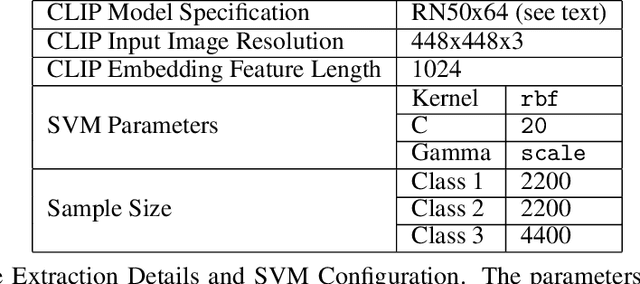
Abstract:The MineRL BASALT competition has served to catalyze advances in learning from human feedback through four hard-to-specify tasks in Minecraft, such as create and photograph a waterfall. Given the completion of two years of BASALT competitions, we offer to the community a formalized benchmark through the BASALT Evaluation and Demonstrations Dataset (BEDD), which serves as a resource for algorithm development and performance assessment. BEDD consists of a collection of 26 million image-action pairs from nearly 14,000 videos of human players completing the BASALT tasks in Minecraft. It also includes over 3,000 dense pairwise human evaluations of human and algorithmic agents. These comparisons serve as a fixed, preliminary leaderboard for evaluating newly-developed algorithms. To enable this comparison, we present a streamlined codebase for benchmarking new algorithms against the leaderboard. In addition to presenting these datasets, we conduct a detailed analysis of the data from both datasets to guide algorithm development and evaluation. The released code and data are available at https://github.com/minerllabs/basalt-benchmark .
Towards Solving Fuzzy Tasks with Human Feedback: A Retrospective of the MineRL BASALT 2022 Competition
Mar 23, 2023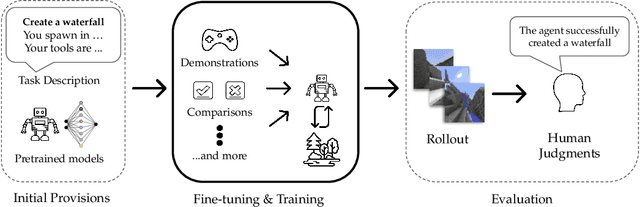

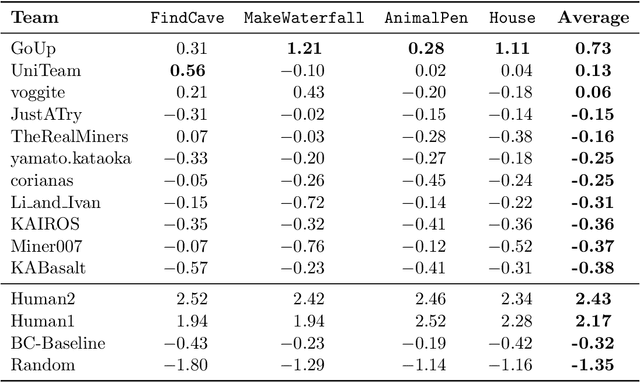
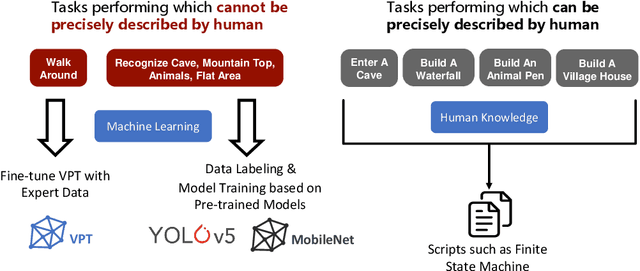
Abstract:To facilitate research in the direction of fine-tuning foundation models from human feedback, we held the MineRL BASALT Competition on Fine-Tuning from Human Feedback at NeurIPS 2022. The BASALT challenge asks teams to compete to develop algorithms to solve tasks with hard-to-specify reward functions in Minecraft. Through this competition, we aimed to promote the development of algorithms that use human feedback as channels to learn the desired behavior. We describe the competition and provide an overview of the top solutions. We conclude by discussing the impact of the competition and future directions for improvement.
Video PreTraining : Learning to Act by Watching Unlabeled Online Videos
Jun 23, 2022

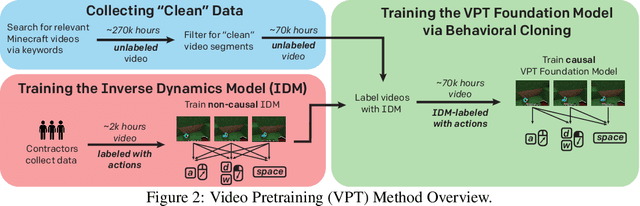
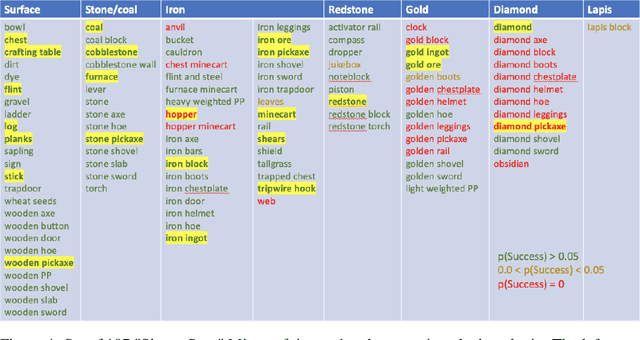
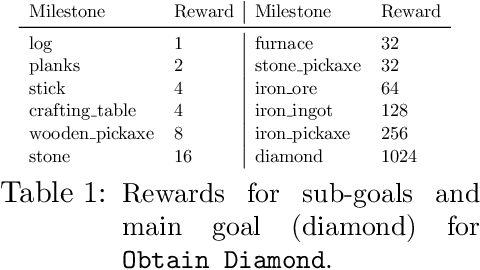
Abstract:Pretraining on noisy, internet-scale datasets has been heavily studied as a technique for training models with broad, general capabilities for text, images, and other modalities. However, for many sequential decision domains such as robotics, video games, and computer use, publicly available data does not contain the labels required to train behavioral priors in the same way. We extend the internet-scale pretraining paradigm to sequential decision domains through semi-supervised imitation learning wherein agents learn to act by watching online unlabeled videos. Specifically, we show that with a small amount of labeled data we can train an inverse dynamics model accurate enough to label a huge unlabeled source of online data -- here, online videos of people playing Minecraft -- from which we can then train a general behavioral prior. Despite using the native human interface (mouse and keyboard at 20Hz), we show that this behavioral prior has nontrivial zero-shot capabilities and that it can be fine-tuned, with both imitation learning and reinforcement learning, to hard-exploration tasks that are impossible to learn from scratch via reinforcement learning. For many tasks our models exhibit human-level performance, and we are the first to report computer agents that can craft diamond tools, which can take proficient humans upwards of 20 minutes (24,000 environment actions) of gameplay to accomplish.
The MineRL BASALT Competition on Learning from Human Feedback
Jul 05, 2021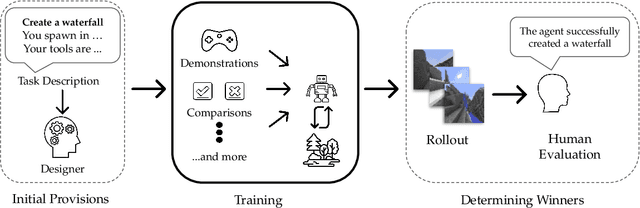

Abstract:The last decade has seen a significant increase of interest in deep learning research, with many public successes that have demonstrated its potential. As such, these systems are now being incorporated into commercial products. With this comes an additional challenge: how can we build AI systems that solve tasks where there is not a crisp, well-defined specification? While multiple solutions have been proposed, in this competition we focus on one in particular: learning from human feedback. Rather than training AI systems using a predefined reward function or using a labeled dataset with a predefined set of categories, we instead train the AI system using a learning signal derived from some form of human feedback, which can evolve over time as the understanding of the task changes, or as the capabilities of the AI system improve. The MineRL BASALT competition aims to spur forward research on this important class of techniques. We design a suite of four tasks in Minecraft for which we expect it will be hard to write down hardcoded reward functions. These tasks are defined by a paragraph of natural language: for example, "create a waterfall and take a scenic picture of it", with additional clarifying details. Participants must train a separate agent for each task, using any method they want. Agents are then evaluated by humans who have read the task description. To help participants get started, we provide a dataset of human demonstrations on each of the four tasks, as well as an imitation learning baseline that leverages these demonstrations. Our hope is that this competition will improve our ability to build AI systems that do what their designers intend them to do, even when the intent cannot be easily formalized. Besides allowing AI to solve more tasks, this can also enable more effective regulation of AI systems, as well as making progress on the value alignment problem.
Multi-task curriculum learning in a complex, visual, hard-exploration domain: Minecraft
Jun 28, 2021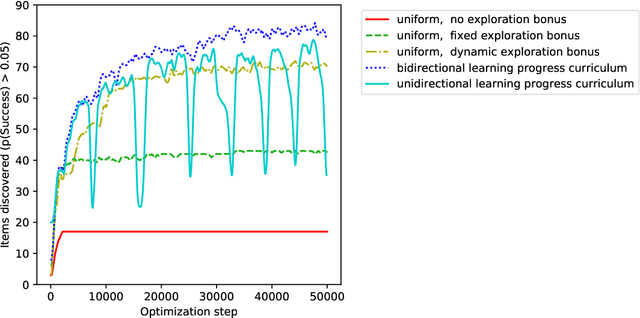
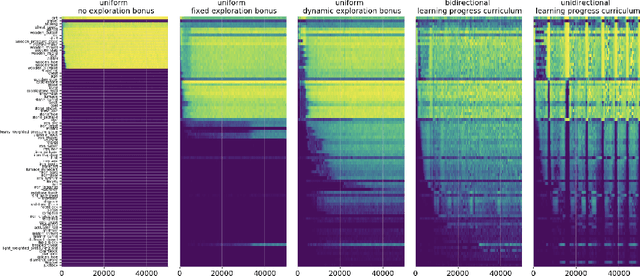
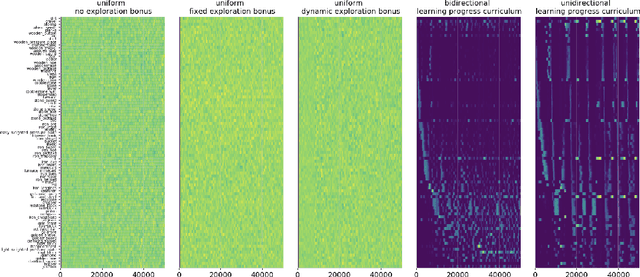
Abstract:An important challenge in reinforcement learning is training agents that can solve a wide variety of tasks. If tasks depend on each other (e.g. needing to learn to walk before learning to run), curriculum learning can speed up learning by focusing on the next best task to learn. We explore curriculum learning in a complex, visual domain with many hard exploration challenges: Minecraft. We find that learning progress (defined as a change in success probability of a task) is a reliable measure of learnability for automatically constructing an effective curriculum. We introduce a learning-progress based curriculum and test it on a complex reinforcement learning problem (called "Simon Says") where an agent is instructed to obtain a desired goal item. Many of the required skills depend on each other. Experiments demonstrate that: (1) a within-episode exploration bonus for obtaining new items improves performance, (2) dynamically adjusting this bonus across training such that it only applies to items the agent cannot reliably obtain yet further increases performance, (3) the learning-progress based curriculum elegantly follows the learning curve of the agent, and (4) when the learning-progress based curriculum is combined with the dynamic exploration bonus it learns much more efficiently and obtains far higher performance than uniform baselines. These results suggest that combining intra-episode and across-training exploration bonuses with learning progress creates a promising method for automated curriculum generation, which may substantially increase our ability to train more capable, generally intelligent agents.
Towards robust and domain agnostic reinforcement learning competitions
Jun 07, 2021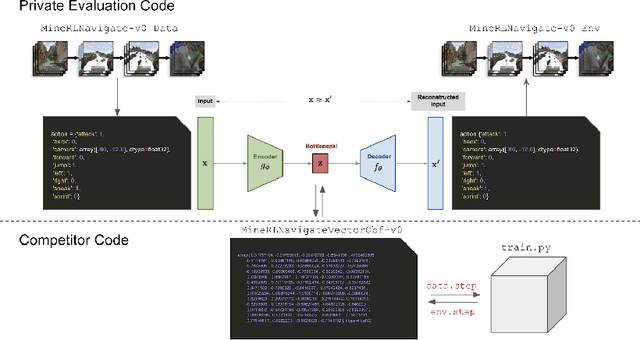
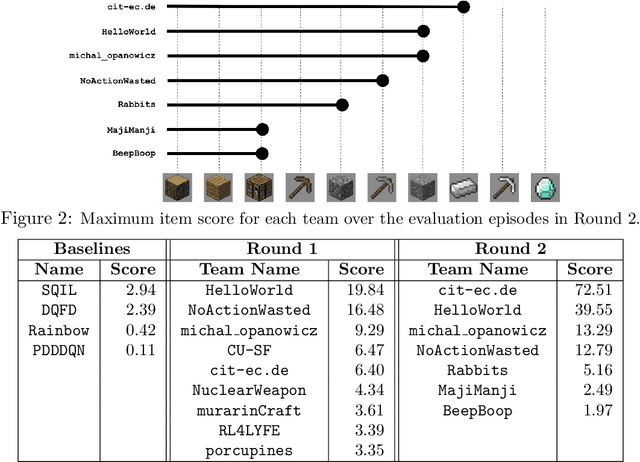
Abstract:Reinforcement learning competitions have formed the basis for standard research benchmarks, galvanized advances in the state-of-the-art, and shaped the direction of the field. Despite this, a majority of challenges suffer from the same fundamental problems: participant solutions to the posed challenge are usually domain-specific, biased to maximally exploit compute resources, and not guaranteed to be reproducible. In this paper, we present a new framework of competition design that promotes the development of algorithms that overcome these barriers. We propose four central mechanisms for achieving this end: submission retraining, domain randomization, desemantization through domain obfuscation, and the limitation of competition compute and environment-sample budget. To demonstrate the efficacy of this design, we proposed, organized, and ran the MineRL 2020 Competition on Sample-Efficient Reinforcement Learning. In this work, we describe the organizational outcomes of the competition and show that the resulting participant submissions are reproducible, non-specific to the competition environment, and sample/resource efficient, despite the difficult competition task.
The MineRL 2020 Competition on Sample Efficient Reinforcement Learning using Human Priors
Jan 26, 2021
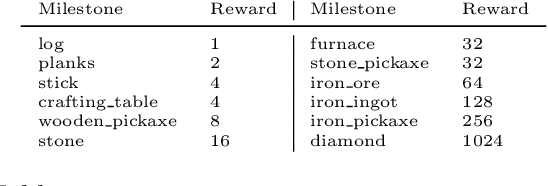
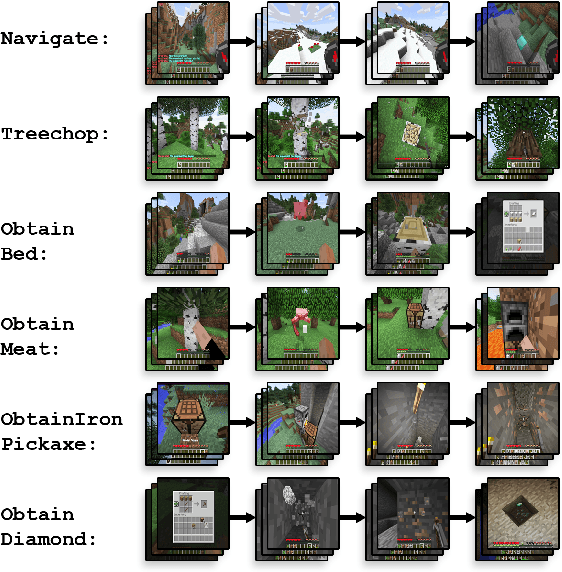
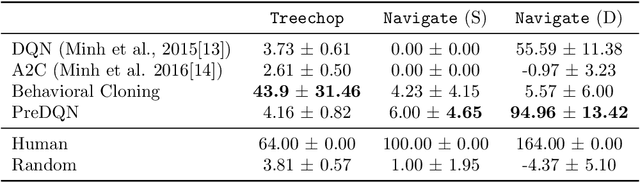
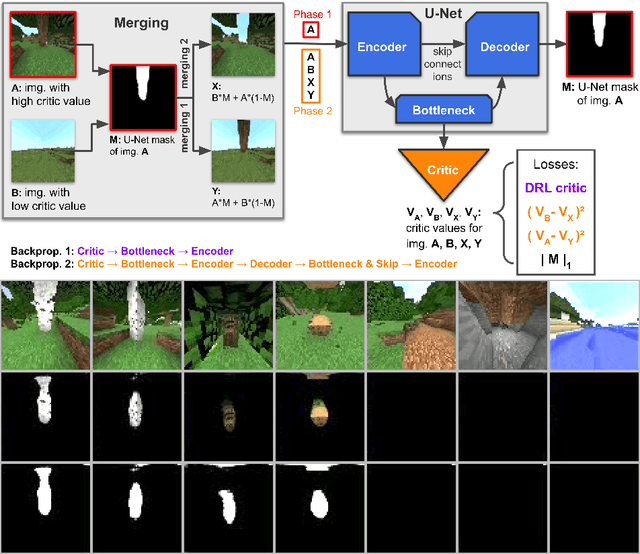
Abstract:Although deep reinforcement learning has led to breakthroughs in many difficult domains, these successes have required an ever-increasing number of samples, affording only a shrinking segment of the AI community access to their development. Resolution of these limitations requires new, sample-efficient methods. To facilitate research in this direction, we propose this second iteration of the MineRL Competition. The primary goal of the competition is to foster the development of algorithms which can efficiently leverage human demonstrations to drastically reduce the number of samples needed to solve complex, hierarchical, and sparse environments. To that end, participants compete under a limited environment sample-complexity budget to develop systems which solve the MineRL ObtainDiamond task in Minecraft, a sequential decision making environment requiring long-term planning, hierarchical control, and efficient exploration methods. The competition is structured into two rounds in which competitors are provided several paired versions of the dataset and environment with different game textures and shaders. At the end of each round, competitors submit containerized versions of their learning algorithms to the AIcrowd platform where they are trained from scratch on a hold-out dataset-environment pair for a total of 4-days on a pre-specified hardware platform. In this follow-up iteration to the NeurIPS 2019 MineRL Competition, we implement new features to expand the scale and reach of the competition. In response to the feedback of the previous participants, we introduce a second minor track focusing on solutions without access to environment interactions of any kind except during test-time. Further we aim to prompt domain agnostic submissions by implementing several novel competition mechanics including action-space randomization and desemantization of observations and actions.
Guaranteeing Reproducibility in Deep Learning Competitions
May 12, 2020Abstract:To encourage the development of methods with reproducible and robust training behavior, we propose a challenge paradigm where competitors are evaluated directly on the performance of their learning procedures rather than pre-trained agents. Since competition organizers re-train proposed methods in a controlled setting they can guarantee reproducibility, and -- by retraining submissions using a held-out test set -- help ensure generalization past the environments on which they were trained.
Retrospective Analysis of the 2019 MineRL Competition on Sample Efficient Reinforcement Learning
Mar 27, 2020



Abstract:To facilitate research in the direction of sample-efficient reinforcement learning, we held the MineRL Competition on Sample-Efficient Reinforcement Learning Using Human Priors at the Thirty-fourth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019). The primary goal of this competition was to promote the development of algorithms that use human demonstrations alongside reinforcement learning to reduce the number of samples needed to solve complex, hierarchical, and sparse environments. We describe the competition and provide an overview of the top solutions, each of which uses deep reinforcement learning and/or imitation learning. We also discuss the impact of our organizational decisions on the competition as well as future directions for improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge