Anaelia Ovalle
Can Large Language Models Understand, Reason About, and Generate Code-Switched Text?
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Code-switching is a pervasive phenomenon in multilingual communication, yet the robustness of large language models (LLMs) in mixed-language settings remains insufficiently understood. In this work, we present a comprehensive evaluation of LLM capabilities in understanding, reasoning over, and generating code-switched text. We introduce CodeMixQA a novel benchmark with high-quality human annotations, comprising 16 diverse parallel code-switched language-pair variants that span multiple geographic regions and code-switching patterns, and include both original scripts and their transliterated forms. Using this benchmark, we analyze the reasoning behavior of LLMs on code-switched question-answering tasks, shedding light on how models process and reason over mixed-language inputs. We further conduct a systematic evaluation of LLM-generated synthetic code-switched text, focusing on both naturalness and semantic fidelity, and uncover key limitations in current generation capabilities. Our findings reveal persistent challenges in both reasoning and generation under code-switching conditions and provide actionable insights for building more robust multilingual LLMs. We release the dataset and code as open source.
Beg to Differ: Understanding Reasoning-Answer Misalignment Across Languages
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Large language models demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities through chain-of-thought prompting, but whether this reasoning quality transfers across languages remains underexplored. We introduce a human-validated framework to evaluate whether model-generated reasoning traces logically support their conclusions across languages. Analyzing 65k reasoning traces from GlobalMMLU questions across 6 languages and 6 frontier models, we uncover a critical blind spot: while models achieve high task accuracy, their reasoning can fail to support their conclusions. Reasoning traces in non-Latin scripts show at least twice as much misalignment between their reasoning and conclusions than those in Latin scripts. We develop an error taxonomy through human annotation to characterize these failures, finding they stem primarily from evidential errors (unsupported claims, ambiguous facts) followed by illogical reasoning steps. Our findings demonstrate that current multilingual evaluation practices provide an incomplete picture of model reasoning capabilities and highlight the need for reasoning-aware evaluation frameworks.
The Cake that is Intelligence and Who Gets to Bake it: An AI Analogy and its Implications for Participation
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:In a widely popular analogy by Turing Award Laureate Yann LeCun, machine intelligence has been compared to cake - where unsupervised learning forms the base, supervised learning adds the icing, and reinforcement learning is the cherry on top. We expand this 'cake that is intelligence' analogy from a simple structural metaphor to the full life-cycle of AI systems, extending it to sourcing of ingredients (data), conception of recipes (instructions), the baking process (training), and the tasting and selling of the cake (evaluation and distribution). Leveraging our re-conceptualization, we describe each step's entailed social ramifications and how they are bounded by statistical assumptions within machine learning. Whereas these technical foundations and social impacts are deeply intertwined, they are often studied in isolation, creating barriers that restrict meaningful participation. Our re-conceptualization paves the way to bridge this gap by mapping where technical foundations interact with social outcomes, highlighting opportunities for cross-disciplinary dialogue. Finally, we conclude with actionable recommendations at each stage of the metaphorical AI cake's life-cycle, empowering prospective AI practitioners, users, and researchers, with increased awareness and ability to engage in broader AI discourse.
The Root Shapes the Fruit: On the Persistence of Gender-Exclusive Harms in Aligned Language Models
Nov 06, 2024

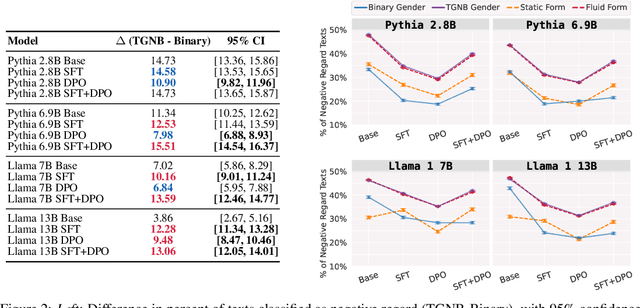

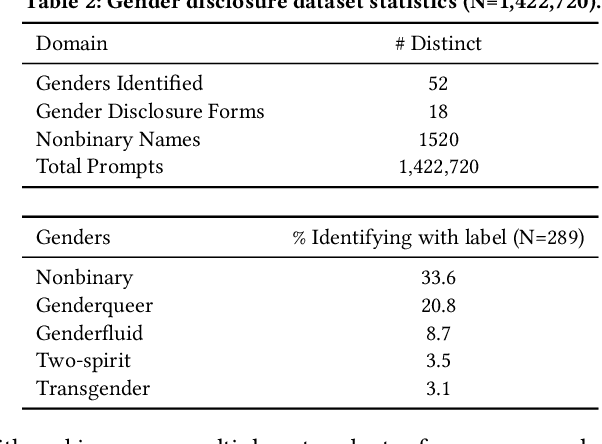
Abstract:Natural-language assistants are designed to provide users with helpful responses while avoiding harmful outputs, largely achieved through alignment to human preferences. Yet there is limited understanding of whether alignment techniques may inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify harmful biases inherited from their pre-aligned base models. This issue is compounded by the choice of bias evaluation benchmarks in popular preference-finetuned models, which predominantly focus on dominant social categories, such as binary gender, thereby limiting insights into biases affecting underrepresented groups. Towards addressing this gap, we center transgender, nonbinary, and other gender-diverse identities to investigate how alignment procedures interact with pre-existing gender-diverse bias in LLMs. Our key contributions include: 1) a comprehensive survey of bias evaluation modalities across leading preference-finetuned LLMs, highlighting critical gaps in gender-diverse representation, 2) systematic evaluation of gender-diverse biases across 12 models spanning Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) stages, uncovering harms popular bias benchmarks fail to detect, and 3) a flexible framework for measuring harmful biases in implicit reward signals applicable to other social contexts. Our findings reveal that DPO-aligned models are particularly sensitive to supervised finetuning (SFT), and can amplify two forms of real-world gender-diverse harms from their base models: stigmatization and gender non-affirmative language. We conclude with recommendations tailored to DPO and broader alignment practices, advocating for the adoption of community-informed bias evaluation frameworks to more effectively identify and address underrepresented harms in LLMs.
Survey of Bias In Text-to-Image Generation: Definition, Evaluation, and Mitigation
Apr 02, 2024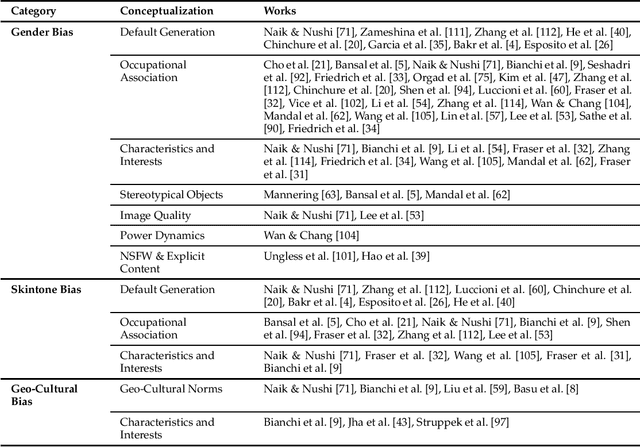
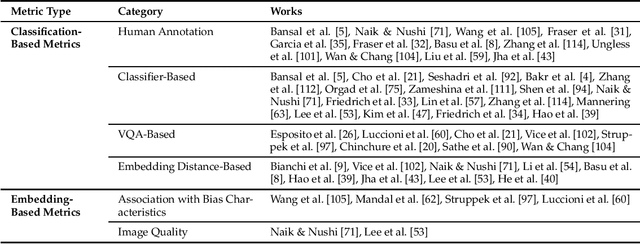

Abstract:The recent advancement of large and powerful models with Text-to-Image (T2I) generation abilities -- such as OpenAI's DALLE-3 and Google's Gemini -- enables users to generate high-quality images from textual prompts. However, it has become increasingly evident that even simple prompts could cause T2I models to exhibit conspicuous social bias in generated images. Such bias might lead to both allocational and representational harms in society, further marginalizing minority groups. Noting this problem, a large body of recent works has been dedicated to investigating different dimensions of bias in T2I systems. However, an extensive review of these studies is lacking, hindering a systematic understanding of current progress and research gaps. We present the first extensive survey on bias in T2I generative models. In this survey, we review prior studies on dimensions of bias: Gender, Skintone, and Geo-Culture. Specifically, we discuss how these works define, evaluate, and mitigate different aspects of bias. We found that: (1) while gender and skintone biases are widely studied, geo-cultural bias remains under-explored; (2) most works on gender and skintone bias investigated occupational association, while other aspects are less frequently studied; (3) almost all gender bias works overlook non-binary identities in their studies; (4) evaluation datasets and metrics are scattered, with no unified framework for measuring biases; and (5) current mitigation methods fail to resolve biases comprehensively. Based on current limitations, we point out future research directions that contribute to human-centric definitions, evaluations, and mitigation of biases. We hope to highlight the importance of studying biases in T2I systems, as well as encourage future efforts to holistically understand and tackle biases, building fair and trustworthy T2I technologies for everyone.
Are you talking to or ? On Tokenization and Addressing Misgendering in LLMs with Pronoun Tokenization Parity
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:A large body of NLP research has documented the ways gender biases manifest and amplify within large language models (LLMs), though this research has predominantly operated within a gender binary-centric context. A growing body of work has identified the harmful limitations of this gender-exclusive framing; many LLMs cannot correctly and consistently refer to persons outside the gender binary, especially if they use neopronouns. While data scarcity has been identified as a possible culprit, the precise mechanisms through which it influences LLM misgendering remain underexplored. Our work addresses this gap by studying data scarcity's role in subword tokenization and, consequently, the formation of LLM word representations. We uncover how the Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE) tokenizer, a backbone for many popular LLMs, contributes to neopronoun misgendering through out-of-vocabulary behavior. We introduce pronoun tokenization parity (PTP), a novel approach to reduce LLM neopronoun misgendering by preserving a token's functional structure. We evaluate PTP's efficacy using pronoun consistency-based metrics and a novel syntax-based metric. Through several controlled experiments, finetuning LLMs with PTP improves neopronoun consistency from 14.5% to 58.4%, highlighting the significant role tokenization plays in LLM pronoun consistency.
Bound by the Bounty: Collaboratively Shaping Evaluation Processes for Queer AI Harms
Jul 25, 2023

Abstract:Bias evaluation benchmarks and dataset and model documentation have emerged as central processes for assessing the biases and harms of artificial intelligence (AI) systems. However, these auditing processes have been criticized for their failure to integrate the knowledge of marginalized communities and consider the power dynamics between auditors and the communities. Consequently, modes of bias evaluation have been proposed that engage impacted communities in identifying and assessing the harms of AI systems (e.g., bias bounties). Even so, asking what marginalized communities want from such auditing processes has been neglected. In this paper, we ask queer communities for their positions on, and desires from, auditing processes. To this end, we organized a participatory workshop to critique and redesign bias bounties from queer perspectives. We found that when given space, the scope of feedback from workshop participants goes far beyond what bias bounties afford, with participants questioning the ownership, incentives, and efficacy of bounties. We conclude by advocating for community ownership of bounties and complementing bounties with participatory processes (e.g., co-creation).
* To appear at AIES 2023
"I'm fully who I am": Towards Centering Transgender and Non-Binary Voices to Measure Biases in Open Language Generation
May 18, 2023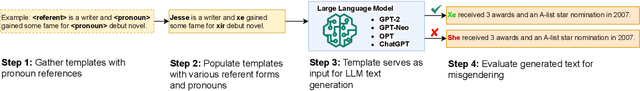


Abstract:Transgender and non-binary (TGNB) individuals disproportionately experience discrimination and exclusion from daily life. Given the recent popularity and adoption of language generation technologies, the potential to further marginalize this population only grows. Although a multitude of NLP fairness literature focuses on illuminating and addressing gender biases, assessing gender harms for TGNB identities requires understanding how such identities uniquely interact with societal gender norms and how they differ from gender binary-centric perspectives. Such measurement frameworks inherently require centering TGNB voices to help guide the alignment between gender-inclusive NLP and whom they are intended to serve. Towards this goal, we ground our work in the TGNB community and existing interdisciplinary literature to assess how the social reality surrounding experienced marginalization by TGNB persons contributes to and persists within Open Language Generation (OLG). By first understanding their marginalization stressors, we evaluate (1) misgendering and (2) harmful responses to gender disclosure. To do this, we introduce the TANGO dataset, comprising of template-based text curated from real-world text within a TGNB-oriented community. We discover a dominance of binary gender norms within the models; LLMs least misgendered subjects in generated text when triggered by prompts whose subjects used binary pronouns. Meanwhile, misgendering was most prevalent when triggering generation with singular they and neopronouns. When prompted with gender disclosures, LLM text contained stigmatizing language and scored most toxic when triggered by TGNB gender disclosure. Our findings warrant further research on how TGNB harms manifest in LLMs and serve as a broader case study toward concretely grounding the design of gender-inclusive AI in community voices and interdisciplinary literature.
Queer In AI: A Case Study in Community-Led Participatory AI
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:We present Queer in AI as a case study for community-led participatory design in AI. We examine how participatory design and intersectional tenets started and shaped this community's programs over the years. We discuss different challenges that emerged in the process, look at ways this organization has fallen short of operationalizing participatory and intersectional principles, and then assess the organization's impact. Queer in AI provides important lessons and insights for practitioners and theorists of participatory methods broadly through its rejection of hierarchy in favor of decentralization, success at building aid and programs by and for the queer community, and effort to change actors and institutions outside of the queer community. Finally, we theorize how communities like Queer in AI contribute to the participatory design in AI more broadly by fostering cultures of participation in AI, welcoming and empowering marginalized participants, critiquing poor or exploitative participatory practices, and bringing participation to institutions outside of individual research projects. Queer in AI's work serves as a case study of grassroots activism and participatory methods within AI, demonstrating the potential of community-led participatory methods and intersectional praxis, while also providing challenges, case studies, and nuanced insights to researchers developing and using participatory methods.
Factoring the Matrix of Domination: A Critical Review and Reimagination of Intersectionality in AI Fairness
Mar 16, 2023

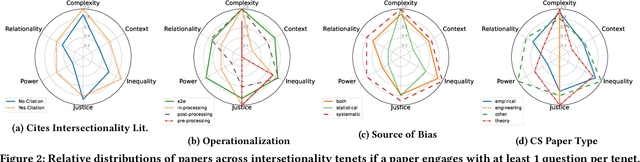
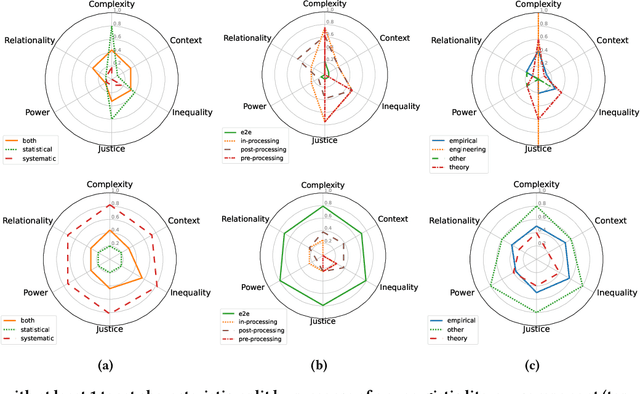
Abstract:Intersectionality is a critical framework that, through inquiry and praxis, allows us to examine how social inequalities persist through domains of structure and discipline. Given AI fairness' raison d'\^etre of ``fairness,'' we argue that adopting intersectionality as an analytical framework is pivotal to effectively operationalizing fairness. Through a critical review of how intersectionality is discussed in 30 papers from the AI fairness literature, we deductively and inductively: 1) map how intersectionality tenets operate within the AI fairness paradigm and 2) uncover gaps between the conceptualization and operationalization of intersectionality. We find that researchers overwhelmingly reduce intersectionality to optimizing for fairness metrics over demographic subgroups. They also fail to discuss their social context and when mentioning power, they mostly situate it only within the AI pipeline. We: 3) outline and assess the implications of these gaps for critical inquiry and praxis, and 4) provide actionable recommendations for AI fairness researchers to engage with intersectionality in their work by grounding it in AI epistemology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge