Peter Zhokhov
Tony
OpenAI GPT-5 System Card
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This is the system card published alongside the OpenAI GPT-5 launch, August 2025. GPT-5 is a unified system with a smart and fast model that answers most questions, a deeper reasoning model for harder problems, and a real-time router that quickly decides which model to use based on conversation type, complexity, tool needs, and explicit intent (for example, if you say 'think hard about this' in the prompt). The router is continuously trained on real signals, including when users switch models, preference rates for responses, and measured correctness, improving over time. Once usage limits are reached, a mini version of each model handles remaining queries. This system card focuses primarily on gpt-5-thinking and gpt-5-main, while evaluations for other models are available in the appendix. The GPT-5 system not only outperforms previous models on benchmarks and answers questions more quickly, but -- more importantly -- is more useful for real-world queries. We've made significant advances in reducing hallucinations, improving instruction following, and minimizing sycophancy, and have leveled up GPT-5's performance in three of ChatGPT's most common uses: writing, coding, and health. All of the GPT-5 models additionally feature safe-completions, our latest approach to safety training to prevent disallowed content. Similarly to ChatGPT agent, we have decided to treat gpt-5-thinking as High capability in the Biological and Chemical domain under our Preparedness Framework, activating the associated safeguards. While we do not have definitive evidence that this model could meaningfully help a novice to create severe biological harm -- our defined threshold for High capability -- we have chosen to take a precautionary approach.
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
Video PreTraining : Learning to Act by Watching Unlabeled Online Videos
Jun 23, 2022

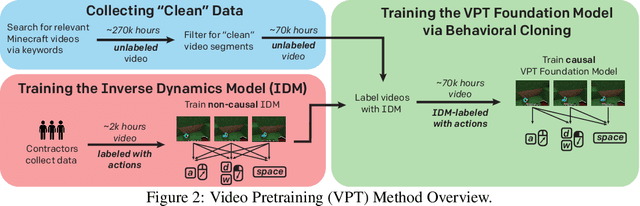
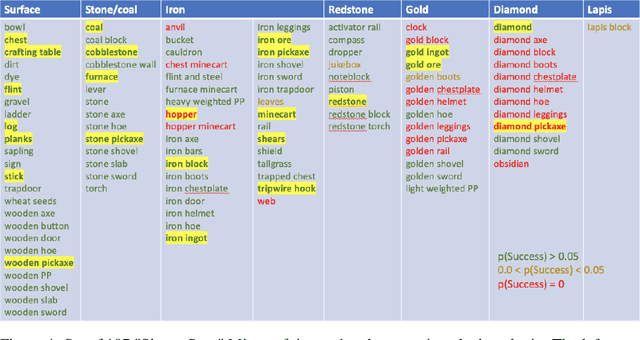
Abstract:Pretraining on noisy, internet-scale datasets has been heavily studied as a technique for training models with broad, general capabilities for text, images, and other modalities. However, for many sequential decision domains such as robotics, video games, and computer use, publicly available data does not contain the labels required to train behavioral priors in the same way. We extend the internet-scale pretraining paradigm to sequential decision domains through semi-supervised imitation learning wherein agents learn to act by watching online unlabeled videos. Specifically, we show that with a small amount of labeled data we can train an inverse dynamics model accurate enough to label a huge unlabeled source of online data -- here, online videos of people playing Minecraft -- from which we can then train a general behavioral prior. Despite using the native human interface (mouse and keyboard at 20Hz), we show that this behavioral prior has nontrivial zero-shot capabilities and that it can be fine-tuned, with both imitation learning and reinforcement learning, to hard-exploration tasks that are impossible to learn from scratch via reinforcement learning. For many tasks our models exhibit human-level performance, and we are the first to report computer agents that can craft diamond tools, which can take proficient humans upwards of 20 minutes (24,000 environment actions) of gameplay to accomplish.
Multi-task curriculum learning in a complex, visual, hard-exploration domain: Minecraft
Jun 28, 2021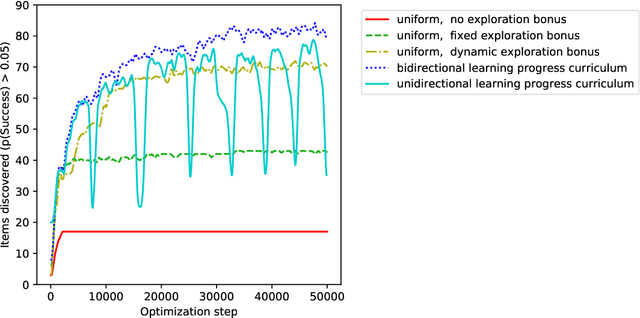
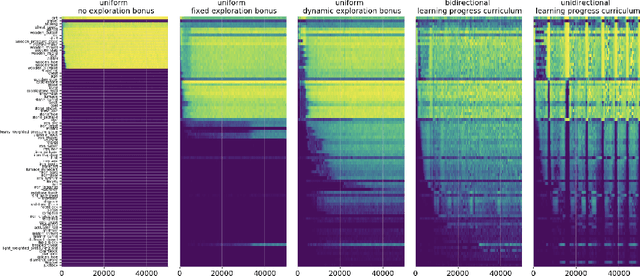
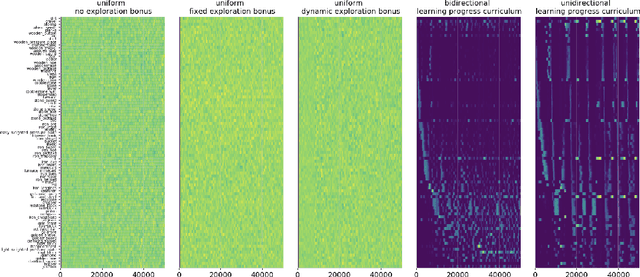
Abstract:An important challenge in reinforcement learning is training agents that can solve a wide variety of tasks. If tasks depend on each other (e.g. needing to learn to walk before learning to run), curriculum learning can speed up learning by focusing on the next best task to learn. We explore curriculum learning in a complex, visual domain with many hard exploration challenges: Minecraft. We find that learning progress (defined as a change in success probability of a task) is a reliable measure of learnability for automatically constructing an effective curriculum. We introduce a learning-progress based curriculum and test it on a complex reinforcement learning problem (called "Simon Says") where an agent is instructed to obtain a desired goal item. Many of the required skills depend on each other. Experiments demonstrate that: (1) a within-episode exploration bonus for obtaining new items improves performance, (2) dynamically adjusting this bonus across training such that it only applies to items the agent cannot reliably obtain yet further increases performance, (3) the learning-progress based curriculum elegantly follows the learning curve of the agent, and (4) when the learning-progress based curriculum is combined with the dynamic exploration bonus it learns much more efficiently and obtains far higher performance than uniform baselines. These results suggest that combining intra-episode and across-training exploration bonuses with learning progress creates a promising method for automated curriculum generation, which may substantially increase our ability to train more capable, generally intelligent agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge